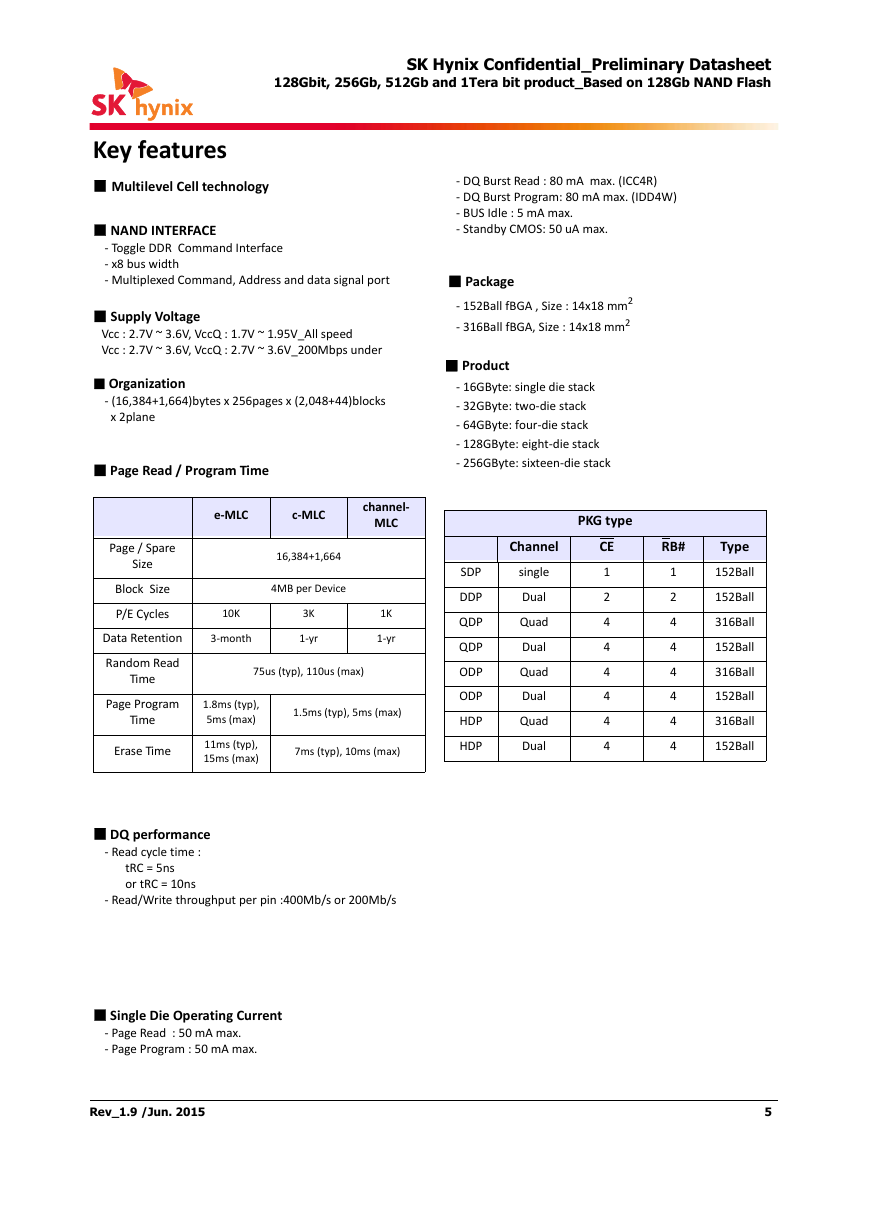
Key features
1. SUMMARY DESCRIPTION
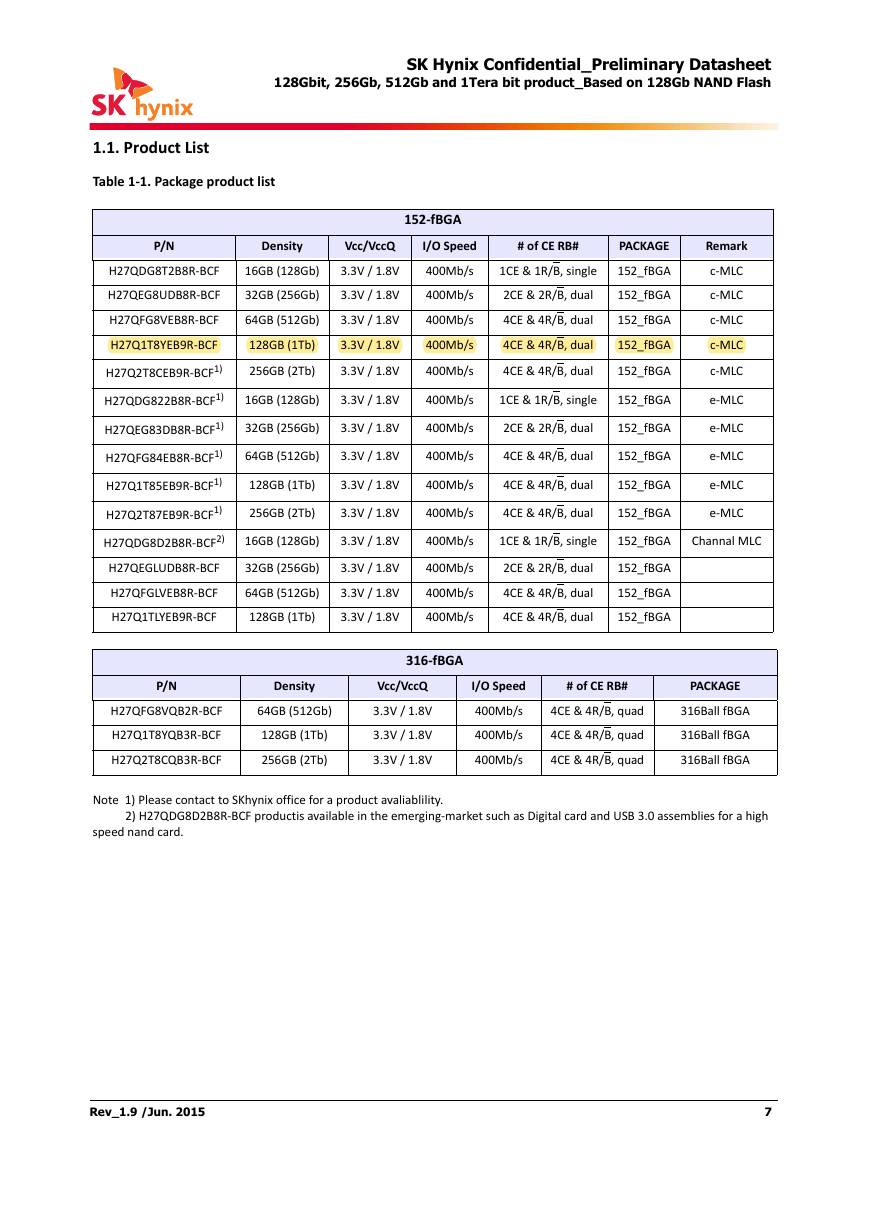
1.1. Product List
1.2. Part number Information
1.3. Definitions and Abbreviations
1.4. Diagram Legend
1.5. Block Diagram
Figure 1-1. NAND Flash Die Functional Block Diagram
2. Physical Interface and Measurement condition
2.1. Package Information
Figure 2-1. H27QDG8T2B8R, H27QDG8D2B8R: 1CE Single Channel ball assignments for 8-bit data sccess
Note 1) For H27QDG8D2B8R-BCF product, K-9 Pin site is a "Not Use".
Figure 2-2. H27QEG8UDB8R: 2CE Dual Channel ball assignments for 8-bit data sccess
(READ)Figure 2-3. H27QFG8VEB8R, H27Q1T8YEB9R & H27Q2T8CEB9R: 4CE Dual Channel ball assignments for 8-bit data sccess
Figure 2-4. TBD: 8CE Dual Channel ball assignments for 8-bit data sccess
Figure 2-5. BGA-152 ball spacing requrements (top & view, dimensions in millimeters)
Table 2-1. 152-fBGA 14x18mm, Package Mechanical Data
Figure 2-6. H27QFG8VQB2R, H27Q1T8YQB3R & H27Q2T8CEB3R: 4CE Quad-Channel, 316 ball assignments for 8- bit data sccess
Figure 2-7. BGA-316 ball spacing requrements (top & view, dimensions in millimeters)
Table 2-2. BGA-316 ball 14mmx18mm, Package Mechanical Data
2.2. PIN DESCRIPTION
Table 2-3. 152Ball fBGA Input/ Output capacitance (TA=25C, VCC=3.3V, f=100MHz)
Table 2-4. 316Ball fBGA Input/ Output capacitance (TA=25C, VCC=3.3V, f=100MHz)
2.3. Absolute Maximum DC Ratings
Table 2-5. Absolute maximum DC ratings
2.4. Operating temperature condition
Table 2-6. Operating Temperature Condition
2.5. Recommended Operating Conditions
Table 2-7. Recommended Operating Condition
2.6. AC Overshoot/Undershoot Requirements
Table 2-8. AC Overshoot/Undershoot Specification
Figure 2-8. Overshoot/Undershoot Diagram
2.7. DC and Operating Characteristics
Table 2-9. DC & Operating Characteristics for VccQ=3.3V (Single Die)
Table 2-10. DC & Operating Characteristics for VccQ=1.8V (Single Die)
2.8. AC Test Condition
Table 2-11. Single Ended without VREFQ AC & DC input level
Table 2-12. Single Ended with VREFQ AC & DC input level
Table 2-13. DC Electrical Characteristics for ODT (not supported)
2.8.1. VREFQ Tolerance
Figure 2-9. VREFQ(DC) tolerance and VREFQ AC-noise limits
2.8.2. Differential Input/Output AC Characteristics (VCCQ=1.8V only)
Table 2-14. Differential AC/DC Input Logic Level
Figure 2-10. Differential signal levels
2.8.3. DQ Driver Strength
Table 2-15. DQ Driver Strength Settings
Table 2-16. Testing Conditions for Impedance Values
Table 2-17. Output Driver Strength Impedance Values
Table 2-18. Pull-up and Pull-down Output Impedance Mismatch
2.8.4. Input/Output Slew rate
Table 2-19.Derating factor
Table 2-20.Input Slew rate
Table 2-21. Testing Conditions for Input Slew Rate
Table 2-22. Output Slew Rate Requirements
Table 2-23. Testing Conditions for Output Slew Rate
Figure 2-11. tRISE and tFALL Definition for Output Slew Rate
2.9. On-Die Termination (Not Supported)
2.9.1. On-Die Termination
2.9.2. ODT Setting
Figure 2-12. Set ODT Sequence
Figure 2-13. ODT Functional Representation
2.9.3. ODT On/Off During Read
2.9.4. ODT On/Off During Program
Figure 2-14. ODT On/Off During Program
2.10. AC and DC Input Measurement Levels
Table 2-24. AC Test condition
2.11. AC Timing Characteristics
2.11.1. Timing Parameters Description
Table 2-25. Toggle DDR Timing Parameters Description
2.11.2. Timing Parameters Table
Table 2-26. AC Timing Characteristics
2.11.3. Read/Program / Erase Characteristics
Table 2-27. NAND Read/Program/Erase Characteristics
3. Memory Organization
3.1. Memory Size
Figure 3-1. Memory organization for 128Gb Logical Unit
3.2. Addressing (I)
3.2.1. Single Die Addressing
Table 3-1. Memory addressing.
3.3. Target Memory Organization
Figure 3-2. Target Memory Organization
3.4. Addressing (II)
Figure 3-3. Row Address Layout
3.4.1. Plane Addressing
Figure 3-4. Position of Plane Address
3.4.2. Extended Block Arrangement
3.4.3. Valid Blocks
Table 3-2. The number of valid block
3. Invalid blocks are one that contains one or more bad bits. The device may contain bad blocks on shipment.
3.5. Factory Defect Mapping
3.5.1. Device Requirements
Figure 3-5. Area marked in first or last page of block indicating defect
3.5.2. Host Requirements
Figure 3-6. Flow chart to create initial invalid block table
3.6. Addressing For Program Operation
Table 3-2. Paired Page Address Information
4. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
4.1. DATA PROTECTION AND POWER TRANSITION SEQUENCE
4.1.1. Data Protection
4.1.2. Power Up Sequence
4.1.3. Power Down Sequence
Figure 4-1. Initialization Timing
4.2. Data Interface / Timing Mode Transitions
4.2.1. The following transitions between data interface are supported:
4.2.2. SDR Transition from DDR
4.3. MLC to SLC mode transition (MLC2SLC)
4.3.1. Difference between MLC and SLC Addressing
Table 4-1. Memory SLC addressing.
Table 4-2. SLC Performance
4.4. Mode Selection
Table 4-3. Mode Selection
4.5. General Timing
4.5.1. Command Latch Cycle
Figure 4-3. Command Latch CycleI
4.5.2. Address Latch Cycle
Figure 4-4. Address Latch Cycle
4.5.3. Basic Data Input Timing
Figure 4-5. Basic Data Input Timing
4.5.4. Basic Data Output Timing
Figure 4-6. Basic Data Output Timing
4.5.5. Read ID Operation
Figure 4-7. Read ID Operation
4.5.6. Read Status Cycle
Figure 4-8. Read Status Cycle
4.5.6.1. Read Status cycle before Toggle DDR setting at Initialization sequence by FFh command
Figure 4-9. Read Status cycle before Toggle DDR setting at Initialization sequence by FFh command
4.5.7. Set Feature
Figure 4-10. Set Feature
4.5.8. Get Feature
Figure 4-11. Get Feature
4.5.9. Page Program Operation
Figure 4-12. Page Program Operation
5. Memory Operation
5.1. BASIC OPERATION
Basic Command sets
5.1.1. Page Read Operation
Figure 5-1. Page Read Sequence
5.1.1.1. Page Read Operation with Random Data Output
Figure 5-2. Page Read with Random Data Output Sequence
5.1.1.2. Data Out After Read Status
Figure 5-3. Data Out After Read Status Sequence
5.1.2. Fast 8KB Read (Fast Half page Read)
Figure 5-4. Fast Half READ sequence
Figure 5-5. Page layout for Fast Half READ
5.1.3. Page Program Operation
Figure 5-6. Page Program Sequence
5.1.3.1. Program Operation with Random Data Input
Figure 5-7. Program operation with Random Data Input Sequence
5.1.4. Block Erase Operation
Figure 5-8. Block Erase Sequence
5.1.5. Copy-Back Program Operation
Figure 5-9. Copy-Back Program Sequence
5.1.5.1. Copy-Back Program Operation with Random Data Input
Figure 5-10. Copy-Back Program with Random Data Input Sequence
5.1.6. Set Feature Operation
Figure 5-11. Set Feature Sequence
Table 5-1. Set feature addresses
5.1.6.1. Timing Mode setting (01h)
Table 5-2. Timing mode setting assignment
5.1.6.2. Toggle 2.0 specific setting (02h)
Table 5-3. Toggle 2.0 specific setting assignment
Table 5-4. Definition of Toggle 2.0 specific setting
Figure 5-12. Example of DQS latency (Write / Read)
5.1.6.3. Driver strength setting (10h)
Table 5-5. Definition of Driver strength setting
5.1.6.4. External VPP (30h)
5.1.7. Get Feature Operation
Figure 5-13. Get Feature Sequence
5.1.8. Read ID Operation
Figure 5-14. Read ID Sequence
5.1.8.1. 00h Address ID Definition
Table 5-7. 00h address ID cycle
Table 5-9. Read ID Definition - Address ID cycle
Table 5-10. 40h Address ID Cycle
Table 5-11. 40h Address ID Cycle
5.1.9. Read Status Operation
Table 5-12. Read Status Definition
Figure 5-15. Read Status Sequence
5.1.10. Reset Operation
Figure 5-16. Reset Sequence
5.1.11. Reset LUN operation
Figure 5-17. Single chip Reset Sequence
5.2. Extended OPERATION
5.2.1. Extended Command Sets
Table 5-13. Extended Command Sets
5.2.2. Two-Plane Page Read Operation
Figure 5-18. Example Timing with Two-plane Page Read (Primary)
Figure 5-19. Example Timing with Two-plane Page Read (Secondary)
5.2.3. Two-Plane Page Program Operation
Figure 5-20. Example Timing with Two-plane Page Program
5.2.4. Two-Plane Block Erase
Figure 5-21. Example Timing with Two-plane Block Erase
5.2.5. Two-Plane Copy-Back Program Operation
Figure 5-22. Example Timing with Two-plane Copy-Back Program (Primary)
Figure 5-23. Example Timing with Two-plane Copy-Back Program (Secondary)
5.2.6. Device Identification Table Read Operation
Figure 5-24. Device Identification Table Read Timing
5.2.7. Device Identification Table Definition
Table 5-14. Parameter Page Definitions
5.2.8. Read Status Enhanced
Table 5-15. Read Status Enhanced Definition
Figure 5-25 Read Status Sequence
5.2.11. Read LUN #0 Status Operation
Table 5-16. Read LUN#0 Status Definition
Figure 5-26. Read LUN#0 Sataus Sequence
5.2.12. Read LUN #1 Status Operation
Table 5-17. Read LUN#1 Status Definition
Figure 5-27. Read LUN#1 Sataus Sequence
5.2.13. Register Read Out Mode 1
Figure 5-28. Register Read Out
5.2.14. Two-Plane Register Read Out Mode 1
Figure 5-29. Two-Plane Register Read Out Mode 1
5.3. Interleaving Operation
5.3.1. Interleaving Page Program
Figure 5-30. Interleaving Page Program
5.3.2. Interleaving Page Read
Figure 5-31. Interleaving Page Read
5.3.3. Interleaving Block Erase
Figure 5-32. Interleaving Block Erase
5.3.4. Interleaving Two-Plane Page Program
Figure 5-33. Interleaving Two-Plane Page Program
5.3.5. Interleaving Two-Plane page Read
Figure 5-34. Interleaving Two-Plane page Read
5.3.6. Interleaving Multi-Plane Block Erase
Figure 5-35. Interleaving Multi-Plane Block Erase
5.3.7. Interleaving Read to Page Program
Figure 5-36. Interleaving Read to Page Program
5.3.8. Interleaving Copy-Back Program (1/2)
Figure 5-37. Interleaving Copy-Back Program (1/2)
5.3.9. Interleaving Copy-Back Program (2/2)
Figure 5-38. Interleaving Copy-Back Program (2/2)
5.3.10. Interleaving Two-Plane Copy Back Program(1/2)
Figure 5-39. Interleaving Two-Plane Copy Back Program(1/2)
5.3.11. Interleaving Two-Plane Copy Back Program(2/2)
Figure 5-40. Interleaving Two-Plane Copy Back Program(2/2)
5.4. Ready/Busy
Figure 5-41. Rp vs tr ,tf & Rp vs ibusy
Addendum
1. Command Description
1.1. Set Parameter
1.1.1. Command Sequence
1.1.2. Timing Diagram
Figure 1. Set Parameter for SDR
Figure 2. Set Parameter for NV-DDR2
1.1.3. Rules and Limitations
1.2. Get Parameter
1.2.1. Command Sequence
Figure 3. Get Parameter for SDR
Figure 4. Get Parameter for NV-DDR2
1.2.3. Rules and Limitations












 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc