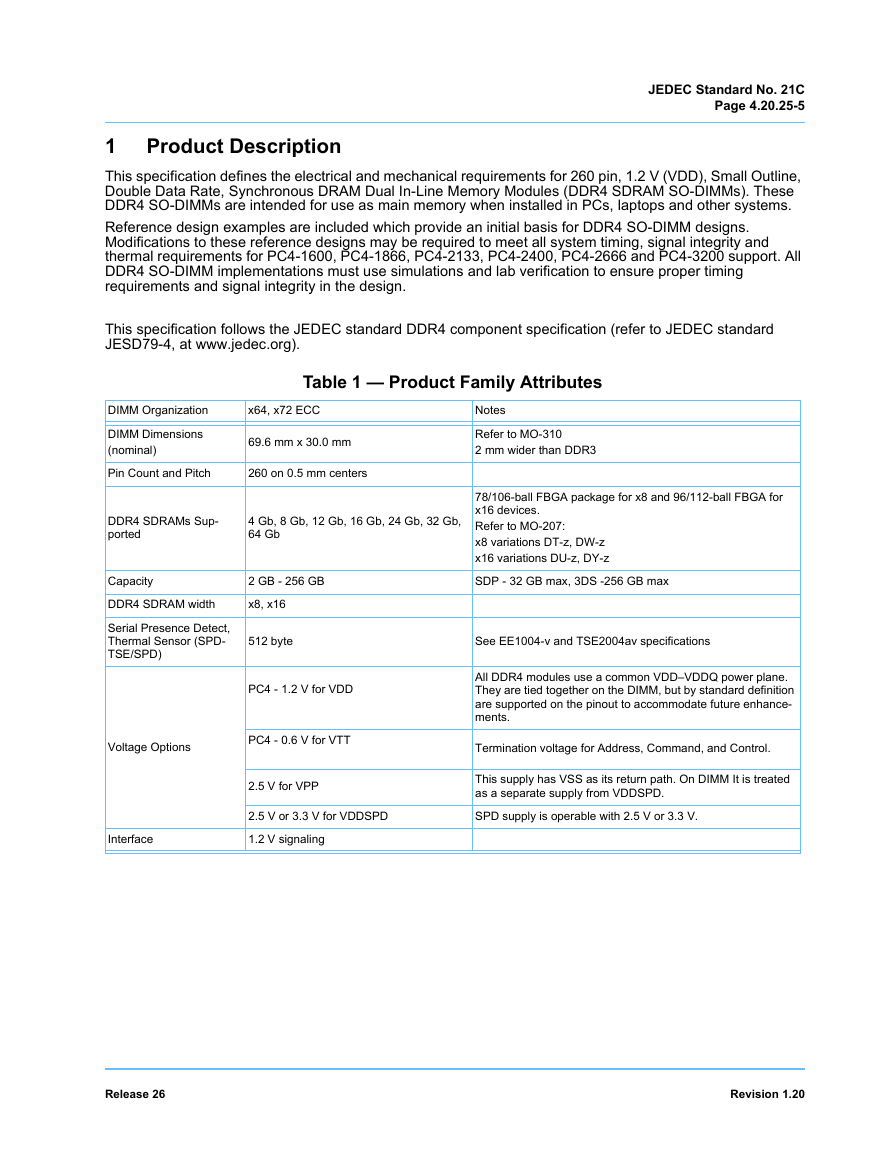
1 Product Description
Table 1 — Product Family Attributes
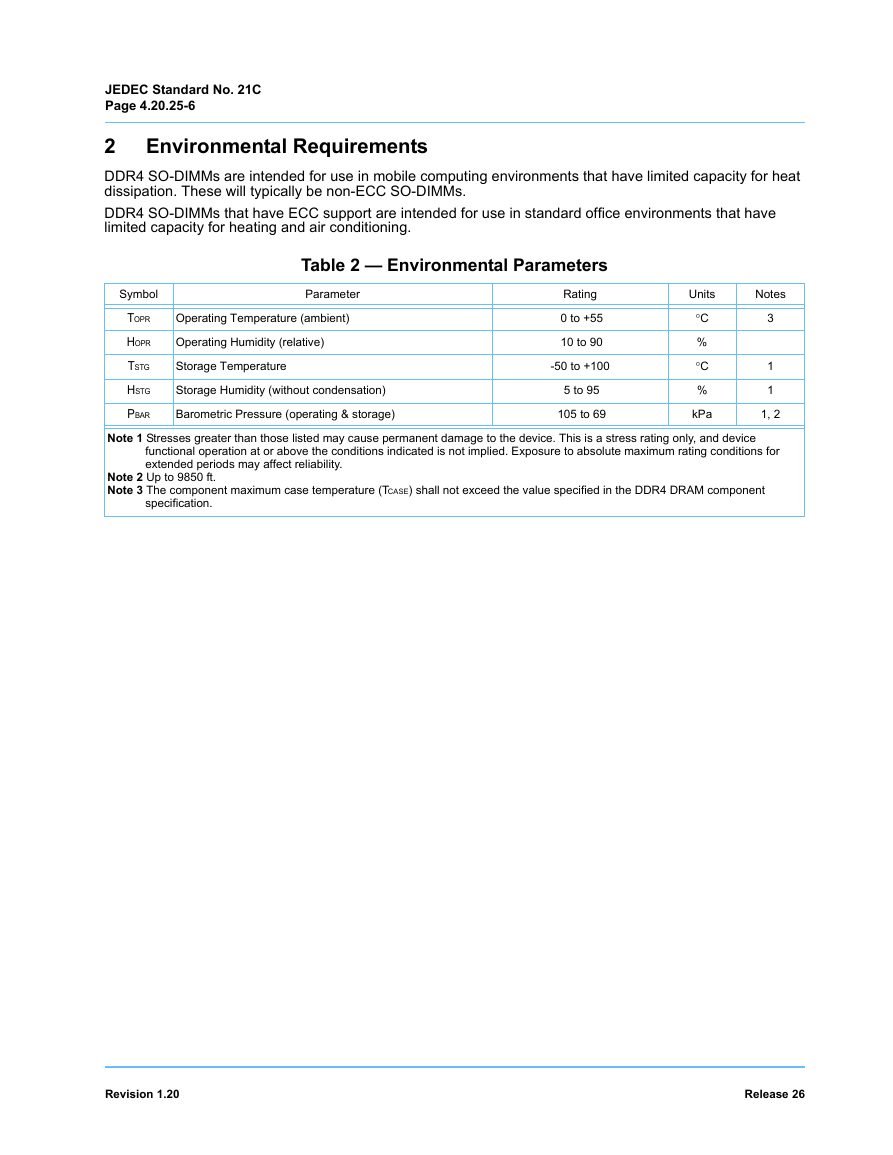
2 Environmental Requirements
Table 2 — Environmental Parameters
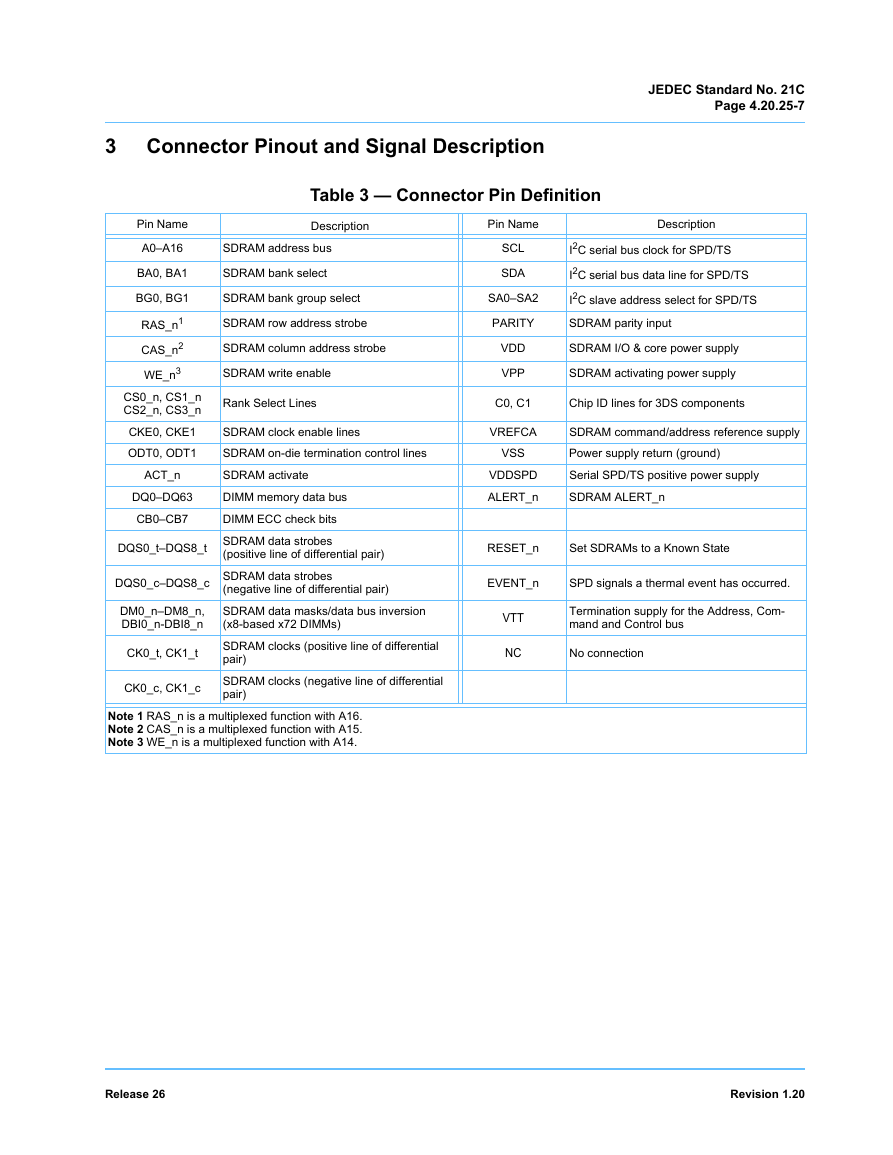
3 Connector Pinout and Signal Description
Table 3 — Connector Pin Definition
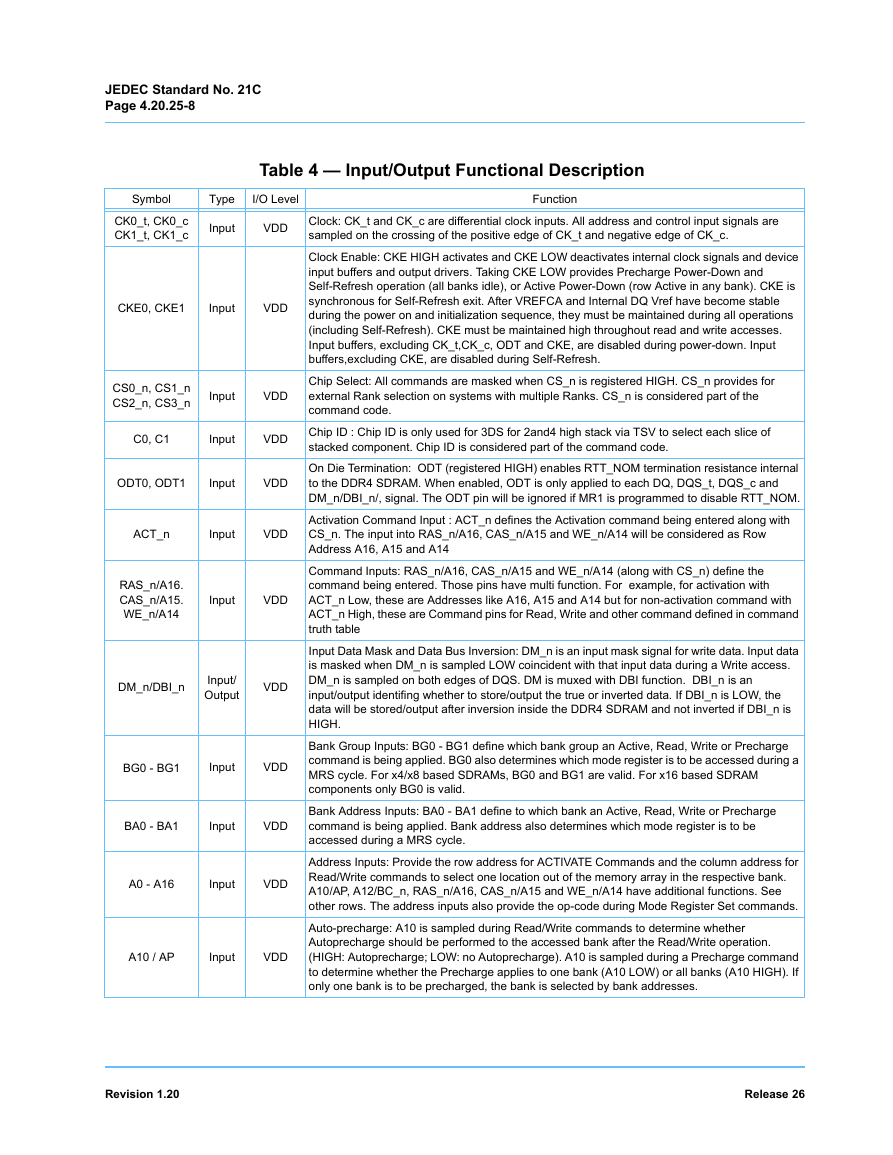
Table 4 — Input/Output Functional Description
3.1 DDR4 SO-DIMM Connector Pin Assignments
Table 5 — DDR4 SO-DIMM 260 Pin Connector Pin Wiring Assignments
4 Power Details
4.1 DIMM Voltage Requirements
Table 6 — DDR4 SO-DIMM DC Operating Voltage1,2,3 - 1.2 V operation
4.2 Rules for Power-Up Sequence
Figure 1 — Graphical View of Recommended Power Sequence
Figure 2 — Graphical View of Recommended Power Down Sequence
4.3 Feed Through Voltage (VFT)
5 Component Details
Figure 3 — DIMM Ball Patterns for DDR4 SDRAM Components
Table 7 — DDR4 x8 SDRAM DIMM Pad Array
Table 8 — DDR4 x16 SDRAM DIMM Pad Array
5.1 Component Types and Placement
5.2 Decoupling Guidelines
Table 9 — DDR4 SO-DIMM Decoupling Capacitor Guidelines
6 DIMM Design Details
6.1 Signal Groups
Figure 4 — Example SO-DIMM Fly-By Topology
6.2 Explanation of Net Structure Diagrams
Figure 5 — Net Structure Example
6.3 General Net Structure Routing Rules
Table 10 — CK, CTRL, and ADD/CMD Group Length Matching Rules
Figure 6 — Example Address routing topology
Table 11 — Data and Strobe Group Length Matching Rules
Figure 7 — ALERT_n Wiring Illustration
Figure 8 — Via Compensation Diagram
Table 12 — Plane Referencing
6.4 Address Mirroring
Table 13 — DIMM Wiring Definition for Address Mirroring
6.5 DIMM Routing Space Constraints
Table 14 — Routing Space Constraints
6.6 DIMM Physical Requirements
6.7 Reference Stackups
Table 15 — Preferred 10 Layer Stackup for SO-DIMMs
Table 16 — Preferred 8 Layer Stackup for SO-DIMMs
Table 17 — Preferred 6 Layer Stackup for SO-DIMMs
6.8 Impedance Targets
Table 18 — Impedance Assignments by Signal Type
6.9 SPD Wiring and Placement
Figure 9 — Block Diagram: SPD-TSE/ SPD
6.10 DQ Mapping to Support CRC
Table 19 — SPD DQ Nibble Map for CRC
Table 20 — Nibble/Byte DQ Map Patterns for CRC
Figure 10 — Example of DQ Wiring with Mapping for CRC
Table 21 — Example of DQ Mapping for CRC
7 Serial Presence Detect Component Specification
7.1 Serial Presence Detect Definition
Table 22 — SPD Address Map
Table 23 — Block 0: Base Configuration and DRAM Parameters
8 Product Label
8.1 DDR4 DIMM Label Format for DRAM-only module types
8.2 DDR4 DIMM Label Format for Hybrid module types
9 JEDEC Process










 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc