算法思想:(字体:宋体)
1. 建立一个空栈;
2. 依次将队列元素全部出队,并逐个入栈;
3. 依次将栈内的全部元素出栈,并逐个将出栈的元素入队;
4. 再次输出队列,即完成队列逆置。
代码:(字体:Times New Roman)
//已知 q 是一非空队列,编写一个算法,
//仅用队列和栈及少量工作变量完成将队列 q 中的所有元素逆置
#include
#include
#define MAXSIZE 30
typedef struct{
char data[MAXSIZE];
int top;
}SeqStack;
//栈顶指针
//顺序栈类型
void Init_SeqStack(SeqStack **s){// 初始化栈
(*s) = (SeqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
(*s)->top = -1;
}
int Empty_SeqStack(SeqStack *s){//判断栈是否为空
if (s->top == -1){
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void Push_SeqStack(SeqStack *s, char x){
if (s->top == MAXSIZE - 1){
printf("The stack is full!\n");
}
else{
s->top++;
s->data[s->top] = x;
}
}
void Pop_SeqStack(SeqStack *s, char *x){
if (s->top == -1){
printf("Stack is empty!\n");
}
else{
*x = s->data[s->top];
�
s->top--;
}
}
typedef struct{
char data[MAXSIZE];//栈中元素存储空间
int rear, front;//队尾和对头指针
}SeQueue;
void Init_SeQueue(SeQueue **q){//循环队列初始化
*q = (SeQueue *)malloc(sizeof(SeQueue));
(*q)->front = 0;
(*q)->rear = 0;
}
int Empty_SeQueue(SeQueue *q){//判断队列空
if (q->front == q->rear){
return 1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
void In_SeQueue(SeQueue *s, char x){//元素入队列
if ((s->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == s->front){
printf("队列已满!\n");
}
else{
s->rear = (s->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;
s->data[s->rear] = x;
}
}
void Out_SeQueue(SeQueue *s, char *x) {//元素出队列
if (s->front == s->rear){
printf("队列为空!\n");
}
else{
s->front = (s->front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
*x = s->data[s->front];
}
}
�
//用栈 s 逆置队列
//当队列*q 非空时
//取出对头元素*p
//将对头元素*p 压入栈 s
//当栈 s 非空时
void print(SeQueue *s){
int i;
i = (s->front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
while (i != s->rear+1){
printf("%4c", s->data[i]);
i = (i + 1) % MAXSIZE;
}
printf("%4c\n", s->data);
}
void Revers_Queue(SeQueue *q, SeqStack *s){
char x, *p = &x;
Init_SeqStack(&s);
while (!Empty_SeQueue(q)){
Out_SeQueue(q, p);
Push_SeqStack(s, *p);
}
while (!Empty_SeqStack(s)){
Pop_SeqStack(s, p);
In_SeQueue(q, *p);
}
}
int main(){
SeqStack *s;
SeQueue *q;
char x, *y = &x;
Init_SeqStack(&s);
Init_SeQueue(&q);
if (Empty_SeQueue(q)){
printf("队列为空!\n");
}
printf("输入字符串:\n");
scanf("%c", &x);
while (x != '\n'){
In_SeQueue(q, x);
scanf("%c", &x);
}
printf("队列的输出元素:\n");
print(q);
printf("转换队列:\n");
Revers_Queue(q, s);
printf("队列的输出元素:\n");
print(q);
�
return 0;
}
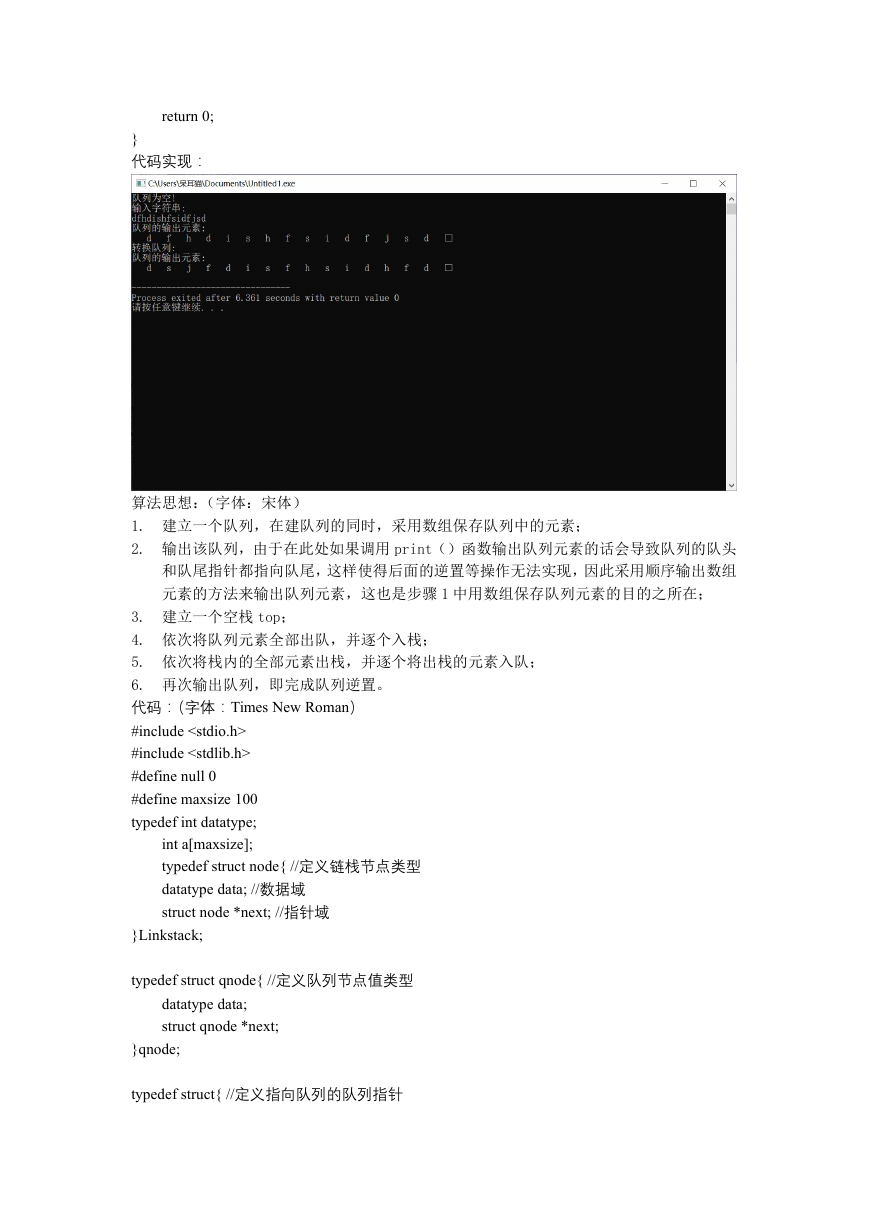
代码实现:
算法思想:(字体:宋体)
1. 建立一个队列,在建队列的同时,采用数组保存队列中的元素;
2. 输出该队列,由于在此处如果调用 print()函数输出队列元素的话会导致队列的队头
和队尾指针都指向队尾,这样使得后面的逆置等操作无法实现,因此采用顺序输出数组
元素的方法来输出队列元素,这也是步骤 1 中用数组保存队列元素的目的之所在;
3. 建立一个空栈 top;
4. 依次将队列元素全部出队,并逐个入栈;
5. 依次将栈内的全部元素出栈,并逐个将出栈的元素入队;
6. 再次输出队列,即完成队列逆置。
代码:(字体:Times New Roman)
#include
#include
#define null 0
#define maxsize 100
typedef int datatype;
int a[maxsize];
typedef struct node{ //定义链栈节点类型
datatype data; //数据域
struct node *next; //指针域
}Linkstack;
typedef struct qnode{ //定义队列节点值类型
datatype data;
struct qnode *next;
}qnode;
typedef struct{ //定义指向队列的队列指针
�
qnode *front;
qnode *rear;
}Linkqueue;
Linkstack *top; //栈顶指针变量
int stackempty(Linkstack *top){//判别空栈
return top? 0 : 1;
}
Linkstack *push( Linkstack *top,datatype x){ //元素 x 入栈
Linkstack *p;
p=( Linkstack *) malloc ( sizeof( Linkstack ) ); //申请空间
p->data=x; //置初值
p->next=top;
top=p;
return top;
}
Linkstack *pop( Linkstack *top){ //出栈
Linkstack *p;
if(!top){//判断栈是否为空
printf("栈上空的!\n");
return null;
}
p=top;//p 指向栈顶
top=top->next; //栈顶指针后移
free(p); //释放元栈顶空间
return top;
}
datatype getstack(Linkstack *top){//取栈顶元素
if(!top){//如果栈为空
printf("栈上空的!\n");
return 0;
}
return top->data; //返回栈顶元素
}
Linkqueue *init(){ //构造一个空队列
Linkqueue *q;
qnode *p;
q=( Linkqueue * ) malloc ( sizeof( Linkqueue ) ); //为队列头尾分配空间
p=( qnode * ) malloc (sizeof ( qnode )); //为头节点分配空间
�
p->next=null;//置头节点的指针域为空
q->front = q->rear = p; //队头指针队尾指针都指向头节点
return q;
}
datatype getqueue( Linkqueue *q ){//取队头
if( q->front == q->rear ){ //判断队列是否为空
printf("链队列为空!\n");
return 0;
}
return q->front->next->data; //返回队头元素
}
Linkqueue *enqueue( Linkqueue *q,datatype x){//入队元素 x
qnode *p;
p=(qnode *) malloc (sizeof ( qnode )); //为新节点分配空间
p->data=x; //设置新节点的值
p->next=null;
q->rear->next=p; //将新节点入队
q->rear=p; //修改队尾指针
return q;
}
datatype dequeue( Linkqueue *q ){ //删除队头元素
qnode *p;
datatype x;
if( q->front == q->rear){//判断队列是否为空
printf("队列为空,无法删除!\n");
return null;
}
p=q->front->next; //让 p 指向队头元素
x=p->data; //将队头元素的值保存在 x 中
q->front->next=p->next; //出队
if(q->rear==p) //若队列为空,则修改队尾指针指向队头
q->rear=q->front;
free(p); //释放空间
return x; //返回出队元素的值
}
int queueempty( Linkqueue *q ){ //判断队列为空
return q->front==q->rear ? 1: 0; //为空返回 1,否则返回 0
}
Linkqueue *print( Linkqueue *q ){ //输出队列
�
Linkqueue *p=q;
if( p->front == p->rear )
printf("这是一个空队列!\n");
else{
do{
printf("%3d",p->front->next->data); //输出队列元素
p->front=p->front->next; //指针后移
}while(p->front!=p->rear); //如果队列不空
printf("\n");
}
return q;
}
Linkqueue *inv( Linkqueue *q){//利用链栈逆置链队列
top=(Linkstack *)malloc(sizeof(Linkstack)); //为栈顶指针分配空间
top->next=null;
while(!queueempty(q)){ //将队列元素依次出队并入栈
top=push(top,getqueue(q));
dequeue(q);
}
while(!stackempty(top)){ //将堆栈元素依次出栈并入队
if(top->next!=null) //剪枝,以免队头指针的空值在出队时干扰结果
q=enqueue(q,getstack(top));
top=pop(top);
}
return q;
}
int main(){
Linkqueue *q;
int i,n;
q=init();
printf("请输入队列元素个数:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("请输入队列元素(以空格分开):\n");
for(i=0;i
printf("逆置后:\n");
print(q);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc