PyQt5 tutorial
This is PyQt5 tutorial. The tutorial is suited for beginners and
intermediate programmers. After reading this tutorial, you will be
able to program non trivial PyQt5 applications.
Table of contents
Introduction
First programs
Menus and toolbars
Layout management
Events and signals
Dialogs
Widgets
Widgets II
Drag & drop
Painting
Custom widgets
The Tetris game
�
Introduction to PyQt5
This is an introductory PyQt5 tutorial. The purpose of this tutorial
is to get you started with the PyQt5 toolkit. The tutorial has been
created and tested on Linux. PyQt4 tutorial covers PyQt4, which is a
blending of the Python language (2.x and 3.x) to the Qt4 library.
About PyQt5
PyQt5 is a set of Python bindings for Qt5 application framework from
Digia. It is available for the Python 2.x and 3.x. This tutorial uses
Python 3. Qt library is one of the most powerful GUI libraries. The
official home site for PyQt5 is www.riverbankcomputing.co.uk/news.
PyQt5 is developed by Riverbank Computing.
PyQt5 is implemented as a set of Python modules. It has over 620
classes and 6000 functions and methods. It is a multiplatform toolkit
which runs on all major operating systems, including Unix, Windows,
and Mac OS. PyQt5 is dual licensed. Developers can choose between a
GPL and a commercial license.
PyQt5's classes are divided into several modules, including the
following:
QtCore
QtGui
QtWidgets
QtMultimedia
QtBluetooth
QtNetwork
QtPositioning
Enginio
QtWebSockets
QtWebKit
QtWebKitWidgets
QtXml
QtSvg
QtSql
QtTest
The QtCore module contains the core non GUI functionality. This
module is used for working with time, files and directories, various
data types, streams, URLs, mime types, threads or processes. The
�
QtGui contains classes for windowing system integration, event
handling, 2D graphics, basic imaging, fonts and text. The QtWidgets
module contains classes that provide a set of UI elements to create
classic desktop-style user interfaces. The QtMultimedia contains
classes to handle multimedia content and APIs to access camera and
radio functionality. The QtBluetooth module contains classes to scan
for devices and connect and interact with them. The QtNetwork module
contains the classes for network programming. These classes
facilitate the coding of TCP/IP and UDP clients and servers by making
the network programming easier and more portable. The QtPositioning
contains classes to determine a position by using a variety of
possible sources, including satellite, Wi-Fi, or a text file. The
Enginio module implements the client-side library for accessing the
Qt Cloud Services Managed Application Runtime. The QtWebSockets
module contains classes that implement the WebSocket protocol. The
QtWebKit contains classes for a web browser implementation based on
the WebKit2 library. The QtWebKitWidgets contains classes for a
WebKit1 based implementation of a web browser for use in QtWidgets
based applications. The QtXml contains classes for working with XML
files. This module provides implementation for both SAX and DOM APIs.
The QtSvg module provides classes for displaying the contents of SVG
files. Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is a language for describing
two-dimensional graphics and graphical applications in XML. The QtSql
module provides classes for working with databases. The QtTest
contains functions that enable unit testing of PyQt5 applications.
PyQt4 and PyQt5 differences
The PyQt5 is not backward compatible with PyQt4; there are several
significant changes in PyQt5. However, it is not very difficult to
adjust older code to the new library. The differences are, among
others, the following:
Python modules have been reorganized. Some modules have been
dropped (QtScript), others have been split into submodules
(QtGui, QtWebKit).
New modules have been introduced, including QtBluetooth,
QtPositioning, or Enginio.
PyQt5 supports only the new-style signal and slots handlig. The
calls to SIGNAL() or SLOT() are no longer supported.
PyQt5 does not support any parts of the Qt API that are marked
as deprecated or obsolete in Qt v5.0.
�
Python
Python is a general-purpose, dynamic, object-
oriented programming language. The design purpose of the Python
language emphasizes programmer productivity and code readability.
Python was initially developed by Guido van Rossum. It was first
released in 1991. Python was inspired by ABC, Haskell, Java, Lisp,
Icon, and Perl programming languages. Python is a high-level, general
purpose, multiplatform, interpreted language. Python is a
minimalistic language. One of its most visible features is that it
does not use semicolons nor brackets. It uses indentation instead.
There are two main branches of Python currently: Python 2.x and
Python 3.x. Python 3.x breaks backward compatibility with previous
releases of Python. It was created to correct some design flaws of
the language and make the language more clean. The most recent
version of Python 2.x is 2.7.9, and of Python 3.x is 3.4.2. Python is
maintained by a large group of volunteers worldwide. Python is open
source software. Python is an ideal start for those who want to learn
programming.
This tutorial uses Python 3.x version.
Python programming language supports several programming styles. It
does not force a programmer to a specific paradigm. Python supports
object-oriented and procedural programming. There is also a limited
support for functional programming.
The official web site for the Python programming language is
python.org
Perl, Python, and Ruby are widely used scripting languages. They
share many similarities and they are close competitors.
Python toolkits
�
For creating graphical user interfaces, Python programmers can choose
among three decent options: PyQt4, PyGTK, and wxPython.
This chapter was an introduction to PyQt4 toolkit.
�
First programs in PyQt5
In this part of the PyQt5 tutorial we learn some basic functionality.
Simple example
This is a simple example showing a small window. Yet we can do a lot
with this window. We can resize it, maximise it or minimise it. This
requires a lot of coding. Someone already coded this functionality.
Because it repeats in most applications, there is no need to code it
over again. PyQt5 is a high level toolkit. If we would code in a
lower level toolkit, the following code example could easily have
hundreds of lines.
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
ZetCode PyQt5 tutorial
In this example, we create a simple
window in PyQt5.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: January 2015
"""
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
w = QWidget()
w.resize(250, 150)
w.move(300, 300)
w.setWindowTitle('Simple')
w.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
�
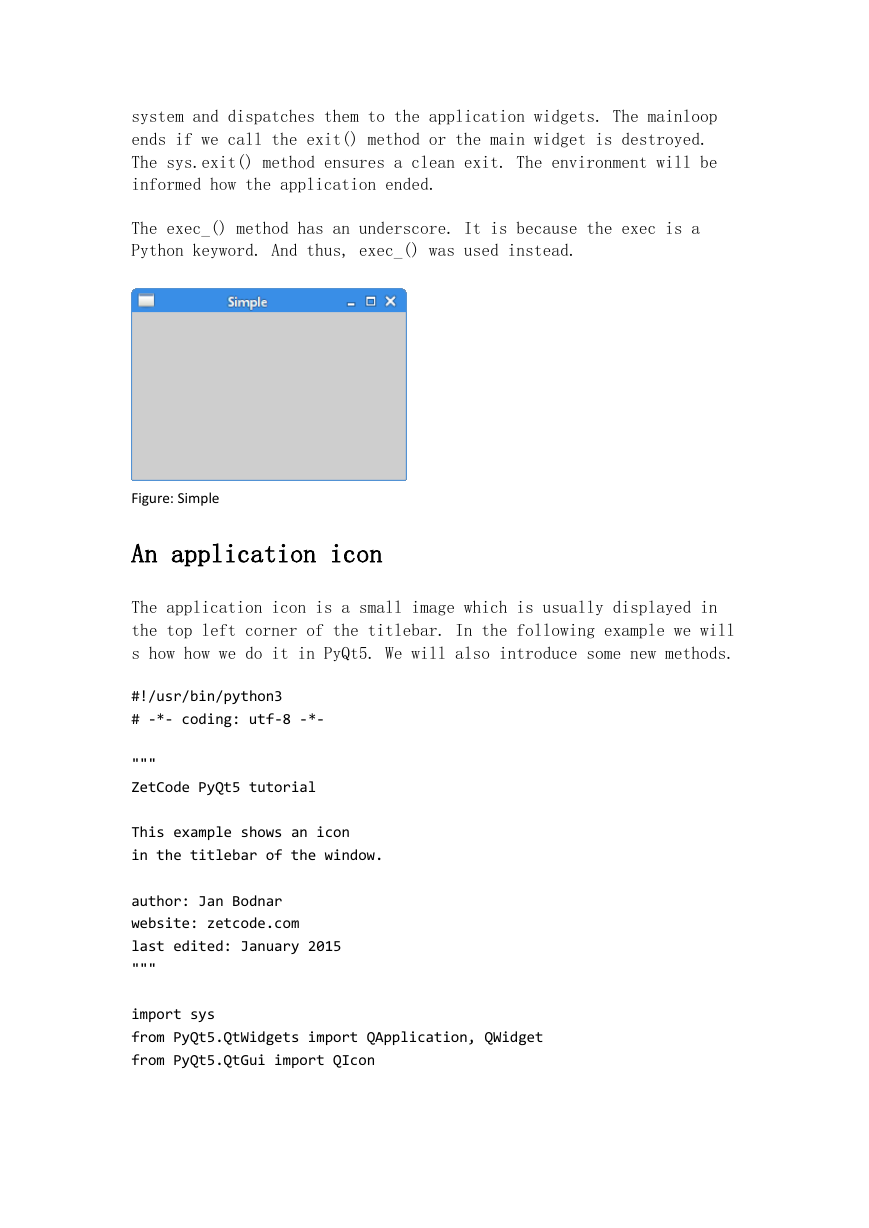
The above code example shows a small window on the screen.
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget
Here we provide the necessary imports. The basic widgets are located
in PyQt5.QtWidgets module.
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
Every PyQt5 application must create an application object. The
sys.argv parameter is a list of arguments from a command line. Python
scripts can be run from the shell. It is a way how we can control the
startup of our scripts.
w = QWidget()
The QWidget widget is the base class of all user interface objects in
PyQt5. We provide the default constructor for QWidget. The default
constructor has no parent. A widget with no parent is called a
window.
w.resize(250, 150)
The resize() method resizes the widget. It is 250px wide and 150px
high.
w.move(300, 300)
The move() method moves the widget to a position on the screen at
x=300, y=300 coordinates.
w.setWindowTitle('Simple')
Here we set the title for our window. The title is shown in the
titlebar.
w.show()
The show() method displays the widget on the screen. A widget is
first created in memory and later shown on the screen.
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Finally, we enter the mainloop of the application. The event handling
starts from this point. The mainloop receives events from the window
�
system and dispatches them to the application widgets. The mainloop
ends if we call the exit() method or the main widget is destroyed.
The sys.exit() method ensures a clean exit. The environment will be
informed how the application ended.
The exec_() method has an underscore. It is because the exec is a
Python keyword. And thus, exec_() was used instead.
Figure: Simple
An application icon
The application icon is a small image which is usually displayed in
the top left corner of the titlebar. In the following example we will
s how how we do it in PyQt5. We will also introduce some new methods.
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
ZetCode PyQt5 tutorial
This example shows an icon
in the titlebar of the window.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: January 2015
"""
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget
from PyQt5.QtGui import QIcon
�













 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc