NOT RECOMMENDED
FOR NEW DESIGNS
Replaced by
ATSHA204A
Features
ATSHA204
Atmel CryptoAuthentication
DATASHEET
Secure authentication and validation device
Integrated capability for both Host and Client operations
Superior SHA-256 Hash algorithm with Message Authentication Code (MAC) and
Hash-Based Message Authentication Code (HMAC) options
Best-in-class, 256-bit key length; storage for up to 16 keys
Guaranteed unique 72-bit serial number
Internal, high-quality Random Number Generator (RNG)
4.5Kb EEPROM for keys and data
512 OTP (One Time Programmable) bits for fixed information
Multiple I/O options
High-Speed, Single-Wire Interface
1MHz I2C interface
2.0V to 5.5V supply voltage range
1.8V to 5.5V communications
<150nA sleep current
Extended, multi-level hardware security
8-lead SOIC, 8-lead TSSOP, 3-lead SOT23, 8-pad UDFN, and 3-lead Contact
packages
Applications
Anti-clone protection for accessories, daughter cards, and consumables
Secure boot validation, software anti-piracy
Network and computer access control
Key exchange for encrypted downloads
Authenticated/encrypted communications for control networks
Atmel-8740H-CryptoAuth-ATSHA204-Datasheet_072014
�
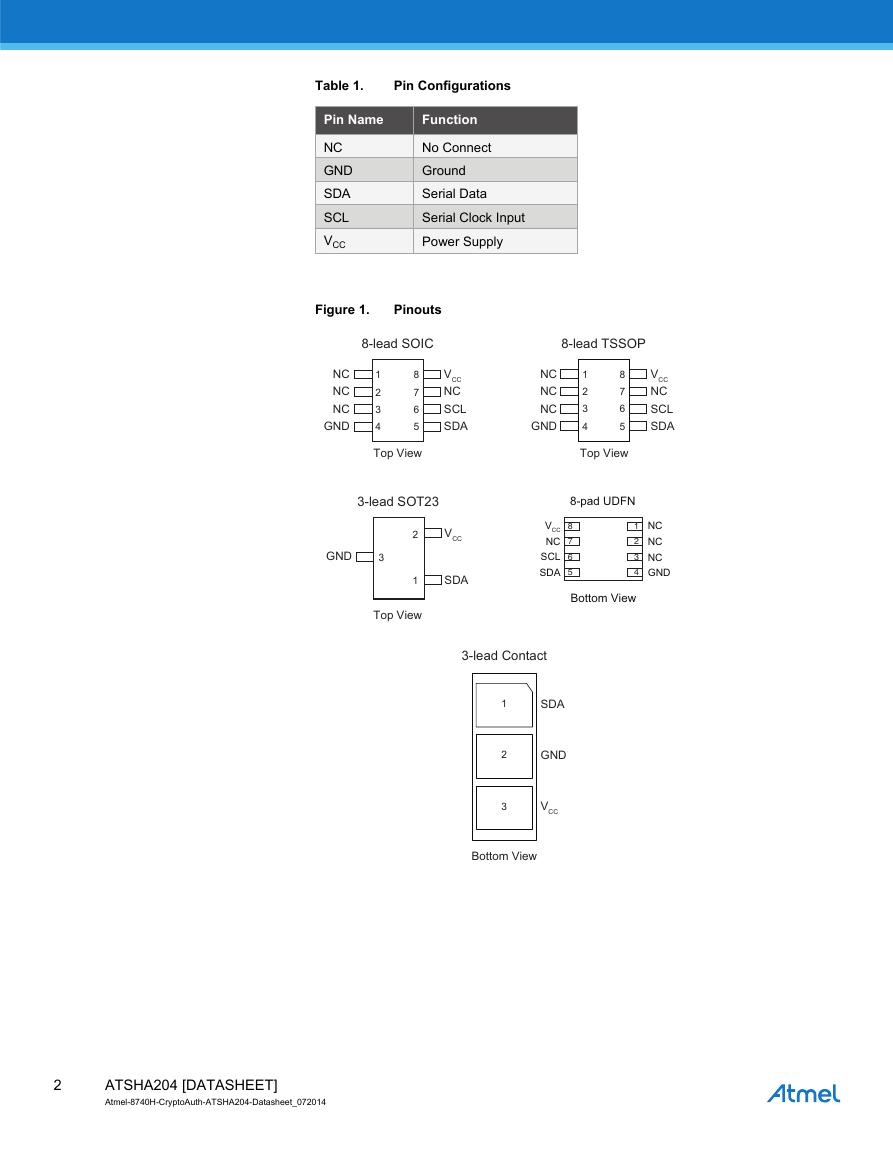
Table 1.
Pin Configurations
Pin Name
Function
NC
GND
SDA
SCL
VCC
No Connect
Ground
Serial Data
Serial Clock Input
Power Supply
Figure 1.
Pinouts
8-lead SOIC
8-lead TSSOP
NC
NC
NC
GND
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
VCC
NC
SCL
SDA
Top View
3-lead SOT23
GND
3
2
1
VCC
SDA
Top View
NC
NC
NC
GND
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
VCC
NC
SCL
SDA
Top View
8-pad UDFN
VCC
NC
SCL
SDA
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
NC
NC
NC
GND
Bottom View
3-lead Contact
1
2
3
SDA
GND
VCC
Bottom View
2
ATSHA204 [DATASHEET]
Atmel-8740H-CryptoAuth-ATSHA204-Datasheet_072014
�
Table of Contents
1.
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.1
1.2
Device Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Cryptographic Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.3
2.1
2. Device Organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
EEPROM Organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1.1
Data Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Configuration Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.1.2
One Time Programmable (OTP) Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.1.3
2.1.4
Device Locking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Static RAM (SRAM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.2.1
TempKey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.2
3. Security Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Physical Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Random Number Generator (RNG) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.1
3.2
4.1
4. General I/O Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Byte and Bit Ordering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Output Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4.1.1
4.1.2
MAC Message Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.3
6.2
5.1
5.2
5. Single-Wire Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
I/O Tokens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
I/O Flags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
5.2.1
Transmit Flag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Synchronization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
I/O Timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
5.3.1
5.3.2
Synchronization Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Sharing the Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
5.4
5.5
Transaction Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.6 Wiring Configuration for Single-Wire Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
I2C Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
I/O Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6.1
Device is Asleep . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6.1.1
6.1.2
Device is Awake . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
I2C Transmission to the ATSHA204 Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.2.1 Word Address Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6.2.2
Command Completion Polling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
I2C Transmission from the ATSHA204 Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Address Counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
I2C Synchronization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Transaction Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
6.3
6.4
6.5
6.6
6.
ATSHA204 [DATASHEET]
Atmel-8740H-CryptoAuth-ATSHA204-Datasheet_072014
3
�
7.4
8.1
7.1
7.2
7.3
7. Electrical Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Reliability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
AC Parameters — All I/O Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
AC Parameters — Single-Wire Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
7.3.1
AC Parameters — I2C Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
7.3.2
DC Parameters — All I/O Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
VIH and VIL Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
7.4.1
8. Control Flags. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
I/O Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
8.1.1
Status/Error Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Sleep Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.2
Idle Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.3
8.4 Wake Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.5 Watchdog Failsafe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Command Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.6
8.6.1
Command Packets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Command Opcodes, Short Descriptions, and Execution Times . . . 41
8.6.2
Zone Encoding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
8.6.3
Address Encoding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
8.6.4
8.6.5
CheckMac Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
DeriveKey Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
8.6.6
DevRev Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
8.6.7
GenDig Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
8.6.8
8.6.9
HMAC Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
8.6.10
Lock Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
8.6.11 MAC Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
8.6.12 Nonce Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
8.6.13 Pause Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
8.6.14 Random Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
8.6.15 Read Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
8.6.16 UpdateExtra Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
8.6.17 Write Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
9. Compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
10. Mechanical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
10.1 Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
11. Package Drawings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
11.1 8-lead SOIC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
11.2 8-lead TSSOP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
11.3 3-lead SOT23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
11.4 8-pad UDFN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
11.5 3-lead Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
12. Ordering Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
13. Errata . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
4
ATSHA204 [DATASHEET]
Atmel-8740H-CryptoAuth-ATSHA204-Datasheet_072014
�
14. Reference and Application Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
14.1 SHA-256 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
14.2 HMAC/SHA-256 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
14.3 Key Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
14.3.1 Diversified Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
14.3.2 Rolled Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
14.3.3 Created Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
14.3.4 Single-use Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
14.3.5
Limited-use Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
14.3.6 Password Checking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
14.3.7 Transport Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
15. Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
ATSHA204 [DATASHEET]
Atmel-8740H-CryptoAuth-ATSHA204-Datasheet_072014
5
�
1.
1.1
1.2
Introduction
The following sections introduce the features and functions of the Atmel® ATSHA204 authentication device.
Applications
The ATSHA204 is a member of the Atmel CryptoAuthentication™ family of high-security hardware authentication
devices. It has a flexible command set that allows use for many applications, including the following:
Anti-counterfeiting
Validate that a removable, replaceable, or consumable Client is authentic. Example Clients could be printer ink
tanks, electronic daughter cards, or other spare parts. It can also be used to validate a software/firmware module
or memory storage element.
Protection for Firmware or Media
Validate code stored in flash memory at boot to prevent unauthorized modifications (also known as secure boot),
encrypt downloaded media files, and uniquely encrypt code images to be usable on a single system only.
Session Key Exchange
Securely and easily exchange stream encryption keys for use by an encryption/decryption engine in the system
microprocessor to manage such things as a confidential communications channel or an encrypted download.
Secure Data Storage
Store secret keys for use by crypto accelerators in standard microprocessors. It can also be used to store small
quantities of data necessary for configuration, calibration, ePurse value, consumption data, or other secrets.
Programmable protection up through encrypted/authenticated reads and writes.
User Password Checking
Validate user entered passwords without letting the expected value become known, map simple passwords to
complex ones, and securely exchange password values with remote system.
Device Features
The ATSHA204 device includes an Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM) array that can
be used for storage of keys, miscellaneous read/write, read-only or secret data, consumption logging, and security
configuration. Access to the various sections of memory can be restricted in a variety of ways and the configuration then
locked to prevent changes. See Section 2.1, “EEPROM Organization” for more details.
The ATSHA204 features a wide array of defensive mechanisms specifically designed to prevent physical attacks on the
device itself or logical attacks on the data transmitted between the device and the system see Section 3., “Security
Features” for more details. Hardware restrictions on the ways in which keys are used or generated provide further
defense against certain styles of attack.
Access to the device is through a standard I2C interface at speeds up to 1Mb/s. see Section 6., “I2C Interface” for more
details. It is compatible with the I2C interface specifications. The device also supports a Single-Wire Interface that can
reduce the number of GPIOs required on the system processor and/or reduce the number of pins on connectors. See
Section 5., “Single-Wire Interface” for more details.
Using the Single-Wire Interface, multiple ATSHA204 devices can share the same bus, which saves processor GPIO
usage in systems with multiple Clients such as different color ink tanks or multiple spare parts. See Section 5.4, “Sharing
the Interface” and Section 8.6.13, “Pause Command” for more details on the way in which this is implemented.
Each ATSHA204 ships with a guaranteed unique 9-byte (72-bit) serial number. Using the cryptographic protocols
supported by the device, a Host system or remote server can prove that the serial number is both authentic and is not a
copy. Serial numbers are often stored in a standard Serial EEPROM, but these can be easily copied, and there is no way
for the Host to know if the serial number is authentic or a clone. The entire serial number must be utilized to guarantee
uniqueness.
The ATSHA204 can generate high-quality random numbers and employ them for any purpose, including as part of the
crypto protocols of this device. Because each 32-byte (256-bit) random number is not dependent on passed numbers
generated on this or any other device, their inclusion in the protocol calculation ensures that replay attacks
6
ATSHA204 [DATASHEET]
Atmel-8740H-CryptoAuth-ATSHA204-Datasheet_072014
�
1.3
(re-transmitting a previously successful transaction) always fail. See Section 3.2, “Random Number Generator (RNG)”
and Section 8.6.14, “Random Command”.
System integration is eased with a wide supply voltage range (2.0V through 5.5V) and an ultra-low sleep current of
<150nA. Complete DC parameters are found in Section 7., “Electrical Characteristics”, which describes multiple package
options, including a tiny SOT23 package with a footprint of only 2.5mm x 3mm. See Section 11., “Package Drawings” for
more details and for ordering codes.
See Section 9., “Compatibility” for information regarding compatibility with the Atmel AT88SA102S and the Atmel
AT88SA10HS (previous members of the Atmel CryptoAuthentication family).
Cryptographic Operation
The ATSHA204 supports a standard challenge-response protocol to simplify programming. At its most basic, the Host
system sends a challenge to the device in the Client, which combines that challenge with a secret key via the Message
Authentication Code (MAC) command from the system, described in Section 8.6.11, “MAC Command” and sends the
response back to the system. The device uses a cryptographic hash algorithm for the combination, which prevents an
observer on the bus from deriving the value of the secret key, but allows the recipient to verify that the response is correct
by performing the same calculation (combining the challenge with the secret) with a stored copy of the secret.
This basic operation can be expanded in many ways with the flexible command set of the ATSHA204. Using the GenDig
command (Section 8.6.8, “GenDig Command”), the values in other slots can be included in the response digest which
provides an effective way of proving that a data read really did come from the device, as opposed to being inserted by a
man-in-the-middle attacker. This same command can be used to combine two keys with the challenge, which is useful
when there are multiple layers of authentication to be performed.
The DeriveKey command (Section 8.6.6, “DeriveKey Command”) implements a key rolling scheme. Depending on the
command mode parameter, the resulting operation can be similar to that implemented in a remote-controlled garage
door opener. Each time the key is used, the current value of the key is cryptographically combined with a value specific to
that system, and the result forms the key for the next cryptographic operation. Even if an attacker gets the value of one
key, that key will be gone forever with the next use.
DeriveKey can also be used to generate new random keys that might be valid only for a particular Host ID, for a particular
time period, or for some other restricted environment. Each generated key is different from any other key ever generated
on any device. By “activating” a Host-Client pair in the field in this manner, a clone of a single Client would not work on
any other Host.
In a Host-Client configuration where the Host (e.g. a mobile phone) needs to verify a Client (e.g. an OEM battery), there
is a need to store the secret in the Host in order to validate the response from the Client. The CheckMac command
(Section 8.6.5, “CheckMac Command”) allows the Host device to securely store the Client secret and hide the correct
response value from the pins, returning only a yes/no answer to the system.
Where a user-entered password is a requirement, the CheckMac command also provides a way to both verify the
password without exposing it on the communications bus as well as map the password to a stored value that can have
much higher entropy. See Section 14.3.6, “Password Checking” for more details.
Finally, the hash combination of a challenge and secret key can be kept on the device and XORed with the contents of a
slot to implement an encrypted read (Section 8.6.15, “Read Command”), or it can be XORed with encrypted input data to
implement an encrypted write (Section 8.6.17, “Write Command”).
Each of these operations can be protected against replay attacks by including a random nonce (Section 8.6.12, “Nonce
Command”) in the calculation.
All security functions are implemented using the industry-standard SHA-256 secure hash algorithm, which is part of the
latest set of high-security cryptographic algorithms recommended by various governments and cryptographic experts.
Section 14.1, “SHA-256” includes a reference to the algorithm details. If desired, the SHA-256 algorithm can also be
included in an HMAC sequence (See Section 8.6.9, “HMAC Command”). The ATSHA204 employs full-sized, 256-bit
secret keys to prevent any kind of exhaustive attack.
ATSHA204 [DATASHEET]
Atmel-8740H-CryptoAuth-ATSHA204-Datasheet_072014
7
�
2.
Device Organization
The device contains the following memory blocks:
EEPROM
SRAM
2.1
EEPROM Organization
The EEPROM contains a total of 664-bytes (5312-bits), and is divided into the following zones:
Data
A 512-byte (4Kb) zone split into 16 general-purpose, read-only, or read/write memory slots of 32 bytes (256 bits)
each that can be used to store keys, calibration data, model number, or other information related to the item to
which the ATSHA204 device is attached. Each slot may have different access restrictions based on the values
stored in the Configuration zone. Within this document the nomenclature slot[yy] indicates the 32-byte value stored
in slot yy of the Data zone.
Configuration
An 88-byte (704-bit) zone that contains serial number and other ID information as well as access permission
information for each slot of the data memory. Within this document the nomenclature SN[a:b] indicates a range of
bytes within a field of the configuration section. The 88-bytes are accessible from within a three-block address
space.
OTP (One Time Programmable)
A 64-byte (512-bit) zone which can be used to store read-only data. Prior to locking the OTP zone, the bits may be
freely written using the standard Write command. The OTP zone is accessible from within a two-block address
space. Within this document the nomenclature OTP[bb] indicates a byte within the OTP zone, while OTP[aa:bb]
indicates a range of bytes.
Within this document, the terms “slot” and “block” are used interchangeably to mean a single, 256-bit (32-byte) area of a
particular memory zone. The industry SHA-256 documentation uses the term “block” to indicate a 512-bit section of the
message input. In addition, the I/O section of this document uses the term “block” to indicate a variable-length aggregate
element transferred between the system and the device.
In this specification, the nomenclature mode:b indicates bit b of the parameter mode.
On shipment from Atmel, the EEPROM contains factory test data that can be used for fixed-value board testing. This
data must be overwritten with the desired contents prior to locking the configuration and/or data sections of the device.
See the Atmel website for the document containing the specific shipment values.
8
ATSHA204 [DATASHEET]
Atmel-8740H-CryptoAuth-ATSHA204-Datasheet_072014
�















 V2版本原理图(Capacitive-Fingerprint-Reader-Schematic_V2).pdf
V2版本原理图(Capacitive-Fingerprint-Reader-Schematic_V2).pdf 摄像头工作原理.doc
摄像头工作原理.doc VL53L0X简要说明(En.FLVL53L00216).pdf
VL53L0X简要说明(En.FLVL53L00216).pdf 原理图(DVK720-Schematic).pdf
原理图(DVK720-Schematic).pdf 原理图(Pico-Clock-Green-Schdoc).pdf
原理图(Pico-Clock-Green-Schdoc).pdf 原理图(RS485-CAN-HAT-B-schematic).pdf
原理图(RS485-CAN-HAT-B-schematic).pdf File:SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
File:SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf ADS1263(Ads1262).pdf
ADS1263(Ads1262).pdf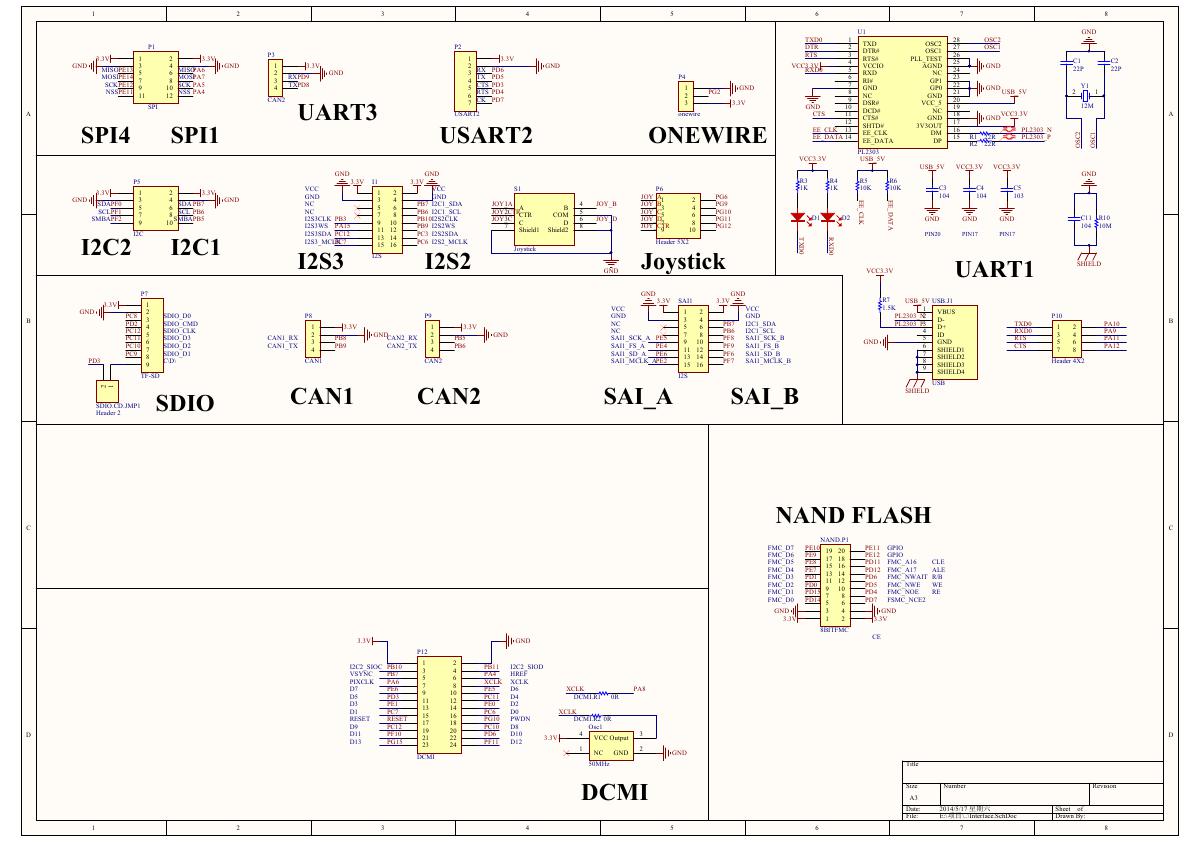 原理图(Open429Z-D-Schematic).pdf
原理图(Open429Z-D-Schematic).pdf 用户手册(Capacitive_Fingerprint_Reader_User_Manual_CN).pdf
用户手册(Capacitive_Fingerprint_Reader_User_Manual_CN).pdf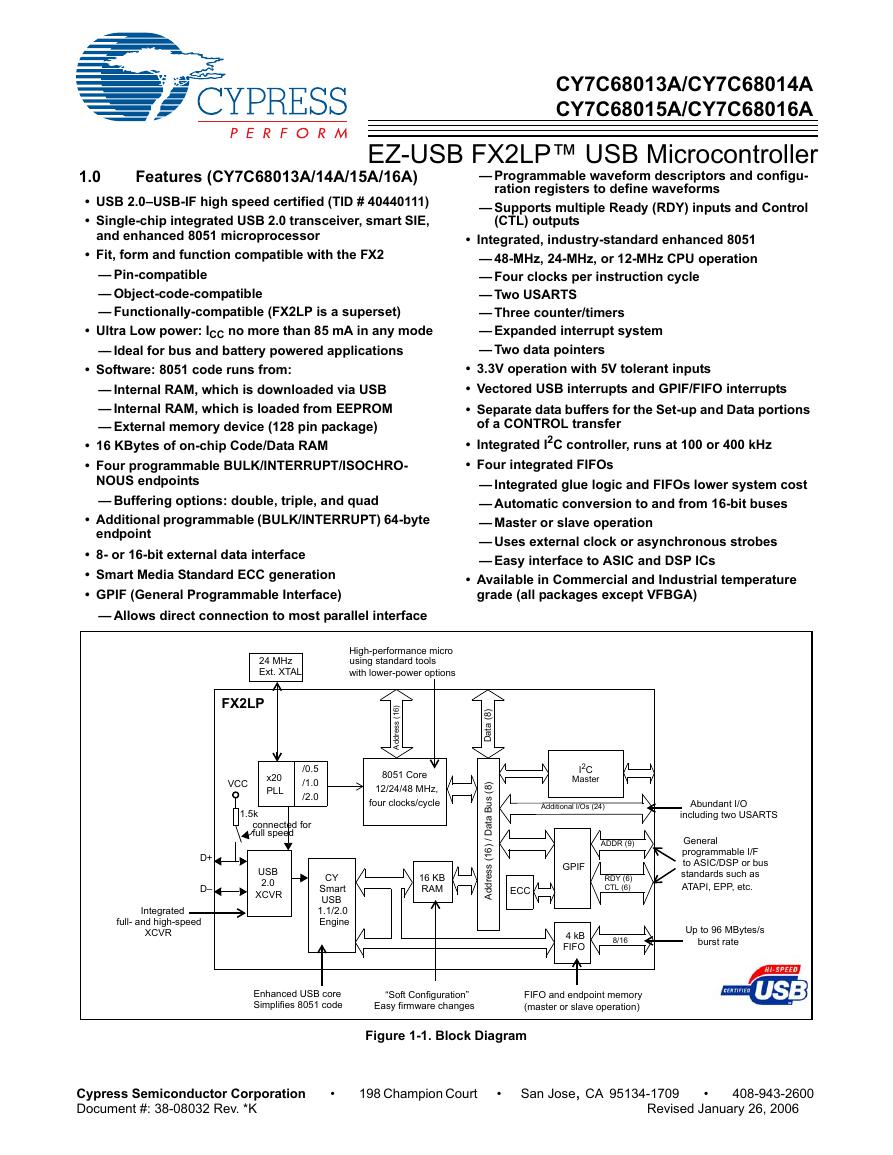 CY7C68013A(英文版)(CY7C68013A).pdf
CY7C68013A(英文版)(CY7C68013A).pdf TechnicalReference_Dem.pdf
TechnicalReference_Dem.pdf