AN2577
Getting Started with Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Configuration Options
Author:
Parthiv Pandya
Microchip Technology, Inc.
INTRODUCTION
Microchip’s family of gigabit Ethernet switches have powerful capabilities that may be enabled using various methods
of configuration. Depending on the features needed in the network application, there are four primary methods to con-
figure these switches. This application note describes available switch configuration methods and options with their
associated trade-offs, allowing the developer to choose the best method for their application.
The following configuration options are available (applicable Microchip parts):
• Configuration Straps (KSZ9896C, KSZ9897R, KSZ9897S)
• Microcontroller Configuration (KSZ9897R, KSZ9897S)
• Ethernet In-Band Access (IBA) Configuration (KSZ9897R, KSZ9897S)
• Host Processor Configuration (KSZ8567R, KSZ9897R, KSZ9897S, KSZ9567R, KSZ9567S, KSZ9477S)
TABLE 1:
AVAILABLE CONFIGURATION METHODS PER FEATURE - REFERENCE TABLE
g
e
N
-
o
t
u
A
X
X
X
X
i
c
s
a
B
X
X
X
X
E
E
E
X
X
X
N
A
L
V
X
X
X
S
o
Q
X
X
X
Config. Strap
8-bit MCU
IBA
Host Processor
2
v
8
8
5
1
E
E
E
I
x
1
.
2
0
8
y
t
i
r
u
c
e
S
L
C
A
E
M
P
L
o
W
B
V
A
R
S
H
R
L
D
/
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Note:
The user should take note of the difference between switch configuration mode and switch management
mode. Switch management mode provides the added ability to send and receive Ethernet frames during
normal operation. Switch configuration mode does not provide this ability.
CONFIGURATION STRAPS
The configuration strap option is a hardware method to configure the switch where pull-up or pull-down resistors are
used to set the logic level high or low on strapping pins of the switch. For example, the KSZ9896C has several strapping
pins with internal weak pull-up or pull-down resistors which allow the switch to operate in the unmanaged mode. A user
can add 1KΩ to 10KΩ external pull-up resistors on non-LED pins, or 750Ω to 1KΩ pull-down resistors on LED strapping
pins to override the effect of the weak internal resistors.
The strapping pins exhibit very high impedance when the device is in reset. They are internally sampled at the rising
edge of the reset pin, RESET_N. Once the RESET_N pin is high, all of these pins become driven outputs.
The user must be aware that the internal pull-up/pull-down resistors are weak. Therefore, if the application board uses
any external pull-up or pull-down resistors, care must be taken. If an external processor is connected with a switch, the
processor should also be checked for internal pull-ups or pull-downs, and it may be necessary to add an external resistor
to reinforce the default internal resistor of the Microchip switch. The KSZ9xxx family’s datasheet lists all the strapping
pins, their functionalities and default values.
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002577A-page 1
�
AN2577
An unmanaged Ethernet switch allows a quick and easy commissioning of the Ethernet network. A wide range of appli-
cations, including industrial control applications, can benefit tremendously from adding an unmanaged Ethernet switch,
as it reduces the cost and complexity for the Ethernet network.
Unlike a managed switch, an unmanaged Ethernet switch does not require any external microcontroller, microprocessor
or SoC to manage its functions. It can easily be configured using strap-in options of the switch. Because of its ease of
use it is also known as a “plug and play” device.
Example Configuration
The Figure 1 example circuit details the KSZ9896C switch in unmanaged mode using configuration straps. The circuit
enables auto-negotiation and the SPI interface (to access the internal registers for debugging purposes), sets port 6 to
100Mbps RMII mode. It can be seen from the datasheet table that apart from configuring port 6 in RMII mode and select-
ing the 100Mbps port 6 speed, the remaining options are set by default. Therefore, a user only needs to use external
pull-up resistors as shown in the Table 2.
TABLE 2:
CONFIGURATION EXAMPLE
PIN NUMBER
CONFIGURATION
STRAP PIN
62, 63
RXD6_3, RXD6_2
Port 6 Mode
01: RMII
DESCRIPTION
65
RXD6_0
Note: RXD6_3 includes an internal pull-down resistor.
Port 6 Speed Select
1: 100Mbps Mode
Note: If Port 6 is configured for MII or RMII, set the speed to
100Mbps.
FIGURE 1:
EXAMPLE CONFIGURATION CIRCUIT
VDDIO
10K Ohm
RXD6_2
VDDIO
10K Ohm
KSZ9896C
RXD6_0
DS00002577A-page 2
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
�
AN2577
MICROCONTROLLER CONFIGURATION
In this switch configuration method, the switch’s serial bus such as, SPI or I2C is connected to a small microcontroller
to configure its internal functions. The switch acts as a I2C slave device in the system. Using this serial bus, the micro-
controller writes configuration registers during power up of the device, as described in the management interface portion
of the data sheet. Configuration strap pins are used to determine the interface mode the switch operates in. For exam-
ple, in the KSZ9897R, the LED4_1 and LED3_1 pins decide the configuration interface:
LED4_1 LED3_1 = 01 = I2C Interface Mode
LED4_1 LED3_1 = 1X = SPI Slave Mode
In this method, the serial interface provides access to the switch and PHY access registers. The serial interface pro-
vides access to the switch and PHY access registers. Between these two interfaces, SPI is the fastest speed. For exam-
ple, the KSZ9897 supports up to a 50 MHz bus speed in SPI mode, whereas it only supports a 400Kb bus speed in I2C
mode.
Example Configuration
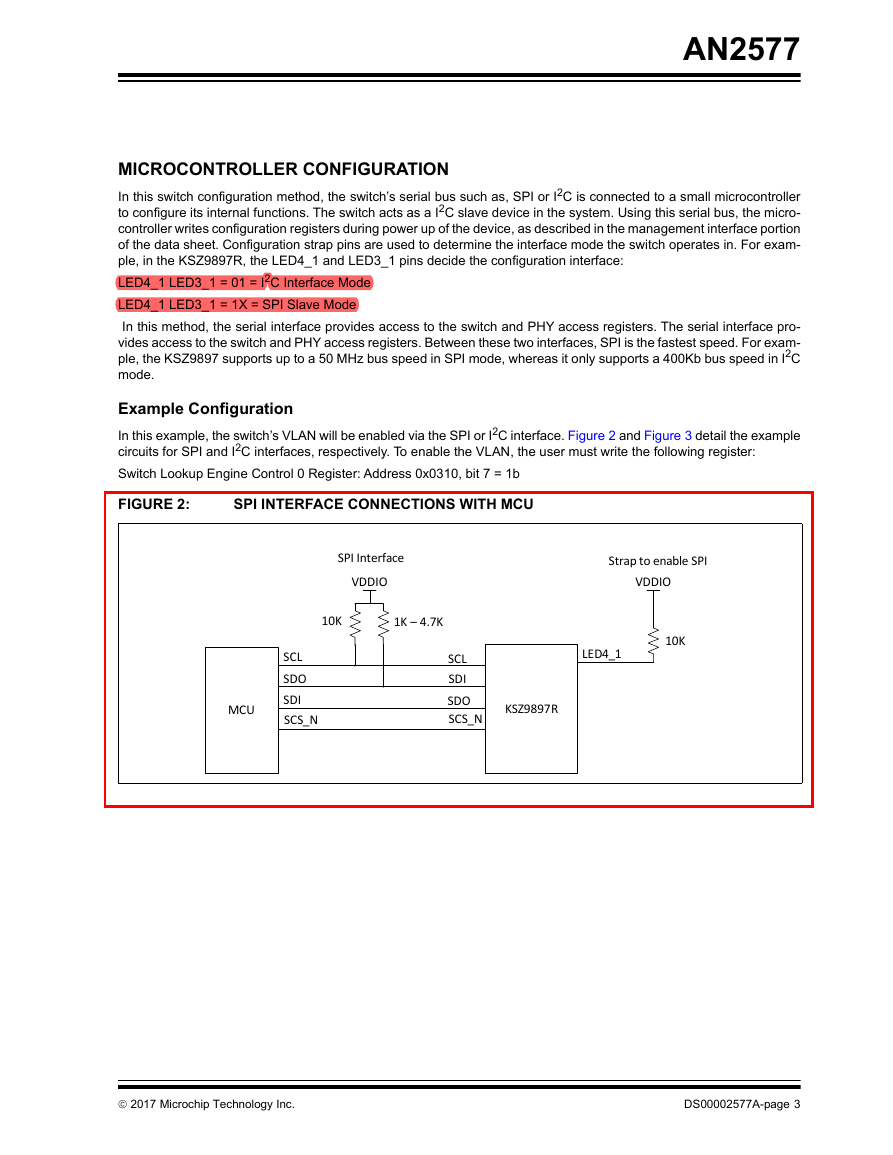
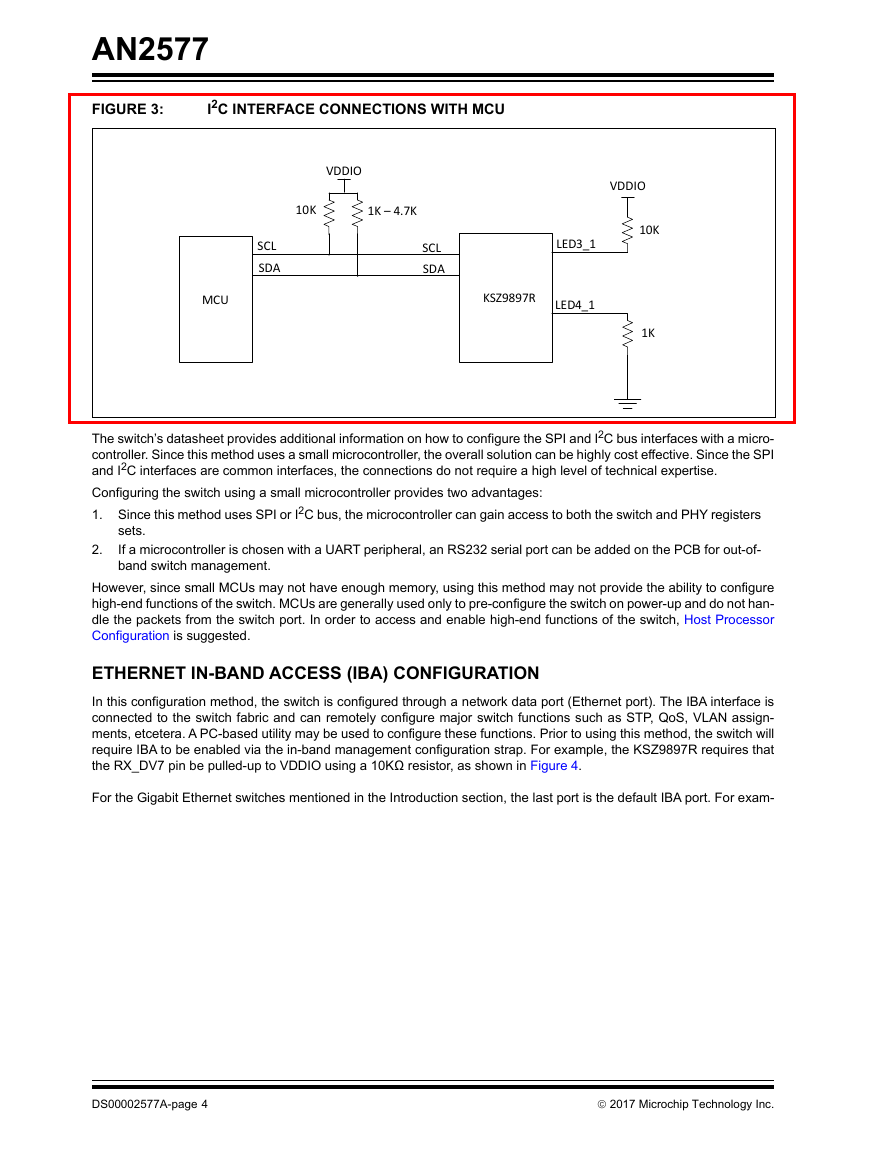
In this example, the switch’s VLAN will be enabled via the SPI or I2C interface. Figure 2 and Figure 3 detail the example
circuits for SPI and I2C interfaces, respectively. To enable the VLAN, the user must write the following register:
Switch Lookup Engine Control 0 Register: Address 0x0310, bit 7 = 1b
FIGURE 2:
SPI INTERFACE CONNECTIONS WITH MCU
SPI Interface
VDDIO
10K
1K – 4.7K
SCL
SDO
SDI
SCS_N
MCU
SCL
SDI
SDO
SCS_N
KSZ9897R
Strap to enable SPI
VDDIO
LED4_1
10K
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002577A-page 3
�
AN2577
FIGURE 3:
I2C INTERFACE CONNECTIONS WITH MCU
VDDIO
10K
1K – 4.7K
SCL
SDA
MCU
SCL
SDA
LED3_1
KSZ9897R
LED4_1
VDDIO
10K
1K
The switch’s datasheet provides additional information on how to configure the SPI and I2C bus interfaces with a micro-
controller. Since this method uses a small microcontroller, the overall solution can be highly cost effective. Since the SPI
and I2C interfaces are common interfaces, the connections do not require a high level of technical expertise.
Configuring the switch using a small microcontroller provides two advantages:
1. Since this method uses SPI or I2C bus, the microcontroller can gain access to both the switch and PHY registers
sets.
If a microcontroller is chosen with a UART peripheral, an RS232 serial port can be added on the PCB for out-of-
band switch management.
2.
However, since small MCUs may not have enough memory, using this method may not provide the ability to configure
high-end functions of the switch. MCUs are generally used only to pre-configure the switch on power-up and do not han-
dle the packets from the switch port. In order to access and enable high-end functions of the switch, Host Processor
Configuration is suggested.
ETHERNET IN-BAND ACCESS (IBA) CONFIGURATION
In this configuration method, the switch is configured through a network data port (Ethernet port). The IBA interface is
connected to the switch fabric and can remotely configure major switch functions such as STP, QoS, VLAN assign-
ments, etcetera. A PC-based utility may be used to configure these functions. Prior to using this method, the switch will
require IBA to be enabled via the in-band management configuration strap. For example, the KSZ9897R requires that
the RX_DV7 pin be pulled-up to VDDIO using a 10KΩ resistor, as shown in Figure 4.
For the Gigabit Ethernet switches mentioned in the Introduction section, the last port is the default IBA port. For exam-
DS00002577A-page 4
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
�
AN2577
ple, for the KSZ9897 switch, port 7 is the default IBA port and for the KSZ9896 switch, port 6 is the default IBA port and
so forth. The IBA port can be changed to a different port of the switch. However, it requires that the switch is connected
to a MCU or MPU via SPI or I2C interface to initially configure the IBA control register to the desired port.
FIGURE 4:
IBA CONNECTIONS
VDDIO
10K
RX_DV7
KSZ9897R
Port1
Port2
Port3
Port4
Port5
Port6
Port7
(IBA access default port)
The IBA configuration method provides the most efficient way to configure and manage the device, since the same
Ethernet data port is used to configure the switch. IBA eliminates the requirements for a separate serial interface and
makes building and managing the network more economical. Therefore, this method is extremely useful in complex
industrial environments, such as where VoIP services are essential. In this situation, when VoIP traffic requires higher
throughput, a user can remotely allocate more bandwidth to the network using the Quality of Service (QoS) function.
The in-band configuration and management method requires a PC application, such as a browser based tool and a host
processor. The switches configuration page is accessed using an IP address. Microchip provides an example web-
based application, as shown in Figure 5, which is available from a GitHub link on the EVB-KSZ9897 product page.
FIGURE 5:
IBA WEB APPLICATION
The application provides an easy way to configure advanced features of the KSZ9897, such as VLAN, STP, ACL, QoS
etc.. However, in-band management includes potential for the switch to be isolated and unmanageable if connection to
the individual device is lost, for example in a spanning tree loop or if the Ethernet connection is cut accidentally. Addi-
tionally, since the switch is easily accessible via a PC and the network, security can be an issue. Because of this, at a
minimum, the following precautions should be followed when using this method:
1. The PC accessing the switch should have an adequate security level (i.e., other than the network engineer, no
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002577A-page 5
�
AN2577
other person should have access to it.)
2. The PC accessing the switch should be free of any malware or virus.
3. The switch should be accessible only through the organization’s internal network and not available to the outside
world.
HOST PROCESSOR CONFIGURATION
In this switch configuration method, a high-end host processor is connected to the switch. The processor firmware pro-
vides a way to program the configuration registers of the switch. The processor can use either an SPI or I2C interface
to enable the switch functions and PHY functions, whereas the MII Management (MIIM – a.k.a MDC/MDIO) interface
can be used to enable the PHY functions of the switch. The switch operates as an SPI or I2C slave in this method.
Compared to the Microcontroller Configuration method, this technique includes a high-end microprocessor (MPU) with
more flash memory and RAM. This allows the MPU to host a complex operating system (OS) such as embedded Linux
with a built-in TCP/IP stack which can manage the switch functions and its traffic in addition to configuring the switch.
In this setup, the user can use Telnet or a web server application to configure the switch. The stack also includes Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP) which can be used to manage the switch.
This configuration method is useful in applications where a system needs to be self-contained. Since the host processor
can support full features such as a TCP/IP stack, use operating systems such as Linux, and switch management ports
such as SPI and I2C, this method of configuration can be used in a self-contained system solution. The on-board Linux
OS can enable and disable switch functions, such as VLAN, which can be difficult in the microcontroller based config-
uration method. Host processor configuration provides the ability to run advanced protocols such as 1588 and AVB.
Microchip provides an example that shows the configuration of the KSZ9477 device using a SAMA5D3 processor. The
hardware and software is available with detailed documentation from the EVB-KSZ9477 evaluation board’s web site.
CONFIGURATION METHOD TRADE-OFFS
Table 3 details the trade-offs of using different configuration methods.
TABLE 3:
CONFIGURATION METHOD TRADE-OFFS (SHEET 1 OF 2)
Microcontroller
Ethernet IBA
Host Processor
Moderate
Hardware requires a
few passive compo-
nents and a free PC
based utility
Moderate
Apart from switch and
PHY registers, adds
remote switch manage-
ment
Easy
Example web GUI pro-
vided by Microchip
Moderate
User can start with an
example web browser
or PC based utility
Most
A high-end MPU is
required with support-
ing circuitry and OS
Advanced
Access to switch and
PHY registers, host
TCP/IP stack, drivers
for advanced features
(e.g., AVB, IEEE1588)
Moderate
Firmware develop-
ment, driver installation,
and switch/PHY config-
uration required
Moderate
Requires knowledge of
Linux OS, MPU devel-
opment environment
Cost
Features
Configuration Straps
Least
Only a few passive
components are
required to configure
the switch
Low
Enables only basic fea-
tures
Moderate
Low end MCU and its
supporting circuitry is
required
Moderate
Enables switch and
PHY registers
Ease of Use
Required
Expertise
Easy
Requires basic elec-
tronic components and
circuit configuration
Basic
Hardware/circuit design
knowledge required by
the developer
Moderate
Requires some knowl-
edge of MCU based
application develop-
ment
Basic to Moderate
Requires knowledge of
MCU, firmware devel-
opment, and develop-
ment tools
DS00002577A-page 6
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
�
AN2577
TABLE 3:
CONFIGURATION METHOD TRADE-OFFS (SHEET 2 OF 2)
System
Development
Time
Configuration Straps
Quickest
All basic features are
configured in hardware
while developing the
PCB
Microcontroller
Ethernet IBA
Host Processor
Moderate
Firmware development
is required for MCU
Moderate
Web based GUI is pro-
vided, but remote man-
agement may require
additional setup
Most
Requires firmware
development and
switch drivers
EVALUATION BOARDS
Microchip provides the following development boards to illustrate the different configuration methods explained in this
application note:
• KSZ9897 Switch Evaluation Board with LAN7801 & KSZ9031 (Part Number: EVB-KSZ9897)
- This board is best suited for Configuration Straps or Ethernet In-Band Access (IBA) Configuration evaluation
• KSZ9477 Managed Switch Evaluation board with SAMA5D36 MPU (Part Number: EVB-KSZ9477)
- This board is best suited for Host Processor Configuration evaluation
A user can access the hardware design files and the software configuration tools from the evaluation board’s product
page at www.microchip.com.
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002577A-page 7
�
AN2577
APPENDIX A: APPLICATION NOTE REVISION HISTORY
TABLE A-1:
REVISION HISTORY
Revision Level & Date
Section/Figure/Entry
Correction
DS00002577A (12-01-17)
All
Initial release.
DS00002577A-page 8
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
�











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc