Cover page
Contents
Preface
I Converters in equilibrium
II converter Dynamics and control
III Magnetics
IV Modern Rectifiers and Power system Harmonics
V Resonant Converters
Appendices
Index
Preface
1 Introduction
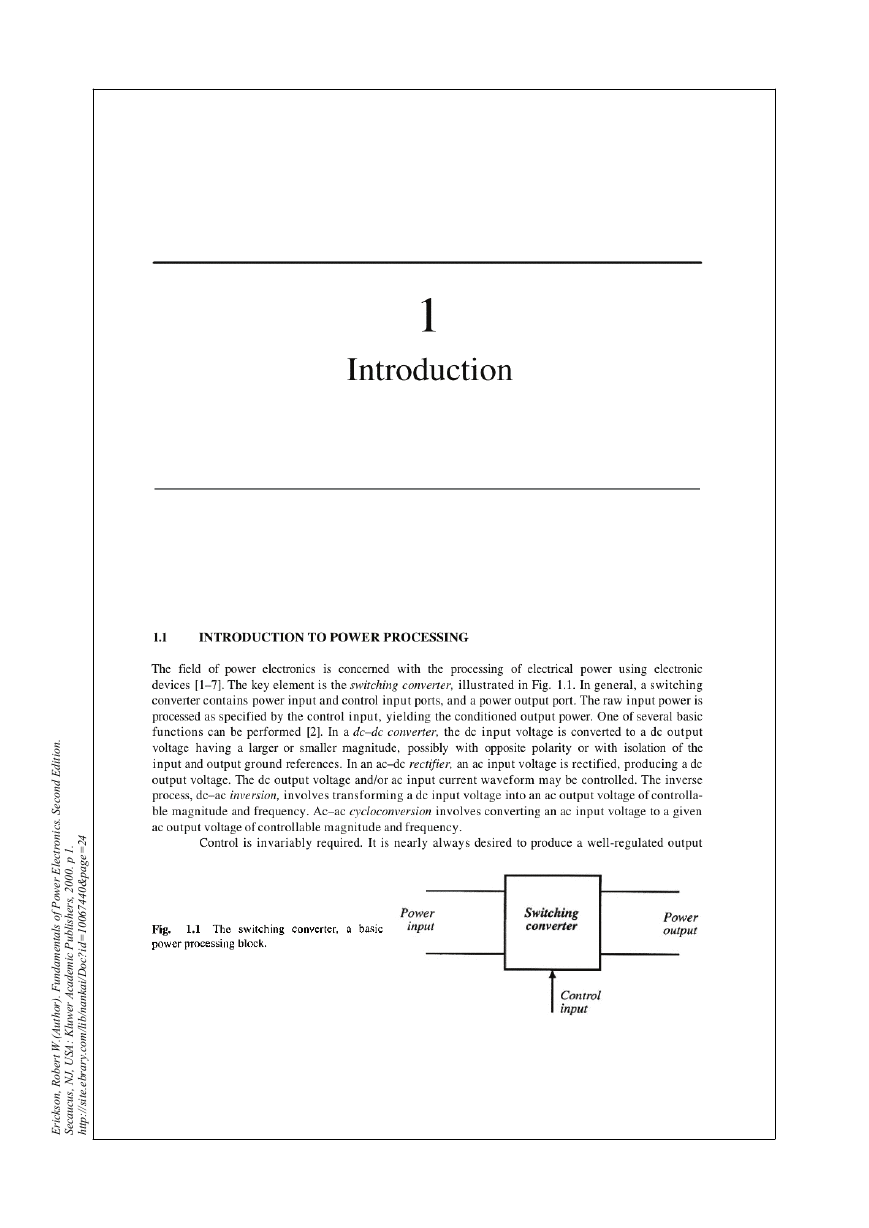
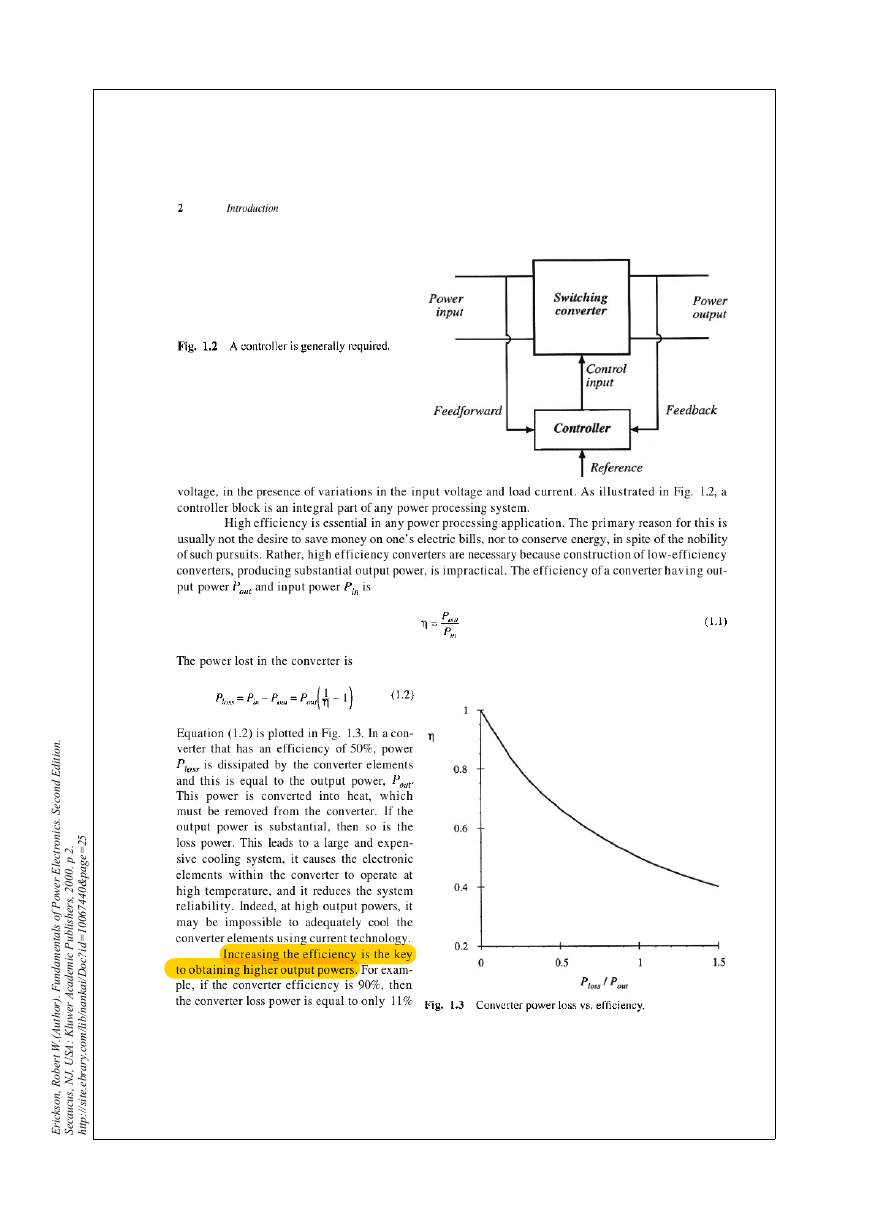
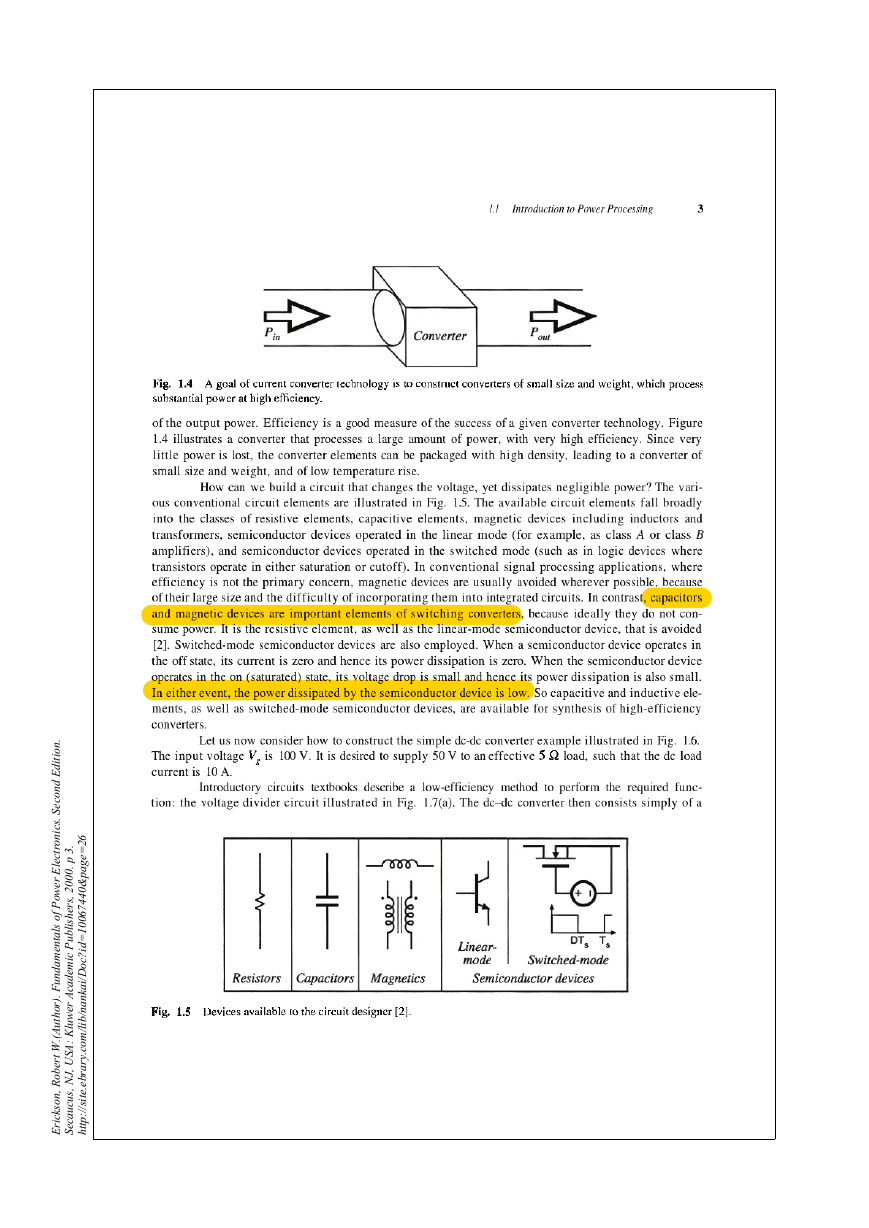
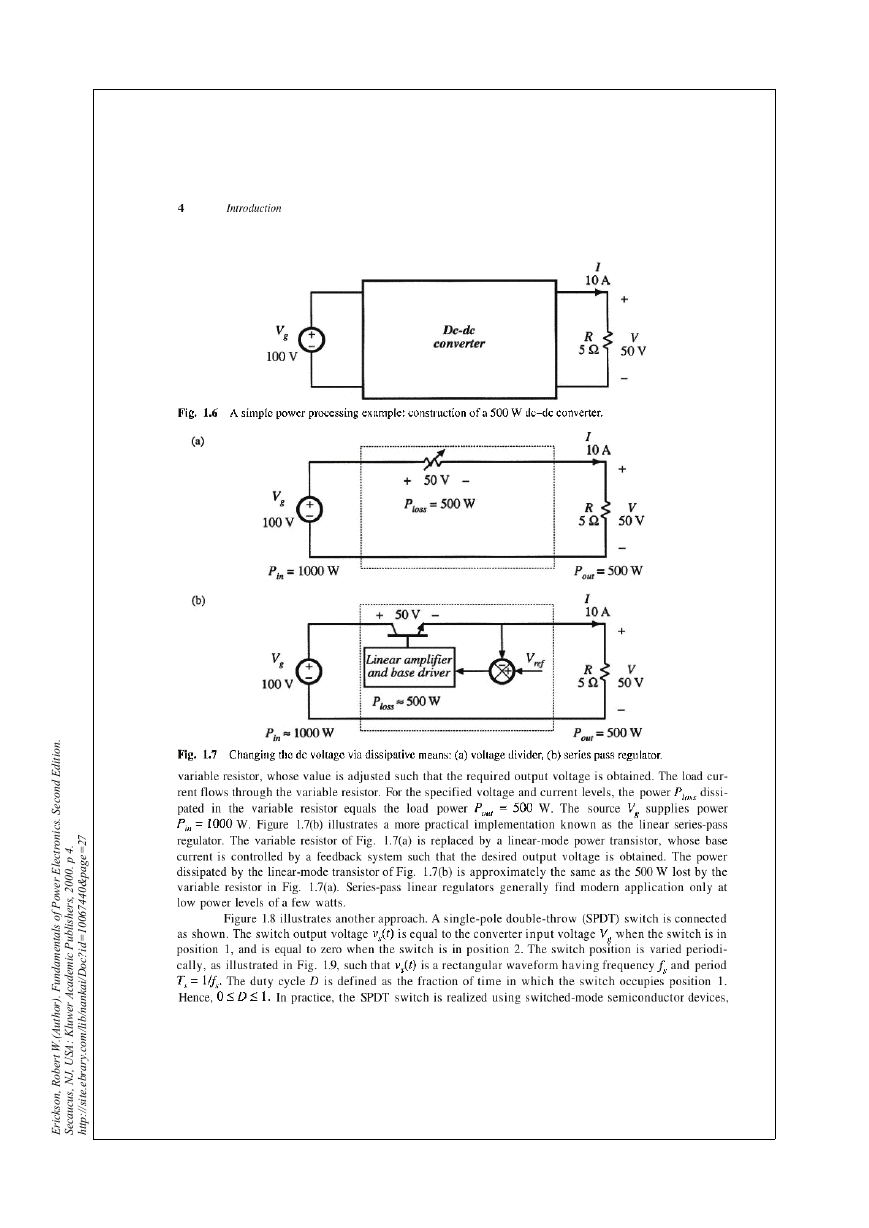
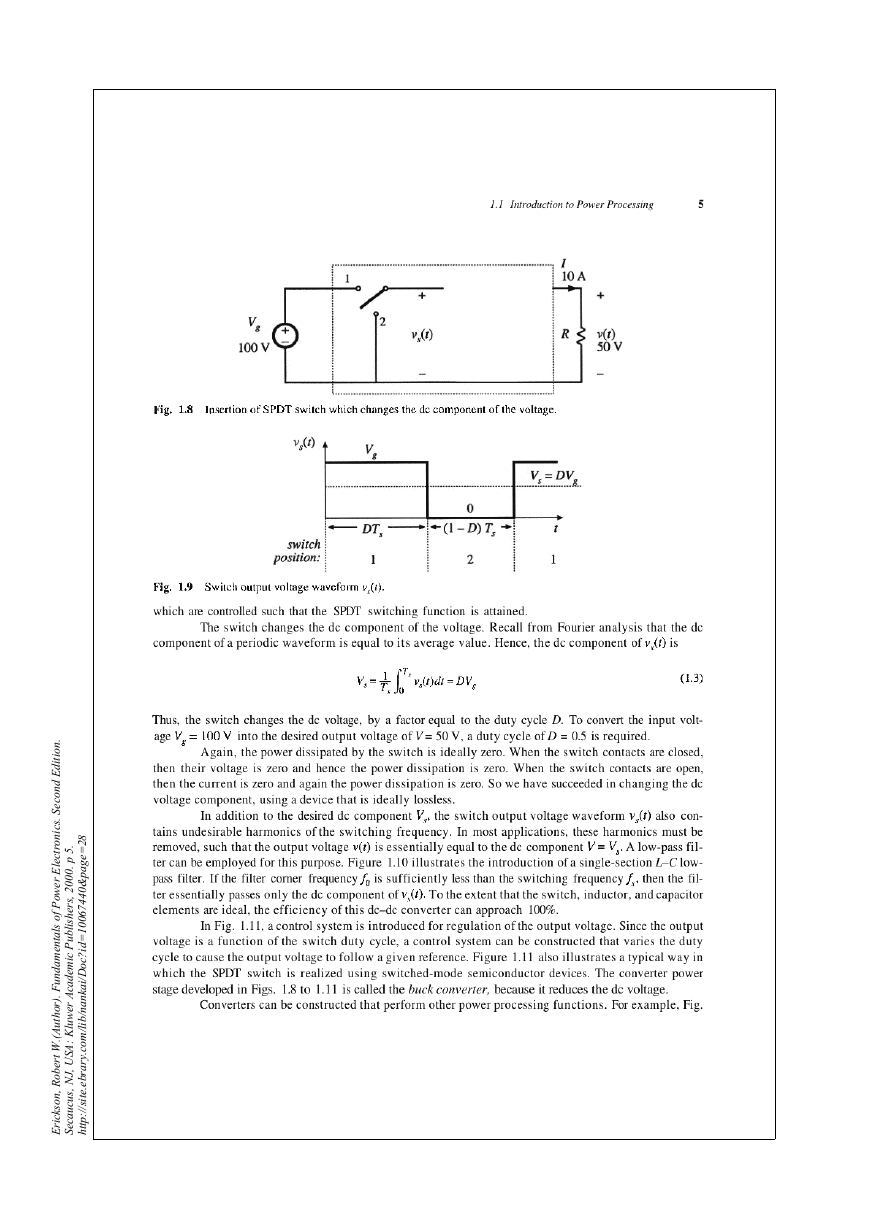
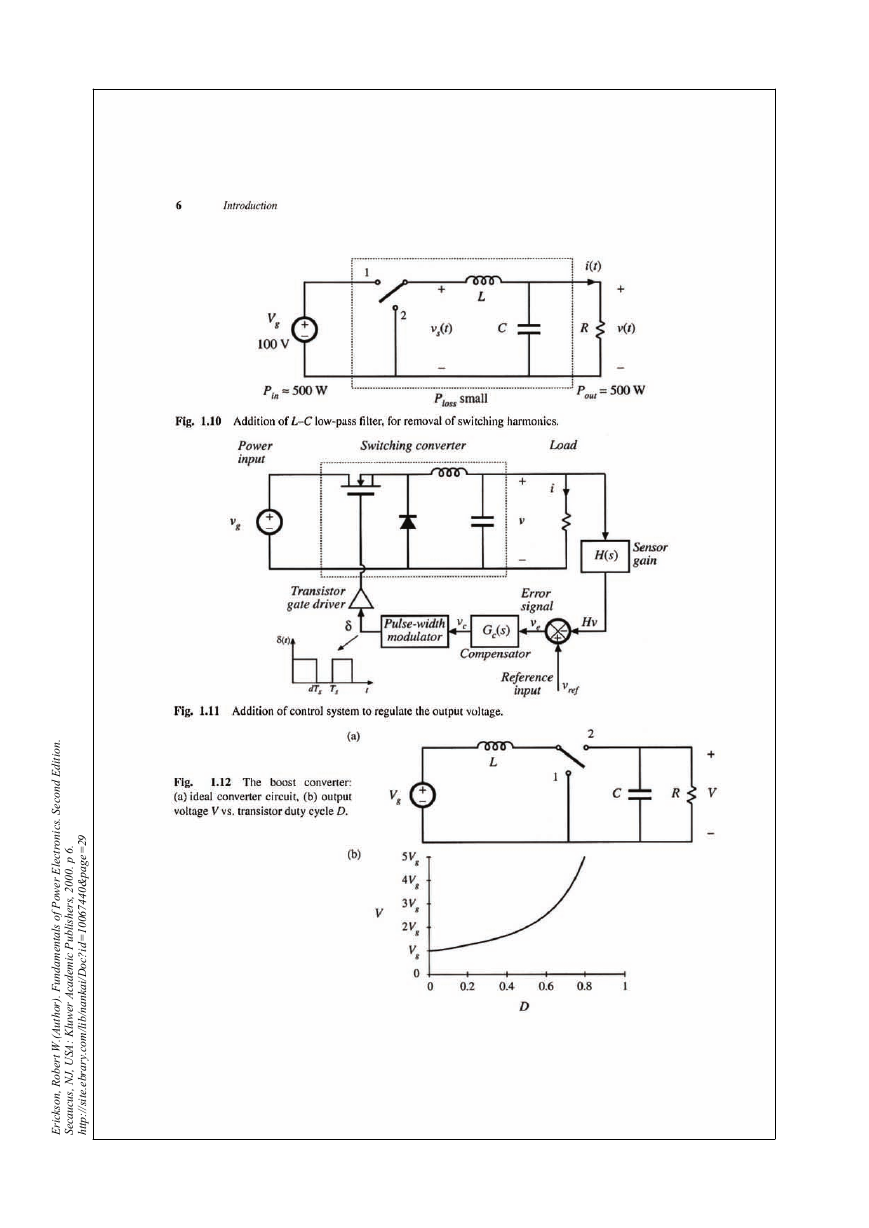
1.1 Introduction to power processing
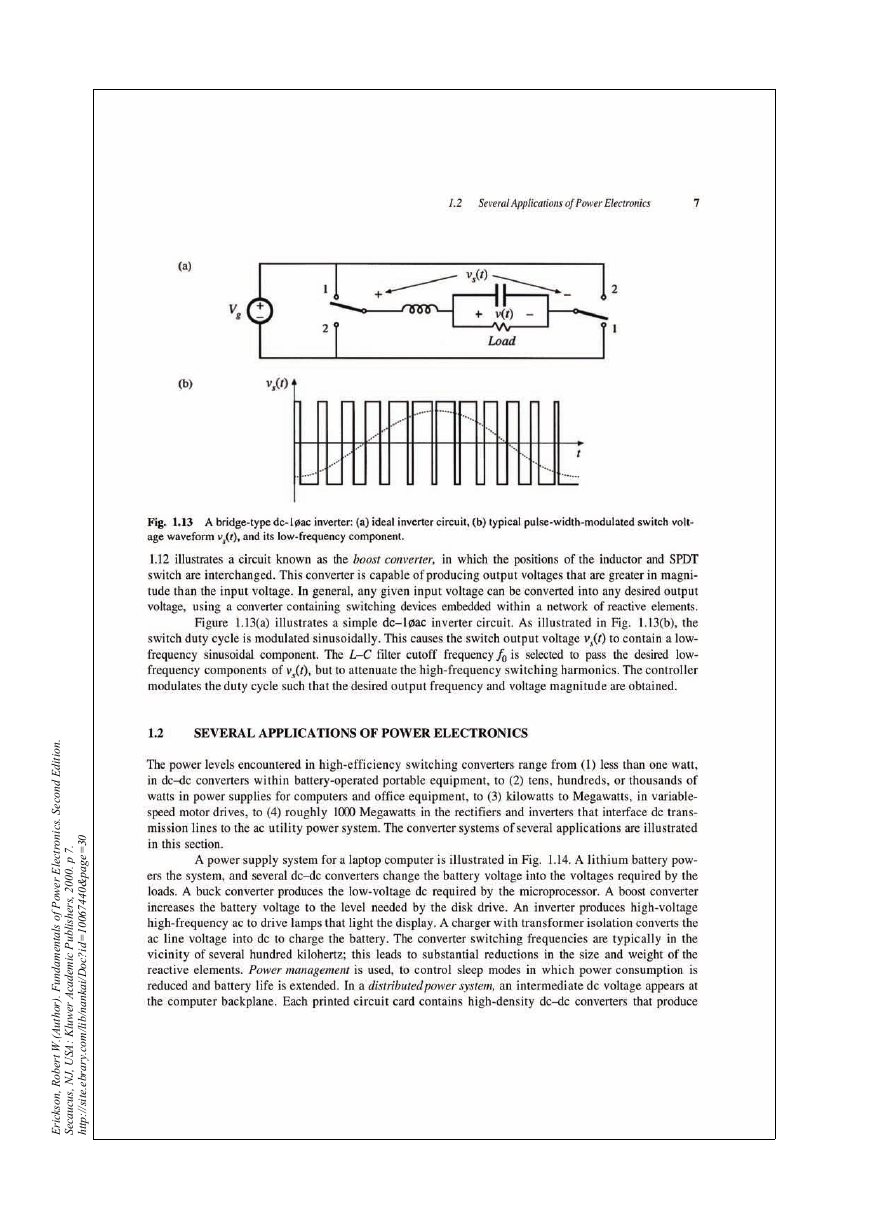
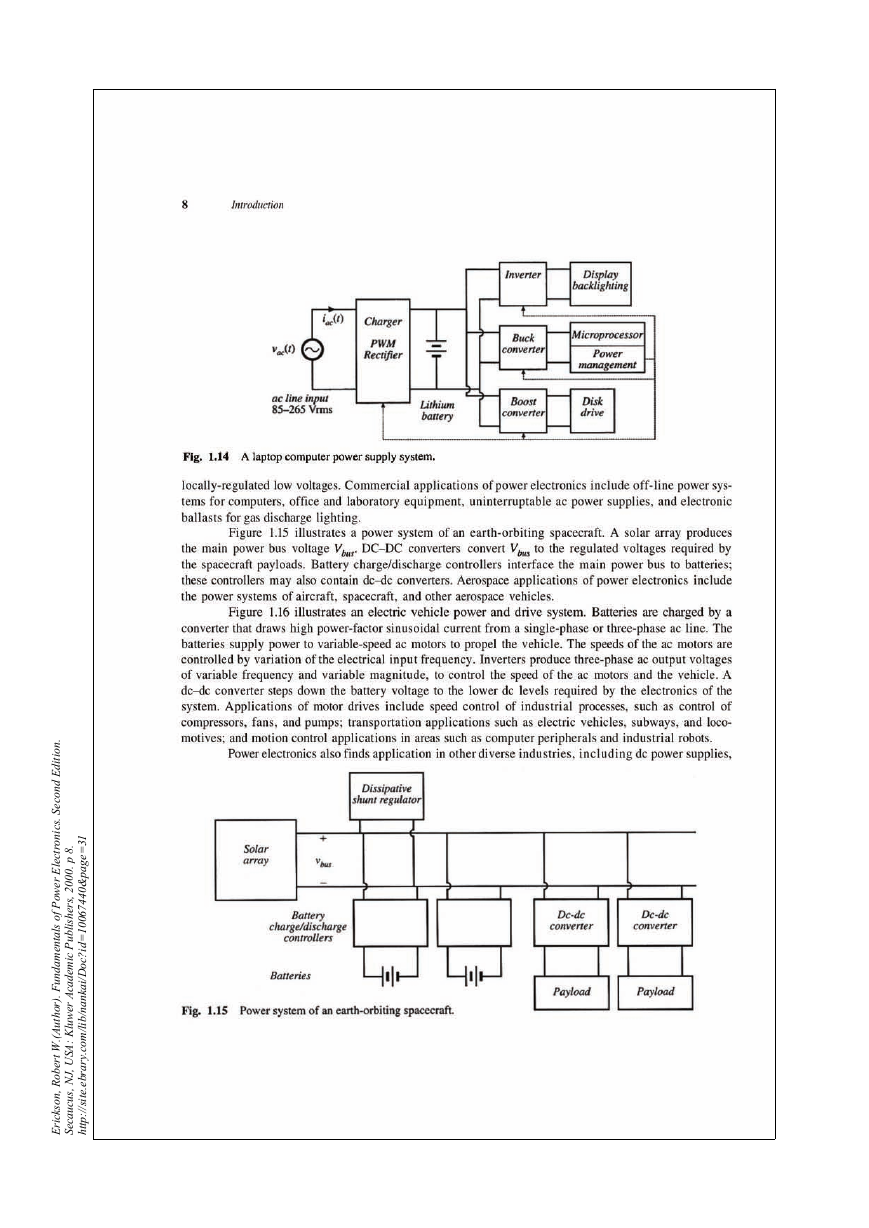
1.2 Several application of power electronics
1.3 Elements of power electronics
References
Part I
2 Priciples of Steady-State converter Analysis
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Inductor volt-second balance,capacitor charge balance,and the small-ripple approximation
2.3 Boost converter example
2.4 Cuk converter example
2.5 Estimating the ouput voltage ripple in converters containing two-ple low-pass filters
2.6 Summary of key points
References
Problems
3 Steady-state Equivalent Circuit Modeling,Losses and Efficiency
3.1 The DC transformer model
3.2 Inclusion of inductor copper loss
3.3 Construction of equivalent circuit model
3.4 How to obtain the input port of the model
3.5 Example : Inclusion of semiconductor conduction losses in the boost converter model
3.6 Summary of key points
References
Problems
4 Switch realization
4.1 Switch applications
4.2 A brief survey of power semiconductor devices
4.3 Switching loss
4.4 Summary of key points
References
Problems
5 The discontinuous conduction mode
5.1 Origin of the discontinuous conductions mode and mode boundary
5.2 Analysis of the conversion ratio M(D,K)
5.3 Boost converter example
5.4 Summary of results and key points
Problems
6 Converter Circuits
6.1 Circuit manipulations
6.2 A short list of converters
Transformer isolation
6.4 Converter evaluation and design
6.5 Summary of key points
References
Problems
Part II
7 AC equivalent circuit modeling
7.1 Introduction
7.2 The basic AC modeling approach
7.3 State-spce averaging
7.4 circuit averaging and vaeraged switch modeling
7.5 The canonical circtuit model
7.6 Modeling the pulse-width modulator
7.7 Summary of key points
References
Problems
8 Converter Transfer Functions
8.1 Review of bode plots
8.2 Analysis of converter transfer functions
8.3 Graphical construction of impedance and transfer functions
Part III
13 Basic Magnetics Theory
13.1 Review of Basic Magnetics
13.1.1 Basic Relationships
13.1.2 Magnetic Circuits
13.2 Transformer Modeling
13.2.1 The Ideal Transformer
13.2.2 The Magnetizing Inductance
13.2.3 Leakage Inductances
13.3 Loss Mechanisms in Magnetic Devices
13.3.1 Core Loss
13.3.2 Low-Frequency Copper Loss
13.4 eddy Currentsin Winding Conductors
13.4.1 Introduction to the Skin and proximity Effects
13.4.2 Leakage Flux in Windings
13.4.3 Foil Windings and Layers
13.4.4 Power Loss in a Layer
13.4.5 Example:Power Loss in a Transformer Winding
13.4.6 Interleaving the Windings
13.4.7 PWM Waveform Harmonics
13.5 Several types of Magnetic Devices,Their B-H Loops,and Core VS. Copper Loss
13.5.1 Filter Inductor
13.5.2 AC Inductor
13.5.3 Transformer
13.5.4 Coupled Inductor
13.5.5 Flyback Transformer
13.6 Summary of Key Points
References
Problems
14 Inductor Design
14.1 Filter Inductor Design Constraints
Part IV
Part V
Appendices
A
B
C
D
Index








 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc