Agile processes
Executive summary
STS are involved with Internet of Things (IoT) products. However, small
software products are currently more popular. The Waterfall process model is not
suitable for many of their future projects. This report will determine the advantages of
agile mindset by comparing agile mindset and waterfall process. The scale of software
is getting smaller and smaller. In order to maintain a competitive advantage and adapt
to the market, this report investigates the situation of agile methods. And based on
Scrum and XP methods to describe how to choose Scrum or XP criteria according to
the project. Analyze its process after selection.
Introduction
1 Overview of Agile Mindset
Agile mindset is a human-centric and iterative and gradual development method.
In agile mindset, the construction of a software project is divided into multiple
sub-projects. During this process, the software is always in a usable state. Its core is
rapid iteration and embrace change. Therefore, the agile mindset can actively accept
changes in requirements, which makes the designed software flexible and expandable.
The agile mindset model has the following notable characteristics:
1. Simple design, avoid over design.
2. Repeat the iteration.
3. Reduce unnecessary documents.
4. The functions that customers care about most are completed first.
5. Customers are required to have time to confirm the results of each iteration
and put forward suggestions for improvement.
6. Communication is very important. All developers should have the same
understanding of project activities. Strengthen communication between teams and
customers.
7. Agile mindset cannot give a complete cost plan for the project at
the
beginning.
8. It is not suitable to start iteration when there are technical problems that have
not been resolved.
�
2 Comparison of the Agile mindset and the Waterfall process
WM: Waterfall Model development is an old and outdated method of computer
software development. Waterfall development no longer has great demand. Waterfall
is no longer suitable for many projects. The main features of waterfall development
are as follows:
(1) Strictly define the inputs and outputs of each development stage.
(2) There is very little feedback between the various stages of the project.
(3) Only through documentation to understand the system in the early stage.
(4) Track each project phase through excessive mandatory completion dates and
milestones.
(5) The outstanding disadvantage of the waterfall model is that it does not adapt
to changes in user needs.
(6) Suitable for large-scale projects with relatively stable demand.
Compared with iterative development, both emphasize submitting software in a
shorter development cycle. However, the cycle of agile development may be shorter.
Agile methods are more accurate to say that agile methods emphasize adaptability
rather than predictability. When the needs of the project change, the team should
adapt quickly.
3 Description of Scrum process and XP methodology
Extreme Programming XP: Extreme Programming is a lightweight and smart
software development method. XP is a near-spiral development method. It breaks
down the complex development process into relatively simple small cycles. In this
way,
the development process can be adjusted in time according to the actual
situation.
Scrum process: Scrum is a process skeleton that includes a series of practices and
predefined roles. The main roles in Scrum include the Scrum supervisor role similar
to the project manager responsible for maintaining processes and tasks. The product
owner represents the interested owner. The development team includes all developers.
Conclusion
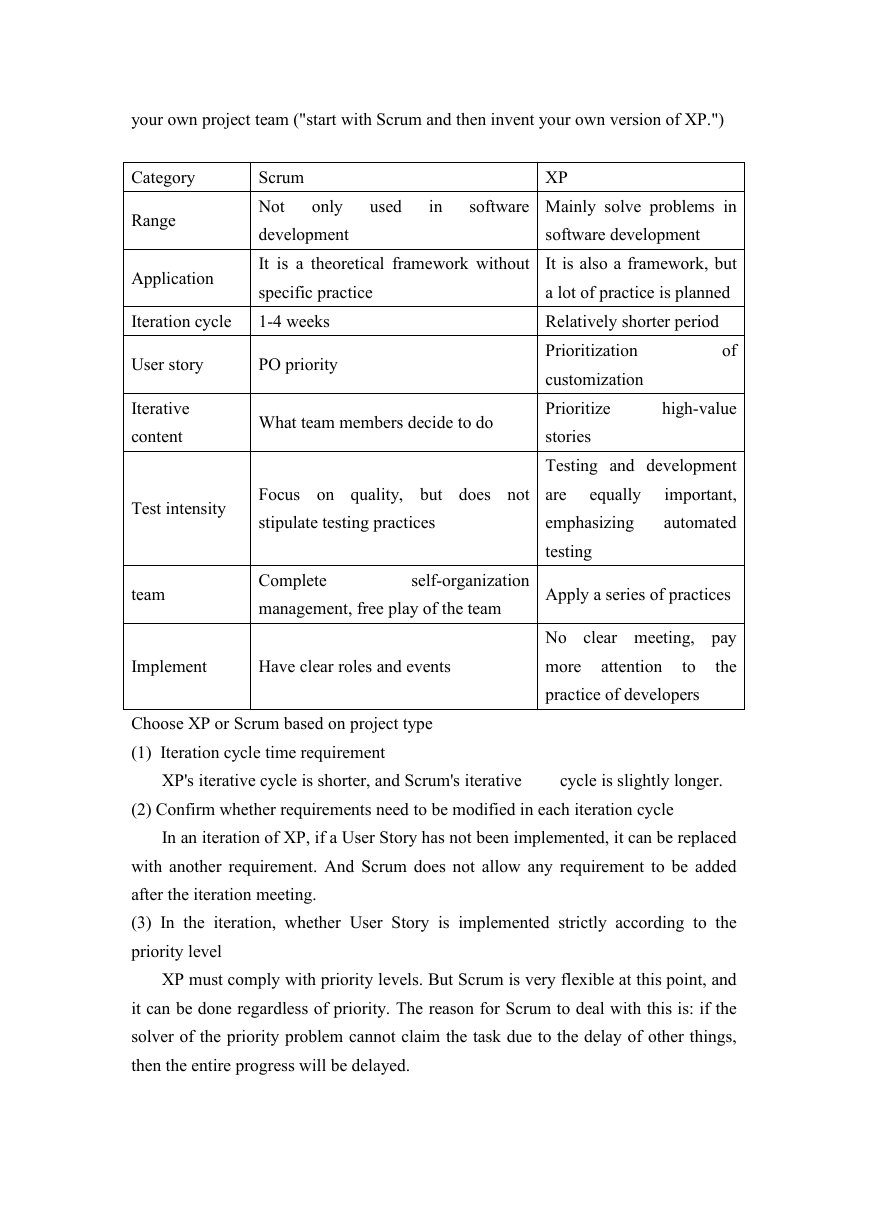
1 Guidelines for choosing Scrum or XP according to types of projects
Scrum highlights Self-Orgnization, XP focuses on strong engineering practice
constraints
Enable Scrum in management mode, and in practice, create an XP suitable for
�
your own project team ("start with Scrum and then invent your own version of XP.")
Category
Range
Application
Iteration cycle
used
in
software
Scrum
Not
only
development
It is a theoretical framework without
specific practice
1-4 weeks
User story
PO priority
Iterative
content
What team members decide to do
Test intensity
Focus on quality, but does not
stipulate testing practices
team
Complete
management, free play of the team
self-organization
Implement
Have clear roles and events
Choose XP or Scrum based on project type
(1) Iteration cycle time requirement
XP
Mainly solve problems in
software development
It is also a framework, but
a lot of practice is planned
Relatively shorter period
Prioritization
customization
Prioritize
stories
Testing and development
important,
are
equally
emphasizing
automated
testing
high-value
of
Apply a series of practices
No clear meeting, pay
more
to
the
practice of developers
attention
XP's iterative cycle is shorter, and Scrum's iterative
cycle is slightly longer.
(2) Confirm whether requirements need to be modified in each iteration cycle
In an iteration of XP, if a User Story has not been implemented, it can be replaced
with another requirement. And Scrum does not allow any requirement to be added
after the iteration meeting.
(3) In the iteration, whether User Story is implemented strictly according to the
priority level
XP must comply with priority levels. But Scrum is very flexible at this point, and
it can be done regardless of priority. The reason for Scrum to deal with this is: if the
solver of the priority problem cannot claim the task due to the delay of other things,
then the entire progress will be delayed.
�
2 XP engineering practice
1.Small Release
Each release version should be as small as possible. This way you can get more
feedback. Customers can understand the progress of the project in real time, so that
they can put forward more opinions to plan in the next iteration. In order to achieve
higher customer satisfaction.
2. The Planning Game/Planning Strategy
The main idea of planning the game is to quickly develop a summary plan and
gradually improve it. The scope of the system, the release time of the next iteration,
and the priority of user stories should be determined by the customer. The
development time required for each user story, the cost of different technologies, how
to form the team, the risk of each user story, and the specific development sequence
should be determined by the development team.
3. On-site Customer
In order to ensure that the development results are close to the customer's expectations,
XP methodology believes that the most important need is to invite customers to the
development site. Therefore, it is very important for the XP project to have customers
clarify user stories on site and make corresponding business decisions in the project.
4. Simple Design
The simple design of XP should not be done all at once before coding
5. Pair programming
All the software is completed by two programmers sitting side by side on the same
machine.
6. Testing
Writing unit tests is a verification activity. Writing unit tests avoids a considerable
number of feedback loops, especially in functional verification.
7.Refractoring
Refactoring is a way to improve the code without affecting the function
implementation. XP requires developers to have the courage to refactor the code.
8. Continuous Integration
The meaning of continuous integration is to require the XP team to do code
integration as many times as possible every day, each time after the unit test to ensure
that the system runs. In this way, errors caused by refactoring and collective code
ownership can be exposed and eliminated early. After one commits, everyone else is
responsible for code integration.
�
9. Collective Code Ownership
Any pair of programmers can improve any code at any time.
10. Code Standards
XP methodology believes that having coding standards can prevent teams from
arguing over details that are not related to the development schedule.
11. System Metaphor
It is the future image of the system, a global view that links the entire system together;
it makes the location and appearance of all individual modules obvious and intuitive.
refactoring, etc. to restrict team behavior.
3 Scrum process
1. Determine a Product Backlog that is responsible for the Product Owner.
2. The Scrum Team estimates and arranges the workload according to the Product
Backlog list.
3. Through the Sprint Planning Meeting, select a Story as the goal for this iteration.
The time period of this goal is 1 to 4 weeks, and then refine the Story to form a Sprint
Backlog.
4. The Sprint Backlog is completed by the Scrum Team, and each member is refined
into smaller tasks according to the Sprint Backlog.
5. When the Scrum Team completes the Sprint Backlog selected in the planning
meeting, a Daily Scrum Meeting is required.
6. Achieve daily integration for testing, and release the version after successful
testing.
7. When
demonstrate to them the software product they have completed.
8. The last is Sprint Retrospective Meeting. Everyone has to speak, summarize and
discuss improvements, and put
round of Sprint product
requirements.
Sprint Backlog is completed, every member of the Scrum Team must
them into the next
Reference
[1]Todd R Weiss. To Create an Agile Company, Find Workers with an Agile
Mindset[J]. SQL Server Pro,2018.
[2]Svenja Hofert. Das agile Mindset[M].Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden:2018-01-01.
[3]Mali Senapathi,Meghann L. Drury-Grogan. Refining a model for sustained usage
of agile methodologies[J]. The Journal of Systems & Software,2017,132.
�
[4]Stephen Denning. Agile’s
Leadership,2016,44(5).
ten implementation challenges[J]. Strategy &
�











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc