1Cognitive Psychology and the Brain
Introduction
Defining Cognitive Psychology
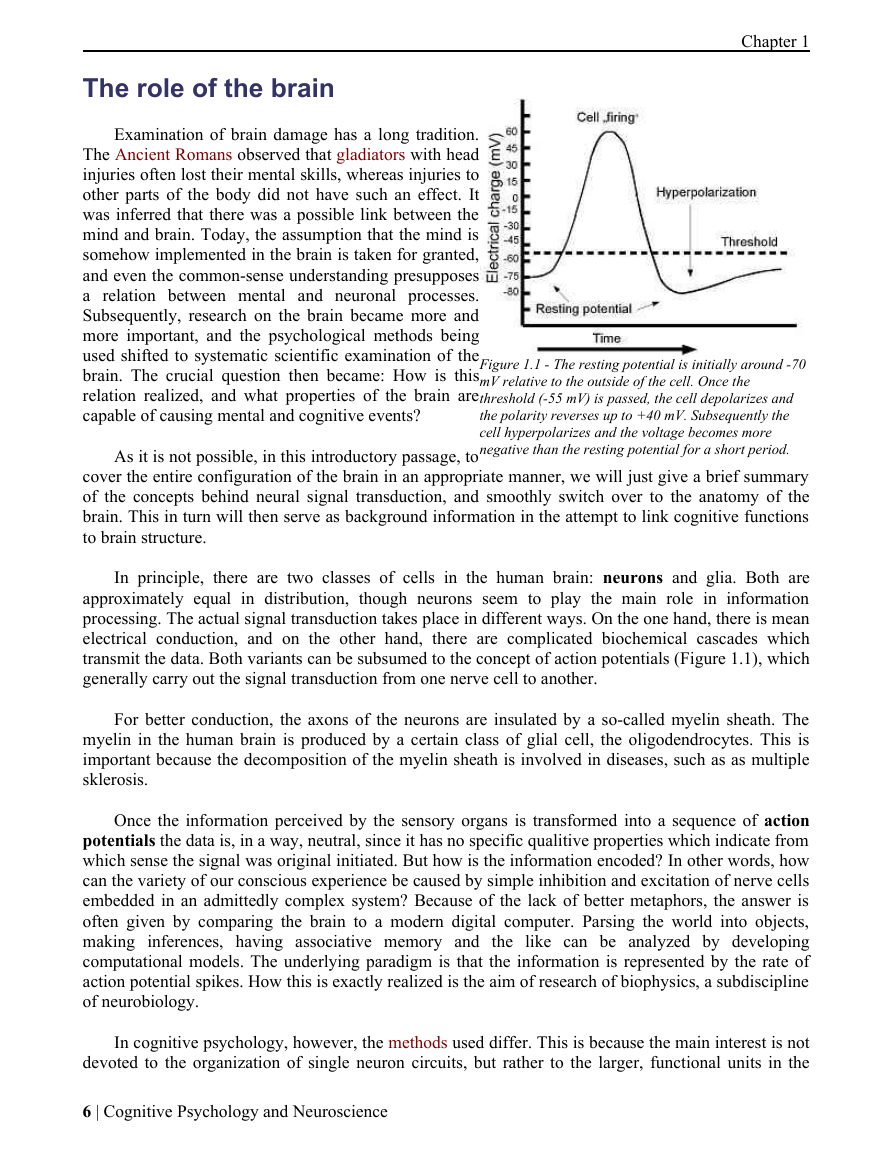
The role of the brain
References
Links
2Problem Solving from an Evolutionary Perspective
Introduction
Insight
Fixation
Problem Solving - Modern Approaches
Problem Solving as a Search Problem
Means-End Analysis
Analogies
Restructuring by Using Analogies
Schema
How do Experts Solve Problems?
Divergent Thinking
The Evolutionary Perspective
Natural Selection
Adaptation As a Result of Natural Selection
Psychological Adaptation
Adaptations May Be Out-of-Date
Sexual Selection
Altruism
Reciprocal Behaviour
(Iterative) Prisoner's Dilemma
Consciousness
Evolution of Consciousness
Neuropsychology and Consciousness
Blindsight[6]
Commissurotomy (split-brain)[6]
Hemineglect[21]
Anosognosia[6]
Problem Solving and Consciousness
Review
References
Links
3Evolutionary Perspective on Social Cognitions
Introduction
From selection to sociality
Group Selection
Kin Selection
Reciprocal Alturism
Possible selection pressures favoring human sociality
Social Cognition
The human faculty of social cognition
Understanding intentional action
Shared intentionality
References
4Behavioral and Neuroscience Methods
Introduction
Studies on humans with brain damages
Lesion method
Areas where it is used
Problems which can occur
single case studies
Techniques for Assessing Brain Anatomy
CAT
MRI
History and Development of MRI
Common Uses of the MRI Procedure
Risks
Techniques for Assessing Physiological Function
PET
fMRI
Electromagnetic Recording Methods
Single cell
EEG
ERP
MEG
Techniques for Modulating Brain Activity
Transcranical magnetic stimulation (TMS)
History and procedure
Mechanisms
Basic applications
Clinical applications
Future of TMS
Techniques for Analyzing Behaviour
Test batteries
Customized neuropsychological assessment
Overall Intelligence tests
Premorbid functioning
Techniques for Modeling Brain-Behaviour Relationships
References
5Motivation and Emotion
Introduction
Motivation - about drives and motives
What is an emotion?
Functional Theories
James-Lange Theory
Cannon-Bard Theory
Two Factor Theory
The Neural Correlate of Emotion
The Hippocampus
The Thalamus
The Cerebral Cortex
The Amygdala
Anatomy
Functions
Processing social signals of emotion
Emotional conditioning
Emotional memories
References
Books
Journals
Links
6Memory
Introduction
What is Memory
What is memory?
Classification by duration
Classification by information type
Classification by temporal direction
Most important brain structures responsible for memory
Types of Memory
Sensory Memory
Short Term Memory
Short Term Memory
Working Memory
Long Term Memory
Declarative Memory
Implicit Memory
Errors in Memory
Biochemical
Hardware Errors
Sources
7Memory and Language
Introduction
Definition
Language
Memory
Brain regions
Memory
Short term/long term Memory
Working Memory
Sensory Memory
Semantic Memory
Correlation between Language and Memory
Acquisition of language
Speech production
Diseases
References
External resources
Books
Links
8Imagery
Introduction
The Imagery Debate
What is it about?
How is it?
Biological reasoning of debate
Spatial Representation
Abstract
Introduction
What is it?
How is spatial knowledge encoded?
Propositional Representation
Theory
Representation
Complex objects
Proofs for propositional representation
Imagery and Perception
Size and the Visual Field
Current state of imagery debate
Imagery and memory
References
Further Reading
Links
9Comprehension
Introduction
Language as a cognitive ability
Historical review on Psycholinguistics & Neurolinguistics
Todays goals of Psycholinguistics
Characteristic features
Non-Human Language - Animal Communication
Forms of Communication
Characteristic Language Features in Animal Communication
Experiments
Can the characteristic language features be found in non-human communication?
Language Comprehension & Production
Language features – Syntax and Semantics
Physiological Approach
Semantics
Syntax
Behavioristic Approach – Parsing a Sentence
The Syntax-First Approach of Parsing
The Interactionist Approch of Parsing
Situation Model
Using Language
Language, Culture and Cognition
What is the connection between language and cognition?
Is thought dependent on, or even caused by language?
References
10Neuroscience of Comprehension
Introduction
Lateralization of language
Anatomical differences between left and right hemisphere
Functional asymmetry
Handedness
Auditory Language Processing
Neurological Perspective
Psychological Perspective
Visual Language Processing
The phonological route
The direct route
The processing of written language in reading
The processing of written language in spelling
Evidence from Advanced Neuroscience Methods
Left hemisphere dominance
Different roles of posterior and anterior regions
Visual versus Auditory Language Processing
Beyond words
Findings from other language systems
Sign language
Sign language grammar
Neuropsychological research of sign language
References & Further Reading
11Situation Models and Inferencing
Introduction
Why do we need situation models?
Integration of information across sentences
Explanation of similarities in comprehension performances across modalities
Domain expertise on comprehension
Multiple source learning
Multidimensionality of Situation Models
Space
Time
Causation
Intentionality
Protagonists and Objects
Processing Frameworks
Introduction
An interactive Model of Comprehension
Early Computational Model
Construction-Integration Model
Event-Indexing Model
The Immersed Experiencer Framework
Levels of Representation in Language and Text Comprehension
Propositional Representation
Three levels of representation
Two levels of representation
KIWi-Model
Inferencing
Anaphoric Inference
Instrumental Inference
Causual Inference
Predictice / Forward Inference
Integrating Inferences into Situation Models
Important Topics of current research
Linguistic Cues versus World Knowledge
Multidimensionality
References
Links
12Knowledge
Knowledge Representation and Hemispheric Distribution/Specialisation
Introduction
Historical and Philosophical Aspects
Theories on Knowledge Representation in the Brain
Concepts and Categories
Concepts
Categories in our Life
Definitional Approach
Prototype Approach
Exemplar Approach
Prototype vs. Exemplar Approach
Hierarchical Organization of Categories
Affecting Factors on Categorization
Representation of Categories in the Brain
Semantic Networks
Collins and Quillian's Model
Cognitive Economy
Correlation between Distance of Concepts and Information Retrieval
Spreading Activation
Criticism
Collins and Loftus Model - A Developed C&Q-Model
Connectionist Approach
Representation of Concepts in Networks
Basic Principles of Connectionism
Operation of Connectionist Networks
Evaluating Connectionism
Mental Representation
Propositional Approach
Propositions
Mental Propositions
Imagery Approach
Knowledge Representation (KR) in Computational Models of Cognition
Knowledge Engineering
Ontology
Frame Problem
Knowledge Representation Formalisms
Different Types of Formal Languages
Expressive Power of Formalisms vs. Deductive Complexity
Application of KR – Databases
Intertranslation between KR Formalisms
Gap between Human and Artificial KR
KR in AI
Hemispheric Distribution
Differences in Anatomy and Chemistry
Historic Approaches
Experiments with Split-Brain-Patients
Experiments with Patients with other Brain-Lesions
Drawbacks
Experiments with Neurologically Intact Individuals
Results
Do the Hemispheres Differ in What or How They Process?
Communication Between the Hemispheres via the Corpus Callosum
Individual Factors may Influence Lateralization
Age
Handedness
Gender
Summary
References
Knowledge Representation
Hemispheric Specialisation/Distribution
Links
Knowledge Representation
Hemispheric Specialisation
13Decision Making and Reasoning
Introduction
Deductive Reasoning
Thinking Categorically
The Normative Approach
The Descriptive Approach
Mental Models of Deductive Reasoning
Effects of Culture on Deductive Reasoning
Thinking Conditionally
Forms of conditionla syllogisms
Why people make errors in conditional reasoning: The Wason Four- Card- problem
Stating the Four – Card task in real – world terms: the role of ‘Regulations’
Pragmatic Reasoning Schemas in the Wason Task: The role of ‘Permission’
An evolutionary approach to the Four – Card – problem: The role of ‘Cheating’
Inductive Reasoning
Induction vs deduction
How reliable are conclusions reached through induction?
Processes and constraints of inductive reasoning
So, why inductive reasoning at all?
Decision Making: Choosing Among Alternatives
About the Process
The Utility Approach
Misleading Effects
Situation Models
Focusing Illusion
Framing Effect
Justification in Decision Making
Executive Functions
Deficits in initiation, cessation and control of action
Impairments in abstract and conceptual thinking
Deficits in cognitive estimation
Lack of Cognitive Flexibility and Deficits in the Response to Novelty
Deficits in goal directed behavior
What characterizes goal directed behavior?
Executive dysfunction and goal directed behavior
Theories of Frontal Lobe Function in Executive Control
Role of Working Memory
Role of Controlled Versus Automatic Processes
Use of Scripts
Role of a goal list
References
Links
Reasoning
Decision making
Executive functions
14Present and Future of Research
Introduction
Until now
Introducing new methods
Possible development
Methods
Experimental Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive Neuropsychology
Cognitive Science
Cognitive Neuroscience
Converging operations
Theory
Unifying Theories
Parallel Processing
Levels of Analysis
Conclusion
References
Links
15History & Document Notes
Wikibook History
PDF Information & History
16Authors & Image Credits
Authors
Image Credits
17GNU Free Documentation License
0. PREAMBLE
1. APPLICABILITY AND DEFINITIONS
2. VERBATIM COPYING
3. COPYING IN QUANTITY
4. MODIFICATIONS
5. COMBINING DOCUMENTS
6. COLLECTIONS OF DOCUMENTS
7. AGGREGATION WITH INDEPENDENT WORKS
8. TRANSLATION
9. TERMINATION
10. FUTURE REVISIONS OF THIS LICENSE
External links















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc