NTFS Log Tracker
FORENSIC INSIGHT;
DIGITAL FORENSICS COMMUNITY IN KOREA
blueangel
blueangel1275@gmail.com
forensic-note.blogspot.kr
Junghoon Oh
�
Index
1.
Introduction
2. $LogFile
3. $UsnJrnl
4. NTFS Log Tracker
5. Conclusion
forensicinsight.org
Page 2
�
Introduction
forensicinsight.org
Page 3
�
Introduction
NTFS’s Log File
•
•
$LogFile : Transaction Log
$UsnJrnl : Change Log
Conventional file system forensics for NTFS
•
•
File system event based analysis primarily focusing on $MFT
$MFT : A file containing meta data for all files and directories in NTFS.
For deleted files it is possible that there is no meta data in $MFT
Finding artifacts of deleted is very difficulty for the following reasons
•
In case of system drive( C: ), the OS creates temp files constantly.
• A periodic garbage collection since Windows 7.
•
In case of SSD, unallocated space is arranged by TRIM operation.
forensicinsight.org
Page 4
�
Introduction
Analysis of $LogFile and $UsnJrnl
• With these files, an investigator can analyze the file system events during a specific period.
•
The file system events that are not in $MFT can still be analyzed
The history of deleted file
The history of a specific file – $MFT provides only last modified/access time of a file.
•
•
Identify history of access time of a particular file.
Identify history of modified time of a particular file.
forensicinsight.org
Page 5
�
$LogFile
-
-
-
$LogFile ?
The Structure of $LogFile
The Event Analysis of $LogFile
forensicinsight.org
Page 6
�
$LogFile ?
The transaction log file of NTFS
•
•
In case of unexpected system shutdown due to power error or critical system failure, the
operating system recovers the status of file system to the previous status with saved
information in "$LogFile" file.
$LogFile contains all file system transaction records.
The creation of file/directory
The deletion of file/directory
The modification of $data
The modification of MFT entry
•
Each record has LSN($LogFile Sequence Number).
This LSN information increase sequentially.
•
•
•
Each record has the operation data and the data before operation for restoration
Redo : The data after operation
Undo : The data before operation
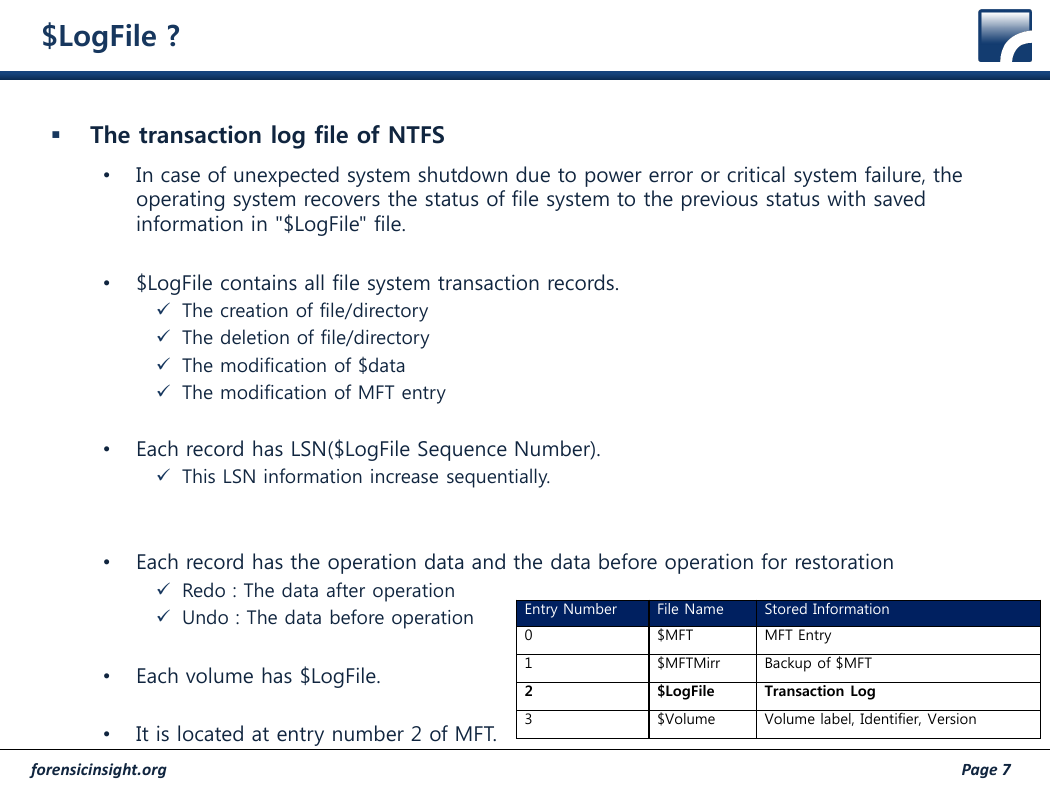
Each volume has $LogFile.
It is located at entry number 2 of MFT.
Entry Number
File Name
Stored Information
0
1
2
3
$MFT
MFT Entry
$MFTMirr
Backup of $MFT
$LogFile
Transaction Log
$Volume
Volume label, Identifier, Version
forensicinsight.org
Page 7
�
$LogFile ?
Size of $LogFile
•
•
•
•
64 MB in typical hard disk volume.
The size can changed based on volume size but typically it is less than 64 MB.
In case of typical computer usage (web surfing, working on documents, etc), the capacity of
64 MB can hold 2 ~ 3 hours of activities in $LogFile records.
For forensic readiness, the size of the file should be increased.
Resize of $LogFile
•
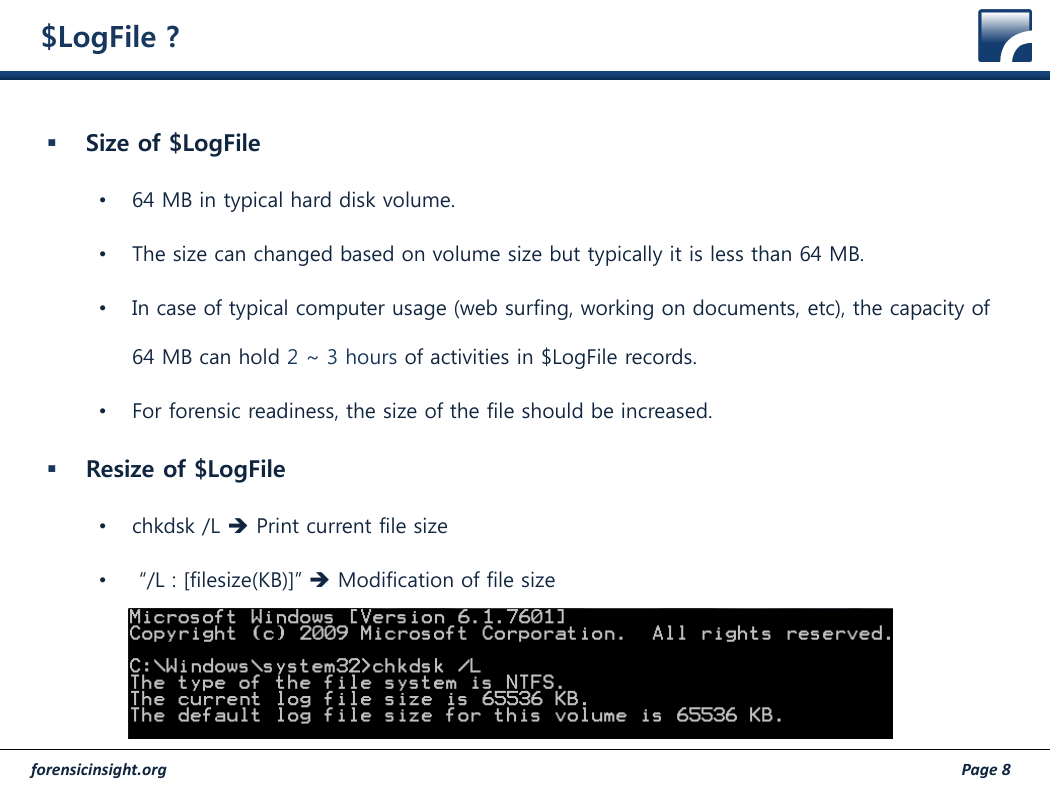
•
chkdsk /L Print current file size
“/L : [filesize(KB)]” Modification of file size
forensicinsight.org
Page 8
�












 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc