UM1848
User manual
Getting started with the software package for L6474 stepper
motor driver X-CUBE-SPN1 expansion for STM32Cube
Introduction
This user manual describes how to use the X-CUBE-SPN1 expansion software within the
STM32Cube software environment. Combined with the use of one or more X-NUCLEO-
IHM01A1 boards, this software allows a Nucleo board to control one or several stepper
motors. The X-NUCLEO-IHM01A1 motor driver expansion board is designed around
STMicroelectronics’ L6474, a fully integrated microstepping motor driver.
This manual does not include information on the operation of the L6474 chip, as this is
covered in the L6474 datasheet “DS8773: easySPIN - fully integrated microstepping motor
driver”, available here on st.com.
The software is based on STM32Cube technology and expands STM32Cube-based
packages.
March 2015
DocID027273 Rev 1
1/62
www.st.com
62
�
Contents
Contents
UM1848
1
2
3
4
Acronyms and abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
What is STM32Cube? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
STM32Cube overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.1
2.2
STM32Cube architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
X-CUBE-SPN1 software expansion for STM32Cube . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.1
3.2
3.3
3.4
3.5
Architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Folder structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
BSP folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.3.1
3.3.2
Projects folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Software required resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
APIs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Motor control functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3.5.1
3.5.2
L6474 Control functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Getting started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Hardware description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
4.1
4.1.1
STM32 Nucleo platform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Stepper motor driver expansion board: X-NUCLEO-IHM01A1 . . . . . . . 52
4.1.2
4.1.3
Miscellaneous HW components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Software description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
4.2
4.3
Hardware and software setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Setup to drive 1 motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
4.3.1
4.3.2
Setup to drive 2 motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Setup to drive 3 motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
4.3.3
5
Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
2/62
DocID027273 Rev 1
�
UM1848
List of tables
List of tables
Table 1.
Table 2.
Table 3.
Acronyms and abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Required resources for the X-CUBE-SPN1 software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
DocID027273 Rev 1
3/62
62
�
List of figures
List of figures
UM1848
Firmware architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 1.
Software architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 2.
STM32 Nucleo board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Figure 3.
X-NUCLEO-IHM01A1 stepper motor driver expansion board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Figure 4.
X-NUCLEO-IHM01A1 stepper motor driver in configuration to drive 1 motor. . . . . . . . . . . 54
Figure 5.
Configuration for 1 motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Figure 6.
X-NUCLEO-IHM01A1 stepper motor driver in configuration to drive motor 1/2 . . . . . . . . . 55
Figure 7.
X-NUCLEO-IHM01A1 stepper motor driver in configuration to drive motor 2/2 . . . . . . . . . 56
Figure 8.
Figure 9.
Configuration for 2 motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Figure 10. X-NUCLEO-IHM01A1 stepper motor driver in configuration to drive motor 1/3 . . . . . . . . . 58
Figure 11. X-NUCLEO-IHM01A1 stepper motor driver in configuration to drive motor 2/3 . . . . . . . . . 58
Figure 12. X-NUCLEO-IHM01A1 stepper motor driver in configuration to drive motor 3/3 . . . . . . . . . 59
Figure 13. Configuration for 3 motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
4/62
DocID027273 Rev 1
�
UM1848
Acronyms and abbreviations
1
Acronyms and abbreviations
Table 1. Acronyms and abbreviations
Acronym
Description
API
BSP
CMSIS
HAL
SPI
IDE
LED
Application programming interface
Board support package
Cortex® microcontroller software interface standard
Hardware abstraction layer
Serial port interface
Integrated development environment
Light emitting diode
DocID027273 Rev 1
5/62
62
�
What is STM32Cube?
UM1848
2
2.1
What is STM32Cube?
STM32Cube overview
STMCubeTM initiative was originated by STMicroelectronics to ease developers' life by
reducing development effort, time and cost. STM32Cube covers the STM32 portfolio.
STM32Cube version 1.x includes:
•
The STM32CubeMX, a graphical software configuration tool that allows to generate C
initialization code using graphical wizards.
A comprehensive embedded software platform, delivered per series (such as
STM32CubeF4 for STM32F4 series)
The STM32Cube HAL, an STM32 abstraction layer embedded software, ensuring
maximized portability across STM32 portfolio
A consistent set of middleware components such as RTOS, USB, TCP/IP, graphics
All embedded software utilities coming with a full set of examples.
•
•
•
•
Information about STM32Cube are available on st.com at:
http://www.st.com/stm32cube
2.2
STM32Cube architecture
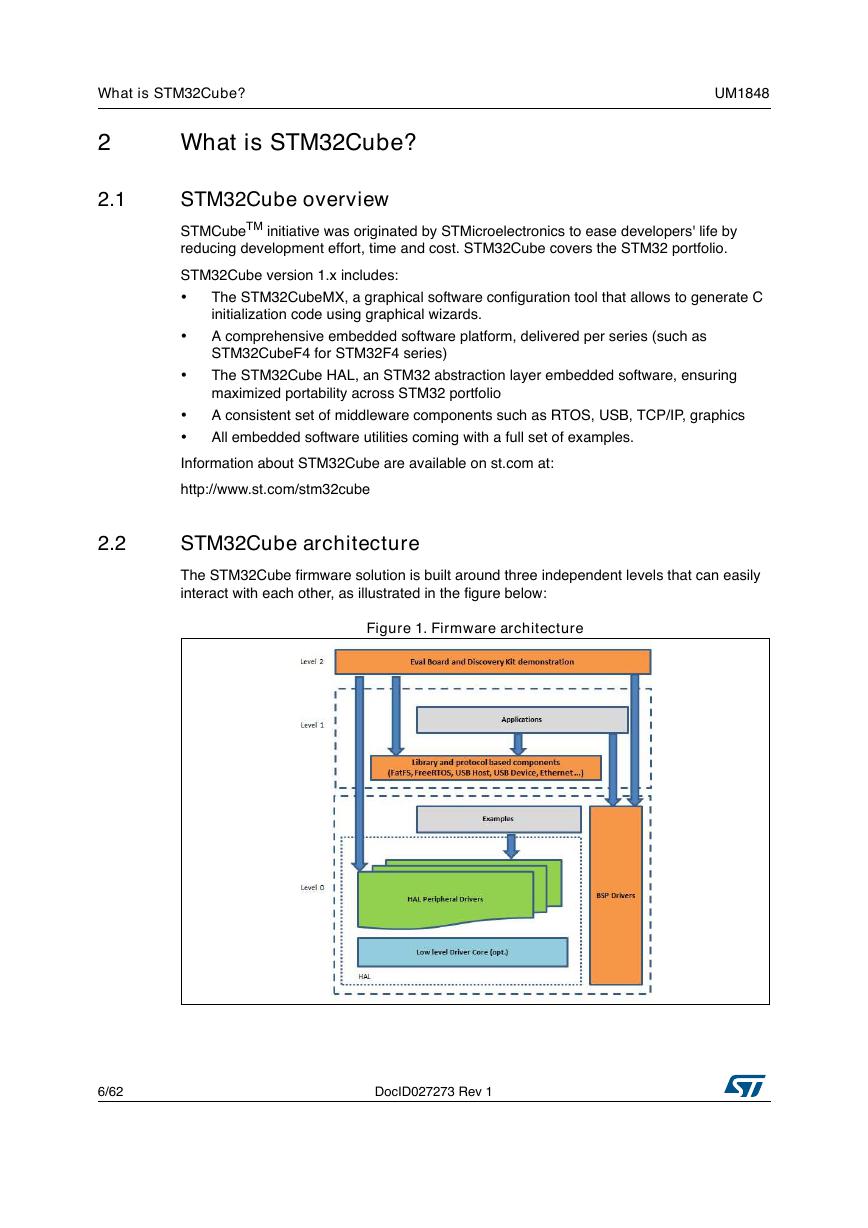
The STM32Cube firmware solution is built around three independent levels that can easily
interact with each other, as illustrated in the figure below:
Figure 1. Firmware architecture
6/62
DocID027273 Rev 1
�
UM1848
What is STM32Cube?
Level 0: This level is divided into three sub-layers:
•
Board support package (BSP): this layer offers a set of APIs relative to the hardware
components in the hardware boards (audio codec, IO expander, touchscreen, SRAM
driver, LCD drivers, etc.) and is composed of two parts:
–
Component driver: the driver relative to the external device on the board and not
related to the STM32, the component driver provides specific APIs to the BSP
driver external components and is portable for use on any other board.
BSP driver: permits the linking of the component driver to a specific board and
provides a set of user-friendly APIs. The API naming rule is
BSP_FUNCT_Action(): ex. BSP_LED_Init(),BSP_LED_On()
–
It is based on modular architecture enabling easily portability to any hardware simply by
implementing the low level routines.
•
Hardware abstraction layer (HAL): this layer provides the low level drivers and the
hardware interfacing methods to interact with the upper layers (application, libraries
and stacks). It provides generic, multi-instance and functionality-oriented APIs which
allow offloading the implementation of the user application by providing a ready-to-use
process. As an example, for the communication peripherals (I2S, UART, etc.) it
provides APIs to initialize and configure the peripheral, manage data transfer based on
polling, interrupt or DMA processes, and manage communication errors that may arise
during communication. The HAL driver APIs are split into two categories, generic APIs,
which provide common and generic functions to all MCUs in the STM32 series, and
extension APIs which provide specific and customized functions for a specific family or
part number.
Basic peripheral usage examples: this layer encloses the examples built over the
STM32 peripheral using only the HAL and BSP resources.
•
Level 1: This level is divided into two sub-layers:
•
Middleware components: set of libraries covering USB host and device libraries,
STemWin, FreeRTOS, FatFS, LwIP, and PolarSSL. Horizontal interaction between the
components of this layer is done directly by calling the feature APIs while the vertical
interaction with the low level drivers is done through specific callbacks and static
macros implemented in the library system call interface. As an example, the FatFs
implements the disk I/O driver to access the microSD drive or the USB mass storage
class.
examples based on the middleware components: each middleware component comes
with one or more examples (called also applications) showing how to use it. Integration
examples that use several middleware components are provided as well.
•
Level 2: This level is composed of a single layer which is a global real-time and graphical
demonstration based on the middleware service layer, the low level abstraction layer and
the basic peripheral usage applications for board-based functionalities.
DocID027273 Rev 1
7/62
62
�
X-CUBE-SPN1 software expansion for STM32Cube
UM1848
3
3.1
X-CUBE-SPN1 software expansion for STM32Cube
Overview
X-CUBE-SPN1 is a software package that expands the functionality provided by
STM32Cube.
The key features of the package are:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
L6474 read/write registers
Nucleo and X-NUCLEO-IHM01A1 configuration (GPIOs, PWMs, IRQs, etc.)
Speed profile configuration
Motion commands
FLAG interrupt handling (alarm reporting)
Microstepping handling
Daisy chain handling
By starting the motor control library, the user specifies the number of L6474 chips which are
connected to the Nucleo board. Once set, the number of L6474 devices must not be
changed.
Depending on the number of devices, the library:
•
•
•
sets up the required GPIOs to handle the motor direction and the FLAG interrupt
initializes the PWMs that will act as the step clock generator
initializes the speed profile (acceleration, deceleration, min and max speed) of each
device by using the parameters of the file “l6474_target_config.h”
starts the SPI library to communicate with the L6474 chips
releases the reset of each of the L6474 chips
disables the power bridge and clear the status flags of the L6474 chips
loads the registers of each of the L6474 with the predefined values from
“l6474_target_config.h”
•
•
•
•
Once the initialization is done, the user can modify the L6474 registers and speed profile
configurations as desired. Most of the functions of the library take a device Id (from 0 to 2)
as input parameter. It gives the user the possibility to specify which of the device
configurations he wishes to modify.
The user can also write a callback function and attach it to the flag interrupt handler
depending on the actions to perform when an alarm is reported (read the flags, clear and
read the flags, etc.)
Then, he can request the movement of one or several motors (still using the same principle
of device Id). This request can be to:
•
•
•
move for a given number of steps in a specified direction
go to a specific position
run until reception of a new instruction
On reception of this request, the library enables the PWM which is used as the step clock of
the corresponding L6474.
At each pulse period, the motor will perform one step and an ISR (interrupt service routine)
is triggered on the microcontroller side.
8/62
DocID027273 Rev 1
�














 V2版本原理图(Capacitive-Fingerprint-Reader-Schematic_V2).pdf
V2版本原理图(Capacitive-Fingerprint-Reader-Schematic_V2).pdf 摄像头工作原理.doc
摄像头工作原理.doc VL53L0X简要说明(En.FLVL53L00216).pdf
VL53L0X简要说明(En.FLVL53L00216).pdf 原理图(DVK720-Schematic).pdf
原理图(DVK720-Schematic).pdf 原理图(Pico-Clock-Green-Schdoc).pdf
原理图(Pico-Clock-Green-Schdoc).pdf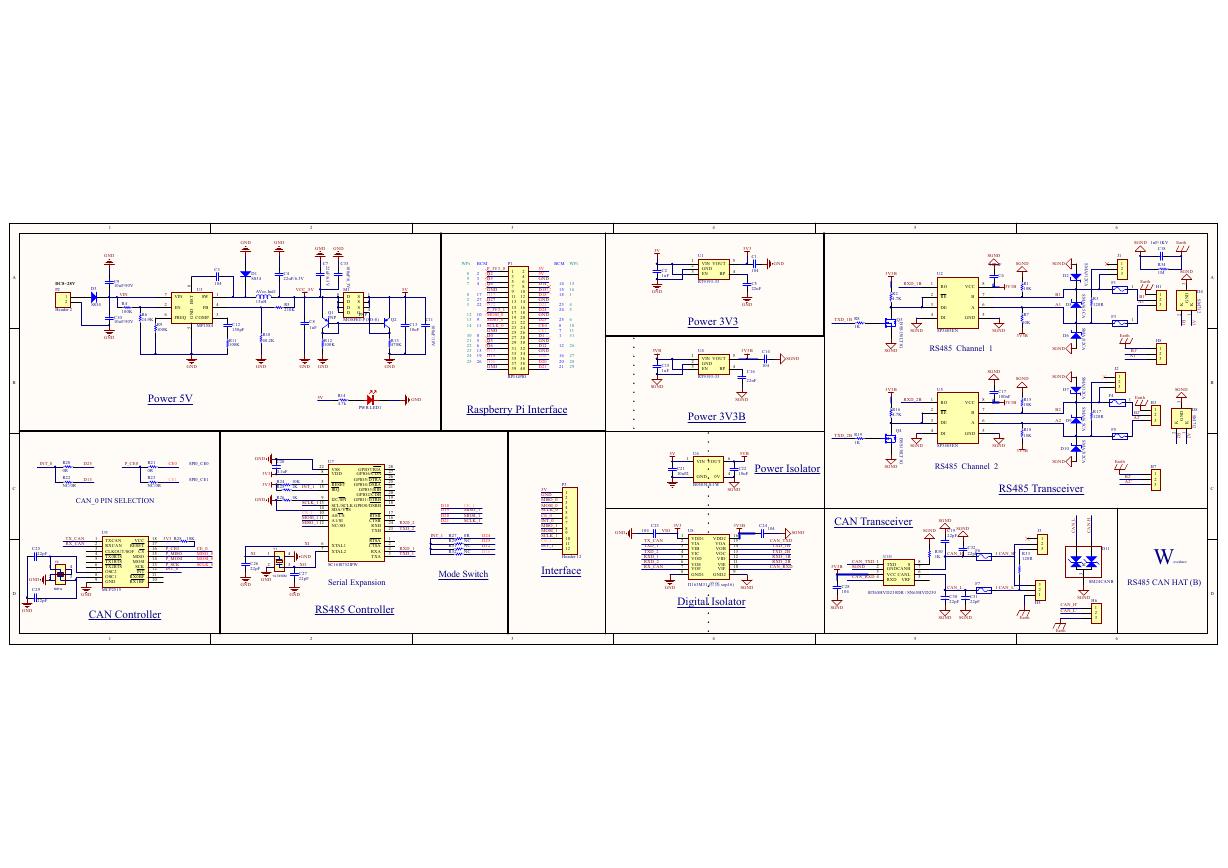 原理图(RS485-CAN-HAT-B-schematic).pdf
原理图(RS485-CAN-HAT-B-schematic).pdf File:SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
File:SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf ADS1263(Ads1262).pdf
ADS1263(Ads1262).pdf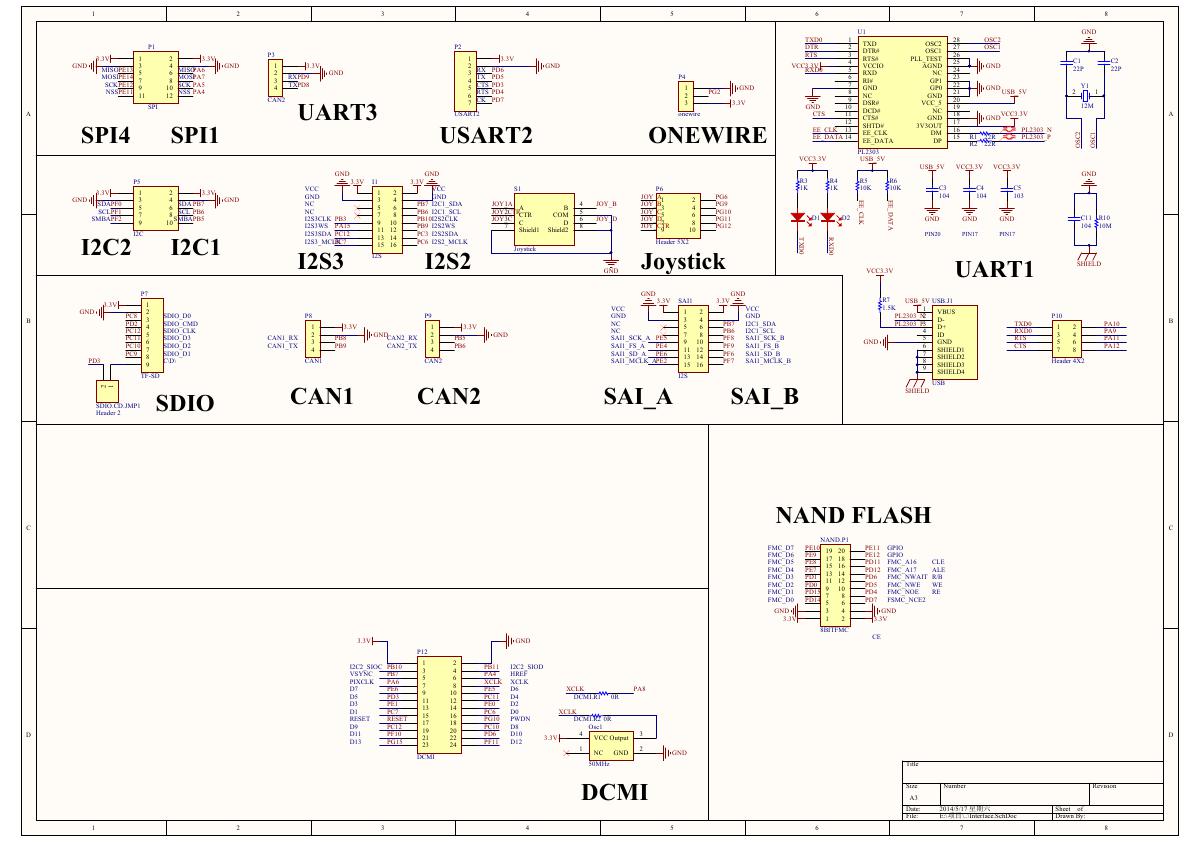 原理图(Open429Z-D-Schematic).pdf
原理图(Open429Z-D-Schematic).pdf 用户手册(Capacitive_Fingerprint_Reader_User_Manual_CN).pdf
用户手册(Capacitive_Fingerprint_Reader_User_Manual_CN).pdf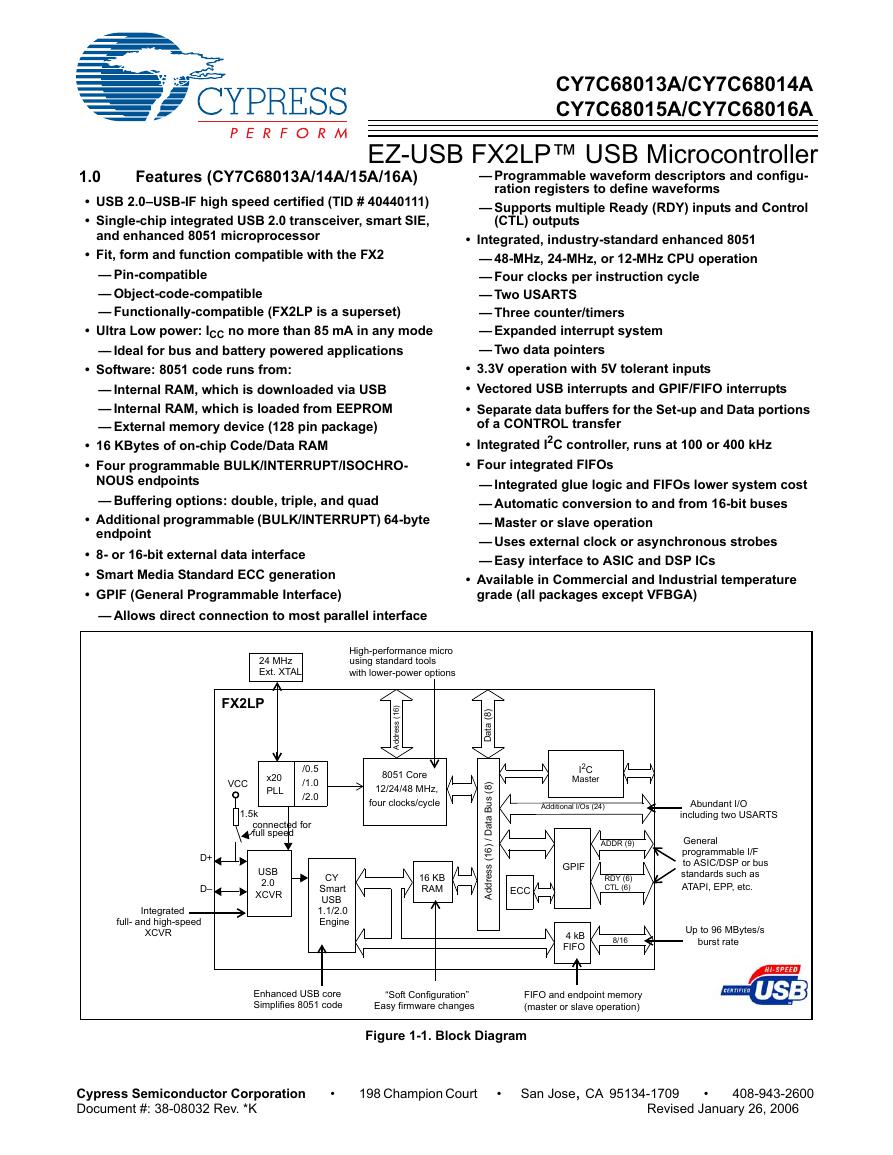 CY7C68013A(英文版)(CY7C68013A).pdf
CY7C68013A(英文版)(CY7C68013A).pdf TechnicalReference_Dem.pdf
TechnicalReference_Dem.pdf