1. General description
2. Features
2.1 RF Interface: ISO 14443 type A
2.2 ISO/IEC 7816 compatibility (only software version 0.6 and higher)
2.3 Non - volatile memory
2.4 NV-memory organisation
2.5 Security
3. Ordering information
4. Block diagram
5. Pinning information
5.1 Pinning
6. Functional description
6.1 Contactless energy and data transfer
6.2 Delivery types
6.3 Anticollision
6.4 UID / serial number
6.5 Memory organisation
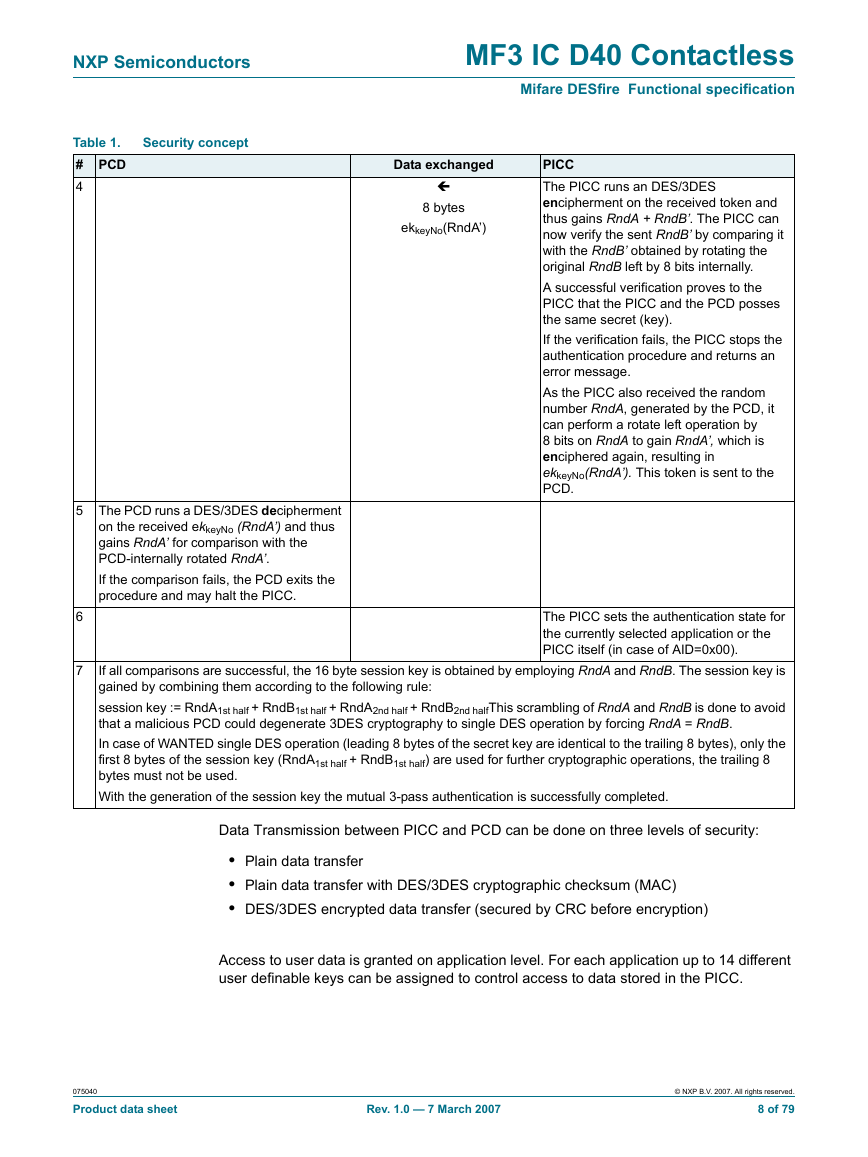
6.6 Security concept
6.7 (3)DES-encryption
6.8 MACing
7. MF3 IC D40 - Coding of security-, application- and file- related features
7.1 Coding of file types
7.2 Coding of communication settings - encryption modes
7.3 Coding of access rights
7.4 Coding of status- and error codes
7.5 DESFire command set overview - ISO 14443-3:
7.6 DESFire command set overview - ISO 14443-4:
7.7 MF3 IC D40 command set overview - security related commands:
7.8 MF3 IC D40 command set overview - PICC level commands:
7.9 MF3 IC D40 command set overview - application level commands:
7.10 MF3 IC D80 command set overview - data manipulation commands
7.11 ISO 7816-4 APDU message structure
7.12 Selection of native DESFire APDU framing versus ISO 7816-4 framing and commands
7.13 Wrapping of native DESFire APDUs
7.14 Pre-Selection after entering 14443-4 (only in 7816-4 framing mode)
8. DESFire command set
8.1 Command set ISO 14443-3:
8.1.1 Request type A (REQA)
8.1.2 Wake-Up (WUPA)
8.1.3 ANTICOLLISION and SELECT of cascade level 1
8.1.4 ANTICOLLISION and SELECT of cascade level 2
8.2 Command set ISO 14443-4:
8.2.1 Request for answer to Select (RATS)
8.2.2 Protocol and parameter selection request (PPS)
8.2.3 Frame waiting extensions (WTX)
8.3 MF3 IC D40 command set - security related commands:
8.3.1 Authenticate
8.3.2 ChangeKeySettings
8.3.2.1 PICC master key settings:
8.3.2.2 Application master key settings:
8.3.3 GetKeySettings
8.3.4 ChangeKey
8.3.5 GetKeyVersion
8.4 MF3 IC D40 command set - PICC level commands:
8.4.1 CreateApplication
8.4.2 DeleteApplication
8.4.3 GetApplicationIDs
8.4.4 SelectApplication
8.4.5 FormatPICC
8.4.6 GetVersion
8.5 MF3 IC D40 command set - application level commands:
8.5.1 GetFileIDs
8.5.2 GetFileSettings
8.5.3 ChangeFileSettings
8.5.4 CreateStdDataFile
8.5.5 CreateBackupDataFile
8.5.6 CreateValueFile
8.5.7 CreateLinearRecordFile
8.5.8 CreateCyclicRecordFile
8.5.9 DeleteFile
8.6 MF3 IC D40 command set - data manipulation commands
8.6.1 ReadData
8.6.2 WriteData
8.6.3 GetValue
8.6.4 Credit
8.6.5 Debit
8.6.6 LimitedCredit
8.6.7 WriteRecord
8.6.8 ReadRecords
8.6.9 ClearRecordFile
8.6.10 CommitTransaction
8.6.11 AbortTransaction
8.7 Command Set ISO 7816-4 - basic interindustry commands:
8.7.1 ISO SELECT APPLICATION command
8.7.2 ISO SELECT DIRECTORY command
8.7.3 ISO SELECT FILE command
8.7.4 ISO READ BINARY command
8.7.5 ISO UPDATE BINARY command
9. Limiting values
10. Recommended operating conditions
11. Characteristics
12. Support information
13. Package outline
14. Revision history
15. Legal information
15.1 Data sheet status
15.2 Definitions
15.3 Disclaimers
15.4 Trademarks
16. Contact information
17. Tables
18. Figures
19. Contents















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc