COMSOL 4.2 Tutorial
COMSOL Multiphysics (formerly FEMLAB) is a finite element analysis, solver
and Simulation
software / FEA Software package
for
various physics and
engineering applications,
especially
coupled phenomena, or multiphysics.
COMSOL Multiphysics also offers an extensive interface to MATLAB and its
toolboxes for a large variety of programming, preprocessing and postprocessing
possibilities. The packages are cross-platform (Windows, Mac, Linux,Unix.) In
addition to conventional physics-based user-interfaces, COMSOL Multiphysics
also allows for entering coupled systems of partial differential equations (PDEs).
How to create a new model in COMSOL
1. Start COMSOL Multiphysics
2. Work through the COMSOL Model Wizard which will require you to select the
coordinate system for the model, the relevant physics to the problem, and the type
of study you wish to perform (Time dependant or stationary).
3. Define the parameters, equations and variables pertinent to the model (sub
directory (Global Definitions).
4. Define the geometry of the model (Geometry).
5. Select the materials you wish to use in your model (Materials).
�
6. Select the boundary, bulk and initial conditions for your system for each physics
you are using (This will be entered separately for each different physics you are
using e.g. you will need to enter these for Laminar Flow and again for Heat
Transfer if you are using both ).
7. Choose the element size to be used (Mesh).
8. Adjust solver parameters and compute (Study).
10. Display the desired results in the most meaningful way (Results).
Not all of these steps are always necessary when building a model. The order is
also variable depending on the complexity of the model.
Example 1. (Heat transfer)
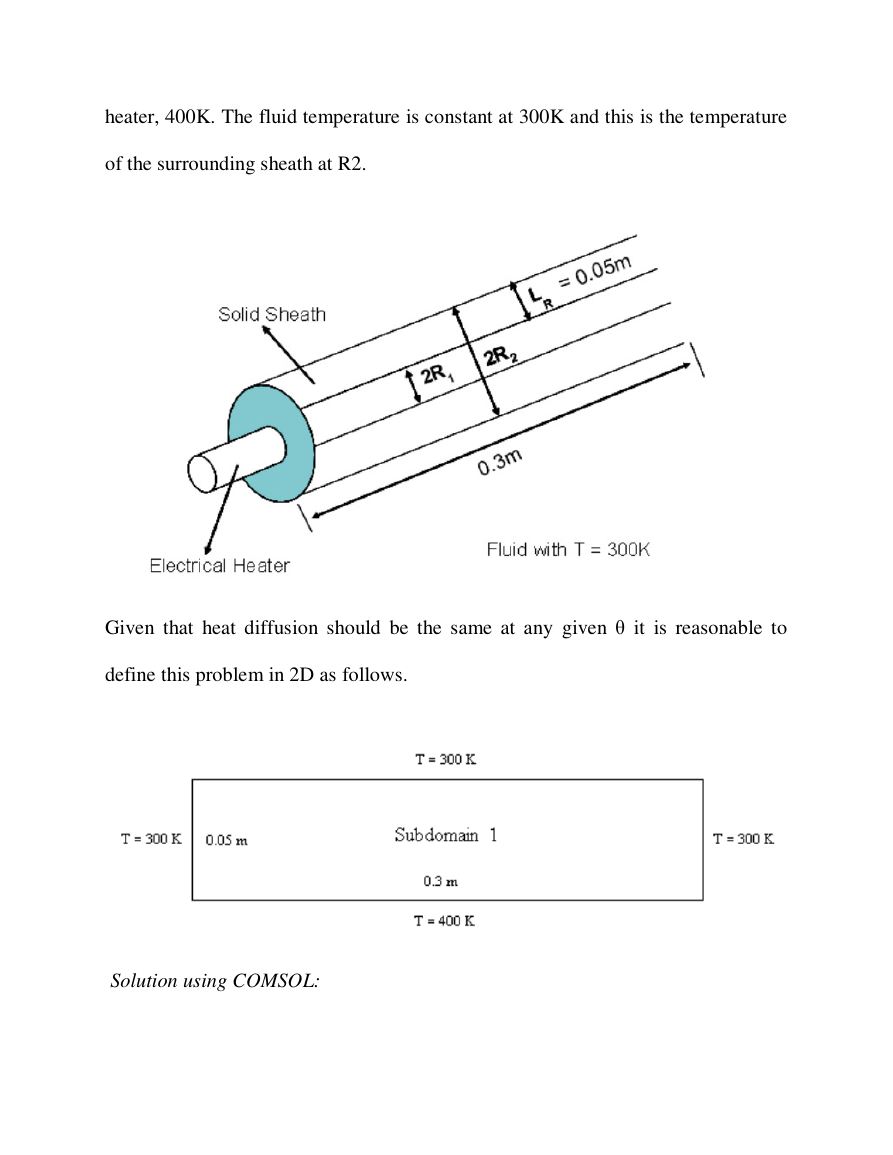
Consider a cylindrical heating rod which is sheathed by a concentric tube of
thickness 0.05 m and which starts 0.05 m away from the center. The entire
assembly is immersed in a fluid and the system is at steady-state, as shown below.
We wish to determine the temperature distribution within the sheath. After
thinking about
the problem, assume
that we arrived at
the following
approximations (make sure you understand how we arrived at following
approximations for your future quiz and test): The temperature of the heater is
constant at 400K. The temperature at R1 is the same as the temperature of the
�
heater, 400K. The fluid temperature is constant at 300K and this is the temperature
of the surrounding sheath at R2.
Given that heat diffusion should be the same at any given θ it is reasonable to
define this problem in 2D as follows.
Solution using COMSOL:
�
Startup
1. Start COMSOL by clicking the
COMSOL Multiphysics 4.2 icon.
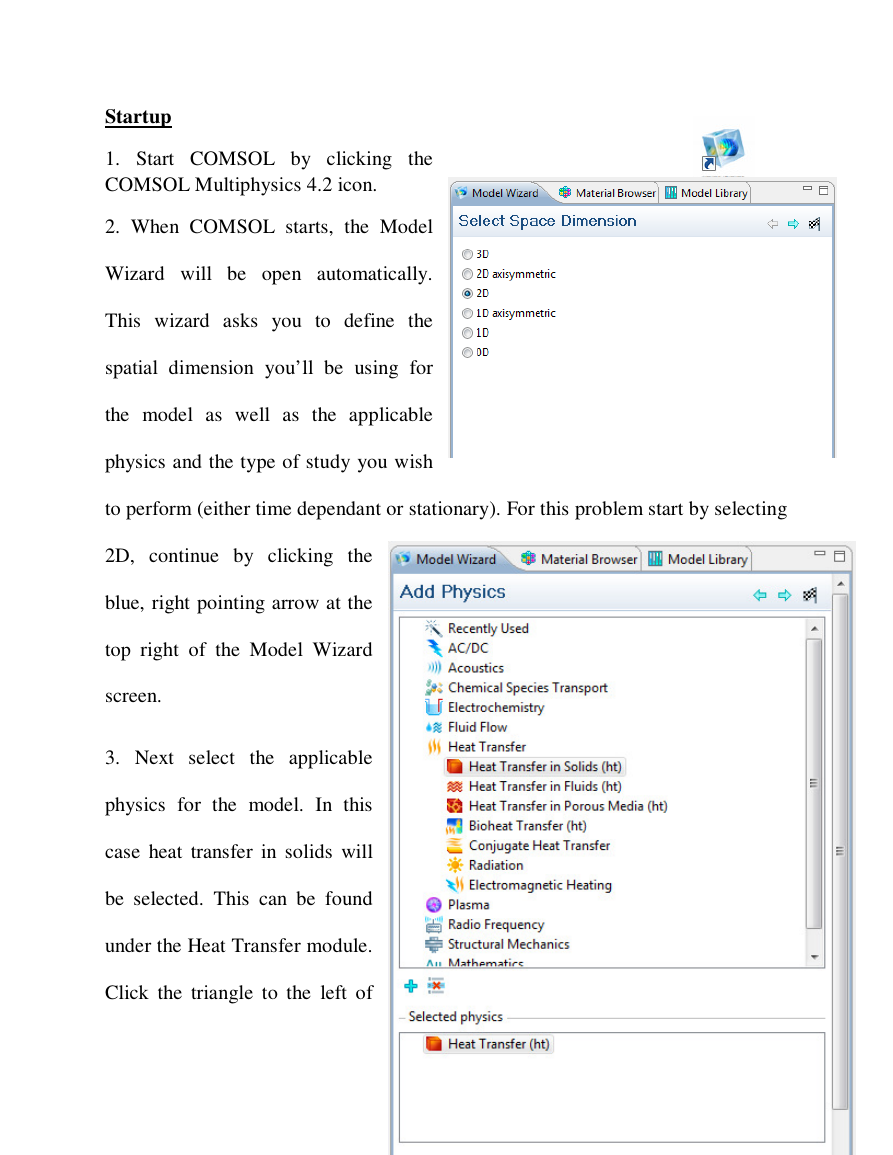
2. When COMSOL starts, the Model
Wizard will be open automatically.
This wizard asks you to define the
spatial dimension you’ll be using for
the model as well as the applicable
physics and the type of study you wish
to perform (either time dependant or stationary). For this problem start by selecting
2D, continue by clicking the
blue, right pointing arrow at the
top right of the Model Wizard
screen.
3. Next select the applicable
physics for the model. In this
case heat transfer in solids will
be selected. This can be found
under the Heat Transfer module.
Click the triangle to the left of
�
the Heat Transfer module to see the drop down menu which contains Heat Transfer
in Solids, left click this so that it is highlighted then click the blue, right pointing
arrow at the top right of the Model Wizard menu screen. Multiple physics can be
added to a single model by left clicking the physics to add and then left clicking
the blue + sign at the bottom left of the Model Wizard menu screen.
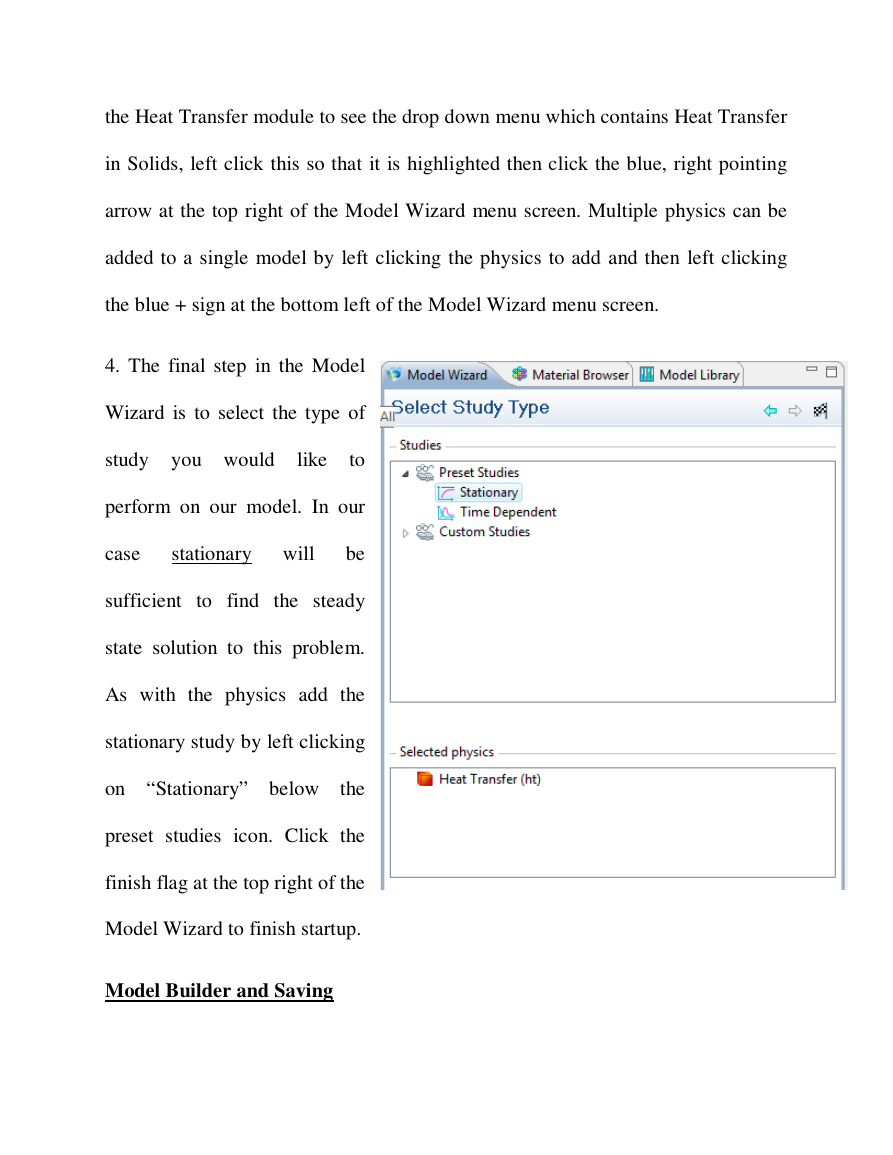
4. The final step in the Model
Wizard is to select the type of
study you would
like
to
perform on our model. In our
case
stationary will
be
sufficient to find the steady
state solution to this problem.
As with the physics add the
stationary study by left clicking
on “Stationary” below
the
preset studies icon. Click the
finish flag at the top right of the
Model Wizard to finish startup.
Model Builder and Saving
�
Now that we are finished with the Model Wizard we will turn our attention to the
Model Builder portion of the program. This
is just to the left of where the Model
Wizard had been. Before we continue with
the Model Builder let us take a second to
save our model. This is done by clicking
“File” at the top left of the screen and then
selecting “Save As” as is the case with most programs. This file will be named
“Heat Transfer Example”. By default COMSOL will save all COMSOL files in a
folder it creates called COMSOL42 however this folder name will change with the
version of COMSOL being used. After giving our file a name and clicking the save
button seen in the above image notice that the first icon within the model builder
now has the name of our file. From
this point on we can essentially just work our way down the Model Builder’s list of
options filling in values and conditions where we need them.
�
Geometry
Now we are ready to add the geometry of
the model. This is very simple because our
assumptions have placed the problem into
only 2 dimensions. Our geometry consists
of only of a rectangle.
1. To create this rectangle first find the
geometry icon in the model builder menus
and right click it, this will bring up the
menu shown at right.
2. Find the “Rectangle” button in this new
menu and left click this.
3. At this point the rectangle has been added, however the dimensions of this
rectangle need to be changed to fit the dimensions in the problem. We do this by
left clicking the white rectangle just to the left of the geometry icon. This will
expand the geometry tab to show all the sub tabs contained within geometry. If you
added the rectangle correctly you will see the tab called Rectangle 1. This contains
all the information regarding this object and to adjust the dimensions and position
of this rectangle this is where we do so. Left click the tab labeled Rectangle 1.
�
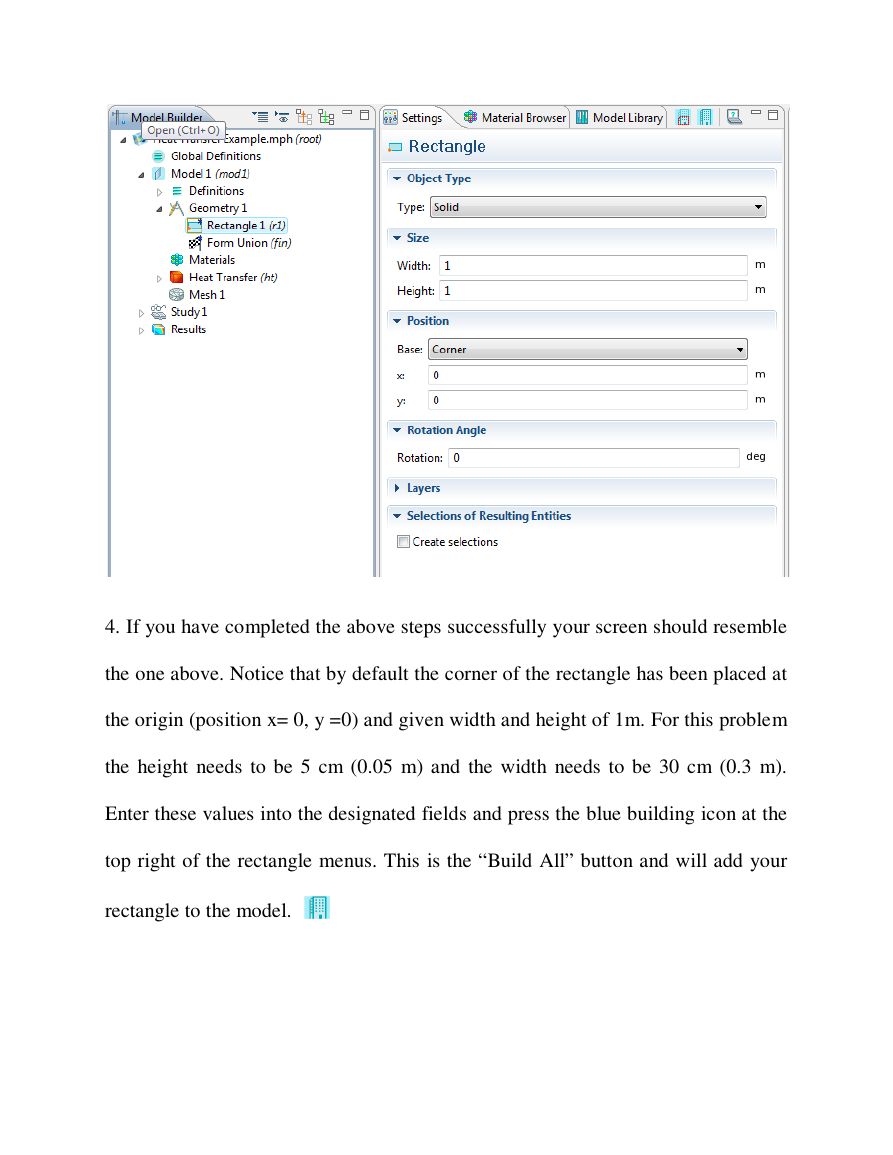
4. If you have completed the above steps successfully your screen should resemble
the one above. Notice that by default the corner of the rectangle has been placed at
the origin (position x= 0, y =0) and given width and height of 1m. For this problem
the height needs to be 5 cm (0.05 m) and the width needs to be 30 cm (0.3 m).
Enter these values into the designated fields and press the blue building icon at the
top right of the rectangle menus. This is the “Build All” button and will add your
rectangle to the model.
�












 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc