GEATbx com
Genetic and Evolutionary Algorithm Toolbox for Matlab
GEATbx Examples
Examples of
Objective Functions
by:
Hartmut Pohlheim
GEATbx version 3.8
(December 2006)
www.geatbx.com
support@geatbx.com
�
�
Contents
1 Introduction ..................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Examples of Parametric Optimization............................................................................ 1
1.2 Examples of Multi-objective Optimization.................................................................... 1
2 Parametric Optimization................................................................................ 3
2.1 De Jong's function 1 ....................................................................................................... 3
2.2 Axis parallel hyper-ellipsoid function............................................................................ 3
2.3 Rotated hyper-ellipsoid function .................................................................................... 4
2.4 Moved axis parallel hyper-ellipsoid function................................................................. 5
2.5 Rosenbrock's valley (De Jong's function 2) ................................................................... 5
2.6 Rastrigin's function 6...................................................................................................... 6
2.7 Schwefel's function 7...................................................................................................... 7
2.8 Griewangk's function 8................................................................................................... 7
2.9 Sum of different power function 9 ................................................................................. 8
2.10 Ackley's Path function 10............................................................................................. 9
2.11 Langermann's function 11 .......................................................................................... 10
2.12 Michalewicz's function 12.......................................................................................... 10
2.13 Branins's rcos function ............................................................................................... 11
2.14 Easom's function......................................................................................................... 12
2.15 Goldstein-Price's function .......................................................................................... 12
2.16 Six-hump camel back function................................................................................... 13
3 Multi-objective Optimization....................................................................... 15
3.1 Fonseca's function 1 and 2............................................................................................ 15
Index ................................................................................................................... 17
www.geatbx.com
GEATbx Examples
�
�
1 Introduction
This document describes a number of test functions implemented for use with the Genetic and Evolutionary Al-
gorithm Toolbox for Matlab (GEATbx). These functions are drawn from the literature on evolutionary algo-
rithms and global optimization. The first Section describes a set of common parametric test problems imple-
mented as Matlab m-files. The second Section presents a number of dynamic systems, implemented in Simulink,
as s-files and m-files as appropriate.
1.1 Examples of Parametric Optimization
Each of the functions in Chapter 2 is described by the function definition, one or more 3-D graphics to show the
properties of the function and a description of the features of the function.
1.2 Examples of Multi-objective Optimization
The functions in Chapter 3 constitute multi-objective example functions. For each of them the definition and a
description of the features of the function are given. Plots of the PARETO-front in search and solution space
enhance the understanding of the functions. If useful, 3-D graphics showing the search space are provided.
All of the test function implementations are scaleable, i.e. the functions can be called with as many dimensions
as necessary and the default dimension of the test functions is adjustable via a single parameter value inside the
function.
For writing own objective functions see Writing objective functions.
www.geatbx.com
GEATbx Examples
�
�
2 Parametric Optimization
2.1 De Jong's function 1
The simplest test function is De Jong's function 1. It is also known as sphere model. It is continuos, convex and
unimodal.
function definition:
( )
xf
1
n
= ∑
x
i
x
2
i
≤
12.5
−
12.5
≤
i
1
=
f1(x)=sum(x(i)^2), i=1:n, -5.12<=x(i)<=5.12.
global minimum:
f(x)=0, x(i)=0, i=1:n.
This function is implemented in objfun1.
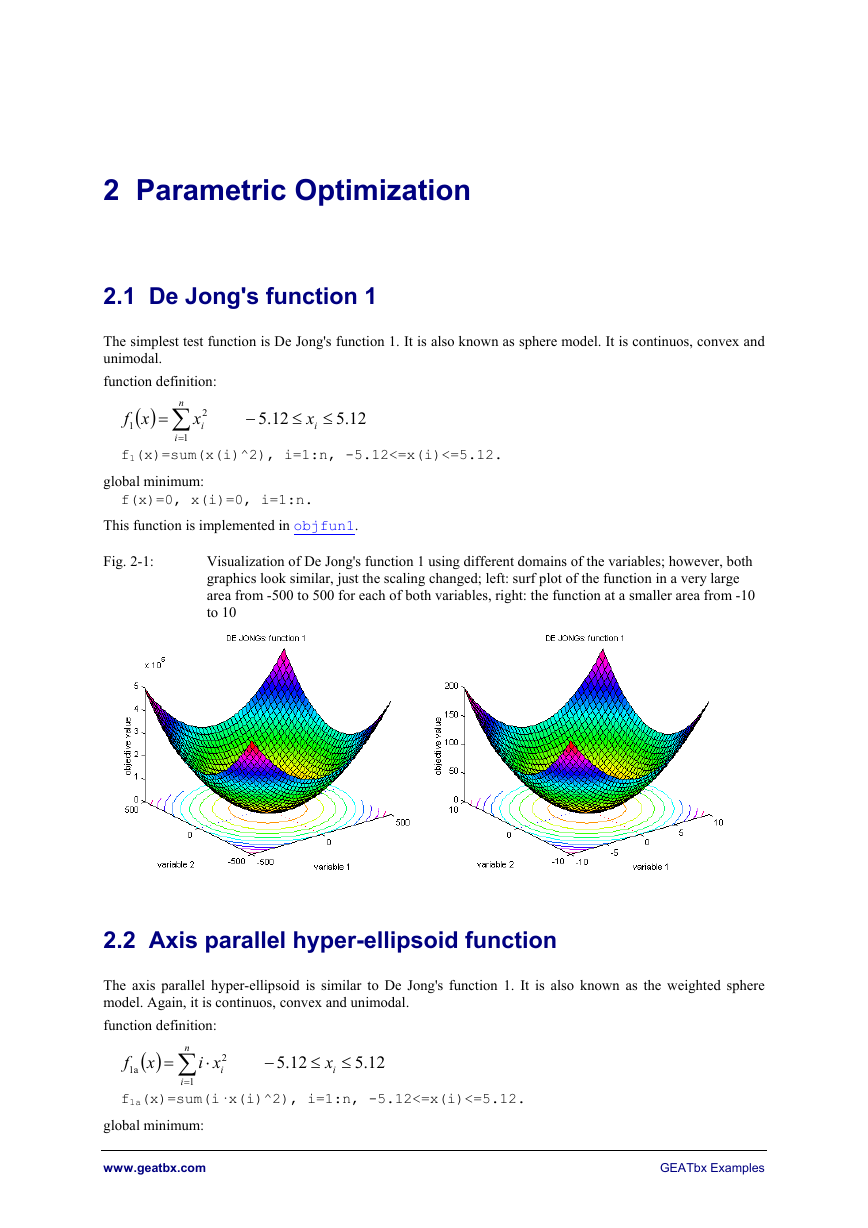
Fig. 2-1:
Visualization of De Jong's function 1 using different domains of the variables; however, both
graphics look similar, just the scaling changed; left: surf plot of the function in a very large
area from -500 to 500 for each of both variables, right: the function at a smaller area from -10
to 10
2.2 Axis parallel hyper-ellipsoid function
The axis parallel hyper-ellipsoid is similar to De Jong's function 1. It is also known as the weighted sphere
model. Again, it is continuos, convex and unimodal.
function definition:
( )
x
n
= ∑
f
a1
xi
2
⋅
i
−
12.5
≤
f1a(x)=sum(i·x(i)^2), i=1:n, -5.12<=x(i)<=5.12.
global minimum:
1
=
i
≤
12.5
x
i
www.geatbx.com
GEATbx Examples
�
4
2 Parametric Optimization
f(x)=0; x(i)= 0, i=1:n.
This function is implemented in objfun1a.
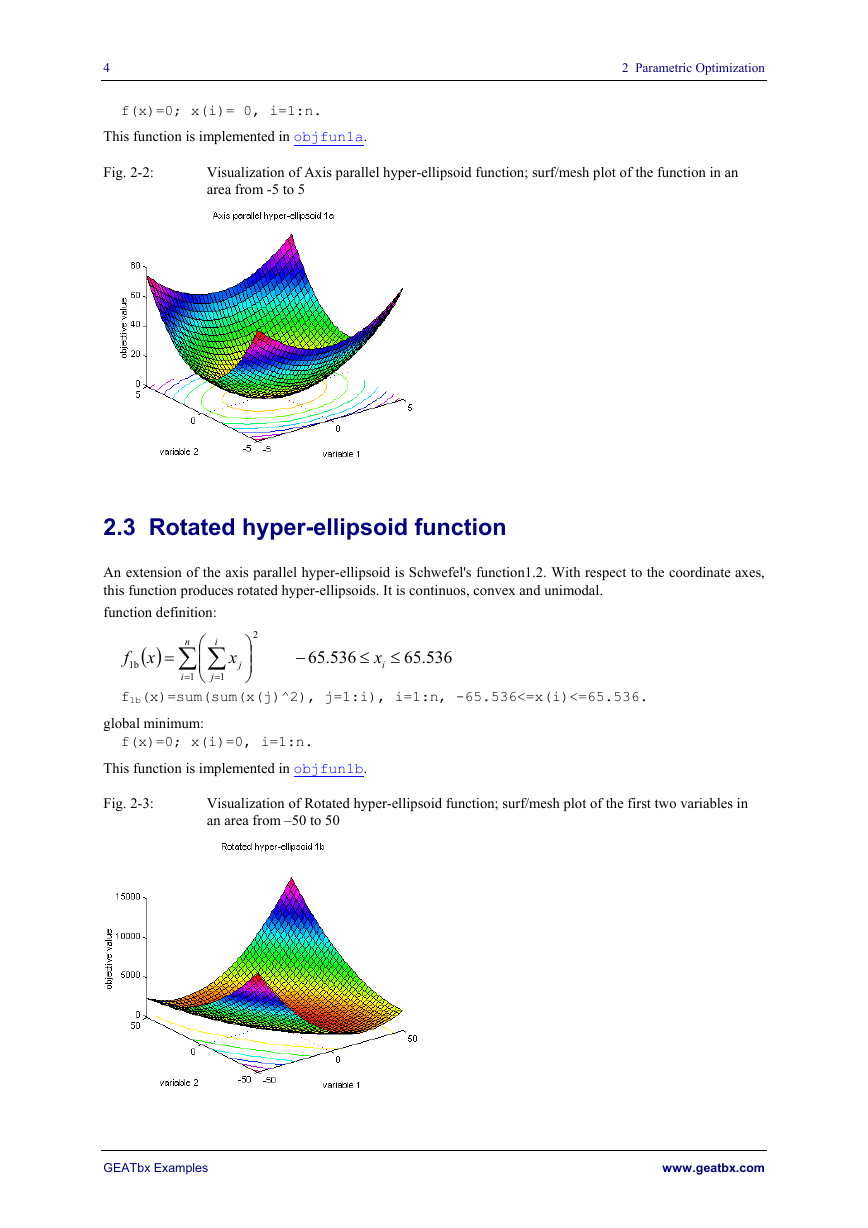
Fig. 2-2:
Visualization of Axis parallel hyper-ellipsoid function; surf/mesh plot of the function in an
area from -5 to 5
2.3 Rotated hyper-ellipsoid function
An extension of the axis parallel hyper-ellipsoid is Schwefel's function1.2. With respect to the coordinate axes,
this function produces rotated hyper-ellipsoids. It is continuos, convex and unimodal.
function definition:
f
b1
( )
x
= ∑ ∑
x
j
i
1
=
j
1
=
2
−
536.65
≤
x
i
≤
536.65
n
i
⎛
⎜⎜
⎝
⎞
⎟⎟
⎠
f1b(x)=sum(sum(x(j)^2), j=1:i), i=1:n, -65.536<=x(i)<=65.536.
global minimum:
f(x)=0; x(i)=0, i=1:n.
This function is implemented in objfun1b.
Fig. 2-3:
Visualization of Rotated hyper-ellipsoid function; surf/mesh plot of the first two variables in
an area from –50 to 50
GEATbx Examples
www.geatbx.com
�














 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc