UM1900
User manual
Getting started with the digital MEMS microphones expansion
board based on MP34DT01-M for STM32 Nucleo
Introduction
The X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 is an evaluation board based on digital MEMS microphones. It is compatible
with the Morpho connector layout and is designed around STMicroelectronics MP34DT01-M digital
microphones. It has two microphones soldered on board and it is compatible with digital microphone
coupon boards such as STEVAL-MKI129Vx and STEVAL-MKI155Vx. The X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1
allows the acquisition and streaming of up to two microphones using the I²S peripheral and up to four
coupon microphones using both I²S and SPI. It represents an easy to use and fast solution for the
development of microphone-based applications as well as a starting point for audio algorithm
implementation.
Figure 1: X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 evaluation board
May 2015
DocID027905 Rev 1
1/15
www.st.com
�
Contents
Contents
UM1900
Getting started ................................................................................ 3
1.1
Hardware requirements .................................................................... 3
System requirements ..................................................................... 4
Hardware description ..................................................................... 5
3.1
3.2
3.3
USB connector and power source .................................................... 5
Audio acquisition strategy ................................................................ 5
Solder bridges configurations ........................................................... 6
3.3.1
3.3.2
Solder bridges roles ........................................................................... 6
Sample use cases ............................................................................. 7
Connectors ................................................................................... 10
Board schematics......................................................................... 11
Layout ........................................................................................... 13
Revision history ........................................................................... 14
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2/15
DocID027905 Rev 1
�
UM1900
Getting started
1
Getting started
This section describes the hardware requirements for the X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1
evaluation board.
1.1
Hardware requirements
The X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 is an expansion board for use with STM32 Nucleo boards
(please refer to UM1724 on www.st.com for further information).
The STM32 Nucleo board must be connected to the X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 board, as
shown in Figure 2: "X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 on top of STM32 Nucleo board".
Figure 2: X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 on top of STM32 Nucleo board
The connection between the STM32 Nucleo and the X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 is designed for
use with any STM32 Nucleo board. When mounting the X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 on the
mainboard, ensure that all the pins are aligned with their corresponding connector. It is very
important to handle both boards carefully during this operation to avoid damaging or
bending the male/female pins and connectors.
ESD prevention measures must also be implemented to avoid damaging any X-NUCLEO-
CCA02M1 board components.
DocID027905 Rev 1
3/15
�
System requirements
2
System requirements
UM1900
Using the Nucleo boards with the X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 expansion board requires the
following software and hardware:
a Windows® (XP, Vista, 7, 8) PC for the software
a USB type A to Mini-B USB cable to connect the Nucleo to the PC for installation of
the board firmware package (order code: X-CUBE-MEMSMIC1); a utility running on
the user's PC will complete the demo.
The user's PC must have the following characteristics:
at least 128 MB of RAM
40 MB of available hard disk space for the X-CUBE-MEMSMIC1 firmware package
and relative documentation, available on www.st.com.
4/15
DocID027905 Rev 1
�
UM1900
3
Hardware description
Hardware description
The board allows the user to test the function of the STMicroelectronics MEMS
microphones. For this purpose two MP34DT01-M digital MEMS microphone are mounted
on the board and 6 headers (4 mounted with 2 additional footprints) are available for
connecting additional microphones using digital microphone coupon boards (STEVAL-
MKI129Vx or STEVAL-MKI155Vx), for further information refer to www.st.com. The
connection between the X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 and the STEVAL-MKI155V1 is shown in
Figure 3: "Connection with STEVAL-MKI155V1". The board interfaces with the STM32
Nucleo microcontrollers via the I²S and SPI peripherals for the synchronized acquisition of
up to 4 microphones. The board also provides USB streaming using the STM32 Nucleo
microcontroller USB peripheral; for this purpose, a USB connector is available as well as
the footprint to mount a dedicated oscillator that can be used to feed the host MCU through
the OSC_IN pin. Solder bridges are used in order to choose from different options,
depending on the number of microphones and the MCU peripherals involved.
Figure 3: Connection with STEVAL-MKI155V1
3.1
USB connector and power source
A USB connector available on the board supports audio streaming to the host PC. It can
also be used to power the whole system, Nucleo board included. To enable system power
sourcing from the X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 expansion board USB connector:
close Jumper J1 on the X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 expansion board
place JP5 in position E5 on the STM32 Nucleo board
3.2
Audio acquisition strategy
A digital MEMS microphone can be acquired by using different peripherals, such as SPI,
I²S or GPIO. It requires an input clock and it outputs a PDM stream at the same frequency
of the input clock. This PDM stream has to be filtered and decimated in order to be in the
standard PCM audio format. Two different digital MEMS microphones can be connected on
the same data line by configuring the first to generate valid data on the rising edge of the
clock and the other on the falling edge by setting the L/R pin of each microphone
differently. On the X-NUCLEO-CCA02M1 expansion board, two microphones share the
same data line and are routed to the Nucleo STM32 I²S peripheral (the first and the second
microphone) and SPI peripheral (the third and the fourth).
DocID027905 Rev 1
5/15
�
Hardware description
UM1900
In this scenario, microphone acquisition functions thus: a precise clock signal is generated
by I²S peripheral while SPI is configured in slave mode and is fed by the same timing signal
generated by I²S. This clock is then halved by a timer and input to the microphones: the
SPI and I²S peripherals operate at twice the microphone frequency, so that they can read
data on both the rising and falling edge of the microphone clock, thus reading the bits of
two microphones each. A software demuxing step is required to separate the signal from
the two microphones and allows further processing like PDM to PCM conversion. Figure 4:
"General acquisition strategy block diagram" shows a simplified diagram of the acquisition
process described in this paragraph. For further information about MEMS microphone and
PDM to PCM decimation, please refer www.st.com and AN3998.
For single microphone acquisition, the correct microphone timer is generated directly by I²S
and one single microphone data line is read by the same peripheral. For an example
application of microphone acquisition, decimation and streaming based on X-NUCLEO-
CCA02M1 board, please refer the board firmware package (order code: X-CUBE-
MEMSMIC1).
Figure 4: General acquisition strategy block diagram
3.3
Solder bridges configurations
Various board configurations are possible, depending on the use cases. MEMS
microphones can be connected (or disconnected) to morpho pins, and thus to MCU
peripherals, using ad hoc solder bridges. Clock routing can als be changed according to
specific needs. This section helps the user understand the role of each solder bridge and
analyzes some of the more common use cases.
3.3.1
Solder bridges roles
In Table 1: "Solder bridge descriptions", the solder bridge dunctions are summarized with
respect to the audio acquisition strategies described in the previous section.
Table 1: Solder bridge descriptions
Function
Solder bridge
Connects USB D- pin to OTG_FS_DM pin on the MCU
Connects USB D+ pin to OTG_FS_DP pin on the MCU
Routes onboard oscillator output to OSC_IN MCU pin
Connect microphone clock to MCU timer output channel
Routes I²S clock to SPI clock
SB1
SB2
SB6
SB7
SB8
6/15
DocID027905 Rev 1
�
UM1900
Function
Hardware description
Solder bridge
Merges onboard microphone PDMs in order to be acquired with a single
interface
Connects MIC34 PDM to MCU SPI MOSI pin
Connects MIC12 PDM to MCU I²S SD pin
Reserved
I²S clock from MCU
Connects I²S clock directly to MIC clock without passing through timer
Connect I²S clock to MCU timer input channel
SB9
SB10
SB11
SB12
SB13
SB14
SB15
3.3.2
Sample use cases
In this section, we analyze specific use cases together with the corresponding solder bridge
configurations. Custom setups are also possible for ad-hoc functionalities. Note that SB1,
SB2, SB6 are reserved for the USB or Oscillator pins and are not part of the audio
acquisition process.
1-microphone acquisition
The I²S peripheral is used to directly acquire and give the right clock to the microphone. For
this configuration, you need the following SB configuration.
Table 2: Solder bridge configuration for 1 microphone acquisition
SB
SB7
SB8
SB9
SB10
SB11
SB12
SB13
SB14
SB15
SB16
SB17
SB18
SB19
SB20
SB21
Status
Open
Open
Open
Open
Close
Open
Close
Close
Open
Open
Open
Open
Open
Open
Open
In addition, J2 is placed in position 1-2 for onboard microphone acquisition or 2-3 for an
external microphone, while J3 is left open. If using external microphones, do not plug
anything in M2_EXT header.
DocID027905 Rev 1
7/15
�
Hardware description
2-microphone acquisition
UM1900
As previously mentioned, this is the case in which the I²S peripheral is used to generate
twice the frequency needed by the microphones. In this scenario, the clock is then halved
by the timer and routed to the microphones to give them the right clock. I²S therefore reads
values from both edges of the merged PDM lines. For this configuration you need the
following SB configuration:
Table 3: Solder bridge configuration for 2-microphone acquisition
SB
SB7
SB8
SB9
SB10
SB11
SB12
SB13
SB14
SB15
SB16
SB17
SB18
SB19
SB20
SB21
Status
Close
Open
Open /Close
Open
Close
Open
Close
Open
Close
Open
Open
Open
Open
Open
Open
In addition, J2 is placed in position 1-2 for onboard microphone acquisition or 2-3 for using
external microphones, while J3 must is open. When acquiring onboard microphones, close
SB9 to acquire both of them.
4-external-microphone acquisition
In this case, the I²S peripheral is used to generate a clock frequency that is twice the
frequency needed by the microphones, and SPI is configured in slave mode in order to use
such timing. As in the previous case, the clock is then halved by the timer and routed to the
microphones to give the right clock. I²S and SPI read values from both the edges of the
merged PDM lines. For this configuration you need the following SB configuration:
Table 4: Solder bridge configuration for 4-microphone acquisition
SB
SB7
SB8
SB9
SB10
SB11
SB12
SB13
SB14
Status
Close
Close
Open
Close
Close
Open
Close
Open
8/15
DocID027905 Rev 1
�
















 V2版本原理图(Capacitive-Fingerprint-Reader-Schematic_V2).pdf
V2版本原理图(Capacitive-Fingerprint-Reader-Schematic_V2).pdf 摄像头工作原理.doc
摄像头工作原理.doc VL53L0X简要说明(En.FLVL53L00216).pdf
VL53L0X简要说明(En.FLVL53L00216).pdf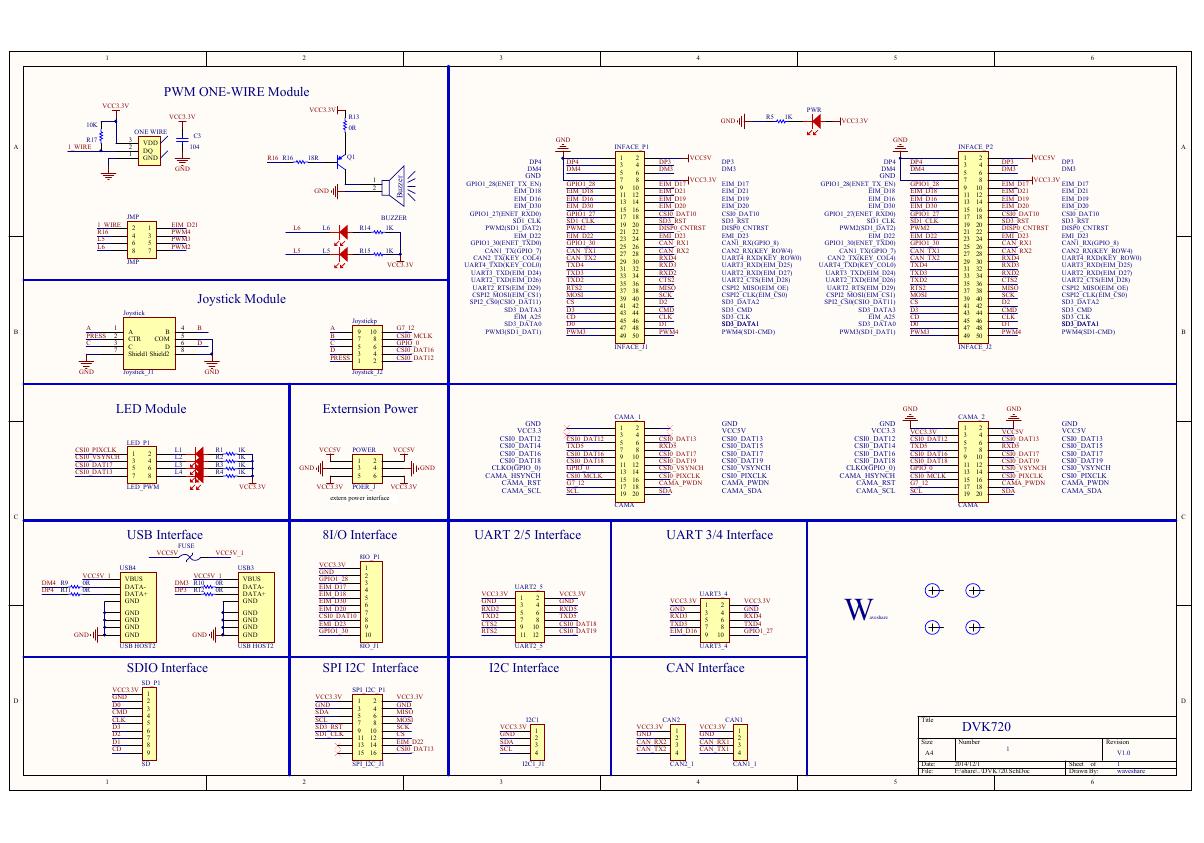 原理图(DVK720-Schematic).pdf
原理图(DVK720-Schematic).pdf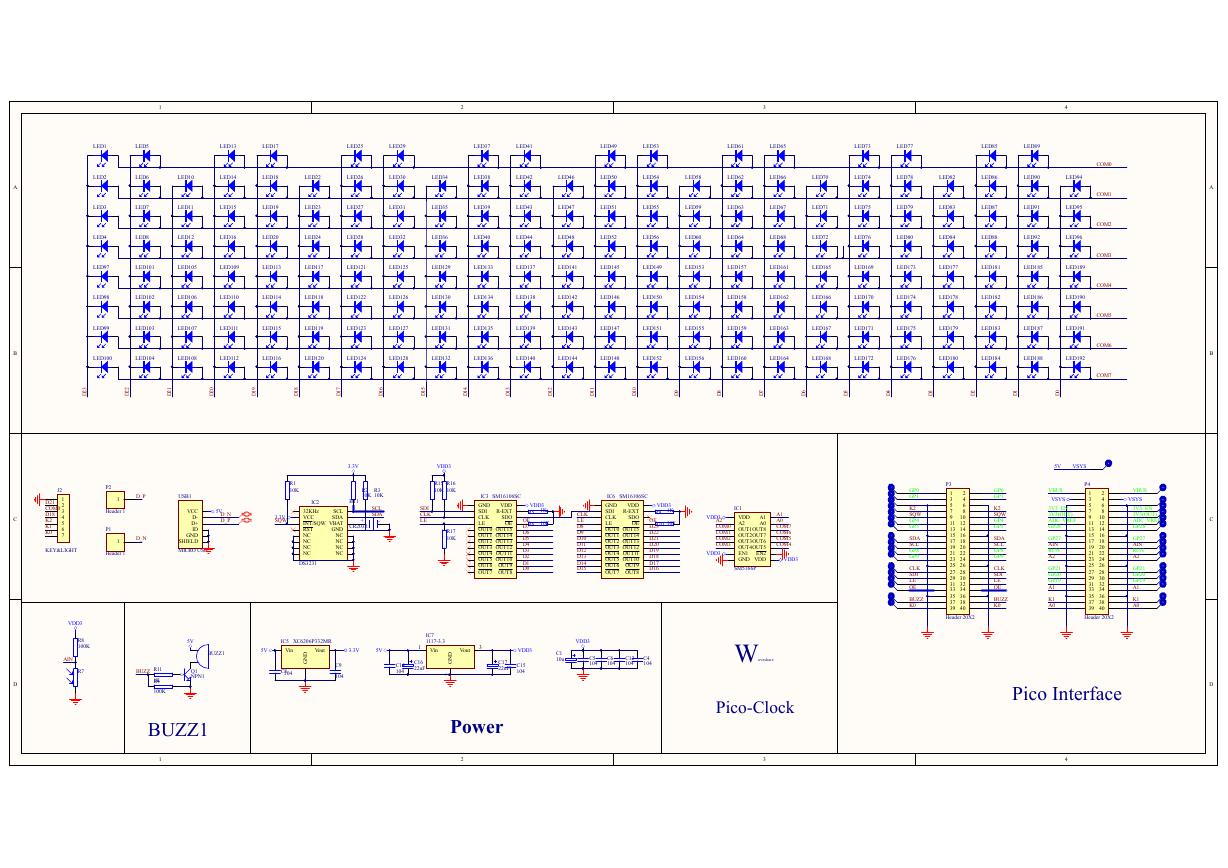 原理图(Pico-Clock-Green-Schdoc).pdf
原理图(Pico-Clock-Green-Schdoc).pdf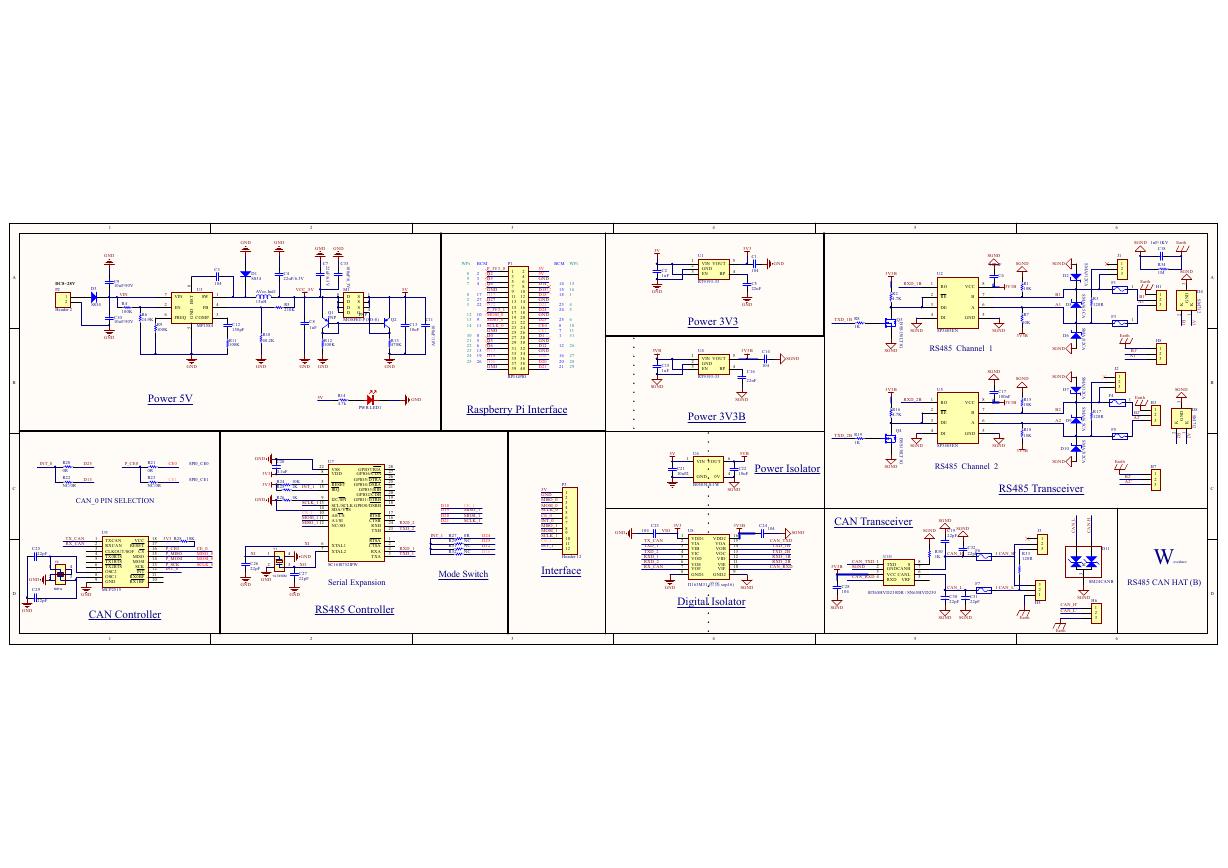 原理图(RS485-CAN-HAT-B-schematic).pdf
原理图(RS485-CAN-HAT-B-schematic).pdf File:SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
File:SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf ADS1263(Ads1262).pdf
ADS1263(Ads1262).pdf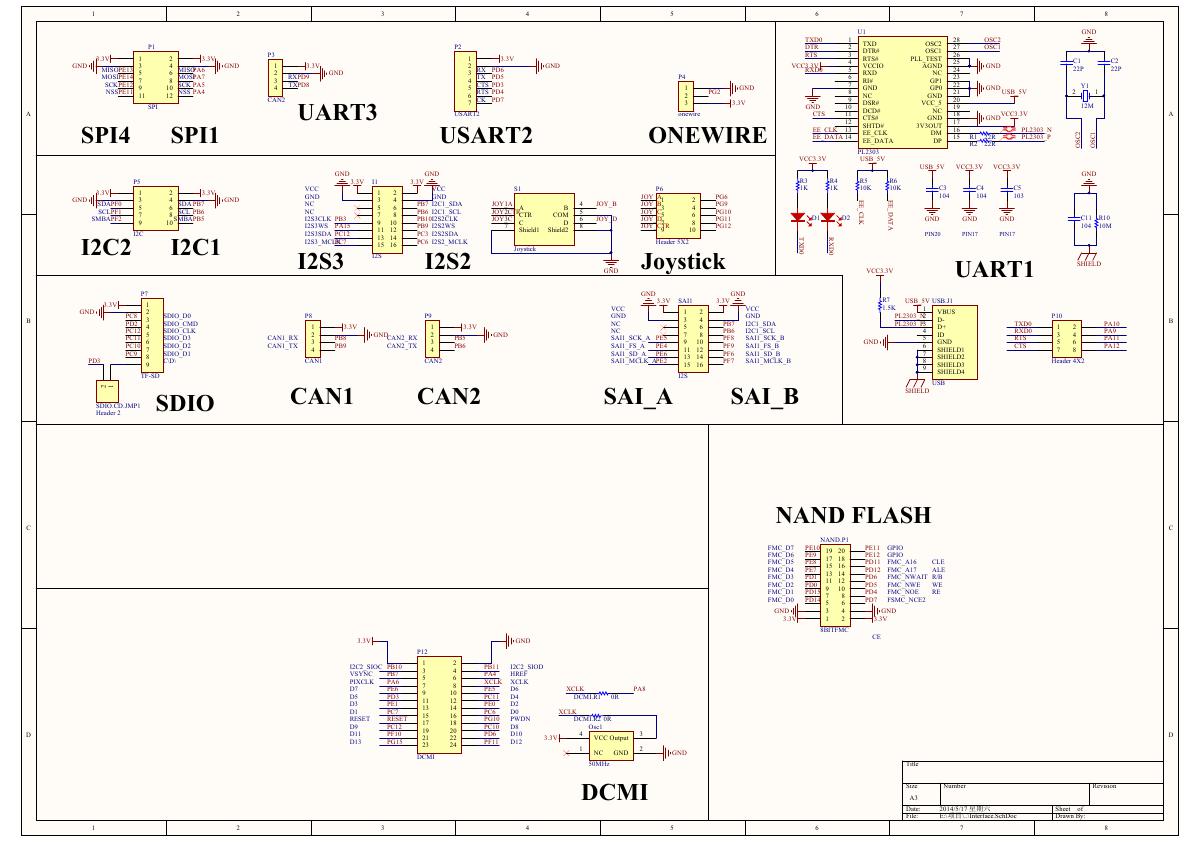 原理图(Open429Z-D-Schematic).pdf
原理图(Open429Z-D-Schematic).pdf 用户手册(Capacitive_Fingerprint_Reader_User_Manual_CN).pdf
用户手册(Capacitive_Fingerprint_Reader_User_Manual_CN).pdf CY7C68013A(英文版)(CY7C68013A).pdf
CY7C68013A(英文版)(CY7C68013A).pdf TechnicalReference_Dem.pdf
TechnicalReference_Dem.pdf