Features
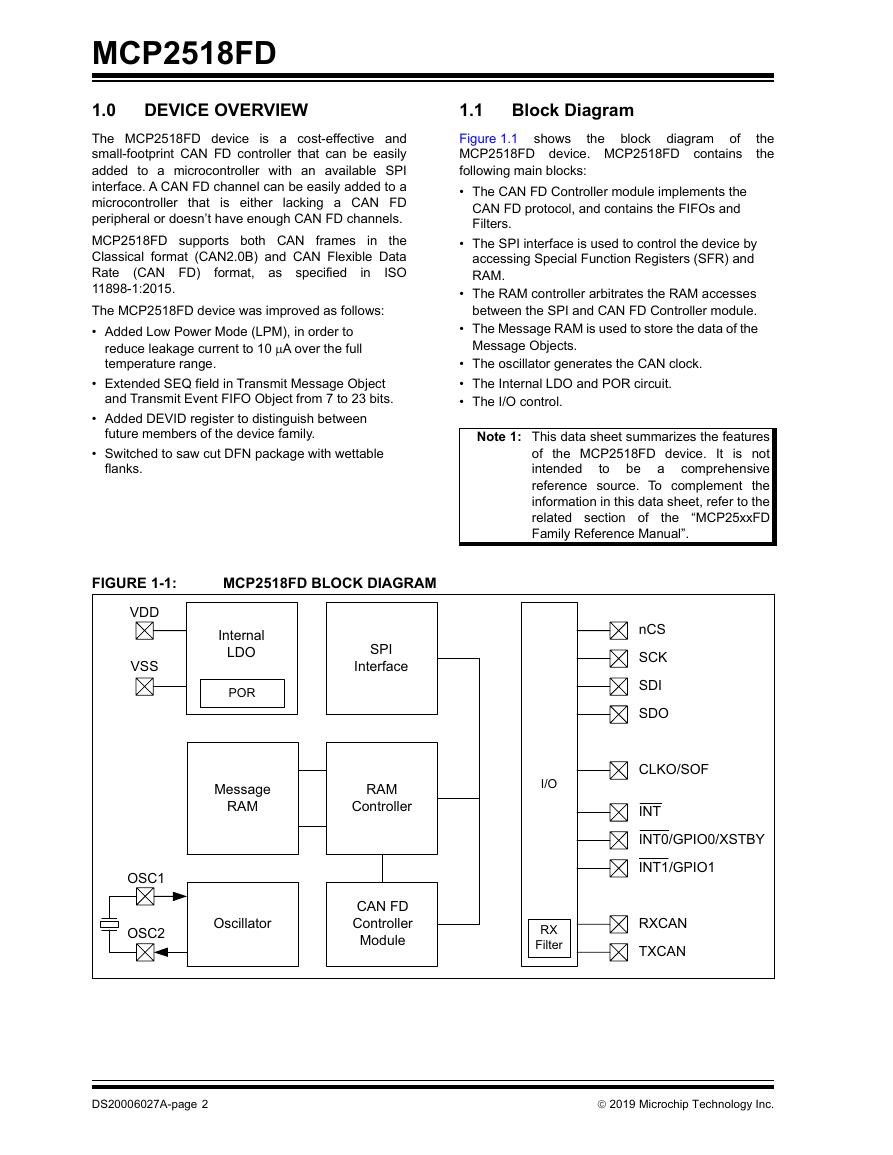
General
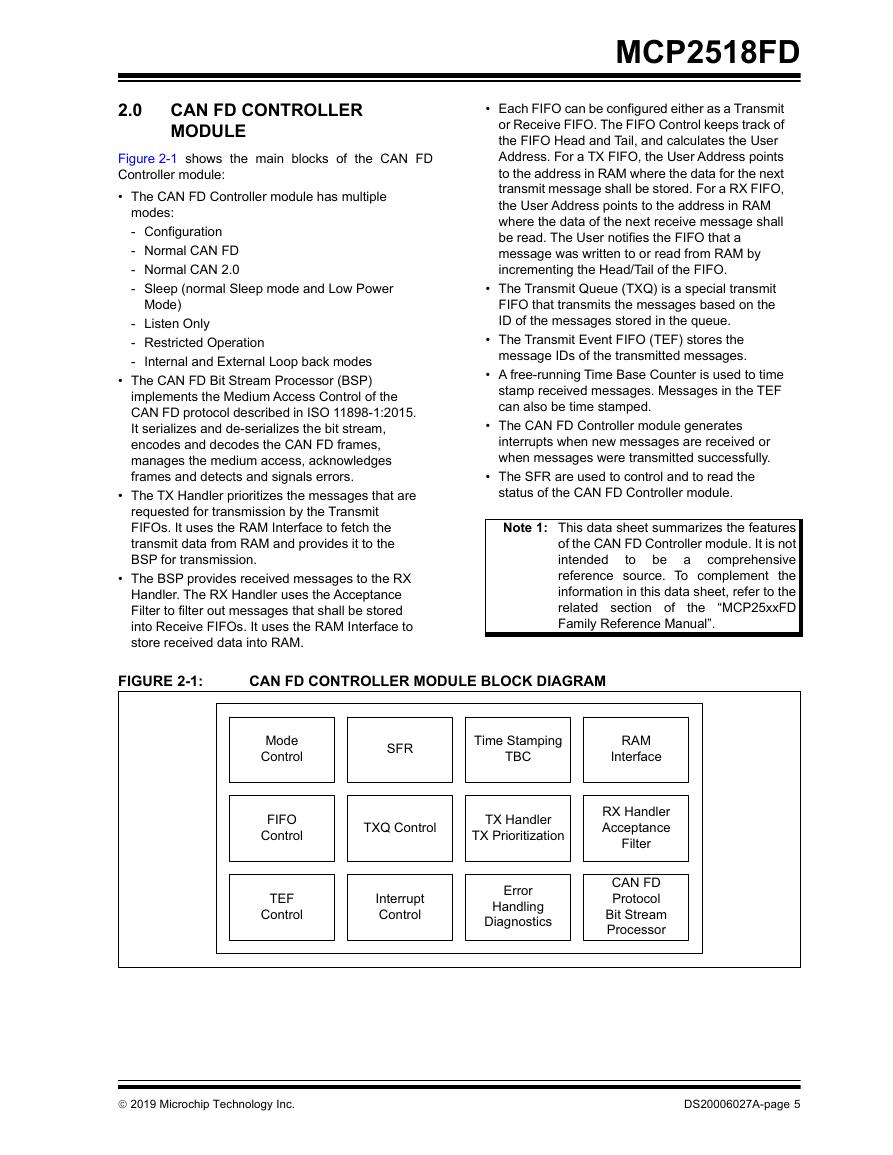
Message FIFOs
Message Transmission
Message Reception
Special Features
Oscillator Options
SPI Interface
Safety Critical Systems
Additional Features
Package Types
1.0 Device Overview
1.1 Block Diagram
FIGURE 1-1: MCP2518FD Block Diagram
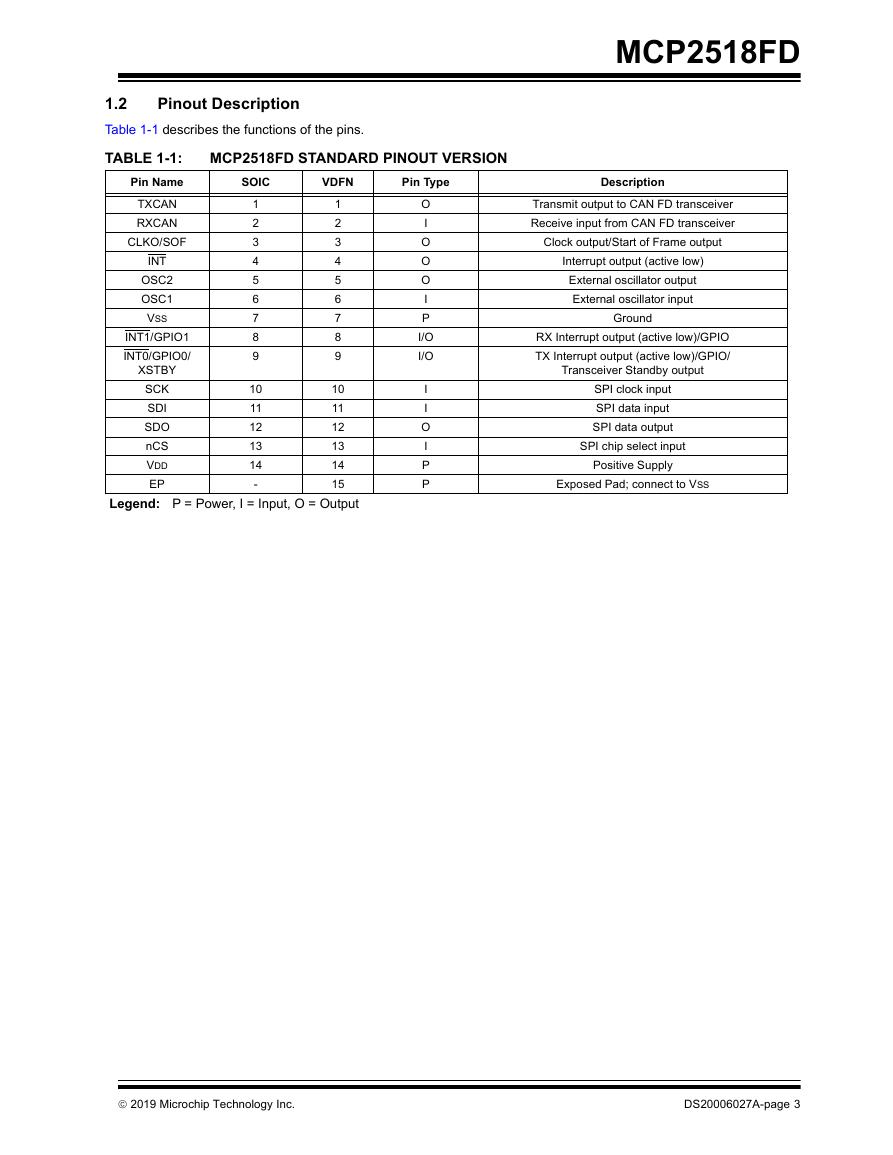
1.2 Pinout Description
TABLE 1-1: MCP2518FD STANDARD PINOUT VERSION
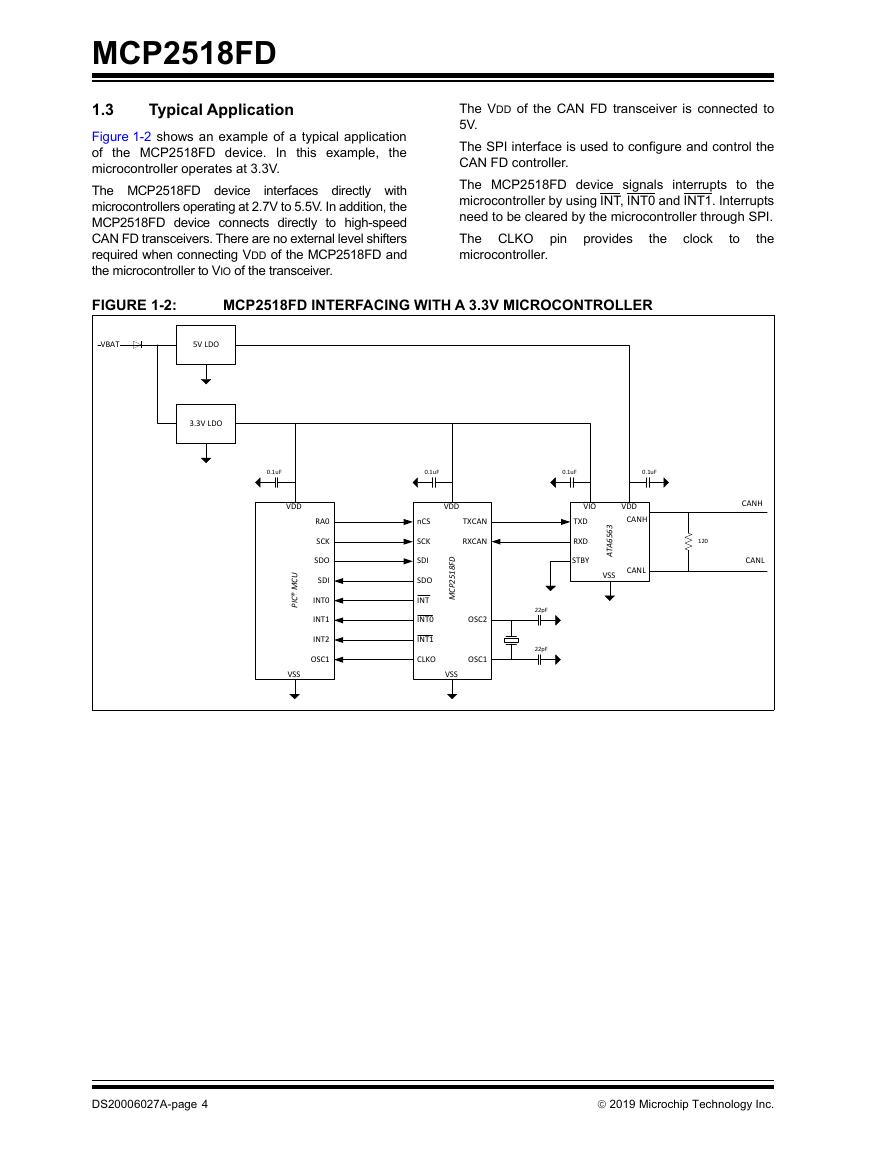
1.3 Typical Application
FIGURE 1-2: MCP2518FD interfacing with a 3.3V microcontroller
2.0 CAN FD Controller module
FIGURE 2-1: CAN FD Controller module Block Diagram
External CAN FD Controller with SPI Interface
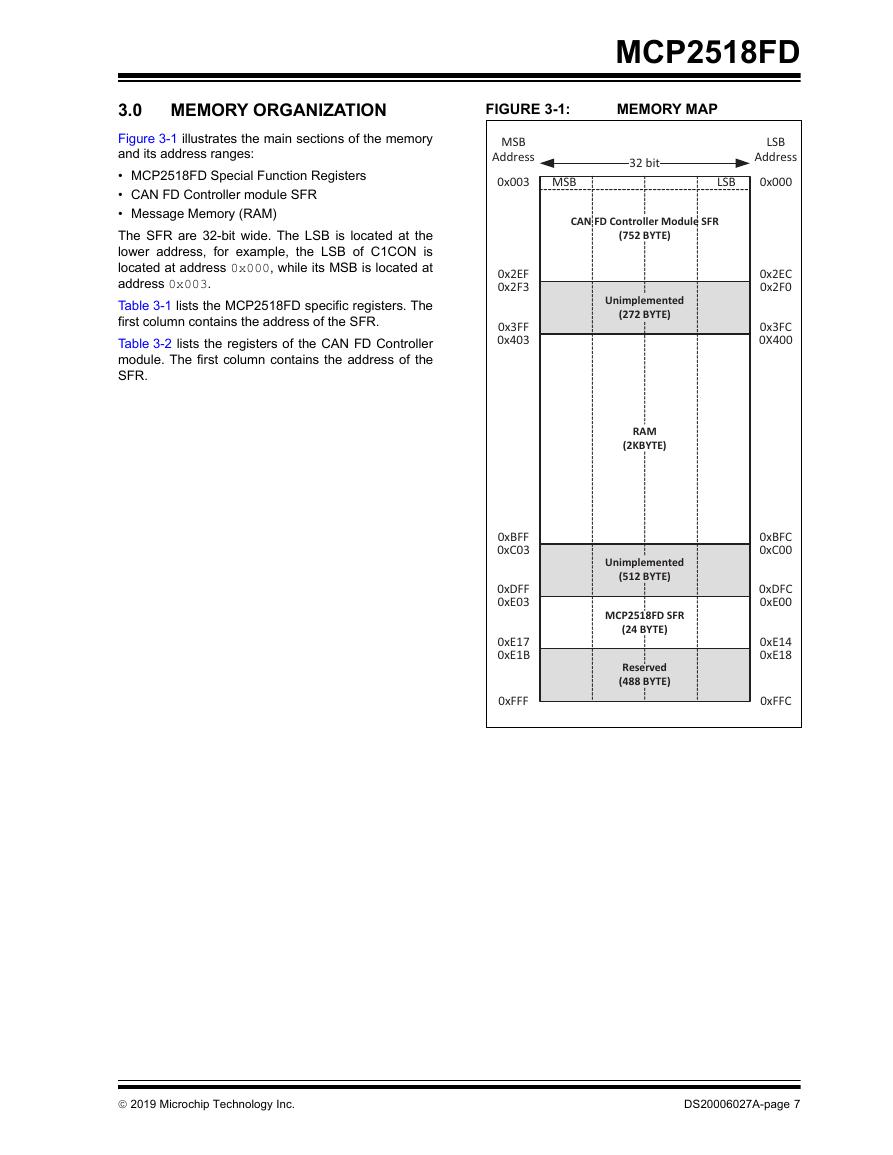
3.0 Memory Organization
FIGURE 3-1: Memory Map
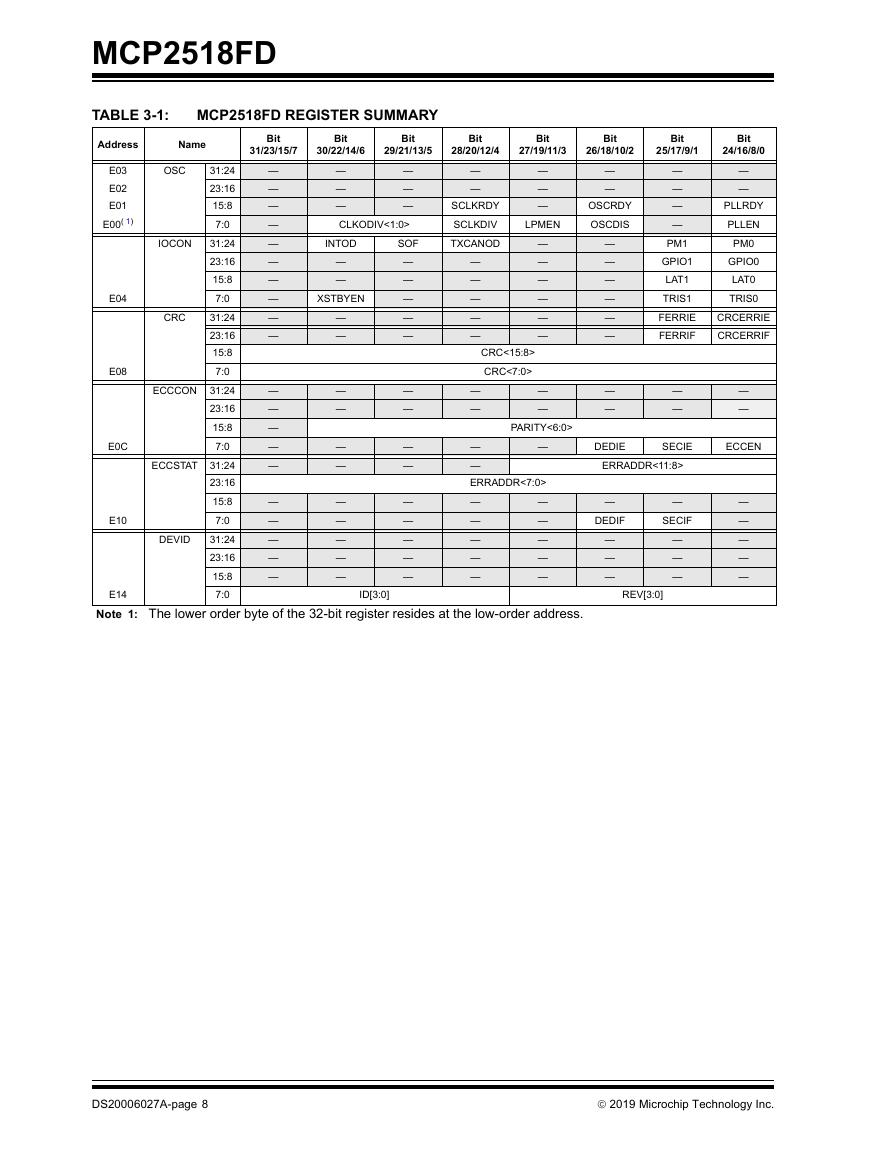
TABLE 3-1: MCP2518FD Register Summary
TABLE 3-2: CAN FD Controller module Register Summary
3.1 MCP2518FD Specific Registers
TABLE 3-3: Register Legend
EXAMPLE 3-1:
Register 3-1: OSC – MCP2518FD Oscillator Control Register
Register 3-2: IOCON – INPUT/OUTPUT Control Register
Register 3-3: CRC – CRC Register
Register 3-4: ECCCON – ECC Control Register
Register 3-5: ECCSTAT – ECC STATUS REGISTER
Register 3-6: DEVID – Device ID Register
3.2 CAN FD Controller Module Registers
TABLE 3-4: Register Legend
EXAMPLE 3-2:
Register 3-7: CiCON – CAN Control Register
Register 3-8: CiNBTCFG – Nominal Bit Time Configuration Register
Register 3-9: CiDBTCFG – Data Bit Time Configuration Register
Register 3-10: CiTDC – Transmitter Delay Compensation Register
Register 3-11: CiTBC – Time Base Counter Register
Register 3-12: CiTSCON – Time Stamp Control Register
Register 3-13: CiVEC – Interrupt Code Register
Register 3-14: CiINT – Interrupt Register
Register 3-15: CiRXIF – Receive Interrupt Status Register
Register 3-16: CiRXOVIF – Receive Overflow Interrupt Status Register
Register 3-17: CiTXIF – Transmit Interrupt Status Register
Register 3-18: CiTXATIF – Transmit Attempt Interrupt Status Register
Register 3-19: citxreq – Transmit Request Register
Register 3-20: CiTREC – Transmit/Receive Error Count Register
Register 3-21: CiBDIAG0 – bus Diagnostic Register 0
Register 3-22: CiBDIAG1 – Bus Diagnostics Register 1
Register 3-23: CiTEFCON – Transmit Event FIFO Control Register
Register 3-24: CiTEFSTA – Transmit Event FIFO Status Register
Register 3-25: CiTEFUA – Transmit Event FIFO User Address Register
Register 3-26: CiTXQCON – Transmit QUEUE Control Register
Register 3-27: CiTXQSTA – Transmit Queue Status Register
Register 3-28: citxqua – Transmit Queue User Address Register
Register 3-29: CiFIFOCONm – FIFO Control Register m, (m = 1 to 31)
Register 3-30: CiFIFOSTAm – FIFO Status Register m, (m = 1 to 31)
Register 3-31: CiFIFOUAm – FIFO User Address Register m, (m = 1 to 31)
Register 3-32: CiFLTCONm – Filter Control Register m, (m = 0 to 7)
Register 3-33: CiFLTOBJm – Filter Object Register m,(m = 0 to 31)
Register 3-34: CiMASKm – Mask Register m, (m = 0 to 31)
3.3 Message Memory
FIGURE 3-2: Message Memory organization
FIGURE 3-3: ECC Logic
TABLE 3-5: TRANSMIT MESSAGE OBJECT (TXQ AND TX FIFO)
TABLE 3-6: RECEIVE MESSAGE OBJECT
TABLE 3-7: Transmit Event FIFO Object
4.0 SPI Interface
FIGURE 4-1: SPI Instruction Format
TABLE 4-1: SPI Instructions
4.1 SFR Access
FIGURE 4-2: Reset Instruction
FIGURE 4-3: SFR Read Instruction
FIGURE 4-4: SFR WRITE Instruction
4.2 Message Memory Access
FIGURE 4-5: Message Memory Read Instruction
FIGURE 4-6: Message Memory WRITE Instruction
4.3 SPI Commands with CRC
FIGURE 4-7: CRC Calculation
FIGURE 4-8: SFR Read with CRC Instruction
FIGURE 4-9: SFR Write with CRC Instruction
FIGURE 4-10: SFR Write SAFE with CRC Instruction
FIGURE 4-11: message Memory Read with CRC Instruction
FIGURE 4-12: Message Memory Write with CRC Instruction
FIGURE 4-13: Message Memory Write SAFE with CRC Instruction
5.0 Oscillator
FIGURE 5-1: MCP2518FD Oscillator Block Diagram
6.0 I/O Configuration
FIGURE 6-1: Interrupt PINs
7.0 Electrical Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings†
TABLE 7-1: DC Characteristics
TABLE 7-2: CLKOUT and SOF AC Characteristics
TABLE 7-3: Crystal Oscillator AC Characteristics
TABLE 7-4: CAN Bit rate
TABLE 7-5: CAN RX Filter AC Characteristics
TABLE 7-6: SPI AC Characteristics
TABLE 7-7: Temperature Specifications
8.0 Typical Performance Curves
FIGURE 8-1: Average IDDS vs. Temperature.
FIGURE 8-2: Average IDDLPM vs. Temperature.
9.0 Packaging Information
9.1 Package Marking Information
Appendix A: Revision History
Revision A (April 2019)
Appendix B: CAN FD Conformance
TABLE B-1: ISO Optional Features
Product Identification System
Worldwide Sales and Service










 V2版本原理图(Capacitive-Fingerprint-Reader-Schematic_V2).pdf
V2版本原理图(Capacitive-Fingerprint-Reader-Schematic_V2).pdf 摄像头工作原理.doc
摄像头工作原理.doc VL53L0X简要说明(En.FLVL53L00216).pdf
VL53L0X简要说明(En.FLVL53L00216).pdf 原理图(DVK720-Schematic).pdf
原理图(DVK720-Schematic).pdf 原理图(Pico-Clock-Green-Schdoc).pdf
原理图(Pico-Clock-Green-Schdoc).pdf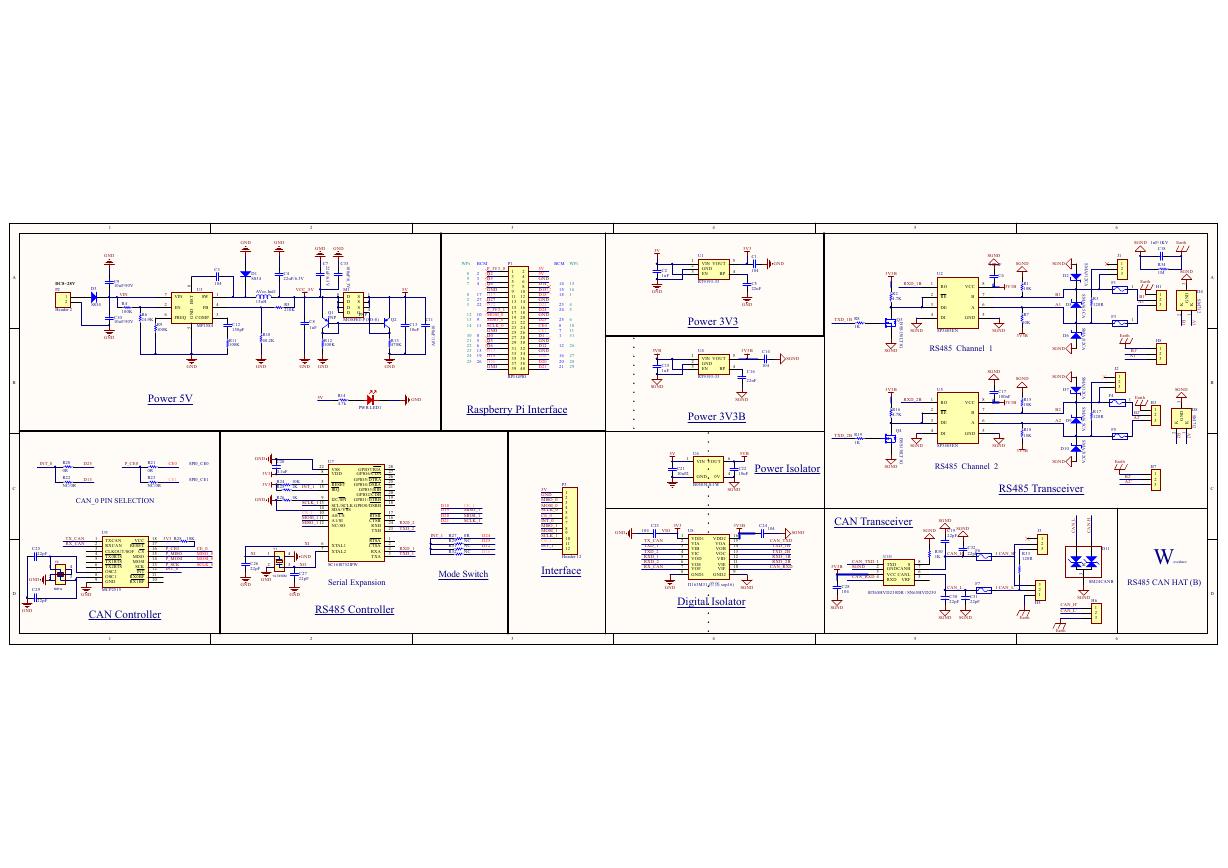 原理图(RS485-CAN-HAT-B-schematic).pdf
原理图(RS485-CAN-HAT-B-schematic).pdf File:SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
File:SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf ADS1263(Ads1262).pdf
ADS1263(Ads1262).pdf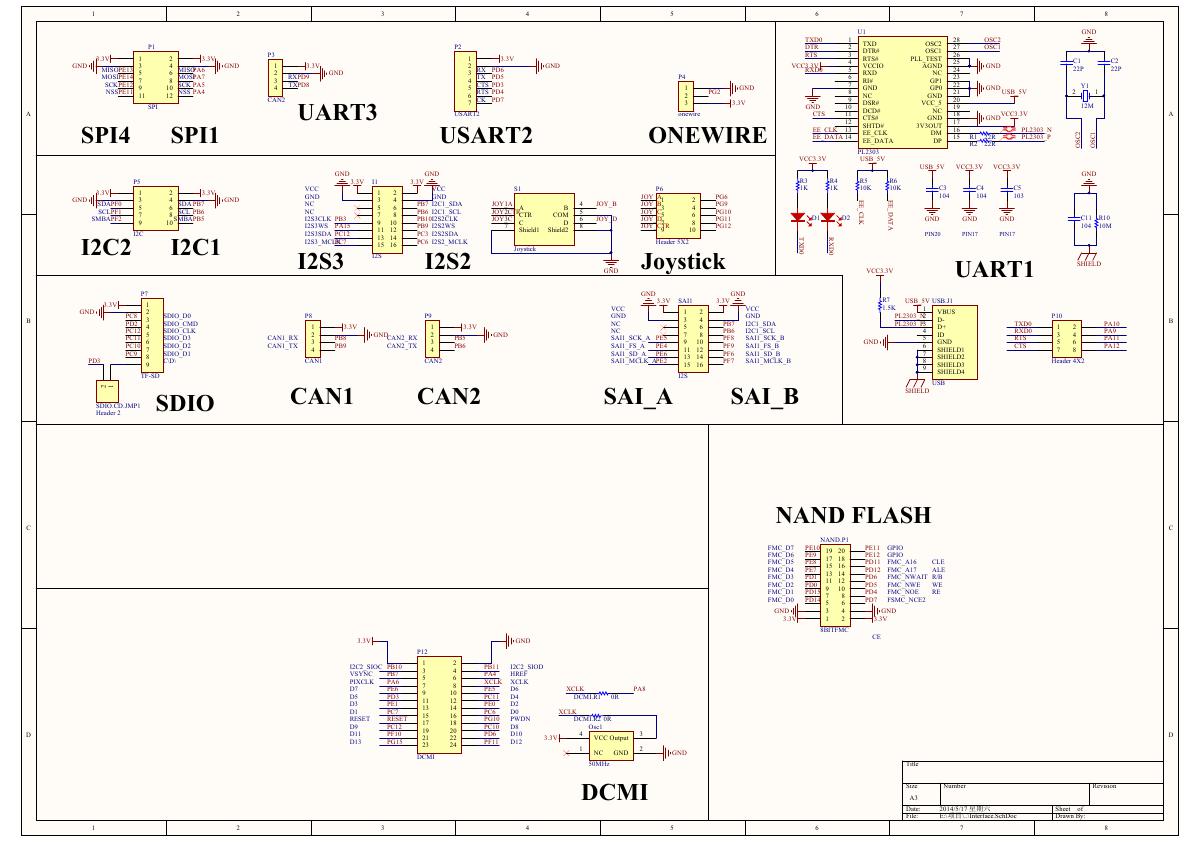 原理图(Open429Z-D-Schematic).pdf
原理图(Open429Z-D-Schematic).pdf 用户手册(Capacitive_Fingerprint_Reader_User_Manual_CN).pdf
用户手册(Capacitive_Fingerprint_Reader_User_Manual_CN).pdf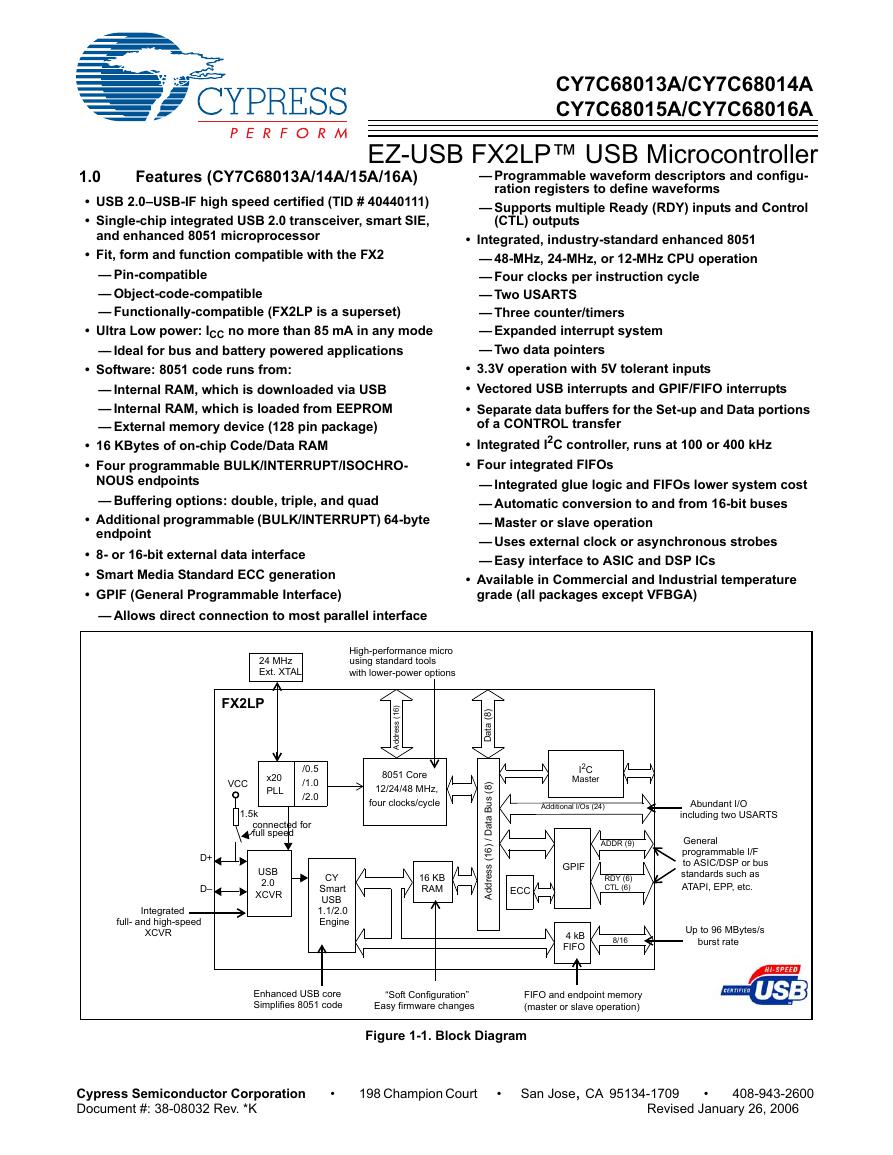 CY7C68013A(英文版)(CY7C68013A).pdf
CY7C68013A(英文版)(CY7C68013A).pdf TechnicalReference_Dem.pdf
TechnicalReference_Dem.pdf