POSITION PAPER
5G APPLICATIONS
�
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
01 The widespread adoption of 5G requires high-performance, low-cost
technology; it needs engagement and investment across the whole industry
02 International standards drive cost efficiencies and adoption
1
3
6
03 Global spectrum harmonization, national exclusive licensing, and contiguous spectrum
10
04 5G applications represent tremendous opportunities for the economy and society
05 Healthy, productive, and supportive 5G ecosystem for sustainable innovation
06 Glossary
13
25
28
�
1.1 5G is not just faster, but a new paradigm
1.2 Investment by all stakeholders – not just operators – will drive growth and economies of scale
that benefit the whole 5G ecosystem
2.1 Standards benefit consumers and companies as they lower investment and deployment costs,
facilitate connectivity and foster interoperability
2.2 Cooperation among standards organizations and all stakeholders has been expanded for 5G
3.1 Multiple spectrum bands are required to address the wide range of 5G use cases and applications
3.2 Regulatory frameworks need to be supportive of 5G deployment and applications
4.1 5G is more than just business: It will have an induced impact on key socio-economic issues
4.2 The industries that will leverage 5G to renew their business models and create more value
4.3 New business models emerging in pilot programs, combining multiple stakeholders to deliver
innovative services
5.1 Governments and regulators define 5G plans and initiatives, with greater transparency in
regulatory policies
5.2 Regulation of other industries must evolve, which will require cooperation between institutions
5.3 Stakeholders should coordinate to build the capabilities required for potential applications, target
business models, and the 5G ecosystem
�
Executive Summary
5G-powered
economy and society
National and
regional plans
Vertical industries'
initiatives
Regulation on
infrastructure
Regulation on
spectrum
Regulation by
vertical industries
Telecoms
Media &
Entertainment
Manufacturing
Transportation
Public
Services
3GPP standards
Research & Development
Vision
Enabling
environment
Applications
Use cases
Pilots
Business models
Technology
5G is a new paradigm
Delivering Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communication (URLLC)
and Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC), 5G applications represent tremendous opportunities for
consumers, homes, businesses and communities.
• 5G is expected to generate USD 12 trillion in revenues in 2035.
• 80% of telecom revenues (broadband, hardware, and services) will be linked to 5G in 2035.
Furthermore, 5G will help reduce inequality by increasing access and lowering the cost of essential services,
such as healthcare and education. By expanding the scope of wireless technologies and making devices more
autonomous, 5G will help to reduce our carbon footprint and conserve natural resources. Last, economic
growth will boost direct and indirect employment in all economies.
Telecom operators, equipment vendors, and industry stakeholders are
transforming their respective industries using 5G applications, supported by
national strategies
New 5G applications are emerging, supported by national strategies:
• Telecom
5G for home (e.g. Fixed Wireless Access) and mobile
• Media
AR/VR gaming, and advertising, multi- broadcasting
• Manufacturing Smart factories & connectivity over the full product lifecycle
• Transportation autonomous driving, in-car infotainment
• Public services healthcare (e.g. telemedicine), education
1
�
International standards drive cost efficiencies and speed 5G adoption
The first standards have been released, supporting the deployment of non-standalone and standalone
5G and the first applications. Next steps are focused on enhancing the 5G ecosystem and expanding the
potential for applications in the coming years, notably with Release 16 (2020) and Release 17 (2021).
• 3GPP is leading the standardization of 5G. As 5G involves operators, equipment vendors, and industry
stakeholders, broad-based cooperation is needed to create consensus.
Spectrum allocation is a critical regulatory and technical issue
5G requires multiple layers of spectrum to address a wide range of use cases.
• A global harmonization of frequency bands would reduce complexity and costs for vendors, operators,
their industry partners, and end-users.
• National licenses should remain the main and preferred authorization model.
• Network synchronization should be considered to mitigate harmful interference.
5G requires a stable and transparent ecosystem to perform
As well as the quality and cost efficiency of the technology itself, the long-term success of 5G will also
depend on a supportive business environment.
• Sustained infrastructure investment should be accompanied by precise and reliable national roadmaps
that offer sufficient transparency for all stakeholders.
• Cooperation between stakeholders with common interests should be led by industry associations, such as
5GAA, 5G-ACIA, 5G AIA.
• A supportive regulatory environment should be provided for telecommunications and other industries,
accompanied by government initiatives to stimulate new business.
5G uptake will depend on the engagement and investment of operators,
vendors, and industry stakeholders
Operators are expected to be the natural investors for 5G. Strong engagement by equipment vendors and
industry stakeholders will help drive economies of scale, benefiting the whole 5G ecosystem.
• 5G adoption will be progressive, as performance and economies of scale materialize.
• New businesses will take advantage of previous investments as appropriate: The first national licenses
have been granted to MNOs, who will provide network access and solutions to vertical sectors using
network slicing technologies.
2
�
01
The adoption of 5G will be progressive, as performance
improves and economies of scale continue to
materialize. Achieving significant economies of scale
is a common goal pursued by operators, equipment
vendors, and other industry stakeholders. Operators
will contribute significantly to economies of scale by
building out 5G networks with national coverage.
In parallel, the whole ecosystem will invest in 5G
applications for various sectors of the economy,
leveraging operators' networks when appropriate.
3
THE WIDESPREAD ADOPTION OF 5G REQUIRES HIGH-PERFORMANCE, LOW-COST TECHNOLOGY;IT NEEDS ENGAGEMENT AND INVESTMENT ACROSS THE WHOLE INDUSTRYTHE WIDESPREAD ADOPTION OF 5G REQUIRES HIGH-PERFORMANCE, LOW-COST TECHNOLOGY;IT NEEDS ENGAGEMENT AND INVESTMENT ACROSS THE WHOLE INDUSTRY�
1.1 5G is not just faster, but a new paradigm
Enhanced Mobile Broadband
Gigabit speeds
Smart buildings
Voice
Smart home/city
Massive Machine
Type Communications
3D video, UHD screens
Work and play in the cloud
Augmented reality
Industry automation
Mission critical
Self-driving cars
Ultra-reliable and
Low-latency Communication
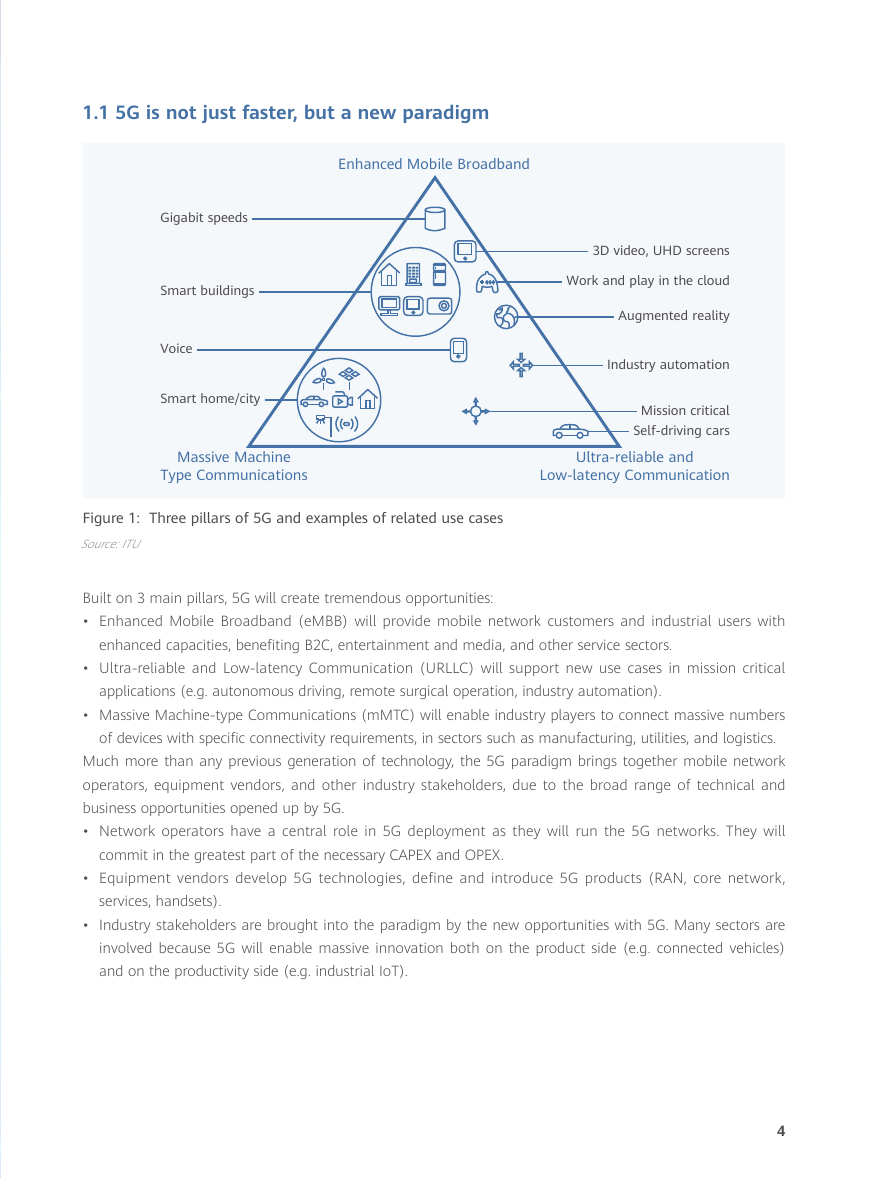
Figure 1: Three pillars of 5G and examples of related use cases
Source: ITU
Built on 3 main pillars, 5G will create tremendous opportunities:
• Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) will provide mobile network customers and industrial users with
enhanced capacities, benefiting B2C, entertainment and media, and other service sectors.
• Ultra-reliable and Low-latency Communication (URLLC) will support new use cases in mission critical
applications (e.g. autonomous driving, remote surgical operation, industry automation).
• Massive Machine-type Communications (mMTC) will enable industry players to connect massive numbers
of devices with specific connectivity requirements, in sectors such as manufacturing, utilities, and logistics.
Much more than any previous generation of technology, the 5G paradigm brings together mobile network
operators, equipment vendors, and other industry stakeholders, due to the broad range of technical and
business opportunities opened up by 5G.
• Network operators have a central role in 5G deployment as they will run the 5G networks. They will
commit in the greatest part of the necessary CAPEX and OPEX.
• Equipment vendors develop 5G technologies, define and introduce 5G products (RAN, core network,
services, handsets).
• Industry stakeholders are brought into the paradigm by the new opportunities with 5G. Many sectors are
involved because 5G will enable massive innovation both on the product side (e.g. connected vehicles)
and on the productivity side (e.g. industrial IoT).
4
�
01
Network operators
03
New
paradigm
01
02
02
03
Source: Roland Berger
1.2 Investment by all stakeholders – not just operators – will drive growth
and economies of scale that benefit the whole 5G ecosystem
Mobile network operators are the natural investors in 5G. Projected investments will reach USD 1 trillion
between 2018 and 20251:
• From an internal development standpoint, operator business models will be stressed by the exponential
growth in demand for data (x6 between 2017 and 20242 ), which will increase the costs of network
management and the level of risk.
• Operators also have external incentives, such as users demand for better services and new applications,
changes in the global competitive landscape, and their home nation's infrastructure needs.
Growing demand for 5G will trigger investment from other industry stakeholders as well.
These massive investments will result in important scale effects. The cost of production and maintenance
for 5G networks will fall, and the value of the networks will increase in the eyes of network users. These
outcomes are supported by theories of network externalities (e.g. Katz and Shapiro3) or Metcalfe's law:
• When more 5G products comply with the same technical standards, customers will benefit more from
affordable devices and high-quality services.
• As more vertical industries adopt 5G technologies, end users will receive more value from these industries,
as broad adoption of technologies increases the potential for interoperability and cooperation and drives
the creation of new services.
Investment and engagement by all stakeholders will lower the costs of 5G deployment and help to fulfill the
potential of this new technology. The result will be better economies of scale and enhanced value creation
throughout the whole 5G value chain, both of which will be key levers for 5G adoption.
1 Investing in 5G, GSMA Intelligence, June 2019
2 BuddComm, Roland Berger analysis
3 "Network Externalities, Competition, and Compatibility," Michael L. Katz and Carl Shapiro, The American Economic Review, Vol. 75, No. 3.
(Jun. 1985), pp. 424-440.
5
Industry stakeholdersVendors�














 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc