Introduction
Definitions
Course
Course Offering
Course Catalog
Faculty
Finance System
Grade
Professor
Report Card
Roster
Student
Schedule
Transcript
Objectives
Scope
References
Functionality
Usability
Reliability
Performance
Supportability
Security
Design Constraints
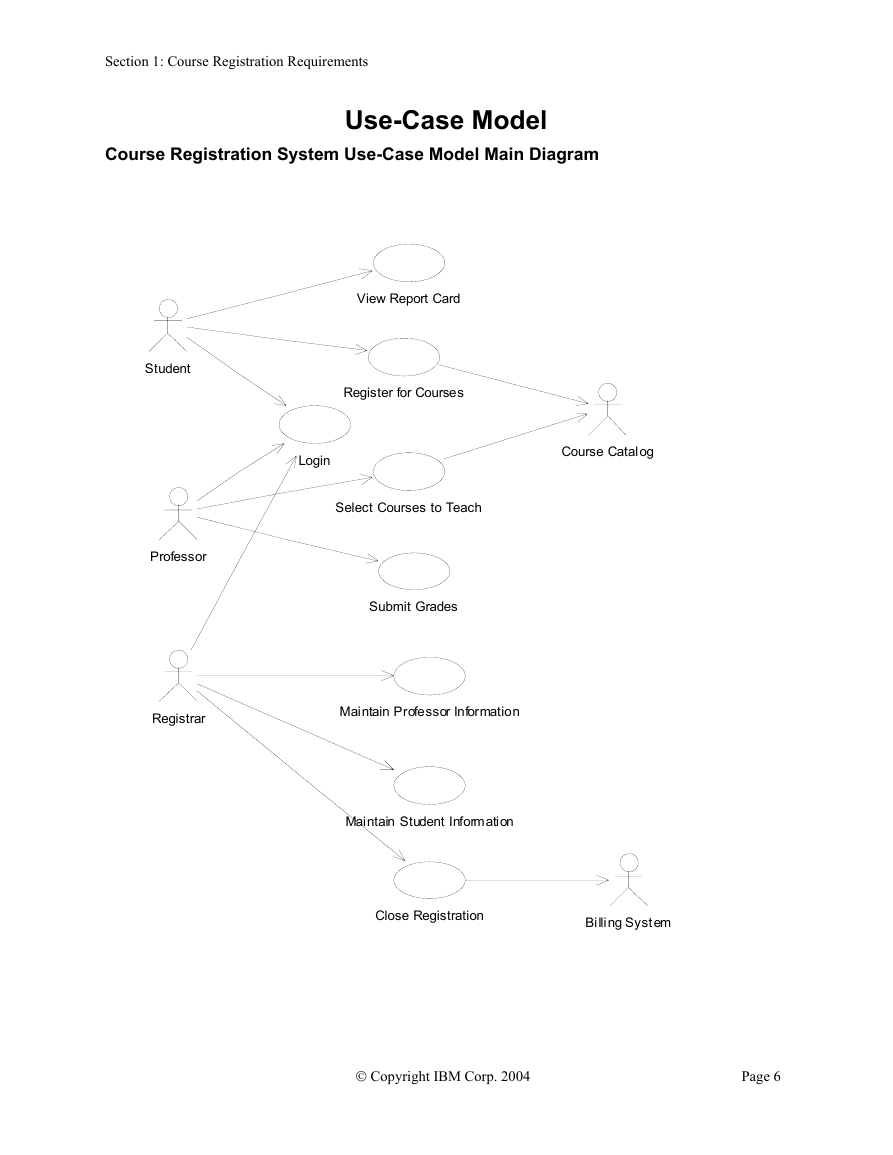
Course Registration System Use-Case Model Main Diagram
Close Registration
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Alternative Flows
No Professor for the Course Offering
Billing System Unavailable
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Login
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Alternative Flows
Invalid Name/Password
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Maintain Professor Information
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Add a Professor
Update a Professor
Delete a Professor
Alternative Flows
Professor Not Found
Delete Cancelled
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Maintain Student Information
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Add a Student
Update a Student
Delete a Student
Alternative Flows
Student Not Found
Delete Cancelled
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Register for Courses
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Create a Schedule
Update a Schedule
Delete a Schedule
Select Offerings
Submit Schedule
Alternative Flows
Save a Schedule
Unfulfilled Prerequisites, Course Full, or Schedule Conflicts
No Schedule Found
Course Catalog System Unavailable
Course Registration Closed
Delete Cancelled
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Select Courses to Teach
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Alternative Flows
No Course Offerings Available
Schedule Conflict
Course Catalog System Unavailable
Course Registration Closed
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Submit Grades
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Alternative Flows
No Course Offerings Taught
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
View Report Card
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Alternative Flows
No Grade Information Available
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Introduction
Definitions
Bank System
Employee
Payroll Administrator
Project Management Database
System Clock
Pay Period
Paycheck
Payment Method
Timecard
Purchase Order
Salaried Employee
Commissioned Employee
Hourly Employee
Objectives
Scope
References
Functionality
Usability
Reliability
Performance
Supportability
Security
Design Constraints
Payroll System Use-Case Model Main Diagram
Create Administrative Report
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Alternative Flows
Requested Information Unavailable
Invalid Format or Insufficient Information
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Create Employee Report
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Alternative Flows
Requested Information Unavailable
Invalid Format or Insufficient Information
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Login
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Alternative Flows
Invalid Name/Password
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Maintain Employee Information
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Add an Employee
Update an Employee
Delete an Employee
Alternative Flows
Employee Not Found
Delete Cancelled
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Maintain Purchase Order
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Create a Purchase Order
Update a Purchase Order
Delete a Purchase Order
Alternative Flows
Purchase Order Not Found
Invalid Access to a Purchase Order
Purchase Order is Closed
Delete Cancelled
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Maintain Timecard
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Submit Timecard
Alternative Flows
Invalid Number of Hours
Timecard Already Submitted
Project Management Database Not Available
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Run Payroll
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Alternative Flows
Bank System Unavailable
Deleted Employees
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Select Payment Method
Brief Description
Flow of Events
Basic Flow
Alternative Flows
Employee Not Found
Special Requirements
Pre-Conditions
Post-Conditions
Extension Points
Description
Architectural Mechanisms
Analysis Mechanisms
Analysis-to-Design-to-Implementation Mechanisms Map
Implementation Mechanisms
Security
Static View: Security
Class Descriptions
Dynamic View: Secure User Set-Up
Dynamic View: Secure Data Access
Persistency - RDBMS - JDBC
Static View: Persistency JDBC
Class Descriptions
Dynamic View: JDBC RDBMS Read
Dynamic View: JDBC RDBMS Update
Dynamic View: JDBC RDBMS Create
Dynamic View: JDBC RDBMS Delete
Dynamic View: JDBC RDBMS Initialize
Persistency - OODBMS - ObjectStore
Static View: Persistency – ObjectStore OODBMS
Class Descriptions
Static View: Persistency - DBManager Detail
Class Descriptions
Dynamic View: ObjectStore – OODBMS Create
Dynamic View: ObjectStore OODBMS Delete
Dynamic View: ObjectStore OODBMS Read
Dynamic View: ObjectStore OODBMS Update
Dynamic View: ObjectStore OODBMS Initialize
Dynamic View: ObjectStore OODBMS Shutdown
Distribution - RMI
Static View: Distribution - RMI
Class Descriptions
Dynamic View: Set Up Remote Connection (details)
Dynamic View: Set Up Remote Connection
Logical View
Architectural Analysis
Upper-Level Layers
Upper-Level Layer Dependencies
Architectural Design
Incorporating ObjectStore
Architectural Layers and Their Dependencies: Main Diagram
Layer Descriptions
Packages and Their Dependencies: Package Dependencies Diagram
Package Descriptions
Process View
Processes
Design Element to Process Mapping
Deployment View
Nodes and Connections
Process-to-Node Map















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc