SIM7070_SIM7080_SIM7090
Series_TCPUDP(S)
_Application Note
LPWA Module
SIMCom Wireless Solutions Limited
SIMCom Headquarters Building, Building 3, No. 289 Linhong
Road, Changning District, Shanghai P.R. China
Tel: 86-21-31575100
support@simcom.com
www.simcom.com
�
SIM7070_SIM7080_SIM7090 Series_TCPUDP(S)_Application Note_V1.03
SIM7070_SIM7080_SIM7090 Series_TCPUDP(S)_Application Note
1.03
2021.03.12
Released
Document Title:
Version:
Date:
Status:
GENERAL NOTES
SIMCOM OFFERS THIS INFORMATION AS A SERVICE TO ITS CUSTOMERS, TO SUPPORT
APPLICATION AND ENGINEERING EFFORTS THAT USE THE PRODUCTS DESIGNED BY SIMCOM.
THE INFORMATION PROVIDED IS BASED UPON REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICALLY PROVIDED TO
SIMCOM BY THE CUSTOMERS. SIMCOM HAS NOT UNDERTAKEN ANY INDEPENDENT SEARCH
FOR ADDITIONAL RELEVANT INFORMATION, INCLUDING ANY INFORMATION THAT MAY BE IN THE
CUSTOMER’S POSSESSION. FURTHERMORE, SYSTEM VALIDATION OF THIS PRODUCT
DESIGNED BY SIMCOM WITHIN A LARGER ELECTRONIC SYSTEM REMAINS THE RESPONSIBILITY
OF THE CUSTOMER OR THE CUSTOMER’S SYSTEM INTEGRATOR. ALL SPECIFICATIONS
SUPPLIED HEREIN ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE.
COPYRIGHT
THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY TECHNICAL INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF SIMCOM WIRELESS SOLUTIONS LIMITED COPYING, TO OTHERS AND USING THIS DOCUMENT,
ARE FORBIDDEN WITHOUT EXPRESS AUTHORITY BY SIMCOM. OFFENDERS ARE LIABLE TO THE
PAYMENT OF INDEMNIFICATIONS. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED BY SIMCOM IN THE PROPRIETARY
TECHNICAL INFORMATION ,INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO REGISTRATION GRANTING OF A
PATENT , A UTILITY MODEL OR DESIGN. ALL SPECIFICATION SUPPLIED HEREIN ARE SUBJECT TO
CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE AT ANY TIME.
SIMCom Wireless Solutions Limited
SIMCom Headquarters Building, Building 3, No. 289 Linhong Road, Changning District, Shanghai P.R.
China
Tel: +86 21 31575100
Email: simcom@simcom.com
For more information, please visit:
https://www.simcom.com/download/list-863-en.html
For technical support, or to report documentation errors, please visit:
https://www.simcom.com/ask/ or email to: support@simcom.com
Copyright © 2021 SIMCom Wireless Solutions Limited All Rights Reserved.
www.simcom.com 2 / 21
�
SIM7070_SIM7080_SIM7090 Series_TCPUDP(S)_Application Note_V1.03
About Document
Version History
Owner
What is new
First Release
2019.10.27 Wei.zhang
2020.02.26 Jiangting.Ding Change AT+SHBOD
2020.07.08 Wei.Zhang
2021.03.12 Wei.Zhang
All
Change response of “AT+CASEND”
Version Date
V1.00
V1.01
V1.02
V1.03
Scope
This document applies to the following products
Name
SIM7080G
SIM7070G/SIM7070E CAT-M/NB/GPRS
SIM7070G-NG
SIM7090G
Size(mm)
17.6*15.7 *2.3 N/A
24*24*2.4
N/A
24*24*2.4
N/A
14.8*12.8*2.0 N/A
Type
CAT-M/NB
NB/GPRS
CAT-M/NB
Comments
www.simcom.com 3 / 21
�
SIM7070_SIM7080_SIM7090 Series_TCPUDP(S)_Application Note_V1.03
Contents
About Document .................................................................................................................... 3
Version History ...................................................................................................................................... 3
Scope .................................................................................................................................................... 3
Contents ................................................................................................................................. 4
Introduction ...................................................................................................................... 5
1
1.1 Purpose of the document ............................................................................................................ 5
1.2 Related documents ..................................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Conventions and abbreviations ................................................................................................... 5
2 TCP/UDP Introduction ..................................................................................................... 6
3.1 Connection-oriented TCP ............................................................................................................ 6
3.2 Connectionless UDP protocol ..................................................................................................... 7
3.3 Differences between TCP and UDP protocols ............................................................................ 8
3 AT Commands that support TCP/UDP(S) .................................................................... 10
4 Bearer Configuration ..................................................................................................... 11
5.1 PDN Auto-activation .................................................................................................................. 11
5.2 APN Manual Configuration........................................................................................................ 12
5.1.1
5.1.2
5.1.3
5 TCPUDP(S) Examples ................................................................................................... 14
5.1 Build a TCP/UDP connection without SSL ................................................................................ 14
Build an ordinary TCP/UDP connection ......................................................................... 14
Build TCP Server ............................................................................................................ 15
Build UDP Server ........................................................................................................... 16
5.2 Build a TCP/UDP connection with SSL ..................................................................................... 17
Configure SSL parameters and Certificate ..................................................................... 17
Build a one-way authentication SSL(TLS) connection ................................................... 17
Build a two-way authentication SSL(TLS) connection .................................................... 18
Build a PSK authentication SSL (DTLS) connection ...................................................... 20
5.2.1
5.2.2
5.2.3
5.2.4
www.simcom.com 4 / 21
�
SIM7070_SIM7080_SIM7090 Series_TCPUDP(S)_Application Note_V1.03
1 Introduction
1.1 Purpose of the document
Based on module AT command manual, this document will introduce TCPUDP(S) application process.
Developers could understand and develop application quickly and efficiently based on this document.
1.2 Related documents
[1] SIM7070_SIM7080_SIM7090 Series_AT Command Manual
[2] SIM7070_SIM7080_SIM7090 Series_SSL_Application Note
1.3 Conventions and abbreviations
In this document, the GSM engines are referred to as following term:
ME (Mobile Equipment);
MS (Mobile Station);
TA (Terminal Adapter);
DCE (Data Communication Equipment) or facsimile DCE (FAX modem, FAX board);
In application, controlling device controls the GSM engine by sending AT Command via its serial interface.
The controlling device at the other end of the serial line is referred to as following term:
TE (Terminal Equipment);
DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) or plainly "the application" which is running on an embedded system;
www.simcom.com 5 / 21
�
SIM7070_SIM7080_SIM7090 Series_TCPUDP(S)_Application Note_V1.03
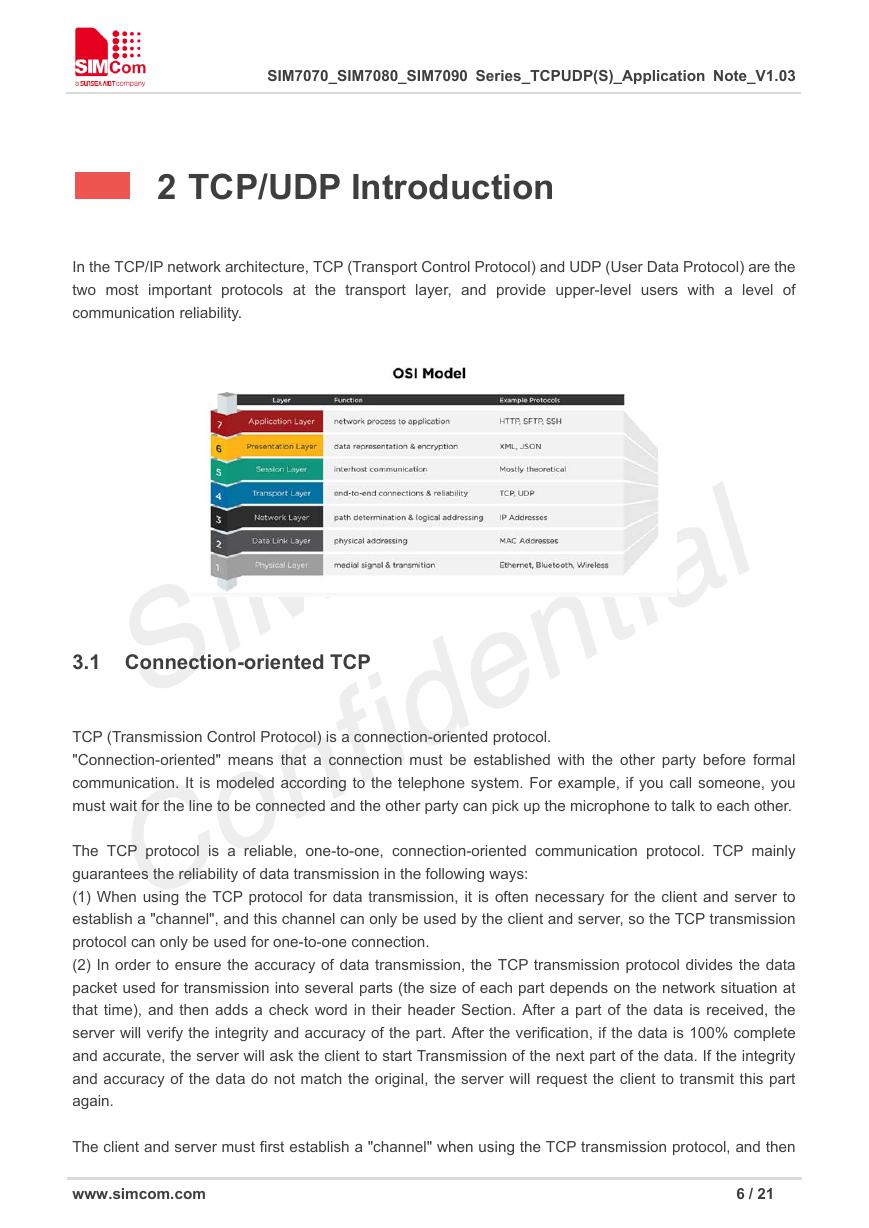
2 TCP/UDP Introduction
In the TCP/IP network architecture, TCP (Transport Control Protocol) and UDP (User Data Protocol) are the
two most important protocols at the transport layer, and provide upper-level users with a level of
communication reliability.
3.1 Connection-oriented TCP
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a connection-oriented protocol.
"Connection-oriented" means that a connection must be established with the other party before formal
communication. It is modeled according to the telephone system. For example, if you call someone, you
must wait for the line to be connected and the other party can pick up the microphone to talk to each other.
The TCP protocol is a reliable, one-to-one, connection-oriented communication protocol. TCP mainly
guarantees the reliability of data transmission in the following ways:
(1) When using the TCP protocol for data transmission, it is often necessary for the client and server to
establish a "channel", and this channel can only be used by the client and server, so the TCP transmission
protocol can only be used for one-to-one connection.
(2) In order to ensure the accuracy of data transmission, the TCP transmission protocol divides the data
packet used for transmission into several parts (the size of each part depends on the network situation at
that time), and then adds a check word in their header Section. After a part of the data is received, the
server will verify the integrity and accuracy of the part. After the verification, if the data is 100% complete
and accurate, the server will ask the client to start Transmission of the next part of the data. If the integrity
and accuracy of the data do not match the original, the server will request the client to transmit this part
again.
The client and server must first establish a "channel" when using the TCP transmission protocol, and then
www.simcom.com 6 / 21
�
SIM7070_SIM7080_SIM7090 Series_TCPUDP(S)_Application Note_V1.03
close the "channel" after the transmission is completed. The former can be visually referred to as a
"three-way handshake", while the latter can be referred to as " Four waves."
Channel establishment-three handshake:
(1) When establishing a channel, the client first sends a SYN synchronization signal to the server.
(2) After receiving this signal, the server will send a SYN synchronization signal and an ACK confirmation
signal to the client.
(3) When the server's ACK and SYN reach the client, the "channel" between the client and the server will be
established.
The closing of the channel-four waves:
(1) After the data transmission is completed, the client will send a FIN termination signal to the server.
(2) After receiving this signal, the server will send an ACK confirmation signal to the client.
(3) If the server does not send data to the client after that, the server will send a FIN termination signal to
the client.
(4) After receiving this signal, the client will reply with a confirmation signal. After the server receives this
signal, the channel between the server and the client will be closed.
The TCP protocol can provide a reliable communication connection for the application program, so that the
byte stream sent by a computer can be sent to other computers on the network without errors. Data
communication systems that require high reliability often use the TCP protocol to transmit data.
3.2 Connectionless UDP protocol
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a connectionless protocol and a simple transport layer protocol for
datagrams. It provides non-connection-oriented, unreliable data streaming.
Connectionless means that it is not necessary to establish a connection with the other party before formal
communication, and it is sent directly regardless of the other party's status. It is very similar to the mobile
phone text message: when you send a text message, you only need to enter the other party's mobile phone
www.simcom.com 7 / 21
�
SIM7070_SIM7080_SIM7090 Series_TCPUDP(S)_Application Note_V1.03
number and it is OK.
UDP transmission protocol is an unreliable, connectionless oriented communication protocol that can
realize many-to-one, one-to-many and one-to-one connections. UDP does not need to establish a channel
before transmitting data, nor does it need to close the channel after data transmission is completed. As long
as the client sends a request to the server, the server will send all the data at once. UDP does not verify the
integrity of the data when transmitting data, and does not require retransmission when data is lost or data is
wrong, so it also saves a lot of time for verifying data packets, so the delay of the connection established
with UDP Will have a lower latency than connections established with TCP. UDP does not control the data
transmission speed according to the current network conditions, so no matter whether the network
conditions are good or bad, the server will send data at a constant rate. Although this sometimes causes
data loss and damage, this is very important for some real-time applications. Based on the above three
points, UDP is faster in data transmission, lower in latency, and better in real-time, so it is widely used in the
communication field and video websites.
UDP is suitable for application environments that only transmit a small amount of data at a time and have
low requirements on reliability. For example, we often use the "ping" command to test whether the TCP/IP
communication between the two hosts is normal. In fact, the principle of the "ping" command is to send
ICMP data packets to the other host, and then the other host confirms that the data packet is received. If the
message of whether the packet arrives is fed back in time, then the network is connected. For example, in
the default state, a "ping" operation sends 4 packets (as shown). As you can see, the number of data
packets sent is 4 packets, and 4 packets are received (because the host of the other party will send back a
data packet confirming receipt). This fully shows that the UDP protocol is a connection-free protocol and
there is no connection establishment process. Because the UDP protocol has no connection process, its
communication efficiency is high; but also because of this, its reliability is not as high as the TCP protocol.
QQ uses UDP to send messages, so sometimes the message may not be received.
3.3 Differences between TCP and UDP protocols
The biggest difference between TCP/IP and UDP is that TCP/IP is connection-oriented and UDP is
connectionless. The TCP and UDP protocols have their own strengths and weaknesses, and they are
suitable for communication environments with different requirements. The differences between the TCP
protocol and UDP protocol are shown in the table below.
Table 1 Difference between TCP and UDP
TCP
Attributes
Whether to connect
connection-oriented
Reliable
Transmission reliability
small amounts of data
Application Scenarios Transfer
Speed
slow
UDP
no connection
Unreliable
Large amounts of data
fast
www.simcom.com 8 / 21
�















 V2版本原理图(Capacitive-Fingerprint-Reader-Schematic_V2).pdf
V2版本原理图(Capacitive-Fingerprint-Reader-Schematic_V2).pdf 摄像头工作原理.doc
摄像头工作原理.doc VL53L0X简要说明(En.FLVL53L00216).pdf
VL53L0X简要说明(En.FLVL53L00216).pdf 原理图(DVK720-Schematic).pdf
原理图(DVK720-Schematic).pdf 原理图(Pico-Clock-Green-Schdoc).pdf
原理图(Pico-Clock-Green-Schdoc).pdf 原理图(RS485-CAN-HAT-B-schematic).pdf
原理图(RS485-CAN-HAT-B-schematic).pdf File:SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
File:SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf ADS1263(Ads1262).pdf
ADS1263(Ads1262).pdf 原理图(Open429Z-D-Schematic).pdf
原理图(Open429Z-D-Schematic).pdf 用户手册(Capacitive_Fingerprint_Reader_User_Manual_CN).pdf
用户手册(Capacitive_Fingerprint_Reader_User_Manual_CN).pdf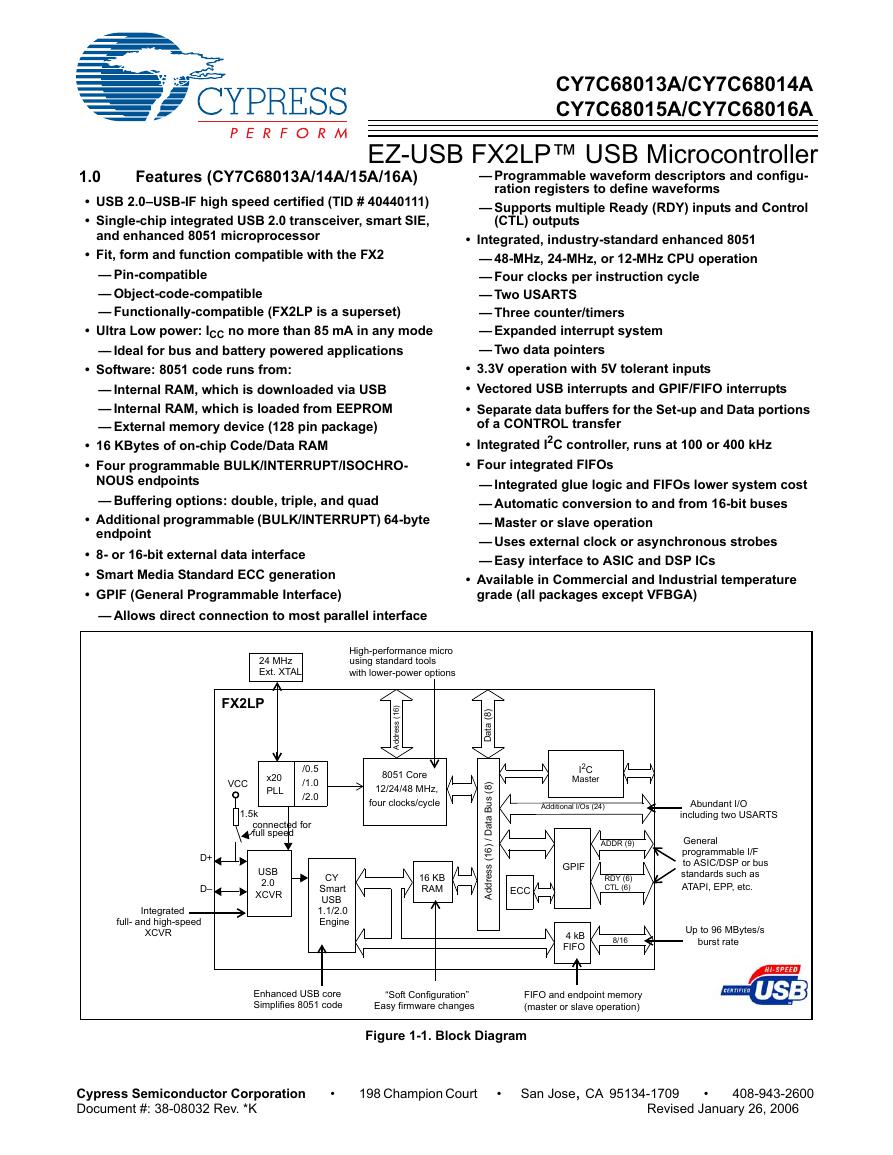 CY7C68013A(英文版)(CY7C68013A).pdf
CY7C68013A(英文版)(CY7C68013A).pdf TechnicalReference_Dem.pdf
TechnicalReference_Dem.pdf