1 Introduction
The features
About this manual
Supporting documentation
Image outputs
2 Best Practices
Basic image capture
Scanner setup
Initiate polling
Feed documents
Disable scanning
Error handling
Controlling image transfer order
Single output bi-tonal only duplex
Single output color only duplex
Single output grayscale only duplex
Simultaneous output bi-tonal and color duplex
Simultaneous output bi-tonal and grayscale duplex
Single output bi-tonal only simplex
Single output color only simplex
Single output grayscale only simplex
Simultaneous output bi-tonal and color simplex
Simultaneous output bi-tonal and grayscale simplex
Jam and fault recovery
Image file storage locations
Bar code recognition
Electronic color dropout
Red Dropout - Complete Dropout
Red Dropout - Near Complete Dropout
Green Dropout - Complete Dropout
Green Dropout - Near Complete Dropout
Blue Dropout - Complete Dropout
Blue Dropout - Near Complete Dropout
Image header information
Zone processing
3 Using the TWAIN Data Source
Installation
Scan Validation Tool dialog box
Kodak Scanner Properties dialog box
Buttons on the Kodak Scanner Properties dialog box
The Imaging tab
Scanning bi-tonal images
Scanning color images
Scanning grayscale images
The Paper tab
Cropping values
Overscan values
Additional paper selections
The Compression tab
The Dropout tab
The Multifeed tab
The Options tab
The Setup tab
The Info tab
4 Using the ISIS Driver
Installation
Scan Validation Tool dialog box
Scanner Settings dialog box
Buttons on the Scanner Settings dialog box
Camera settings area
Image Processing settings
Page layout
More Scanner Settings dialog box
Camera settings area
Image Control options
Noise Filter
Color Dropout
Scanner Control dialog box
Setting Multi-feed detection
Defining the Scan Area
















 V2版本原理图(Capacitive-Fingerprint-Reader-Schematic_V2).pdf
V2版本原理图(Capacitive-Fingerprint-Reader-Schematic_V2).pdf 摄像头工作原理.doc
摄像头工作原理.doc VL53L0X简要说明(En.FLVL53L00216).pdf
VL53L0X简要说明(En.FLVL53L00216).pdf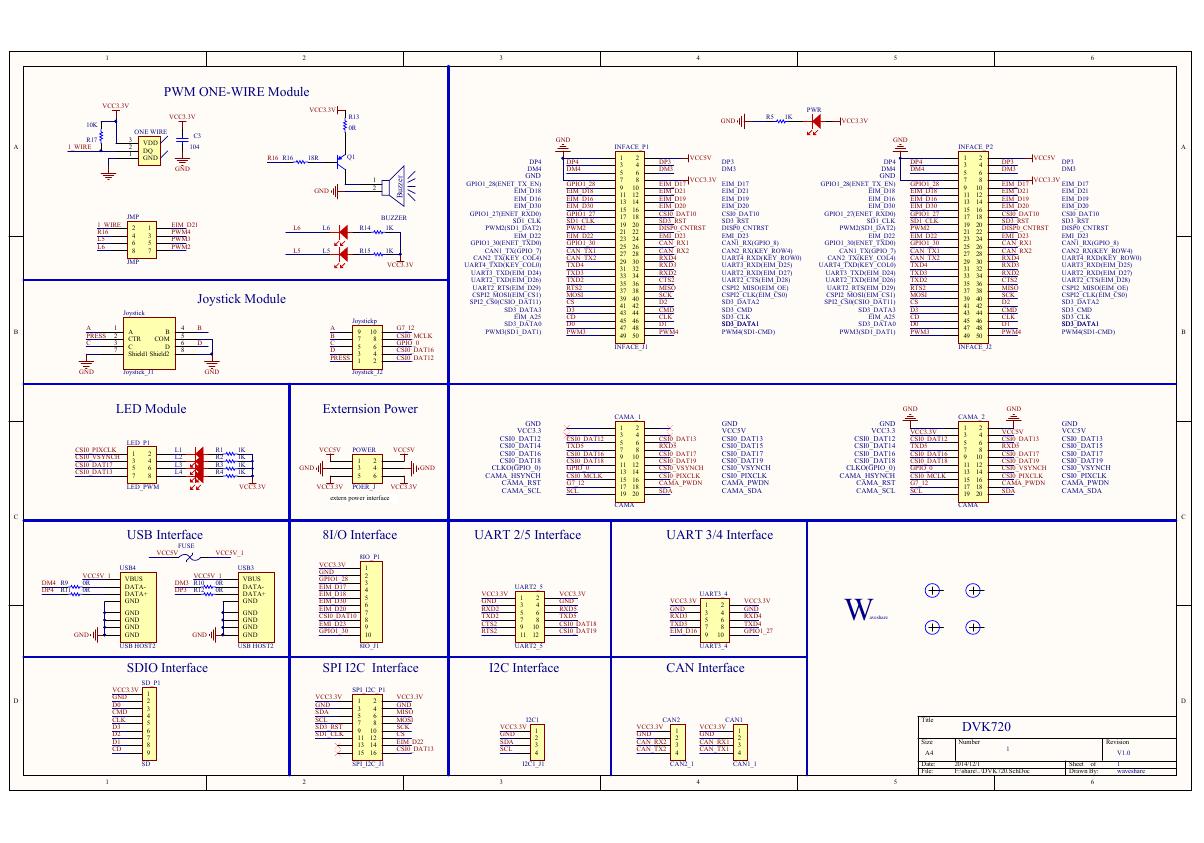 原理图(DVK720-Schematic).pdf
原理图(DVK720-Schematic).pdf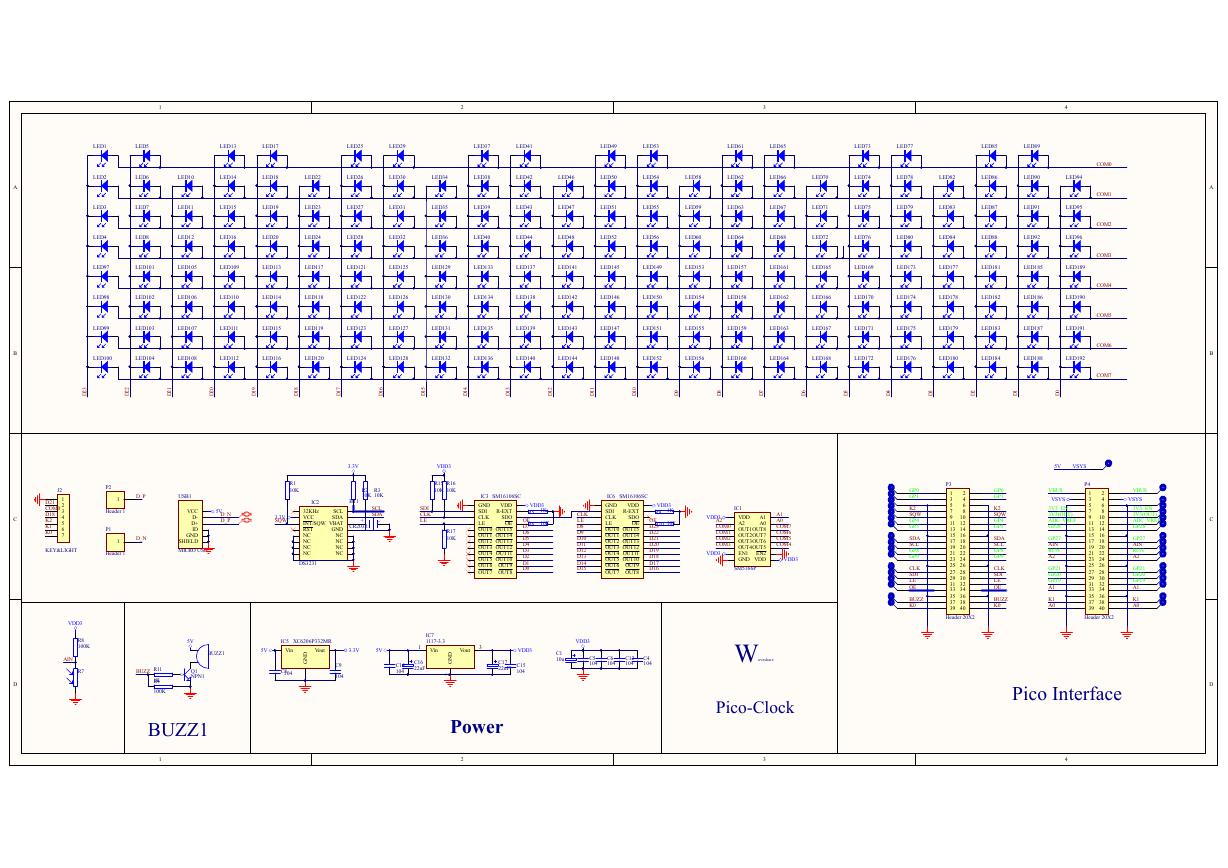 原理图(Pico-Clock-Green-Schdoc).pdf
原理图(Pico-Clock-Green-Schdoc).pdf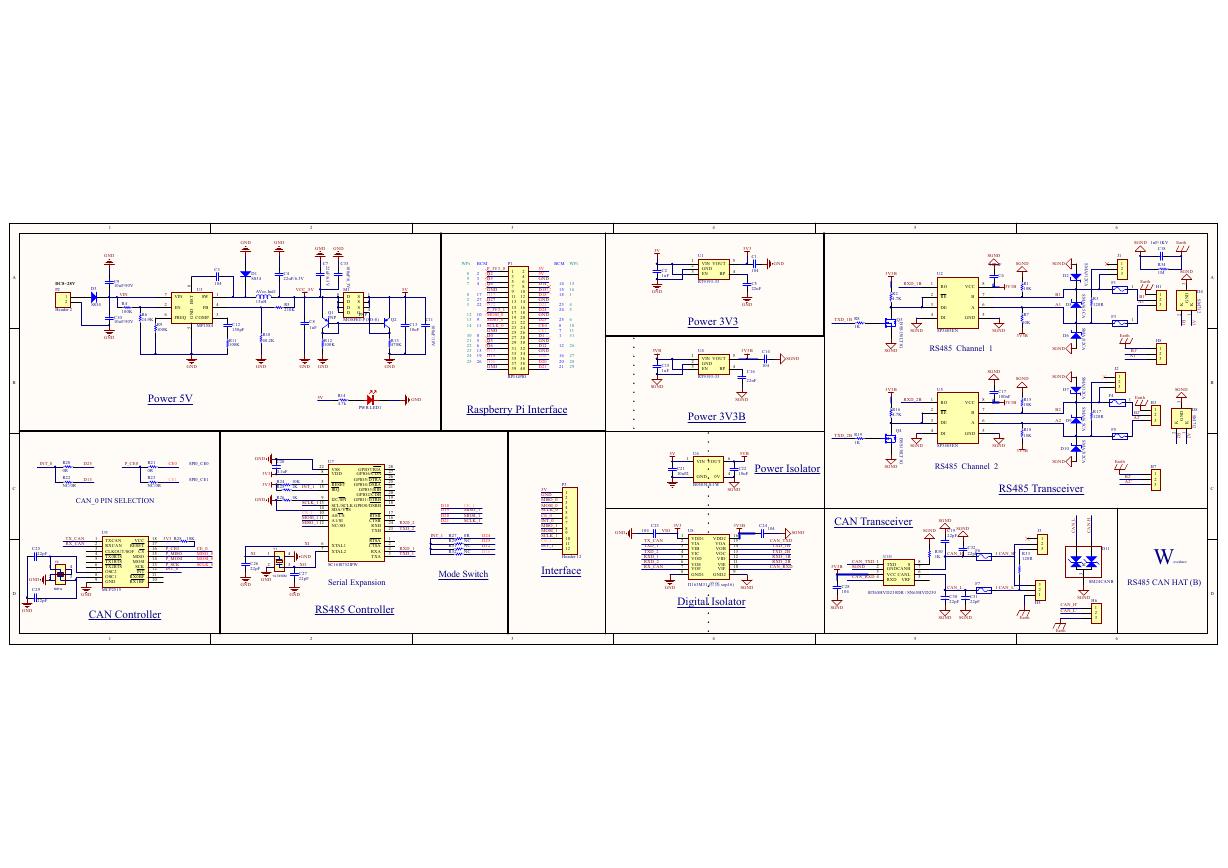 原理图(RS485-CAN-HAT-B-schematic).pdf
原理图(RS485-CAN-HAT-B-schematic).pdf File:SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
File:SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf ADS1263(Ads1262).pdf
ADS1263(Ads1262).pdf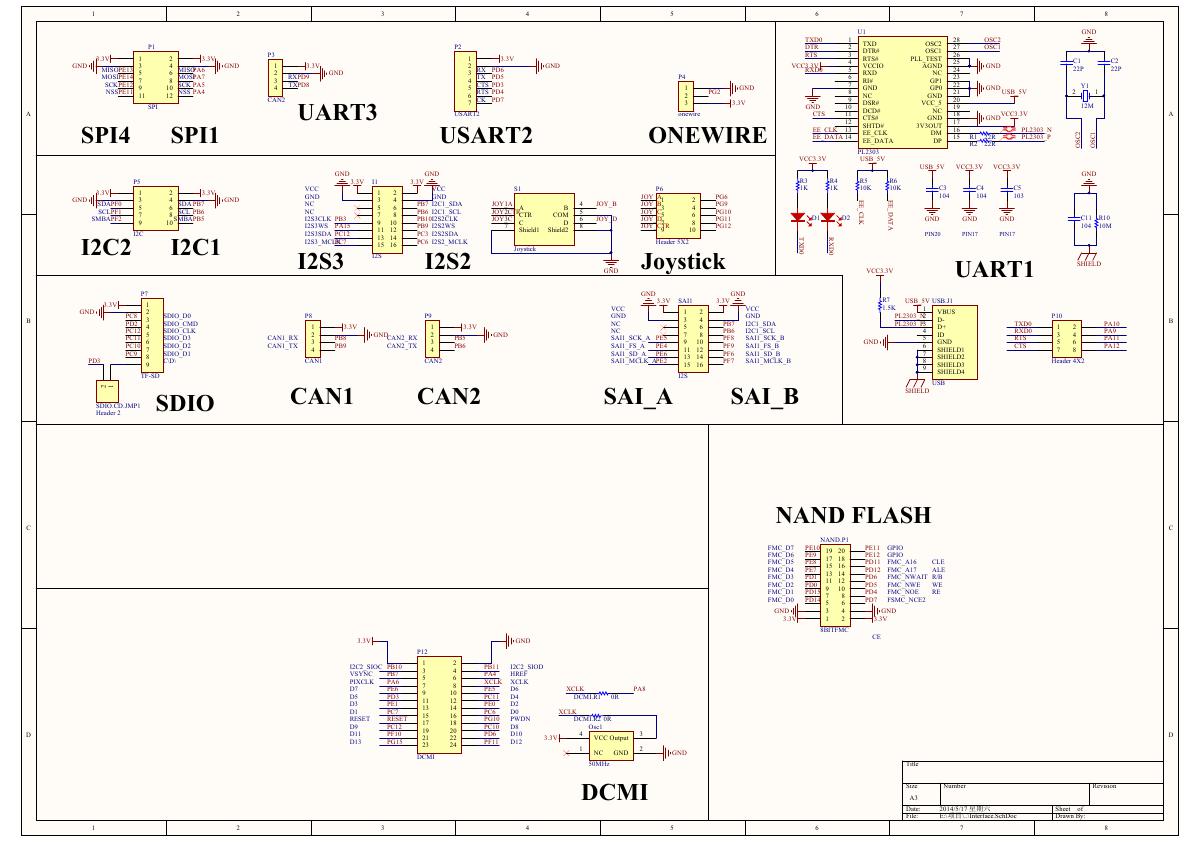 原理图(Open429Z-D-Schematic).pdf
原理图(Open429Z-D-Schematic).pdf 用户手册(Capacitive_Fingerprint_Reader_User_Manual_CN).pdf
用户手册(Capacitive_Fingerprint_Reader_User_Manual_CN).pdf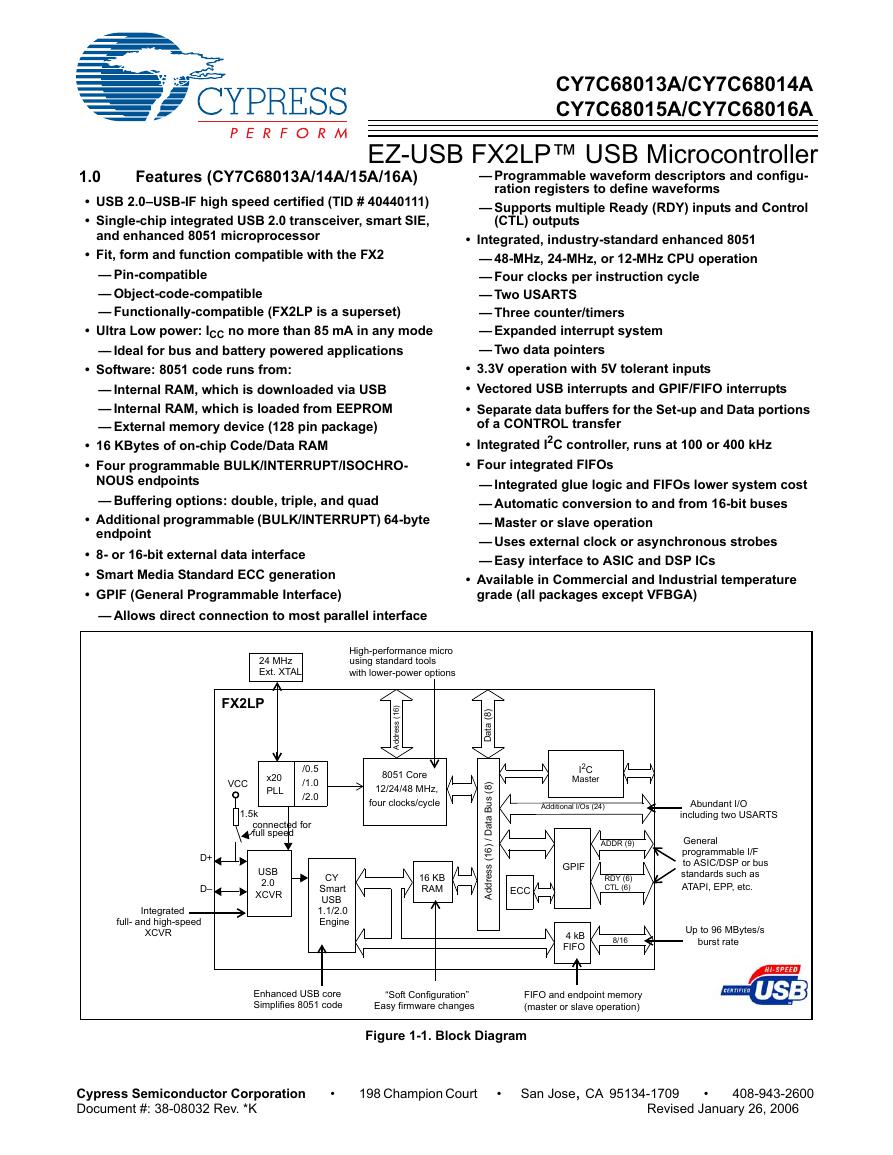 CY7C68013A(英文版)(CY7C68013A).pdf
CY7C68013A(英文版)(CY7C68013A).pdf TechnicalReference_Dem.pdf
TechnicalReference_Dem.pdf