10 Gigabit Ethernet Subsystem v3.1
Table of Contents
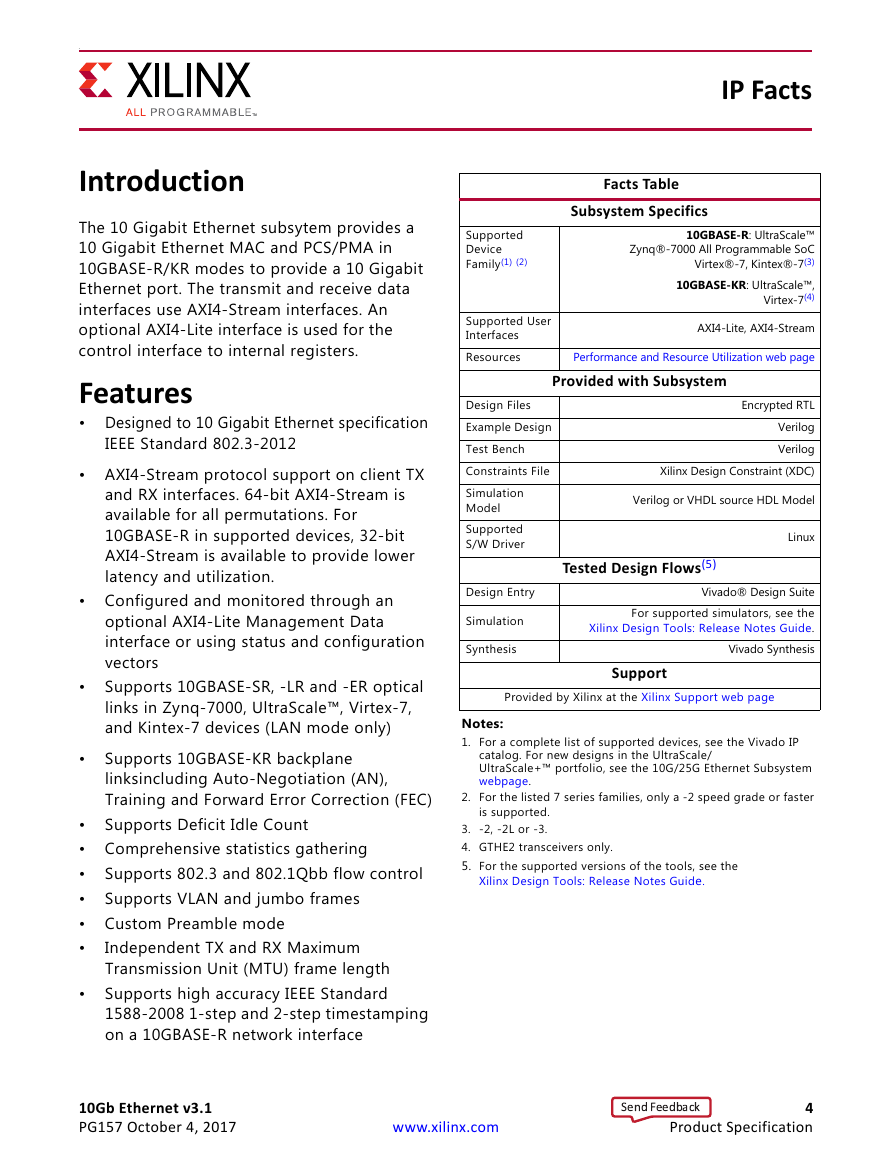
IP Facts
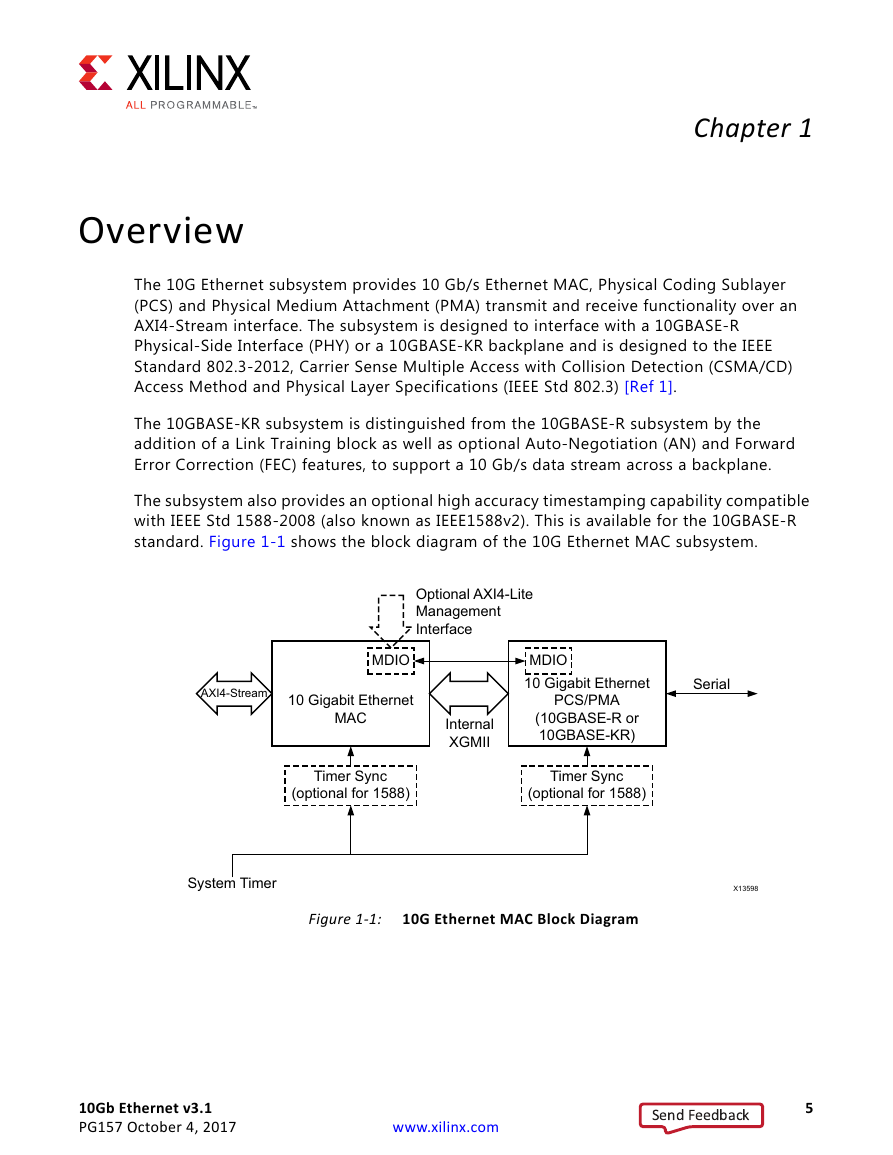
Ch. 1: Overview
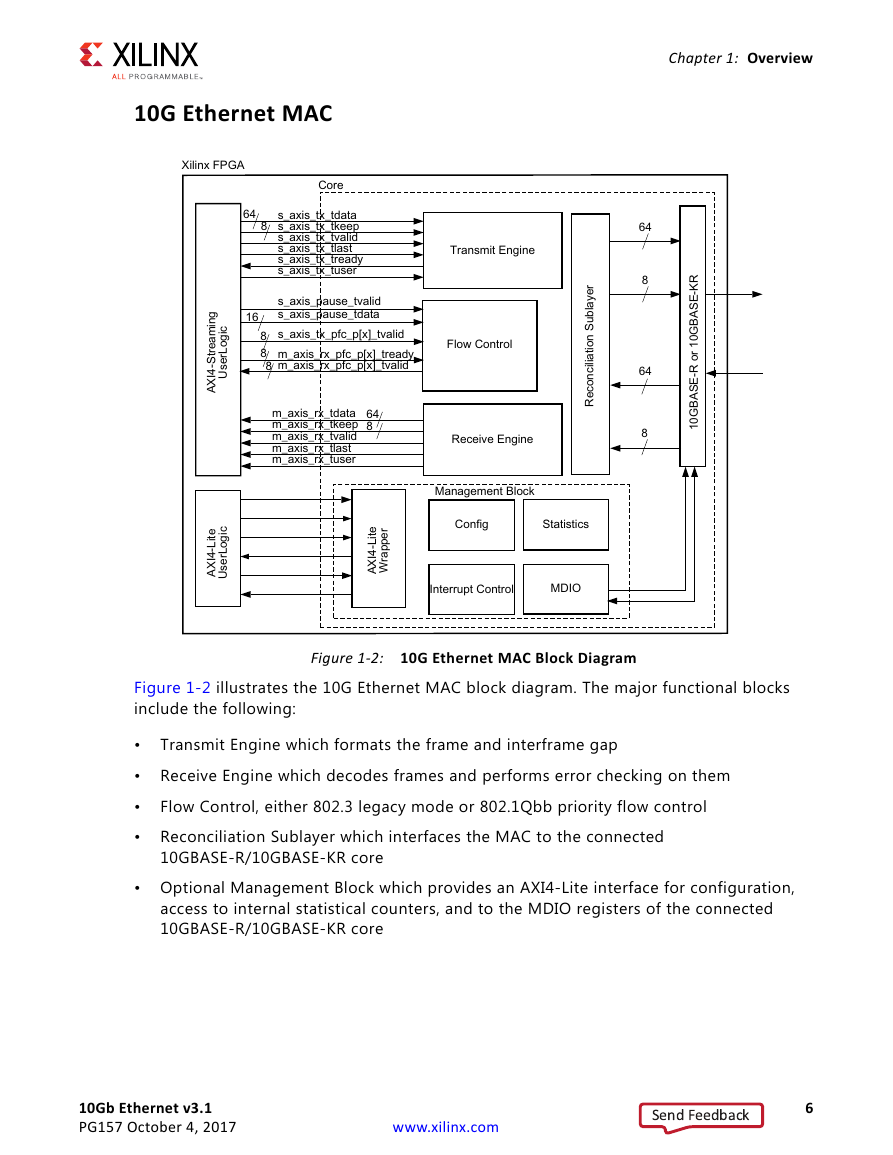
10G Ethernet MAC
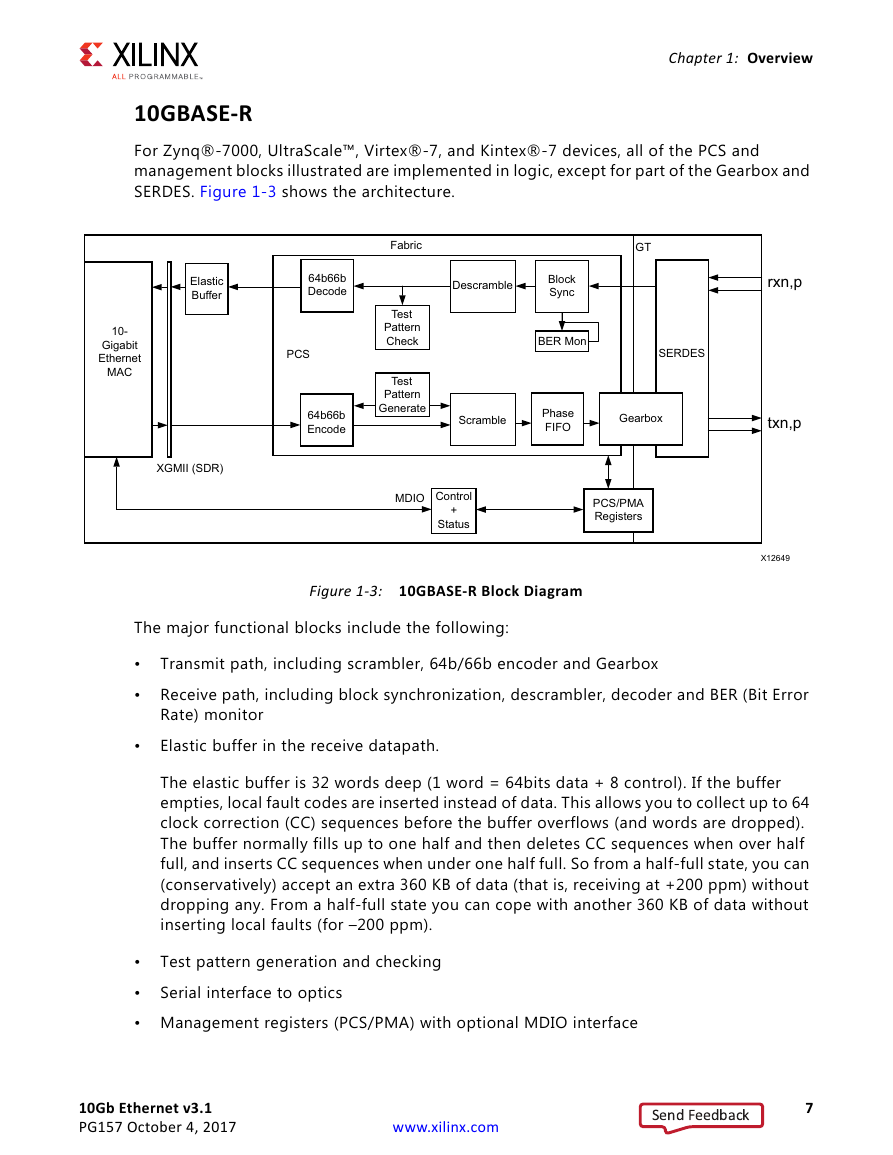
10GBASE-R
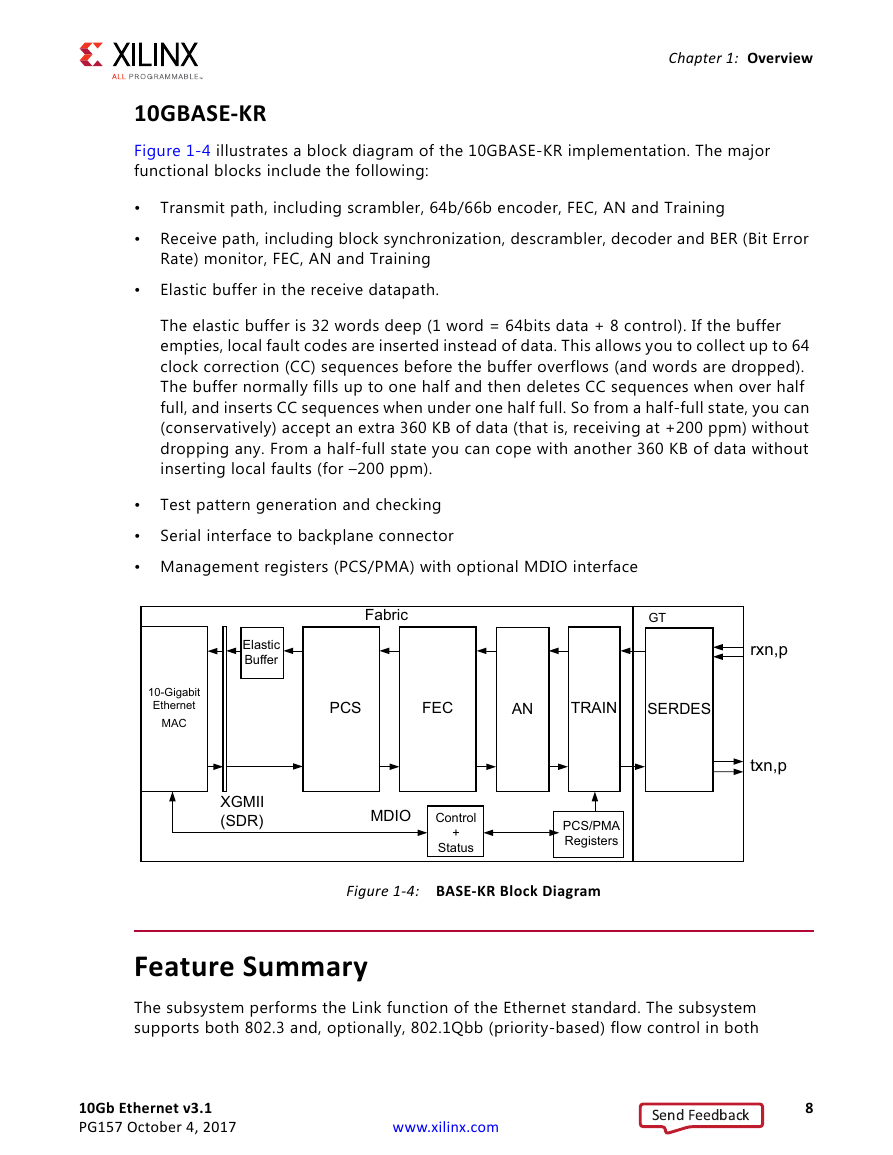
10GBASE-KR
Feature Summary
Applications
Unsupported Features
Licensing and Ordering
License Checkers
License Type
Ch. 2: Product Specification
Standards
Performance
Resource Utilization
Latency
32-bit Datapath
Transmit Path Latency
Receive Path Latency
64-bit Datapath
Transmit Path Latency
Receive Path Latency
Port Descriptions
AXI4-Stream Transmit Interface
AXI4-Stream Receive Interface
Flow Control Interface (IEEE 802.3)
Priority Flow Control Interface (802.1Qbb)
Serial Data Ports
Optical Module Interface Ports
Clock and Reset Ports
Shared Logic Included in Example Design
Shared Logic Included in Core
Tx Buffer Bypass Manual Phase Alignment Ports
10GBASE-KR Training Interface
DRP Interface Ports
Zynq-7000, Virtex-7, and Kintex-7 Devices
UltraScale Architecture
PCS/PMA Miscellaneous Ports
Speeding up Simulation
Transceiver Debug Ports
AXI4-Lite Management Interface Ports
10G Ethernet MAC Configuration and Status Signals
Statistics Vector Signals
Transmit Statistics Vector
Receive Statistics Vector
PCS/PMA Configuration and Status Signals
BASE-R
BASE-KR
Interrupt Signal
IEEE 1588 Transmitted Timestamp Ports
IEEE 1588 Received Timestamp Ports
IEEE 1588 System Timer Ports
Time-of-Day (ToD) System Timer Format
Correction Field System Timer Format
Register Space
Statistics Counters
10G Ethernet MAC Configuration Registers
MDIO Control Registers
Interrupt Output Registers
PCS/PMA Register Map
MDIO Register 1.0: PMA/PMD Control 1
MDIO Register 1.1: PMA/PMD Status 1
MDIO Register 1.4: PMA/PMD Speed Ability
MDIO Registers 1.5 and 1.6: PMA/PMD Devices in Package
MDIO Register 1.7: 10G PMA/PMD Control 2
MDIO Register 1.8: 10G PMA/PMD Status 2
MDIO Register 1.9: 10G PMD Transmit Disable
MDIO Register 1.10: 10G PMD Signal Receive OK
MDIO Register 1.150: 10GBASE-KR PMD Control
MDIO Register 1.151: 10GBASE-KR PMD Status
MDIO Register 1.152: 10GBASE-KR LP Coefficient Update
MDIO Register 1.153: 10GBASE-KR LP Status
MDIO Register 1.154: 10GBASE-KR LD Coefficient Update
MDIO Register 1.155: 10GBASE-KR LD Status
MDIO Register 1.170: 10GBASE-R FEC Ability
MDIO Register 1.171: 10GBASE-R FEC Control
MDIO Register 1.172: 10GBASE-R FEC Corrected Blocks (Lower)
MDIO Register 1.173: 10GBASE-R FEC Corrected Blocks (Upper)
MDIO Register 1.174: 10GBASE-R FEC Uncorrected Blocks (Lower)
MDIO Register 1.175: 10GBASE-R FEC Uncorrected Blocks (Upper)
MDIO Register: 1.65520: Vendor-Specific LD Training
MDIO Register 1.65535: Core Version Info for 10G PCS/PMA Subcore
MDIO Register 3.0: PCS Control 1
MDIO Register 3.1: PCS Status 1
MDIO Register 3.4: PCS Speed Ability
MDIO Registers 3.5 and 3.6: PCS Devices in Package
MDIO Register 3.7: 10G PCS Control 2
MDIO Register 3.8: 10G PCS Status 2
MDIO Register 3.32: 10GBASE-R Status 1
MDIO Register 3.33: 10GBASE-R Status 2
MDIO Register 3.34–37: 10GBASE-R Test Pattern Seed A0–3
MDIO Register 3.38–41: 10GBASE-R Test Pattern Seed B0–3
MDIO Register 3.42: 10GBASE-R Test Pattern Control
MDIO Register 3.43: 10GBASE-R Test Pattern Error Counter
MDIO Register 3.65520: IEEE1588 Control
MDIO Register 3.65521: RX Fixed Latency, Integer ns
MDIO Register 3.65522: RX Fixed Latency, Fractional ns
MDIO Register 3.65535: 125 Microsecond Timer Control
MDIO Register 7.0: AN Control
MDIO Register 7.1: AN Status
MDIO Register 7.16:17:18: AN Advertisement
MDIO Register 7.19, 20, 21: AN LP Base Page Ability
MDIO Register 7.22, 23, 24: AN XNP Transmit
MDIO Register 7.25, 26, 27: AN LP XNP Ability
MDIO Register 7.48: Backplane Ethernet Status
Ch. 3: Designing with the Subsystem
Clocking
Resets
7 Series Clocking and Shared Logic
Shared Logic
Core Level Logic
UltraScale Device Clocking and Shared Logic Using the RX Elastic Buffer
GTHE3/GTYE3 (32-bit Datapath)
Shared Logic
Core Level Logic
GTHE3 with the 64-bit Datapath
UltraScale Device Clocking and Shared Logic Omitting the RX Elastic Buffer
Shared Logic
Core Level Logic
Shared Logic for 7 Series IEEE 1588 Support
Ethernet Protocol Description
Ethernet Sublayer Architecture
MAC and MAC CONTROL Sublayer
Physical Sublayers PCS, PMA, and PMD
Ethernet Data Format
Preamble
Start of Frame Delimiter
MAC Address Fields
MAC Address
Destination Address
Source Address
Length/Type
Data
Pad
FCS
Frame Transmission and Interframe Gap
Deficit Idle Count
Connecting the Data Interfaces
Transmit AXI4-Stream Interface
Normal Frame Transmission
In-Band Ethernet Frame Fields
Padding
Transmission with In-Band FCS Passing
Aborting a Transmission
Back-to-Back Continuous Transfers
Transmission of Custom Preamble
VLAN Tagged Frames
Transmitter Maximum Permitted Frame Length
Interframe Gap Adjustment
Deficit Idle Count (DIC)
Transmission of Frames During Local/Remote Fault or Link Interruption Reception
Receive AXI4-Stream Interface
Normal Frame Reception
Timing for a Good or a Bad Frame
Frame Reception with Errors
Reception with In-Band FCS Passing
Reception of Custom Preamble
VLAN Tagged Frames
Receiver Maximum Permitted Frame Length
Length/Type Field Error Checks
Enabled
Disabled
IEEE 1588 Timestamping
Transmit
Frame-by-Frame Timestamping Operation
Transmitter Latency and Timestamp Adjustment
Transmit – Providing the Command Field In-band
Transmit - Providing the Command Field Out-of-Band
Receive
Receiver Latency and Timestamp Adjustment
Receive – Timestamp In Line With Frame Reception
Connecting the Management Interface
MDIO Interface
MDIO Transaction Types
Set Address Transaction
Write Transaction
Read Transaction
Post-Read-Increment-Address Transaction
Using the AXI4-Lite Interface to Access PHY Registers over MDIO
IEEE 802.3 Flow Control
Flow Control Requirement
Flow Control Basics
IEEE 802.3 Pause Control Frames
Transmitting a Pause Control Frame
Core-Initiated Pause Request
XON/XOFF Extended Functionality
Client-Initiated Pause Request
Receiving a Pause Control Frame
Core-Initiated Response to a Pause Request
Client-Initiated Response to a Pause Request
Flow Control Implementation Example
Method
Operation
Priority Flow Control
Priority Flow Control Requirement
Priority-Based Flow Control Frames
Transmitting a PFC Frame
Core-Initiated Request
Client-Initiated Request
Receiving a PFC Frame
Core-Initiated Response to a PFC request
PFC Frame Reception Disabled
Pause Frame Reception Enabled
Client-Initiated Response to a Pause Request
PFC Implementation Example
Method
Operation
Receiver Termination
Special Design Considerations
Connecting Multiple Subsystem Instances (No IEEE 1588 Support)
Zynq-7000, Virtex-7, and Kintex-7 Devices
UltraScale Devices
Using Training and Auto-Negotiation with the Management Interface
Using Training and Auto-Negotiation with No Management Interface
Using FEC in the Subsystem with Auto-Negotiation
Using FIFOs in IP Integrator
Ch. 4: Design Flow Steps
Customizing and Generating the Subsystem
Component Name
Ethernet Standard
PCS/PMA Standard
AXI4-Stream datapath width
MAC Options
AXI4-Lite for Configuration and Status
AXI4-Lite Frequency (MHz)
Statistics Gathering
IEEE802.1Qbb Priority-based Flow Control
PCS/PMA Options
Auto-Negotiation
Forward Error Correction (FEC)
Exclude RX Elastic Buffer
DRP Clocking
Transceiver Type
Transceiver Location
Transceiver RefClk Location
Reference Clock Frequency (MHz)
IEEE 1588 Options
IEEE 1588 Hardware Timestamping Support
1588 Timer Format
Shared Logic
User Parameters
Output Generation
Constraining the Subsystem
Required Constraints
Device, Package, and Speed Grade Selections
Clock Frequencies
Clock Management
Clock Placement
Banking
Transceiver Placement
I/O Standard and Placement
Simulation
Synthesis and Implementation
Ch. 5: Example Design
Ethernet FIFO
RX FIFO
TX FIFO
Basic Pattern Generator Module
Address Swap
Pattern Generator
Pattern Checker
AXI4-Lite Control State Machine
Shared Logic and the Support Layer
Ch. 6: Test Bench 重要
DEMO Mode
BIST Mode
Changing the Test Bench
Changing Frame Data in Demo Mode
Changing Frame Length
Changing Frame Error Status
Appx. A: Upgrading
Migrating to the Vivado Design Suite
Upgrading in the Vivado Design Suite
Parameter Changes
Port Changes in Version 2.0
Ports Added in Version 3.0
Ports Changed in Version 3.0
Ports Changed in Version 3.1
Appx. B: Debugging
Finding Help on Xilinx.com
Documentation
Solution Centers
Answer Records
Technical Support
Debug Tools
Vivado Design Suite Debug Feature
Hardware Debug
General Checks
What Can Cause a Local or Remote Fault?
Local Fault
Remote Fault
Link Bring Up – Basic
High Level Link Up (10GBASE-R or 10GBASE-KR with Auto-Negotiation + Training Disabled)
Stage 1: Device A Powered Up, but Device B Powered Down
Stage 2: Device B Powers Up and Resets
Stage 3: Device A Receives Idle Sequence
Stage 4: Normal Operation
Link Bring Up—BASE-KR
Using the Configuration Vector for Link Bring-Up
Using the MDIO interface for Link Bring-Up
What Can Cause Block Lock to Fail?
What Can Cause the 10Gb PCS/PMA Core to Insert Errors?
Transceiver Specific Checks
Link Training
Appx. C: Additional Resources and Legal Notices
Xilinx Resources
Documentation Navigator and Design Hubs
References
Revision History
Please Read: Important Legal Notices











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc