TDA8922B
2 · 50 W class-D power amplifier
Rev. 01 — 1 October 2004
Preliminary data sheet
1. General description
2. Features
The TDA8922B is a high efficiency class-D audio power amplifier with very low
dissipation. The typical output power is 2 · 50 W.
The device is available in the HSOP24 power package and in the DBS23P through-hole
power package. The amplifier operates over a wide supply voltage range from – 12.5 V
to – 30 V and consumes a very low quiescent current.
n Zero dead time switching
n Advanced current protection: output current limiting
n Smooth start-up: no pop-noise due to DC offset
n High efficiency
n Operating supply voltage from – 12.5 V to – 30 V
n Low quiescent current
n Usable as a stereo Single-Ended (SE) amplifier or as a mono amplifier in Bridge-Tied
Load (BTL)
n Fixed gain of 30 dB in Single-Ended (SE) and 36 dB in Bridge-Tied Load (BTL)
n High supply voltage ripple rejection
n Internal switching frequency can be overruled by an external clock
n Full short-circuit proof across load and to supply lines
n Thermally protected.
3. Applications
n Television sets
n Home-sound sets
n Multimedia systems
n All mains fed audio systems
n Car audio (boosters).
�
Philips Semiconductors
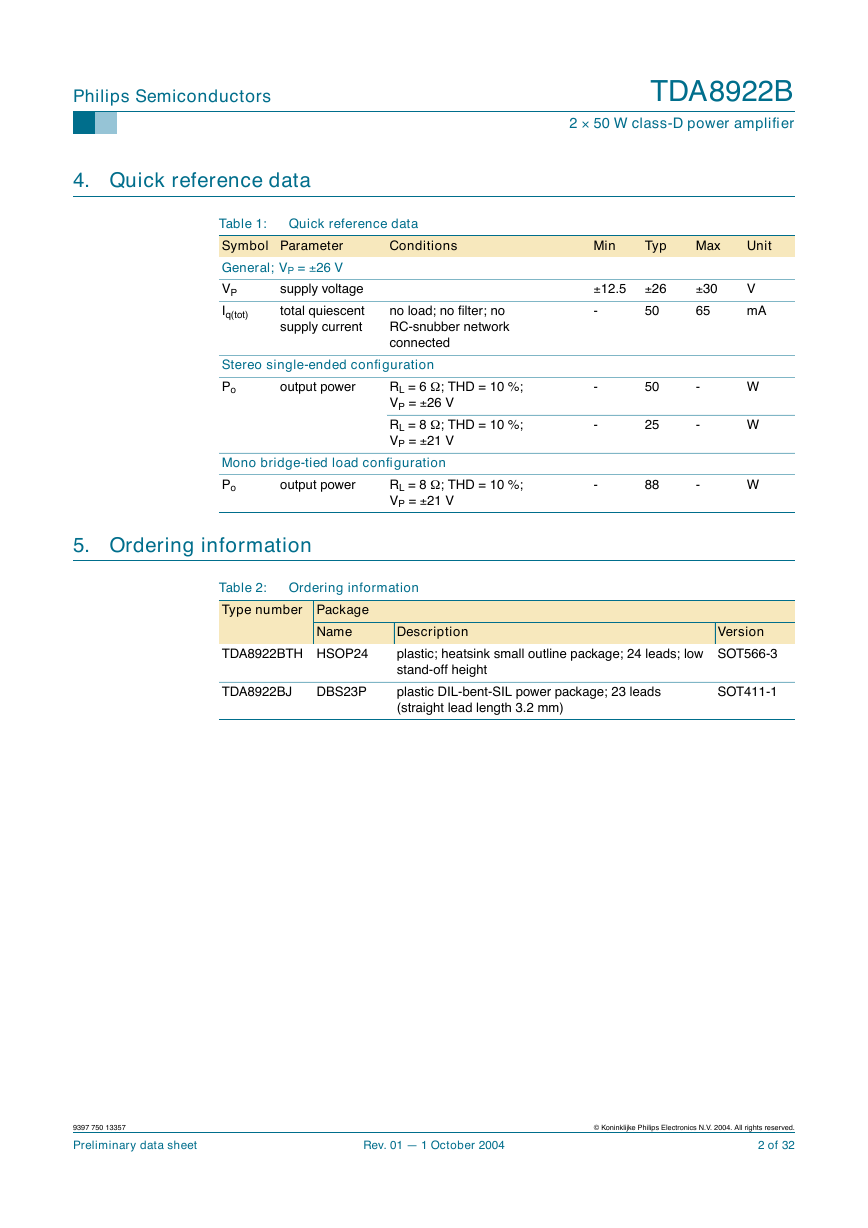
4. Quick reference data
TDA8922B
2 · 50 W class-D power amplifier
Conditions
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
– 12.5
-
– 26
50
– 30
65
V
mA
-
-
-
50
25
88
-
-
-
W
W
W
Quick reference data
Table 1:
Symbol Parameter
General; VP = – 26 V
VP
Iq(tot)
supply voltage
total quiescent
supply current
no load; no filter; no
RC-snubber network
connected
output power
Stereo single-ended configuration
RL = 6 W
Po
VP = – 26 V
RL = 8 W
VP = – 21 V
Mono bridge-tied load configuration
Po
output power
; THD = 10 %;
; THD = 10 %;
RL = 8 W
VP = – 21 V
; THD = 10 %;
5. Ordering information
Table 2:
Type number Package
Ordering information
Name
TDA8922BTH HSOP24
TDA8922BJ
DBS23P
Description
plastic; heatsink small outline package; 24 leads; low
stand-off height
plastic DIL-bent-SIL power package; 23 leads
(straight lead length 3.2 mm)
Version
SOT566-3
SOT411-1
9397 750 13357
Preliminary data sheet
Rev. 01 — 1 October 2004
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
2 of 32
�
Philips Semiconductors
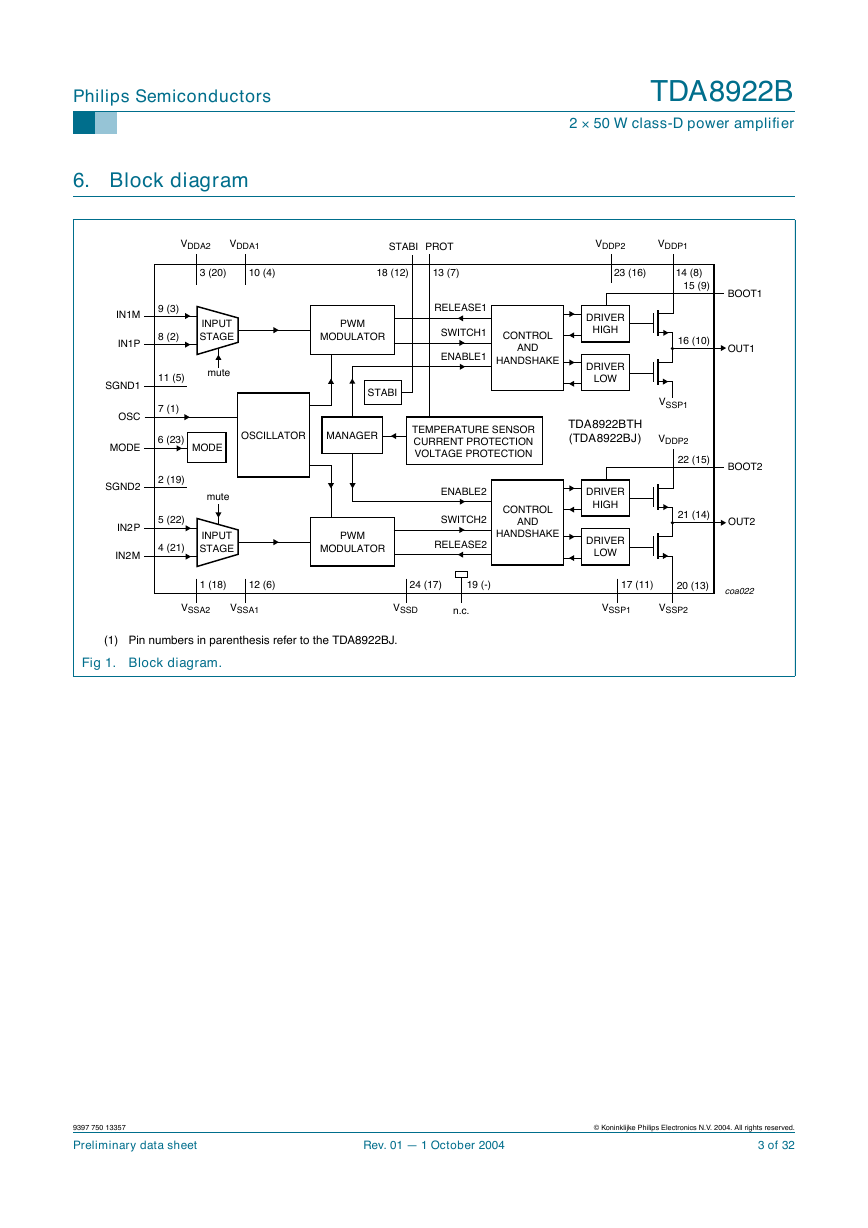
6. Block diagram
TDA8922B
2 · 50 W class-D power amplifier
VDDA2
VDDA1
STABI
PROT
VDDP2
VDDP1
3 (20)
10 (4)
18 (12)
13 (7)
23 (16)
14 (8)
15 (9)
BOOT1
IN1M
IN1P
SGND1
OSC
MODE
SGND2
IN2P
IN2M
9 (3)
8 (2)
11 (5)
7 (1)
6 (23)
2 (19)
5 (22)
4 (21)
INPUT
STAGE
mute
MODE
mute
INPUT
STAGE
PWM
MODULATOR
STABI
RELEASE1
SWITCH1
ENABLE1
CONTROL
AND
HANDSHAKE
DRIVER
HIGH
DRIVER
LOW
16 (10)
OUT1
OSCILLATOR
MANAGER
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
CURRENT PROTECTION
VOLTAGE PROTECTION
TDA8922BTH
(TDA8922BJ)
VSSP1
VDDP2
ENABLE2
SWITCH2
RELEASE2
CONTROL
AND
HANDSHAKE
DRIVER
HIGH
DRIVER
LOW
PWM
MODULATOR
22 (15)
BOOT2
21 (14)
OUT2
1 (18)
12 (6)
VSSA2
VSSA1
24 (17)
19 (-)
VSSD
n.c.
17 (11)
20 (13)
coa022
VSSP1
VSSP2
(1) Pin numbers in parenthesis refer to the TDA8922BJ.
Fig 1. Block diagram.
9397 750 13357
Preliminary data sheet
Rev. 01 — 1 October 2004
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
3 of 32
�
Philips Semiconductors
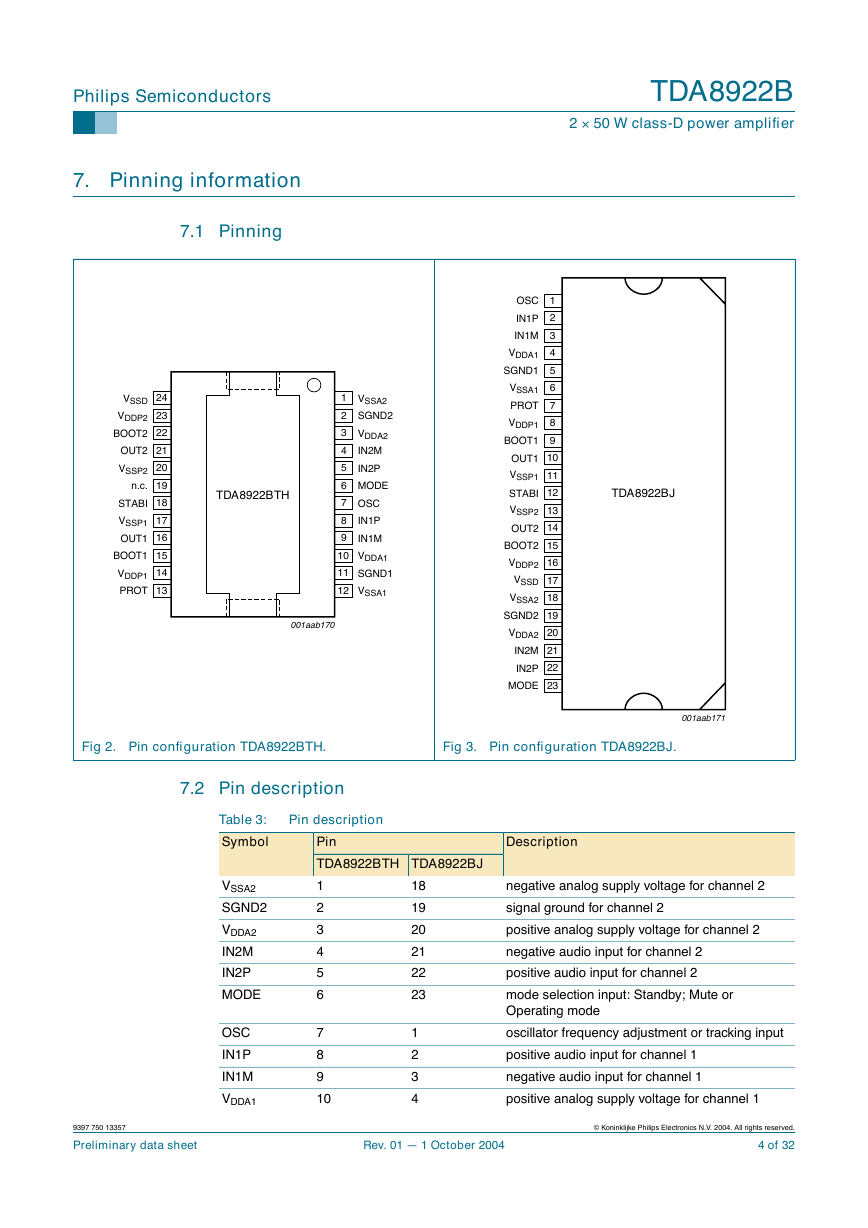
7. Pinning information
7.1 Pinning
VSSD
VDDP2
BOOT2
OUT2
VSSP2
n.c.
STABI
VSSP1
OUT1
BOOT1
VDDP1
PROT
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
TDA8922BTH
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
VSSA2
SGND2
VDDA2
IN2M
IN2P
MODE
OSC
IN1P
IN1M
VDDA1
SGND1
VSSA1
001aab170
TDA8922B
2 · 50 W class-D power amplifier
OSC
IN1P
IN1M
VDDA1
SGND1
VSSA1
PROT
VDDP1
BOOT1
OUT1
VSSP1
STABI
VSSP2
OUT2
BOOT2
VDDP2
VSSD
VSSA2
SGND2
VDDA2
IN2M
IN2P
MODE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
TDA8922BJ
Fig 2. Pin configuration TDA8922BTH.
Fig 3. Pin configuration TDA8922BJ.
001aab171
7.2 Pin description
Table 3:
Symbol
VSSA2
SGND2
VDDA2
IN2M
IN2P
MODE
OSC
IN1P
IN1M
VDDA1
Pin description
Pin
TDA8922BTH TDA8922BJ
1
2
3
4
5
6
18
19
20
21
22
23
7
8
9
10
1
2
3
4
Description
negative analog supply voltage for channel 2
signal ground for channel 2
positive analog supply voltage for channel 2
negative audio input for channel 2
positive audio input for channel 2
mode selection input: Standby; Mute or
Operating mode
oscillator frequency adjustment or tracking input
positive audio input for channel 1
negative audio input for channel 1
positive analog supply voltage for channel 1
9397 750 13357
Preliminary data sheet
Rev. 01 — 1 October 2004
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
4 of 32
�
Philips Semiconductors
TDA8922B
2 · 50 W class-D power amplifier
Table 3:
Symbol
SGND1
VSSA1
PROT
VDDP1
BOOT1
OUT1
VSSP1
STABI
n.c.
VSSP2
OUT2
BOOT2
VDDP2
VSSD
Pin description …continued
Pin
TDA8922BTH TDA8922BJ
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
-
13
14
15
16
17
Description
signal ground for channel 1
negative analog supply voltage for channel 1
decoupling capacitor for protection (OCP)
positive power supply voltage for channel 1
bootstrap capacitor for channel 1
PWM output from channel 1
negative power supply voltage for channel 1
decoupling of internal stabilizer for logic supply
not connected
negative power supply voltage for channel 2
PWM output from channel 2
bootstrap capacitor for channel 2
positive power supply voltage for channel 2
negative digital supply voltage
8. Functional description
8.1 General
The TDA8922B is a two channel audio power amplifier using class-D technology.
The audio input signal is converted into a digital Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) signal via
an analog input stage and PWM modulator. To enable the output power transistors to be
driven, this digital PWM signal is applied to a control and handshake block and driver
circuits for both the high side and low side. In this way a level shift is performed from the
low power digital PWM signal (at logic levels) to a high power PWM signal which switches
between the main supply lines.
A 2nd-order low-pass filter converts the PWM signal to an analog audio signal across the
loudspeakers.
The TDA8922B one-chip class-D amplifier contains high power D-MOS switches, drivers,
timing and handshaking between the power switches and some control logic. For
protection a temperature sensor and a maximum current detector are built-in.
The two audio channels of the TDA8922B contain two PWMs, two analog feedback loops
and two differential input stages. It also contains circuits common to both channels such
as the oscillator, all reference sources, the mode functionality and a digital timing
manager.
The TDA8922B contains two independent amplifier channels with high output power, high
efficiency, low distortion and a low quiescent current. The amplifier channels can be
connected in the following configurations:
• Mono Bridge-Tied Load (BTL) amplifier
• Stereo Single-Ended (SE) amplifiers.
9397 750 13357
Preliminary data sheet
Rev. 01 — 1 October 2004
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
5 of 32
�
Philips Semiconductors
TDA8922B
2 · 50 W class-D power amplifier
The amplifier system can be switched in three operating modes with pin MODE:
• Standby mode; with a very low supply current
• Mute mode; the amplifiers are operational; but the audio signal at the output is
suppressed by disabling the VI-converter input stages
• Operating mode; the amplifiers fully are operational with output signal.
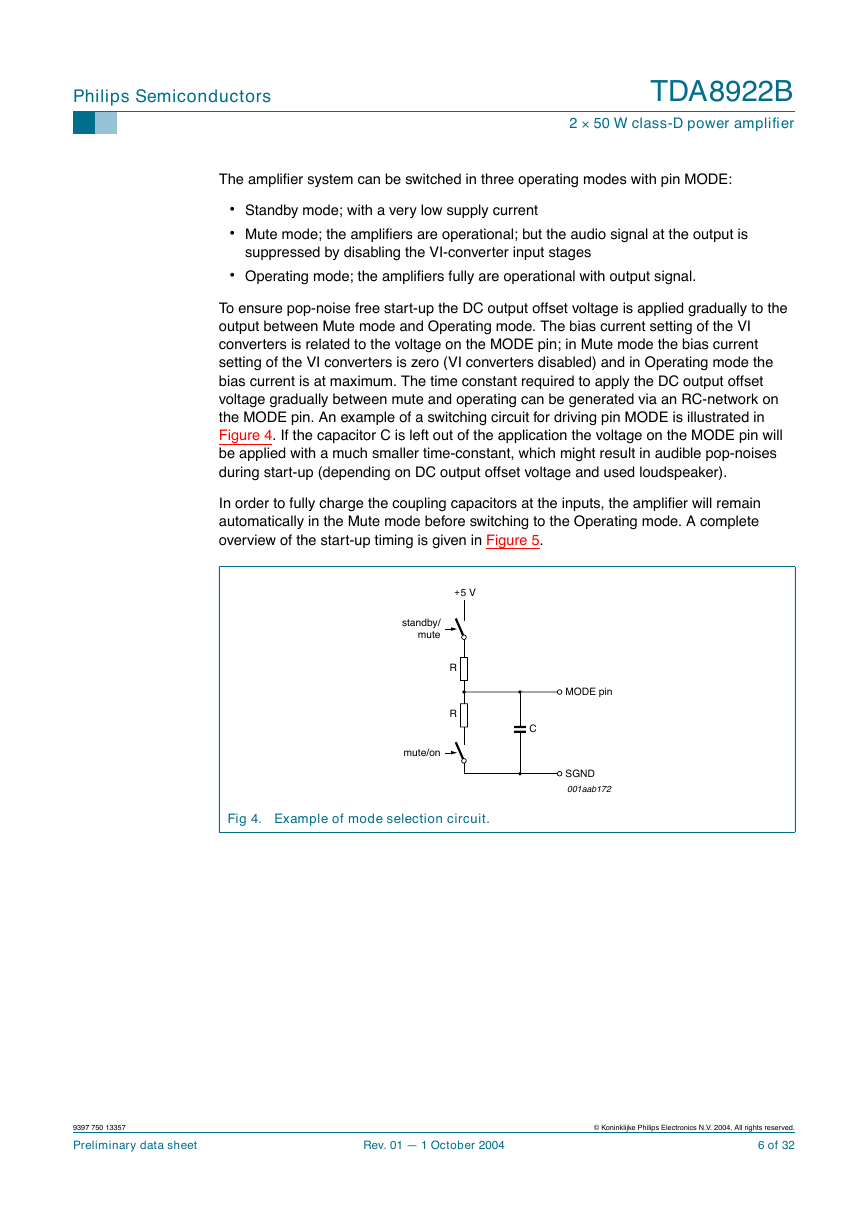
To ensure pop-noise free start-up the DC output offset voltage is applied gradually to the
output between Mute mode and Operating mode. The bias current setting of the VI
converters is related to the voltage on the MODE pin; in Mute mode the bias current
setting of the VI converters is zero (VI converters disabled) and in Operating mode the
bias current is at maximum. The time constant required to apply the DC output offset
voltage gradually between mute and operating can be generated via an RC-network on
the MODE pin. An example of a switching circuit for driving pin MODE is illustrated in
Figure 4. If the capacitor C is left out of the application the voltage on the MODE pin will
be applied with a much smaller time-constant, which might result in audible pop-noises
during start-up (depending on DC output offset voltage and used loudspeaker).
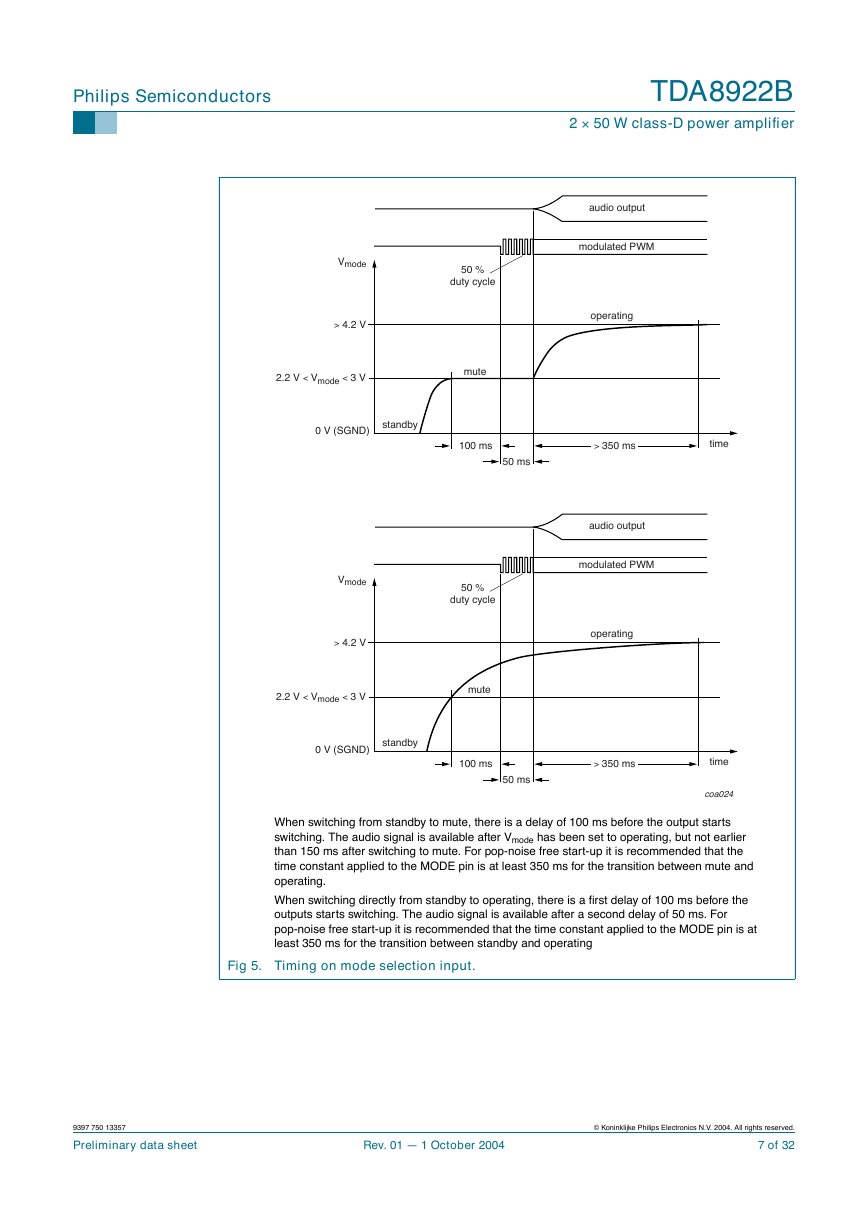
In order to fully charge the coupling capacitors at the inputs, the amplifier will remain
automatically in the Mute mode before switching to the Operating mode. A complete
overview of the start-up timing is given in Figure 5.
+5 V
R
R
standby/
mute
mute/on
C
MODE pin
SGND
001aab172
Fig 4. Example of mode selection circuit.
9397 750 13357
Preliminary data sheet
Rev. 01 — 1 October 2004
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
6 of 32
�
Philips Semiconductors
TDA8922B
2 · 50 W class-D power amplifier
audio output
modulated PWM
operating
Vmode
> 4.2 V
50 %
duty cycle
2.2 V < Vmode < 3 V
mute
0 V (SGND)
standby
100 ms
50 ms
> 350 ms
time
audio output
modulated PWM
operating
Vmode
> 4.2 V
50 %
duty cycle
2.2 V < Vmode < 3 V
mute
0 V (SGND)
standby
100 ms
50 ms
> 350 ms
time
coa024
When switching from standby to mute, there is a delay of 100 ms before the output starts
switching. The audio signal is available after Vmode has been set to operating, but not earlier
than 150 ms after switching to mute. For pop-noise free start-up it is recommended that the
time constant applied to the MODE pin is at least 350 ms for the transition between mute and
operating.
When switching directly from standby to operating, there is a first delay of 100 ms before the
outputs starts switching. The audio signal is available after a second delay of 50 ms. For
pop-noise free start-up it is recommended that the time constant applied to the MODE pin is at
least 350 ms for the transition between standby and operating
Fig 5. Timing on mode selection input.
9397 750 13357
Preliminary data sheet
Rev. 01 — 1 October 2004
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
7 of 32
�
Philips Semiconductors
TDA8922B
2 · 50 W class-D power amplifier
8.2 Pulse width modulation frequency
The output signal of the amplifier is a PWM signal with a carrier frequency of
approximately 317 kHz. Using a 2nd-order LC demodulation filter in the application results
in an analog audio signal across the loudspeaker. This switching frequency is fixed by an
external resistor ROSC connected between pin OSC and VSSA. An optimal setting for the
carrier frequency is between 300 kHz and 350 kHz.
Using an external resistor of 30 kW
317 kHz.
on the OSC pin, the carrier frequency is set to
If two or more class-D amplifiers are used in the same audio application, it is advisable to
have all devices operating at the same switching frequency by using an external clock
circuit.
8.3 Protections
The following protections are included in TDA8922B:
• OverTemperature Protection (OTP)
• OverCurrent Protection (OCP)
• Window Protection (WP)
• Supply voltage protections:
– UnderVoltage Protection (UVP)
– OverVoltage Protection (OVP)
– UnBalance Protection (UBP).
The reaction of the device on the different fault conditions differs per protection:
8.3.1 OverTemperature Protection (OTP)
If the junction temperature Tj > 150 C, then the power stage will shut-down immediately.
The power stage will start switching again if the temperature drops to approximately
130 C, thus there is a hysteresis of approximately 20 C.
8.3.2 OverCurrent Protection (OCP)
When the loudspeaker terminals are short-circuited or if one of the demodulated outputs
of the amplifier is short-circuited to one of the supply lines, this will be detected by the
OverCurrent Protection (OCP). If the output current exceeds the maximum output current
of 5 A, this current will be limited by the amplifier to 5 A while the amplifier outputs remain
switching (the amplifier is NOT shut-down completely).
The amplifier can distinguish between an impedance drop of the loudspeaker and
low-ohmic short across the load. In the TDA8922B this impedance threshold (Zth)
depends on the supply voltage used.
When a short is made across the load causing the impedance to drop below the threshold
level (< Zth) then the amplifier is switched off completely and after a time of 100 ms it will
try to restart again. If the short circuit condition is still present after this time this cycle will
be repeated. The average dissipation will be low because of this low duty cycle.
9397 750 13357
Preliminary data sheet
Rev. 01 — 1 October 2004
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
8 of 32
�










 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc