USB 2.0
Front Matter
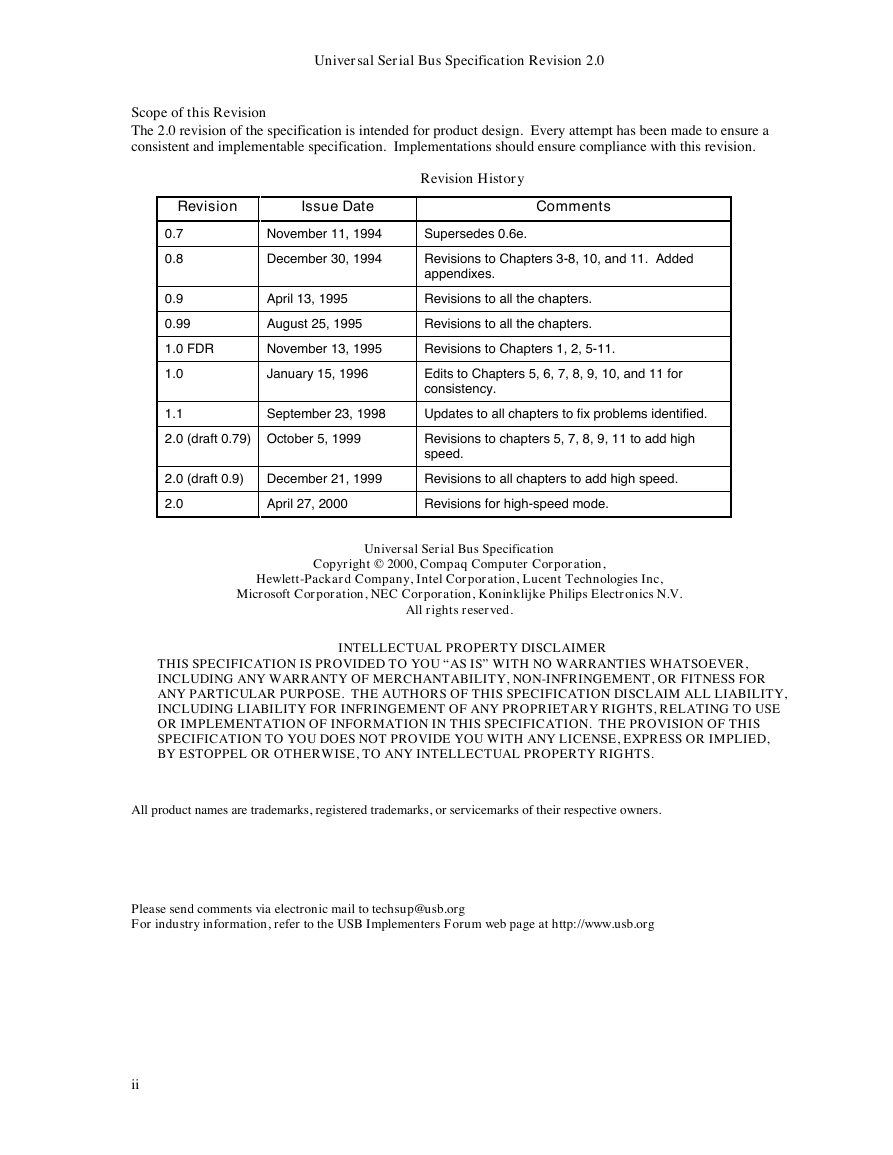
Scope of this Revision
Revision History
Intellectual Property Disclaimer
Acknowledgement of USB 2.0 Technical Contribution
Contents
Figures
Tables
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Motivation
1.2 Objective of the Specification
1.3 Scope of the Document
1.4 USB Product Compliance
1.5 Document Organization
Chapter 2 Terms and Abbreviations
Chapter 3 Background
3.1 Goals for the Universal Serial Bus
3.2 Taxonomy of Application Space
3.3 Feature List
Chapter 4 Architectural Overview
4.1 USB System Description
4.1.1 Bus Topology
4.1.1.1 USB Host
4.1.1.2 USB Devices
4.2 Physical Interface
4.2.1 Electrical
4.2.2 Mechanical
4.3 Power
4.3.1 Power Distribution
4.3.2 Power Management
4.4 Bus Protocol
4.5 Robustness
4.5.1 Error Detection
4.5.2 Error Handling
4.6 System Configuration
4.6.1 Attachment of USB Devices
4.6.2 Removal of USB Devices
4.6.3 Bus Enumeration
4.7 Data Flow Types
4.7.1 Control Transfers
4.7.2 Bulk Transfers
4.7.3 Interrupt Transfers
4.7.4 Isochronous Transfers
4.7.5 Allocating USB Bandwidth
4.8 USB Devices
4.8.1 Device Characterizations
4.8.2 Device Descriptions
4.8.2.1 Hubs
4.8.2.2 Functions
4.9 USB Host: Hardware and Software
4.10 Architectural Extensions
Chapter 5 USB Data Flow Model
5.1 Implementer Viewpoints
5.2 Bus Topology
5.2.1 USB Host
5.2.2 USB Devices
5.2.3 Physical Bus Topology
5.2.4 Logical Bus Topology
5.2.5 Client Software-to-function Relationship
5.3 USB Communication Flow
5.3.1 Device Endpoints
5.3.1.1 Endpoint Zero Requirements
5.3.1.2 Non-endpoint Zero Requirements
5.3.2 Pipes
5.3.2.1 Stream Pipes
5.3.2.2 Message Pipes
5.3.3 Frames and Microframes
5.4 Transfer Types
5.4.1 Table Calculation Examples
5.5 Control Transfers
5.5.1 Control Transfer Data Format
5.5.2 Control Transfer Direction
5.5.3 Control Transfer Packet Size Constraints
5.5.4 Control Transfer Bus Access Constraints
5.5.5 Control Transfer Data Sequences
5.6 Isochronous Transfers
5.6.1 Isochronous Transfer Data Format
5.6.2 Isochronous Transfer Direction
5.6.3 Isochronous Transfer Packet Size Constraints
5.6.4 Isochronous Transfer Bus Access Constraints
5.6.5 Isochronous Transfer Data Sequences
5.7 Interrupt Transfers
5.7.1 Interrupt Transfer Data Format
5.7.2 Interrupt Transfer Direction
5.7.3 Interrupt Transfer Packet Size Constraints
5.7.4 Interrupt Transfer Bus Access Constraints
5.7.5 Interrupt Transfer Data Sequences
5.8 Bulk Transfers
5.8.1 Bulk Transfer Data Format
5.8.2 Bulk Transfer Direction
5.8.3 Bulk Transfer Packet Size Constraints
5.8.4 Bulk Transfer Bus Access Constraints
5.8.5 Bulk Transfer Data Sequences
5.9 High-Speed, High Bandwidth Endpoints
5.9.1 High Bandwidth Interrupt Endpoints
5.9.2 High Bandwidth Isochronous Endpoints
5.10 Split Transactions
5.11 Bus Access for Transfers
5.11.1 Transfer Management
5.11.1.1 Client Software
5.11.1.2 USB Driver
5.11.1.3 Host Controller Driver
5.11.1.4 Transaction List
5.11.1.5 Host Controller
5.11.2 Transaction Tracking
5.11.3 Calculating Bus Transaction Times
5.11.4 Calculating Buffer Sizes in Functions and Software
5.11.5 Bus Bandwidth Reclamation
5.12 Special Considerations for Isochronous Transfers
5.12.1 Example Non-USB Isochronous Application
5.12.2 USB Clock Model
5.12.3 Clock Synchronization
5.12.4 Isochronous Devices
5.12.4.1 Synchronization Type
5.12.4.1.1 Asynchronous
5.12.4.1.2 Synchronous
5.12.4.1.3 Adaptive
5.12.4.2 Feedback
5.12.4.3 Implicit Feedback
5.12.4.4 Connectivity
5.12.4.4.1 Audio Connectivity
5.12.4.4.2 Synchronous Data Connectivity
5.12.5 Data Prebuffering
5.12.6 SOF Tracking
5.12.7 Error Handling
5.12.8 Buffering for Rate Matching
Chapter 6 Mechanical
6.1 Architectural Overview
6.2 Keyed Connector Protocol
6.3 Cable
6.4 Cable Assembly
6.4.1 Standard Detachable Cable Assemblies
6.4.2 High-/full-speed Captive Cable Assemblies
6.4.3 Low-speed Captive Cable Assemblies
6.4.4 Prohibited Cable Assemblies
6.5 Connector Mechanical Configuration and Material Requirements
6.5.1 USB Icon Location
6.5.2 USB Connector Termination Data
6.5.3 Series “A” and Series “B” Receptacles
6.5.3.1 Receptacle Injection Molded Thermoplastic Insulator Material
6.5.3.2 Receptacle Shell Materials
6.5.3.3 Receptacle Contact Materials
6.5.4 Series “A” and Series “B” Plugs
6.5.4.1 Plug Injection Molded Thermoplastic Insulator Material
6.5.4.2 Plug Shell Materials
6.5.4.3 Plug (Male) Contact Materials
6.6 Cable Mechanical Configuration and Material Requirements
6.6.1 Description
6.6.2 Construction
6.6.3 Electrical Characteristics
6.6.4 Cable Environmental Characteristics
6.6.5 Listing
6.7 Electrical, Mechanical, and Environmental Compliance Standards
6.7.1 Applicable Documents
6.8 USB Grounding
6.9 PCB Reference Drawings
Chapter 7 Electrical
7.1 Signaling
7.1.1 USB Driver Characteristics
7.1.1.1 Full-speed (12 Mb/s) Driver Characteristics
7.1.1.2 Low-speed (1.5 Mb/s) Driver Characteristics
7.1.1.3 High-speed (480 Mb/s) Driver Characteristics
7.1.2 Data Signal Rise and Fall, Eye Patterns
7.1.2.1 Low-speed and Full-speed Data Signal Rise and Fall
7.1.2.2 High-speed Signaling Eye Patterns and Rise and Fall Time
7.1.2.3 Driver Usage
7.1.3 Cable Skew
7.1.4 Receiver Characteristics
7.1.4.1 Low-speed and Full-speed Receiver Characteristics
7.1.4.2 High-speed Receiver Characteristics
7.1.5 Device Speed Identification
7.1.5.1 Low-/Full-speed Device Speed Identification
7.1.5.2 High-speed Device Speed Identification
7.1.6 Input Characteristics
7.1.6.1 Low-speed and Full-speed Input Characteristics
7.1.6.2 High-speed Input Characteristics
7.1.7 Signaling Levels
7.1.7.1 Low-/Full-speed Signaling Levels
7.1.7.2 Full-/High-speed Signaling Levels
7.1.7.3 Connect and Disconnect Signaling
7.1.7.4 Data Signaling
7.1.7.4.1 Low-/Full-Speed Signaling
7.1.7.4.2 High-speed Signaling
7.1.7.5 Reset Signaling
7.1.7.6 Suspending
7.1.7.6.1 Global Suspend
7.1.7.6.2 Selective Suspend
7.1.7.7 Resume
7.1.8 Data Encoding/Decoding
7.1.9 Bit Stuffing
7.1.9.1 Full-/low-speed
7.1.9.2 High-Speed
7.1.10 Sync Pattern
7.1.11 Data Signaling Rate
7.1.12 Frame Interval
7.1.13 Data Source Signaling
7.1.13.1 Data Source Jitter
7.1.13.1.1 Low-/full-speed Data Source Jitter
7.1.13.1.2 High-speed Data Source Jitter
7.1.13.2 EOP Width
7.1.13.2.1 Low-/full-speed EOP
7.1.13.2.2 High-speed EOP
7.1.14. Hub Signaling Timings
7.1.14.1 Low-/full-speed Hub Signaling Timings
7.1.14.2 High-speed Hub Signaling Timings
7.1.15 Receiver Data Jitter
7.1.15.1 Low-/full-speed Receiver Data Jitter
7.1.15.2 High-speed Receiver Data Jitter
7.1.16 Cable Delay
7.1.17 Cable Attenuation
7.1.18 Bus Turn-around Time and Inter-packet Delay
7.1.18.1 Low-/Full-Speed Bus Turn-around Time and Inter-packet Delay
7.18.2 High-Speed Bus Turn-around Time and Inter-packet Delay
7.1.19 Maximum End-to-end Signal Delay
7.1.19.1 Low-/full-speed End-to-end Signal Delay
7.1.19.2 High-Speed End-to-end Delay
7.1.20 Test Mode Support
7.2 Power Distribution
7.2.1 Classes of Devices
7.2.1.1 Bus-powered Hubs
7.2.1.2 Self-powered Hubs
7.2.1.2.1 Over-current Protection
7.2.1.3 Low-power Bus-powered Functions
7.2.1.4 High-power Bus-powered Functions
7.2.1.5 Self-powered Functions
7.2.2 Voltage Drop Budget
7.2.3 Power Control During Suspend/Resume
7.2.4 Dynamic Attach and Detach
7.2.4.1 Inrush Current Limiting
7.2.4.2 Dynamic Detach
7.3 Physical Layer
7.3.1 Regulatory Requirements
7.3.2 Bus Timing/Electrical Characteristics
7.3.3 Timing Waveforms
Chapter 8 Protocol Layer
8.1 Byte/Bit Ordering
8.2 SYNC Field
8.3 Packet Field Formats
8.3.1 Packet Identifier Field
Address Fields
Address Field
Endpoint Field
Frame Number Field
Data Field
Cyclic Redundancy Checks
Token CRCs
Data CRCs
8.4 Packet Formats
8.4.1 Token Packets
8.4.2 Split Transaction Special Token Packets
8.4.2.1 Split Transactions
8.4.2.2 Start-Split Transaction Token
8.4.2. 3 Complete-Split Transaction Token
8.4.3 Start-of-Frame Packets
8.4.3.1 USB Frames and Microframes
8.4.4 Data Packets
8.4.5 Handshake Packets
8.4.6 Handshake Responses
8.4.6.1 Function Response to IN Transactions
8.4.6.2 Host Response to IN Transactions
8.4.6.3 Function Response to an OUT Transaction
8.4.6.4 Function Response to a SETUP Transaction
8.5 Transaction Packet Sequences
8.5.1 NAK Limiting via Ping Flow Control
8.5.1.1 NAK Responses to OUT/DATA During PING Protocol
8.5.2 Bulk Transactions
8.5.3 Control Transfers
8.5.3.1 Reporting Status Results
8.5.3.2 Variable-length Data Stage
8.5.3.3 Error Handling on the Last Data Transaction
8.5.3.4 STALL Handshakes Returned by Control Pipes
8.5.4 Interrupt Transactions
8.5.5 Isochronous Transactions
8.6 Data Toggle Synchronization and Retry
8.6.1 Initialization via SETUP Token
8.6.2 Successful Data Transactions
8.6.3 Data Corrupted or Not Accepted
8.6.4 Corrupted ACK Handshake
8.6.5 Low-speed Transactions
8.7 Error Detection and Recovery
8.7.1 Packet Error Categories
8.7.2 Bus Turn-around Timing
8.7.3 False EOPs
8.74 Babble and Loss of Activity Recovery
Chapter 9 USB Device Framework
9.1 USB Device States
9.1.1 Visible Device States
9.1.1.1 Attached
9.1.1.2 Powered
9.1.1.3 Default
9.1.1.4 Address
9.1.1.5 Configured
9.1.1.6 Suspended
9.1.2 Bus Enumeration
9.2 Generic USB Device Operations
9.2.1 Dynamic Attachment and Removal
9.2.2 Address Assignment
9.2.3 Configuration
9.2.4 Data Transfer
9.2.5 Power Management
9.2.5.1 Power Budgeting
9.2.5.2 Remote Wakeup
9.2.6 Request Processing
9.2.6.1 Request Processing Timing
9.2.6.2 Reset/Resume Recovery Time
9.2.6.3 Set Address Processing
9.2.6.4 Standard Device Requests
9.2.6.5 Class-specific Requests
9.2.6.6 Speed Dependent Descriptors
9.2.7 Request Error
9.3 USB Device Requests
9.3.1 bmRequestType
9.3.2 bRequest
9.3.3 wValue
9.3.4 wIndex
9.3.5 wLength
9.4 Standard Device Requests
9.4.1 Clear Feature
9.4.2 Get Configuration
9.4.3 Get Descriptor
9.4.4 Get Interface
9.4.5 Get Status
9.4.6 Set Address
9.4.7 Set Configuration
9.4.8 Set Descriptor
9.4.9 Set Feature
9.4.10 Set Interface
9.4.11 Synch Frame
9.5 Descriptors
9.6 Standard USB Descriptor Definitions
9.6.1 Device
9.6.2 Device_Qualifier
9.6.3 Configuration
9.6.4 Other_Speed_Configuration
9.6.5 Interface
9.6.6 Endpoint
9.6.7 String
9.7 Device Class Definitions
9.7.1 Descriptors
9.7.2 Interface(s) and Endpoint Usage
9.7.3 Requests
Chapter 10 USB Host: Hardware and Software
10.1 Overview of the USB Host
10.1.1 Overview
10.1.2 Control Mechanisms
10.1.3 Data Flow
10.1.4 Collecting Status and Activity Statistics
10.1.5 Electrical Interface Considerations
10.2 Host Controller Requirements
10.2.1 State Handling
10.2.2 Serializer/Deserializer
10.2.3 Frame and Microframe Generation
10.2.4 Data Processing
10.2.5 Protocol Engine
10.2.6 Transmission Error Handling
10.2.7 Remote Wakeup
10.2.8 Root Hub
10.2.8.1 Port Resets
10.2.9 Host System Interface
10.3 Overview of Software Mechanisms
10.3.1 Device Configuration
10.3.2 Resource Management
10.3.3 Data Transfers
10.3.4 Common Data Definitions
10.4 Host Controller Driver
10.5 Universal Serial Bus Driver
10.5.1 USBD Overview
10.5.1.1 USBD Initialization
10.5.1.2 USBD Pipe Usage
10.5.1.2.1 Default Pipes
10.5.1.2.2 Client Pipes
10.5.1.3 USBD Service Capabilities
10.5.2 USBD Command Mechanism Requirements
10.5.2.1 Interface State Control
10.5.2.2 Pipe State Control
10.5.2.3 Getting Descriptors
10.5.2.4 Getting Current Configuration Settings
10.5.2.5 Adding Devices
10.5.2.6 Removing Devices
10.5.2.7 Managing Status
10.5.2.8 Sending Class Commands
10.5.2.9 Sending Vendor Commands
10.5.2.10 Establishing Alternate Settings
10.5.2.11 Establishing a Configuration
10.5.2.12 Setting Descriptors
10.5.3 USBD Pipe Mechanisms
10.5.3.1 Supported Pipe Types
10.5.3.1.1 Isochronous Data Transfers
10.5.3.1.2 Interrupt Transfers
10.5.3.1.3 Bulk Transfers
10.5.3.1.4 Control Transfers
10.5.3.2 USBD Pipe Mechanism Requirements
10.5.3.2.1 Aborting IRPs
10.5.3.2.2 Managing Pipe Policy
10.5.3.2.3 Queuing IRPs
10.5.4 Managing the USB via the USBD Mechanisms
10.5.4.1 Configuration Services
10.5.4.1.1 Configuration Management
10.5.4.1.2 Initial Device Configuration
10.5.4.1.3 Modifying a Device Configuration
10.5.4.1.4 Device Removal
10.5.4.2 Power Control
10.5.4.3 Event Notifications
10.5.4.4 Status Reporting and Error Recovery Services
10.5.4.t Managing Remote Wakeup Devices
10.5.5 Passing USB Preboot Control to the Operating System
10.6 Operating System Environment Guides
Chapter 11 Hub Specification
11.1 Overview
11.1.1 Hub Architecture
11.1.2 Hub Connectivity
11.1.2.1 Packet Signaling Connectivity
11.1.2.2 Resume Connectivity
11.2.3 Hub Fault Recovery Mechanisms
11.2 Hub Frame/Microframe Timer
11.2.1 High-speed Microframe Timer Range
11.2.2 Full-speed Frame Timer Range
11.2.3 Frame/Microframe Timer Synchronization
11.2.3.1 Example (Micro)frame Timer Synchronization Method
11.2.3.2 EOF Advancement
11.2.3.3 Effect of Synchronization on Repeater Behavior
11.2.4 Microframe Jitter Related to Frame Jitter
11.2.5 EOF1 and EOF2 Timing Points
11.2.5.1 High-speed EOF1 and EOF2 Timing Points
11.2.5.2 Full-speed EOF1 and EOF2 Timing Points
11.3 Host Behavior at End-of-Frame
11.3.1 Full-/low-speed Latest Host Packet
11.3.2 Full-/low-speed Packet Nullification
11.3.3 Full-/low-speed Transaction Completion Prediction
11.4 Internal Port
11.4.1 Inactive
11.4.2 Suspend Delay
11.4.3 Full Suspend (Fsus)
11.4.4 Generate Resume (GResume)
11.5 Downstream Facing Ports
11.5.1 Downstream Facing Port State Descriptions
11.5.1.1 Not Configured
11.5.1.2 Powered-off
11.5.1.3 Disconnected
11.5.1.4 Disabled
11.5.1.5 Resetting
11.5.1.6 Enabled
11.5.1.7 Transmit
11.5.1.8 TransmitR
11.5.1.9 Suspended
11.5.1.10 Resuming
11.5.1.11 SendEOR
11.5.1.12 Restart_S
11.5.1.13 Restart_E
11.5.1.14 Testing
11.5.2 Disconnect Detect Timer
11.5.2.1 High-speed Disconnect Detection
11.5.2.2 Full-/low-speed Disconnect Detection
11.5.3 Port Indicator
11.5.3.1 Labeling
11.6 Upstream Facing Port
11.6.1 Full-speed
11.6.2 High-speed
11.6.3 Receiver
11.6.3.1 ReceivingIS
11.6.3.2 ReceivingHJ
11.6.3.3 ReceivingJ
11.6.3.4 Suspend
11.6.3.5 ReceivingHK
11.6.3.6 ReceivingK
11.6.3.7 Resume
11.6.3.8 ReceivingSE0
11.6.3.9 Bus_Reset
11.6.4 Transmitter
11.6.4.1 Inactive
11.6.4.2 Active
11.6.4.3 RepeatingSE0
11.6.4.4 SendJ
11.6.4.5 Generate End of Packet Towards Upstream Port (GEOPTU)
11.6.4.6 Send Resume (Sresume)
11.7 Hub Repeater
11.7.1 High-speed Packet Connectivity
11.7.1.1 Squelch Circuit
11.7.1.2 Data Recovery Unit
11.7.1.3 Elasticity Buffer
11.7.1.4 High-Speed Port Selector State Machine
11.7.1.4.1 Inactive
11.7.1.4.2 Priming
11.7.1.4.3 Enable Transmit
11.7.1.4.4 Not Packet
11.7.2 Hub Repeater State Machine
11.7.2.1 High-speed Repeater Operation
11.7.2.2 Full-/low-speed Repeater Operation
11.7.2.3 Repeater State Machine
11.7.3 Wait for Start of Packet from Upstream Port (WFSOPFU)
11.7.4 Wait for End of Packet from Upstream Port (WFEOPFU)
11.7.5 Wait for Start of Packet (WFSOP)
11.7.6 Wait for End of Packet (WFEOP)
11.8 Bus State Evaluation
11.8.1 Port Error
11.8.2 Speed Detection
11.8.3 Collision
11.8.4 Low-speed Port Behavior
11.8.4.1 Low-speed Keep-alive
11.9 Suspend and Resume
11.10 Hub Reset Behavior
11.11 Hub Port Power Control
11.11.1 Multiple Gangs
11.12 Hub Controller
11.12.1 Endpoint Organization
11.12.2 Hub Information Architecture and Operation
11.12.3 Port Change Information Processing
11.12.4 Hub and Port Status Change Bitmap
11.12.5 Over-current Reporting and Recovery
11.12.6 Enumeration Handling
11.13 Hub Configuration
11.14 Transaction Translator
11.14.1 Overview
11.14.1.1 Data Handling Between High-speed and Full-/low-speed
11.14.1.2 Host Controller and TT Split Transactions
11.14.1.3 Multiple Transaction Translators
11.14.2 Transaction Translator Scheduling
11.14.2.1 TT Isochronous/Interrupt (Periodic) Transaction Buffering
11.14.2.2 TT Bulk/Control (Non-Periodic) Transaction Buffering
11.14.2.3 Full-/low-speed Handler Transaction Scheduling
11.15 Split Transaction Notation Information
11.16 Common Split Transaction State Machines
11.16.1 Host Controller State Machine
11.16.1.1 HC_Process_command State Machine
11.16.1.1.1 HC_Do_start State Machine
11.16.1.1.2 HC_Do_complete State Machine
11.16.2 Transaction Translator State Machine
11.16.2.1 TT_Process_packet State Machine
11.16.2.1.1 TT_Do_Start State Machine
11.16.2.1.2 TT_Do_Complete State Machine
11.16.2.1.3 TT_BulkSS State Machine
11.16.2.1.4 TT_BulkCS State Machine
11.16.2.1.5 TT_IntSS State Machine
11.16.2.1.6 TT_IntCS State Machine
11.16.2.1.17 TT_IsochSS State Machine
11.17 Bulk/Control Transaction Translation Overview
11.17.1 Bulk/Control Split Transaction Sequences
11.17.2 Bulk/Control Split Transaction State Machines
11.17.3 Bulk/Control Sequencing
11.17.4 Bulk/Control Buffering Requirements
11.17.5 Other Bulk/Control Details
11.18 Periodic Split Transaction Pipelining and Buffer Management
11.18.1 Best Case Full-Speed Budget
11.18.2 TT Microframe Pipeline
11.18.3 Generation of Full-speed Frames
11.18.4 Host Split Transaction Scheduling Requirements
11.18.5 TT Response Generation
11.18.6 TT Periodic Transaction Handling Requirements
11.18.6.1 Abort of Current Transaction
11.18.6.2 Free of Pending Start-splits
11.18.6.3 Maximum Full-/low-speed Transactions per Microframe
11.18.7 TT Transaction Tracking
11.18.8 TT Complete-split Transaction State Searching
11.19 Approximate TT Buffer Space Required
11.20 Interrupt Transaction Translation Overview
11.20. 1 Interrupt Split Transaction Sequences
11.20.2 Interrupt Split Transaction State Machines
11.20.3 Interrupt OUT Sequencing
11.20.4 Interrupt IN Sequencing
11.21 Isochronous Transaction Translation Overview
11.21.1 Isochronous Split Transaction Sequences
11.21.2 Isochronous Split Transaction State Machines
11.21.3 Isochronous OUT Sequencing
11.21.4 Isochronous IN Sequencing
11.22 TT Error Handling
11.22.1 Loss of TT Synchronization With HS SOFs
11.22.2 TT Frame and Microframe Timer Synchronization Requirements
11.23 Descriptors
11.23.1 Standard Descriptors for Hub Class
11.23.2 Class-specific Descriptors
11.23.2.1 Hub Descriptor
11.24 Requests
11.24.1 Standard Requests
11.24.2 Class-specific Requests
11.24.2.1 Clear Hub Feature
11.24.2.2 Clear Port Feature
11.24.2.3 Clear TT Buffer
11.24.2.4 Get Bus State
11.24.2.5 Get Hub Descriptor
11.24.2.6 Get Hub Status
11.24.2.7 Get Port Status
11.24.2.7.1 Port Status Bits
11.24.2.7.1.1 PORT_CONNECTION
11.24.2.7.1.2 PORT_ENABLE
11.24.2.7.1.3 PORT_SUSPEND
11.24.2.7.1.4 PORT_OVER-CURRENT
11.24.2.7.1.5 PORT_RESET
11.24.2.7.1.6 PORT_POWER
11.24.2.7.1.7 PORT_LOW_SPEED
11.24.2.7.1.8 PORT_HIGH_SPEED
11.24.2.7.1.9 PORT_TEST
11.24.2.7.1.10 PORT_INDICATOR
11.24.2.7.2 Port Status Change Bits
11.24.2.7.2.1 C_PORT_CONNECTION
11.24.2.7.2.2 C_PORT_ENABLE
11.24.2.7.2.3 C_PORT_SUSPEND
11.24.2.7.2.4 C_PORT_OVER-CURRENT
11.24.2.7.2.5 C_PORT_RESET
11.24.2.8 Get_TT_State
11.24.2.9 Reset_TT
11.24.2.10 Set Hub Descriptor
11.24.2.11 Stop_TT
11.24.2.12 Set Hub Feature
11.24.2.13 Set Port Feature
Appendix A Transaction Examples
A.1 Bulk/Control OUT and SETUP Transaction Examples
A.2 Bulk/Control IN Transaction Examples
A.3 Interrupt OUT Transaction Examples
A.4 Interrupt IN Transaction Example
A.5 Isochronous OUT Split-transaction Examples
A.6 Isochronous IN Split Transaction Examples
Appendix B Example Declarations for State Machines
B.1 Global Declarations
B.2 Host Controller Declarations
B.3 Transaction Translator Declarations
Appendix C Reset Protcol State Diagrams
C.1 Downstream Facing Port State Diagram
C.2 Upstream Facing Port State Diagram
C.2.1 Reset From Suspended State
C.2.2 Reset From Full-speed Non-suspended State
C.2.3 Reset From High-speed Non-suspended State
C.2.4 Reset Handshake
Index















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc