程序如下:
1.重构
% mallet_wavelet.m
% 此函数用于研究 Mallet 算法及滤波器设计
% 此函数仅用于消噪
a=pi/8; %角度赋初值
b=pi/8;
%低通重构 FIR 滤波器 h0(n)冲激响应赋值
h0=cos(a)*cos(b);
h1=sin(a)*cos(b);
h2=-sin(a)*sin(b);
h3=cos(a)*sin(b);
low_construct=[h0,h1,h2,h3];
L_fre=4; %滤波器长度
low_decompose=low_construct(end:-1:1); %确定 h0(-n),低通分解滤波器
for i_high=1:L_fre; %确定 h1(n)=(-1)^n,高通重建滤波器
if(mod(i_high,2)==0);
coefficient=-1;
else
coefficient=1;
end
high_construct(1,i_high)=low_decompose(1,i_high)*coefficient;
end
high_decompose=high_construct(end:-1:1); %高通分解滤波器 h1(-n)
L_signal=100; %信号长度
n=1:L_signal; %信号赋值
f=10;
t=0.001;
y=10*cos(2*pi*50*n*t).*exp(-20*n*t);
�
figure(1);
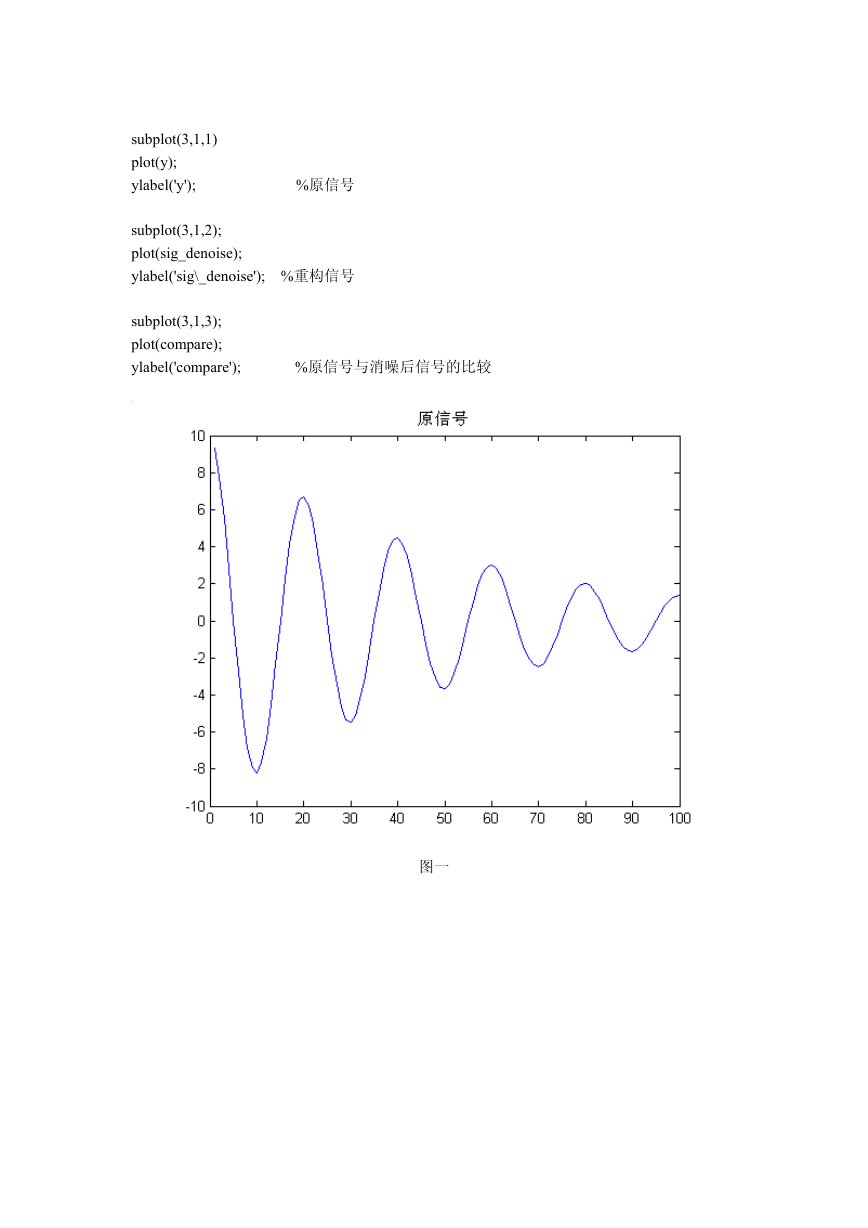
plot(y);
title('原信号');
check1=sum(high_decompose); %h0(n)性质校验
check2=sum(low_decompose);
check3=norm(high_decompose);
check4=norm(low_decompose);
l_fre=conv(y,low_decompose); %卷积
l_fre_down=dyaddown(l_fre); %抽取,得低频细节
h_fre=conv(y,high_decompose);
h_fre_down=dyaddown(h_fre); %信号高频细节
figure(2);
subplot(2,1,1)
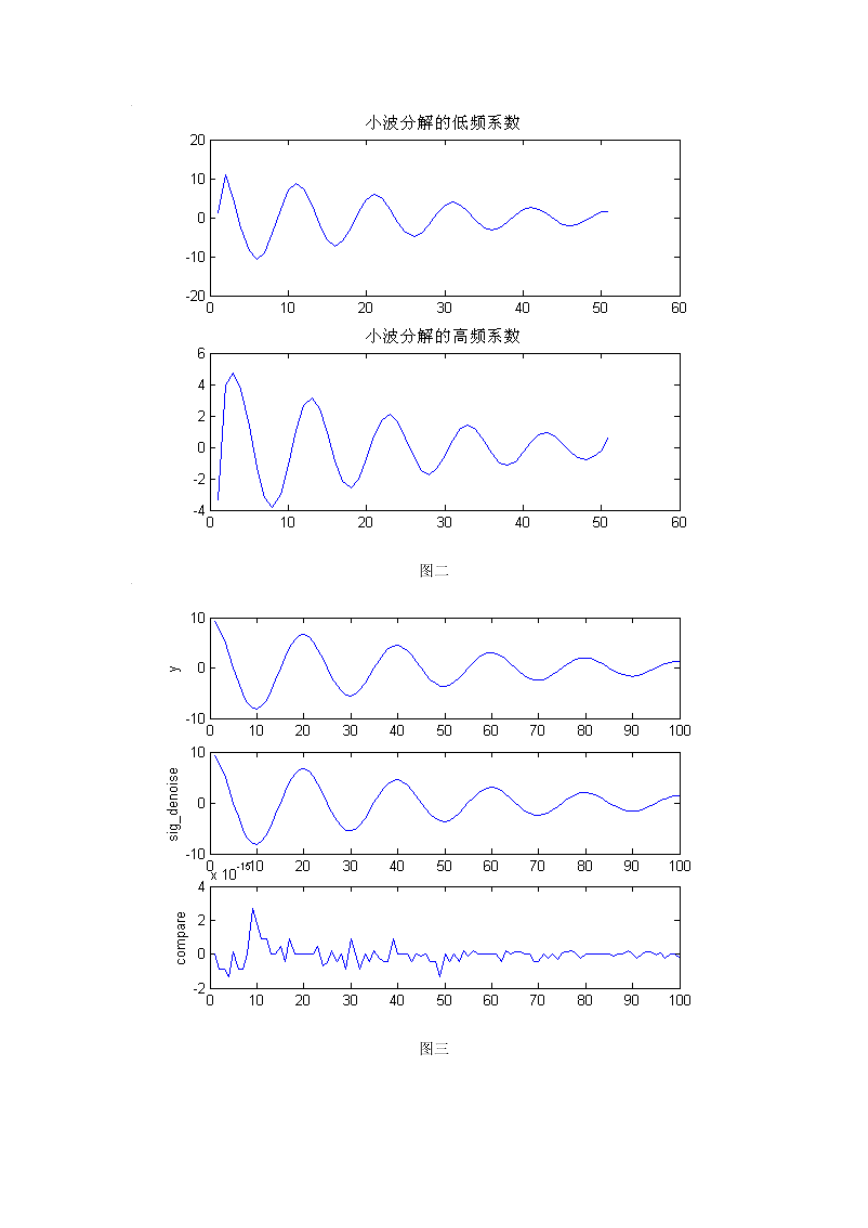
plot(l_fre_down);
title('小波分解的低频系数');
subplot(2,1,2);
plot(h_fre_down);
title('小波分解的高频系数');
l_fre_pull=dyadup(l_fre_down); %0 差值
h_fre_pull=dyadup(h_fre_down);
l_fre_denoise=conv(low_construct,l_fre_pull);
h_fre_denoise=conv(high_construct,h_fre_pull);
l_fre_keep=wkeep(l_fre_denoise,L_signal); %取结果的中心部分,消除卷积影响
h_fre_keep=wkeep(h_fre_denoise,L_signal);
sig_denoise=l_fre_keep+h_fre_keep; %信号重构
compare=sig_denoise-y; %与原信号比较
figure(3);
�
subplot(3,1,1)
plot(y);
ylabel('y'); %原信号
subplot(3,1,2);
plot(sig_denoise);
ylabel('sig\_denoise'); %重构信号
subplot(3,1,3);
plot(compare);
ylabel('compare'); %原信号与消噪后信号的比较
图一
�
图二
图三
�
2.消噪
% mallet_wavelet.m
% 此函数用于研究 Mallet 算法及滤波器设计
% 此函数用于消噪处理
%角度赋值
%此处赋值使滤波器系数恰为 db9
%分解的高频系数采用 db9 较好,即它的消失矩较大
%分解的有用信号小波高频系数基本趋于零
%对于噪声信号高频分解系数很大,便于阈值消噪处理
[l,h]=wfilters('db10','d');
low_construct=l;
L_fre=20; %滤波器长度
low_decompose=low_construct(end:-1:1); %确定 h0(-n),低通分解滤波器
for i_high=1:L_fre; %确定 h1(n)=(-1)^n,高通重建滤波器
if(mod(i_high,2)==0);
coefficient=-1;
else
coefficient=1;
end
high_construct(1,i_high)=low_decompose(1,i_high)*coefficient;
end
high_decompose=high_construct(end:-1:1); %高通分解滤波器 h1(-n)
L_signal=100; %信号长度
n=1:L_signal; %原始信号赋值
f=10;
t=0.001;
�
y=10*cos(2*pi*50*n*t).*exp(-30*n*t);
zero1=zeros(1,60); %信号加噪声信号产生
zero2=zeros(1,30);
noise=[zero1,3*(randn(1,10)-0.5),zero2];
y_noise=y+noise;
figure(1);
subplot(2,1,1);
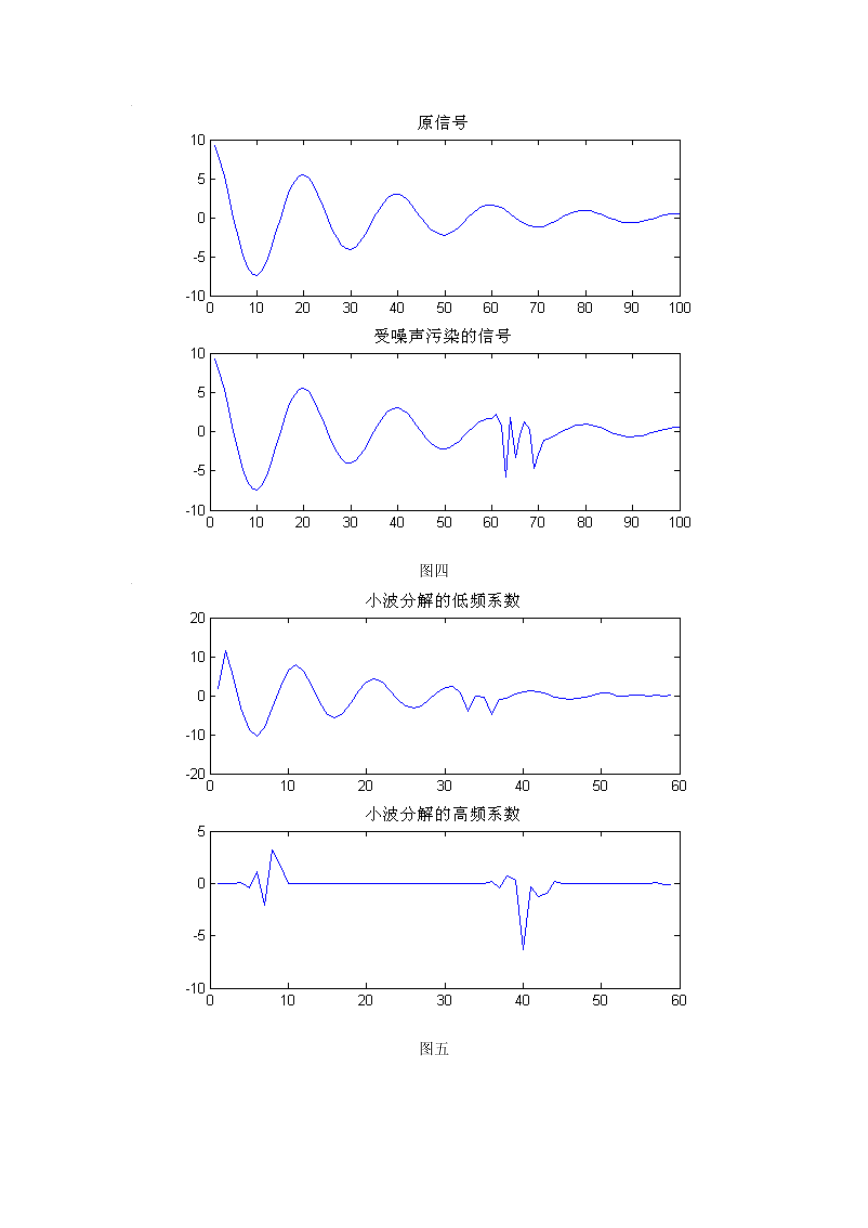
plot(y);
title('原信号');
subplot(2,1,2);
plot(y_noise);
title('受噪声污染的信号');
check1=sum(high_decompose); %h0(n),性质校验
check2=sum(low_decompose);
check3=norm(high_decompose);
check4=norm(low_decompose);
l_fre=conv(y_noise,low_decompose); %卷积
l_fre_down=dyaddown(l_fre); %抽取,得低频细节
h_fre=conv(y_noise,high_decompose);
h_fre_down=dyaddown(h_fre); %信号高频细节
figure(2);
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(l_fre_down);
title('小波分解的低频系数');
subplot(2,1,2);
plot(h_fre_down);
title('小波分解的高频系数');
% 消噪处理
for i_decrease=31:44;
if abs(h_fre_down(1,i_decrease))>=0.000001
h_fre_down(1,i_decrease)=(10^-7);
end
�
end
l_fre_pull=dyadup(l_fre_down); %0 差值
h_fre_pull=dyadup(h_fre_down);
l_fre_denoise=conv(low_construct,l_fre_pull);
h_fre_denoise=conv(high_construct,h_fre_pull);
l_fre_keep=wkeep(l_fre_denoise,L_signal); %取结果的中心部分,消除卷积影响
h_fre_keep=wkeep(h_fre_denoise,L_signal);
sig_denoise=l_fre_keep+h_fre_keep; %消噪后信号重构
%平滑处理
for j=1:2
for i=60:70;
sig_denoise(i)=sig_denoise(i-2)+sig_denoise(i+2)/2;
end;
end;
compare=sig_denoise-y; %与原信号比较
figure(3);
subplot(3,1,1)
plot(y);
ylabel('y'); %原信号
subplot(3,1,2);
plot(sig_denoise);
ylabel('sig\_denoise'); %消噪后信号
subplot(3,1,3);
plot(compare);
ylabel('compare'); %原信号与消噪后信号的比较
�
图四
图五
�













 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc