中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
球体表面温度周期变化时的非傅里叶导热
求解与分析#
赵伟涛,吴九汇**
5
10
(西安交通大学机械学院,西安 710049)
摘要:本文基于具有热流延迟相的双曲型非 Fouier 热传导方程,研究了球体表面在一周期
温度变化下的温度响应。采用分离变量法和 Duhamel 积分原理得到了该问题的解析解。使
用获得的解析表达式,分析了球内温度响应在不同位置处以及随不同热松弛时间的变化趋
势,并与经典的 Fouier 热传导方程所得到结果进行了比较。结果表明,非 Fouier 热传导模
型所给的温度响应与经典的 Fouier 热传导模型具有显著的差别。
关键词:热传导;非 Fouier;球体;温度响应;周期变化
中图分类号:TG113.2
15
Analytical Study of the Non-Fourier Heat Conduction in a
Solid Sphere with Periodic Surface Temperature
ZHAO Weitao, WU Jiuhui
20
25
(School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710049)
Abstract: Based on hyperbolic heat conduction equation accounting for the phase lag between the
heat flux and the temperature, the temperature responses of solid sphere subjected to a periodic
surface temperature disturbance are analytically studied. The solution is based on the separation of
variables method and Duhamel’s principle. Using the obtained analytical expression, the
temperature response depending on the different position and the thermal relaxation time are
examined quantitatively. A comparison of the present results with those obtained by using Fourier
heat conduction equation is given. It shows that there exists a big difference between the
temperature response obtained by using non-Fouier model and Fourier model.
Key words: heat conduction; non-fouier; sphere; temperature responses; periodic variation
0 引言
30
自从 17 实际 Fourier 建立了导热的数学模型,Fourier 定律广泛应用于导热问题分析的
各个领域。但是,Fourier 定律不涉及传热时间项,换句话说,一旦物体表面的温度在某个
瞬间发生变化,则物体内部任意位置上都能立即感受到其变化,Fourier 定律隐含了热扰动
传播速度为无限大的假设。对于热作用时间较长的稳态传热过程以及热传播速度较快的非稳
态常规传热过程,采用 Fourier 定律来描述热流密度与温度梯度之间的关系是可以满足精度
35
要求的。随着科学技术的进步,超短激光脉冲的出现和制冷水平的提高,存在着极高(低)
温条件下的传热问题和超急速传热问题,使得 Fourier 定律中的准平衡条件假设不再成立[1]。
为了克服 Fourier 定律的局限性,Cattaneo[2]和 Vernotte[3]独立的提出了具有热流延迟相
的非 Fourier 模型,计及热流变化率对热传导的影响,其修正的 Fourier 热传导方程为
(1)
基金项目:高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助项目(20090201120047)
作者简介:赵伟涛(1986-),男,在读博士,主要研究方向:工程热物理
通信联系人:吴九汇(1970-),男,教授、博士生导师,主要研究方向:纳米力学、光子晶体. E-mail:
ejhwu@mail.xjtu.edu.cn
- 1 -
0kTtqq�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
40
其中, 是热流矢量, 为温度, 为热传导率, 是时间, 为热松弛时间。方程(1)结合
能量守恒方程得到以温度 描述的双曲线型热传导方程
(2)
45
50
55
其中,
为热扩散系数, 为密度, 为常应变比热。
为了描述热以有限速度传播这一超常规热传导现象,研究者们在不同的初始和边界条件
下对方程(2)进行了求解。Ozisik[4]给出了在表面绝热,有内部热源条件下有限平板内的双曲
型热传导方程的解析解。Frankel[5]研究了有限平板在矩形脉冲边界条件下的双曲型热传导方
程。Tang[6,7]求解了表面周期性加热条件下有限介质的非 Fourier 热传导问题。Moosaie[8,9]在
Tang 的工作基础上,运用 Fourier 积分表达式,求解了在周期[8]或者非周期[9]表面热扰动条
件下有限介质的非 Fourier 热传导问题。Barletta[10]分析了无限圆柱体存在内热源以及与外界
流体有热对流的情况下的双曲型热传导。Sadd[11]使用 Laplace 变换法求解了圆筒内外区域一
维轴对称非 Fourier 热传导问题。Atefi[12]使用分离变量法求解了边界条件不随时间变化的无
限长圆筒的非 Fourie 温度场。Jiang[13]运用 Laplace 变换法研究了空心球体在内外两个表面温
度突然变化时的双曲型热传导问题。Moosaie[14]求解了在不随时间变化的线性边界条件下空
心球体的三维非 Fourier 温度场。Shirmohammadi[15]采用分离变量法得到空心球体在周期表
面热流条件下的解析解。
本文运用 Duhamel 积分得到了球体表面温度任意变化时双曲型热传导方程的解析解。
首先分析了温度突变边界条件和周期边界条件这两类特殊的情况下解的形式,之后应用
Fourier 级数展开法研究了一般边界条件下解的形式。按照这些表达式,不同边界条件下球
体的双曲线热传导行为得到分析和研究。这为工程应用和数值计算的验证提供了便利。
60
1 数学模型
考虑一半径为 ,热物性为常数的球体,假设其初始温度
,从时间 时起,
球体外表面
处遭受一温度为
的作用。在不考虑内热源和忽略热传导与热辐射的
情况下,一维球体的双曲线热传导方程为
65
其边界条件为
初始条件为
(3)
(4)
(5)
,
,
其中,
为任意给定的函数。
70
为了获得控制方程(3)、(4)、(5)的无量纲形式,特引入以下无量纲量
,
,
,
(6)
为了简便,省掉无量纲符号上方的‘ ’,则方程(3)、(4)、(5)无量纲化之后为
(7)
- 2 -
qTkt0T2202TTaTttakcc0r(,0)0Tr0t0rr0fft220222TTTaTattrrr0,0rTrtr00,Trtfft,00Tr0,0tTrtr0fft0TTf0rrr20attr0020ar220222TTTTttrrr�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
75
2 问题求解
,
,
(8)
(9)
由于边界条件(8)中的
是任意函数,这就使得直接求解方程(7)变得不可能。因此,
首先假定
为一时间无关量 ,求解此条件下的温度场;其次运用 Duhamel 积分,求解
在任意边界条件
下的温度场。现在,采用“边界条件齐次化”的方法求解在边界条件
(10)
(11)
,
(12)
80
下方程(7)的定解。
设解
且
85
90
要满足方程(11)和边界条件(12), 不妨设
( , , 是三个待定系
数),代入上式,求出 , , ,可得
。
的定解问题为
(13)
,
(14)
(15a)
(15b)
采用分离变量法求解偏微分方程(13),令
95
将式(13)代入方程(10),得到以下两个常微分方程
(16)
(17)
(18)
其中 为分离常数。球贝塞尔方程(17)在边界条件(14)下的本征值及相应的本征函数分别为
(19)
(20)
100
式中,
为半奇数阶贝塞尔函数。
方程(18)在边界条件(15b)下的解为
- 3 -
0,0rTrtr1,Ttft,00Tr0,0tTrtrftftfftf,=,,Trtrtrt220222ttrrr0,0rrtr1,tf,rt2,rtArBrCABCABC,rtf,rt220222ttrrr0,0rrtr1,0t1,0f0,0trtt,rtXrYt22220dXdXXdrrdr22020dYdYYdtdtnn12nnnnnAXrJrAQrr12nJr�
中国科技论文在线
式中
105
把式(20)和(21)代入方程(16)得
http://www.paper.edu.cn
(21)
(22)
(23)
式中,当
时, 为实数。
110
式(23)满足边界条件(15a),再利用特征函数(20)的正交性可得
因此
可以用下式表示
式中
115
(24)
(25)
(26)
(27)
方程(25)表示在边界条件不随时间变化时的温度场,当边界条件为任意随时间变化的量
时,运用 Duhamel 积分求解此条件下的温度场。
(28)
120
把式(24)代入(26)得到表面温度任意变化时,球体内部的温度场分布
式中
(29)
(30)
当
时,方程(7)对应傅里叶导热的情形。此时 为实数,式(30)变为
125
(31)
把式(22)代入式(31)进行整理得
(32)
- 4 -
002002111100sinhcosh 22sincos 22tnnnnnntnnnnnnttBeYtttBe实数20=1-4nn0022111110000,sinhcoshsincos2222ttNnnnnnnnnnnnnNttttrtCeQrCeQrnNn1201220cos2nnnnnnnnrQrdrCfffrQrdr,Trt,=,TrtRrtf1,1nnnnRrtGtQr002002111100sinhcosh 22sincos 22tnnnnntnnnnntteGttte实数ft0,,tRrtTrtfttdtt1,nnnnTrtMtQr0022000221110001sinh 221sin 22ttnnnnttnnnntefttdtMttefttdt实数00n002200001limsinh 22ttnnntMtefttdt220nttnnMtefttdt�
中国科技论文在线
3 计算与结果分析
http://www.paper.edu.cn
当半径为 的球体表面遭受一幅值为 ,角频率为 的周期温度变化时,无量纲化后
130
(33)
把式(33)代入式(29)得球体表面温度周期变化时球体内部的温度场分布
(34)
式中
(35)
135
对于 Fourier 导热,当
时,把式(33)代入(32)可得
把式(36)代入(29)得 Fourier 导热的温度分布
(36)
(37)
140
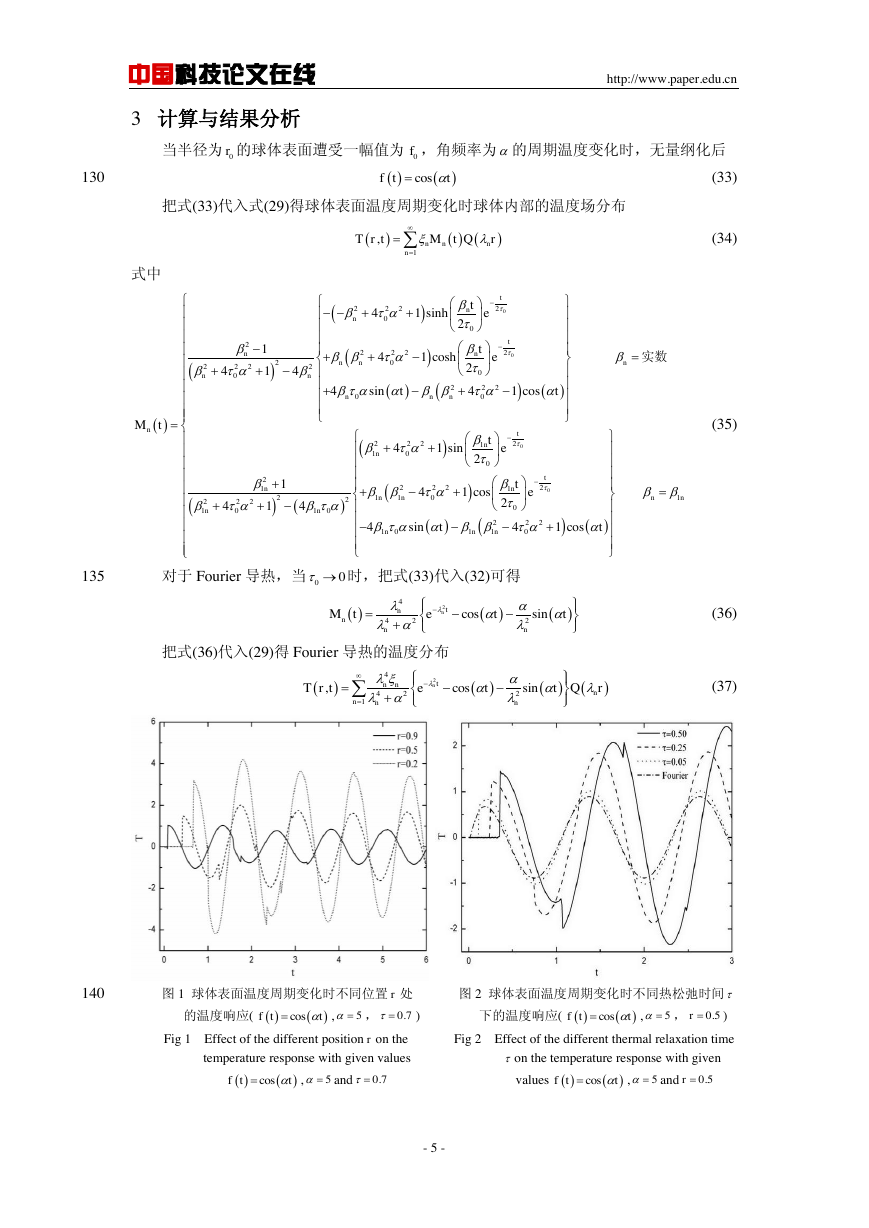
图 1 球体表面温度周期变化时不同位置 处 图 2 球体表面温度周期变化时不同热松弛时间
的温度响应(
,
,
) 下的温度响应(
,
,
)
Fig 1 Effect of the different position on the Fig 2 Effect of the different thermal relaxation time
temperature response with given values
on the temperature response with given
,
and
values
,
and
- 5 -
0r0fcosftt1,nnnnTrtMtQr00222200222220222220022200212222101041sinh2141cosh 24144sin41cos1414tnntnnnnnnnnnnnnnntetettMt实数0022221100222211101202221011041sin241cos 24sin41costnntnnnnnnnntetett0024422cossinntnnnnMtett244221,cossinntnnnnnnTrtettQrrcosftt50.7cosftt50.5rrcosftt50.7cosftt50.5r�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
145
使用式(34),我们可以计算得到半径为 的球体表面温度周期变化时球体内的温度分布。
图 1 给出了当球体表面温度周期变化(角频率
,热松弛时间
)时,球体不同位置 处
的温度相应,反映出了非 Fourier 热传导的瞬态温度特性。从图 3 可以看出每条曲线都存在
一系列阶跃点,它们表示温度波波前经过边界的传播和反射到达的时刻。由于热波的传播速
度为
,所以在位置 处,阶跃点位置为
,
,
,
,…。
150
由于扩散的作用,温度波的阶跃值和幅值随着 的减小而减小。图 1 还给出了同一位置的温
度波曲线的阶跃点随着时间的增加而减小并逐渐消失,曲线最终变成光滑的周期曲线。
图 2 给出了在角频率
的情况下,不同无量纲热松弛时间 下球体内(
处)无量
纲温度随无量纲时间的变化曲线,以及采用式(37)得到 Fourier 热传导模型下的温度响应曲
线。从图中可以看出,随着热松弛时间 的减小,热波的传播速度增大,热量能够迅速的传
155
递从而导致球体内温度响应的幅值也随之减小,非 Fourier 效应逐渐减弱。 越小,非 Fourier
和 Fourier 的温度响应曲线越接近。
4 结论
通过对球体在表面遭受一温度周期变化时的非 Fouier 热传导问题的分析求解与理论
计算,得到了非 Fouier 热传导模型的温度响应。通过与经典的 Fouier 热传导模型相比较,
160
非 Fouier 热传导模型具有明显的波前以及有限的热传播速度。温度波在具有一系列的阶跃
点,阶跃点位置和 成线性关系。热传导中非 Fouier 效应的存在主要取决于热松弛时间。
[参考文献] (References)
165
170
175
180
185
190
[1] 田晓耕,沈亚鹏. 广义热弹性问题研究进展[J]. 力学进展,2012,42(1):18-28.
[2] CATTANEO C. Sulla conduzione del calore[J]. Atti del Seminario Matematico e Fisico della Universita di
Modena, 1948, 3(3): 83-101.
[3] VERNOTTE P. Les paradoxes de la theorie continue deI'equation de la chaleur[J]. Compute Rendus, 1958,
246(22): 3154-3155.
[4] OZISIK M N, VICK B. Propagation and reflection of thermal waves in a finite medium[J]. International
Journal of Heat and Mass TransferInt, 1984, 27(10): 1845-1854.
[5] FRANKEL J I, VICK B,Ozisik M N. Flux formulation of hyperbolic heat conduction[J]. Journal of Applied
Physics, 1985, 58(9): 3340-3345.
[6] TANG D W, ARAKI N. Non-Fourier heat conduction in a finite medium under periodic surface thermal
disturbance[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1996, 39(8): 1585-1590.
[7] TANG D W, ARAKI N. Non-Fourier heat conduction in a finite medium under periodic surface thermal
disturbance-II. Another form of solution[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1996, 39(15):
3305-3308.
[8] MOOSAIE A. Non-Fourier heat conduction in a finite medium subjected to arbitrary periodic surface
disturbance[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2007, 34(8): 996-1002.
[9] MOOSAIE A. Non-Fourier heat conduction in a finite medium subjected to arbitrary non-periodic surface
disturbance[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2008, 35(3): 376-383.
[10] BARLETTA A, ZANCHINI E. Thermal-wave heat conduction in a solid cylinder which undergoes a change
of boundary temperature[J]. Heat Mass Transf, 1997, 32(4): 285-291.
[11] SADD N H, CHA C Y. Axisymmetric non-Fourier temperatures in cylindrically bounded domains[J].
International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 1982, 17(3): 129-136.
[12] ATEFI G, TALAEE M R. Non-fourier temperature field in a solid homogeneous finite hollow cylinder[J].
Archive of Applied Mechanics, 2011, 81(5): 569-583.
[13] JIANG F. Solution and analysis of hyperbolic heat propagation in hollow spherical objects[J]. Heat and Mass
Transfer, 2006 42(12): 1083-1091.
[14] MOOSAIE A. Axisymetric non-Fourier temperature field in a hollow sphere[J]. Archive of Applied
Mechanics, 2009, 79(8): 679-694.
[15] SHIRMOHAMMADI R, MOOSAIE A. Non-Fourier heat conduction in a hollow sphere with periodic surface
heat flux[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2009, 36(8): 827-833.
- 6 -
0r50.7r1r1tr1r3r3rr50.5r�











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc