Table 1. Device summary
1 Introduction
2 Description
Table 2. STM32F405xx and STM32F407xx: features and peripheral counts (continued)
2.1 Full compatibility throughout the family
Figure 1. Compatible board design between STM32F10xx/STM32F4xx for LQFP64
Figure 2. Compatible board design STM32F10xx/STM32F2xx/STM32F4xx for LQFP100 package
Figure 3. Compatible board design between STM32F10xx/STM32F2xx/STM32F4xx for LQFP144 package
Figure 4. Compatible board design between STM32F2xx and STM32F4xx for LQFP176 package
2.2 Device overview
Figure 5. STM32F40x block diagram
2.2.1 ARM® Cortex™-M4F core with embedded Flash and SRAM
2.2.2 Adaptive real-time memory accelerator (ART Accelerator™)
2.2.3 Memory protection unit
2.2.4 Embedded Flash memory
2.2.5 CRC (cyclic redundancy check) calculation unit
2.2.6 Embedded SRAM
2.2.7 Multi-AHB bus matrix
Figure 6. Multi-AHB matrix
2.2.8 DMA controller (DMA)
2.2.9 Flexible static memory controller (FSMC)
2.2.10 Nested vectored interrupt controller (NVIC)
2.2.11 External interrupt/event controller (EXTI)
2.2.12 Clocks and startup
2.2.13 Boot modes
2.2.14 Power supply schemes
2.2.15 Power supply supervisor
2.2.16 Voltage regulator
Figure 7. Regulator ON/internal reset OFF
Figure 8. Startup in regulator OFF: slow VDD slope - power-down reset risen after VCAP_1/VCAP_2 stabilization
Figure 9. Startup in regulator OFF mode: fast VDD slope - power-down reset risen before VCAP_1/VCAP_2 stabilization
2.2.17 Real-time clock (RTC), backup SRAM and backup registers
2.2.18 Low-power modes
2.2.19 VBAT operation
2.2.20 Timers and watchdogs
Table 3. Timer feature comparison
2.2.21 Inter-integrated circuit interface (I²C)
2.2.22 Universal synchronous/asynchronous receiver transmitters (USART)
Table 4. USART feature comparison
2.2.23 Serial peripheral interface (SPI)
2.2.24 Inter-integrated sound (I2S)
2.2.25 Audio PLL (PLLI2S)
2.2.26 Secure digital input/output interface (SDIO)
2.2.27 Ethernet MAC interface with dedicated DMA and IEEE 1588 support
2.2.28 Controller area network (bxCAN)
2.2.29 Universal serial bus on-the-go full-speed (OTG_FS)
2.2.30 Universal serial bus on-the-go high-speed (OTG_HS)
2.2.31 Digital camera interface (DCMI)
2.2.32 Random number generator (RNG)
2.2.33 General-purpose input/outputs (GPIOs)
2.2.34 Analog-to-digital converters (ADCs)
2.2.35 Temperature sensor
2.2.36 Digital-to-analog converter (DAC)
2.2.37 Serial wire JTAG debug port (SWJ-DP)
2.2.38 Embedded Trace Macrocell™
3 Pinouts and pin description
Figure 10. STM32F40x LQFP64 pinout
Figure 11. STM32F40x LQFP100 pinout
Figure 12. STM32F40x LQFP144 pinout
Figure 13. STM32F40x LQFP176 pinout
Figure 14. STM32F40x UFBGA176 ballout
Table 5. Legend/abbreviations used in the pinout table (continued)
Table 6. STM32F40x pin and ball definitions (continued)
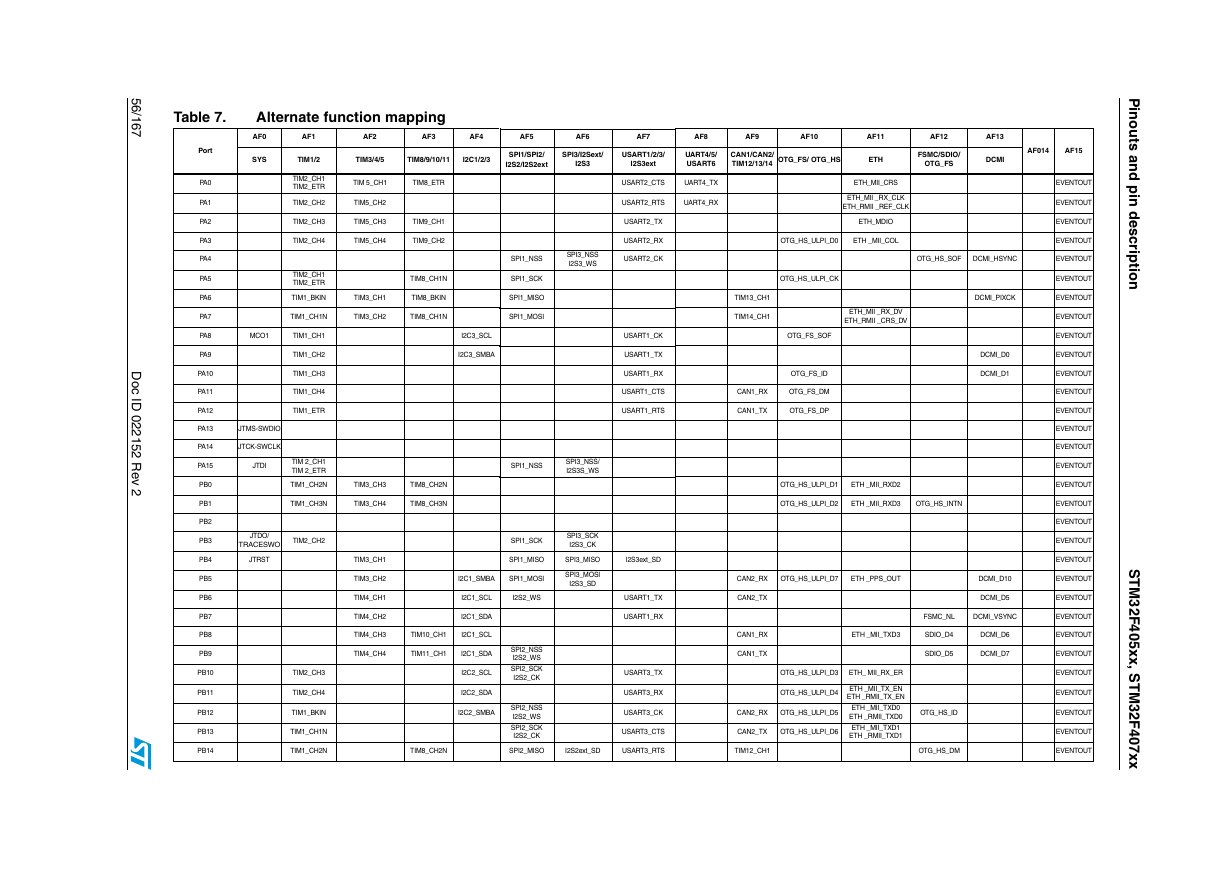
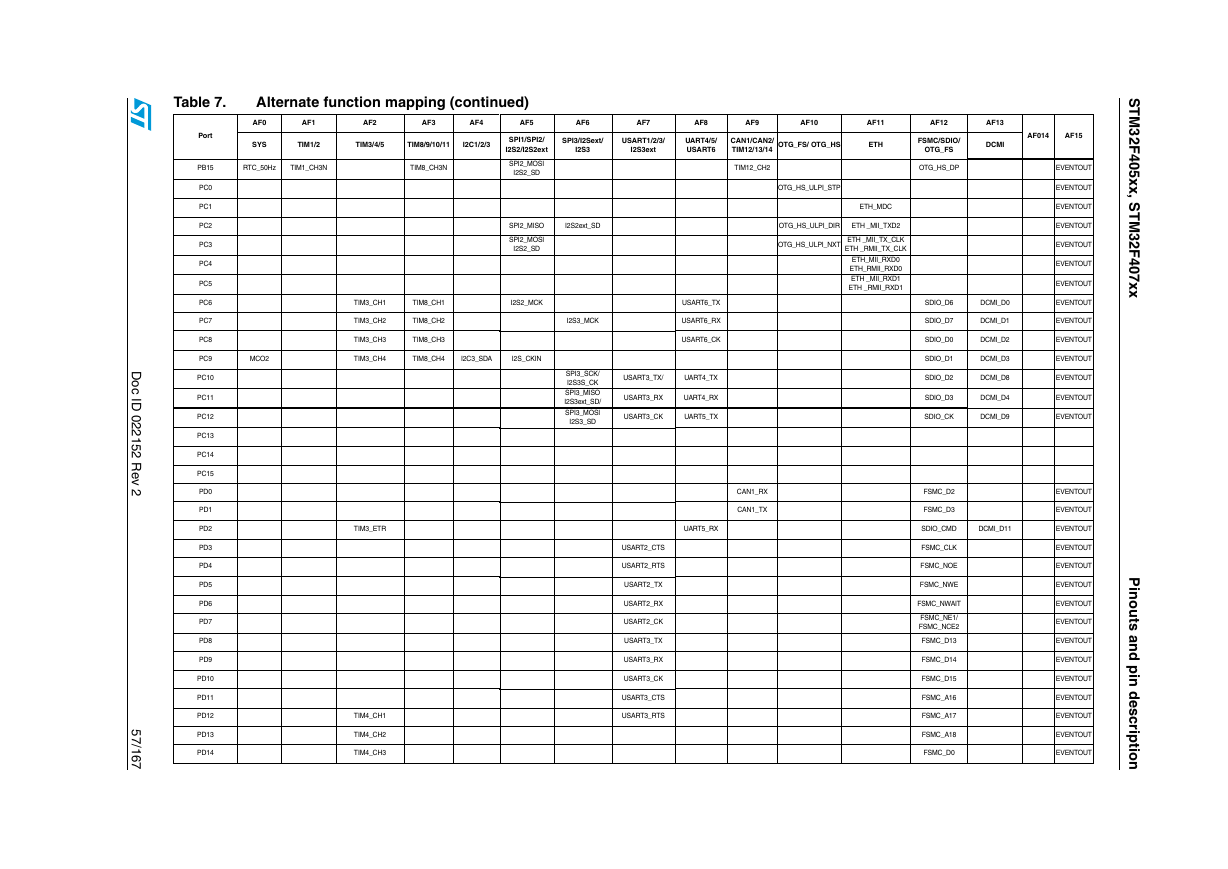
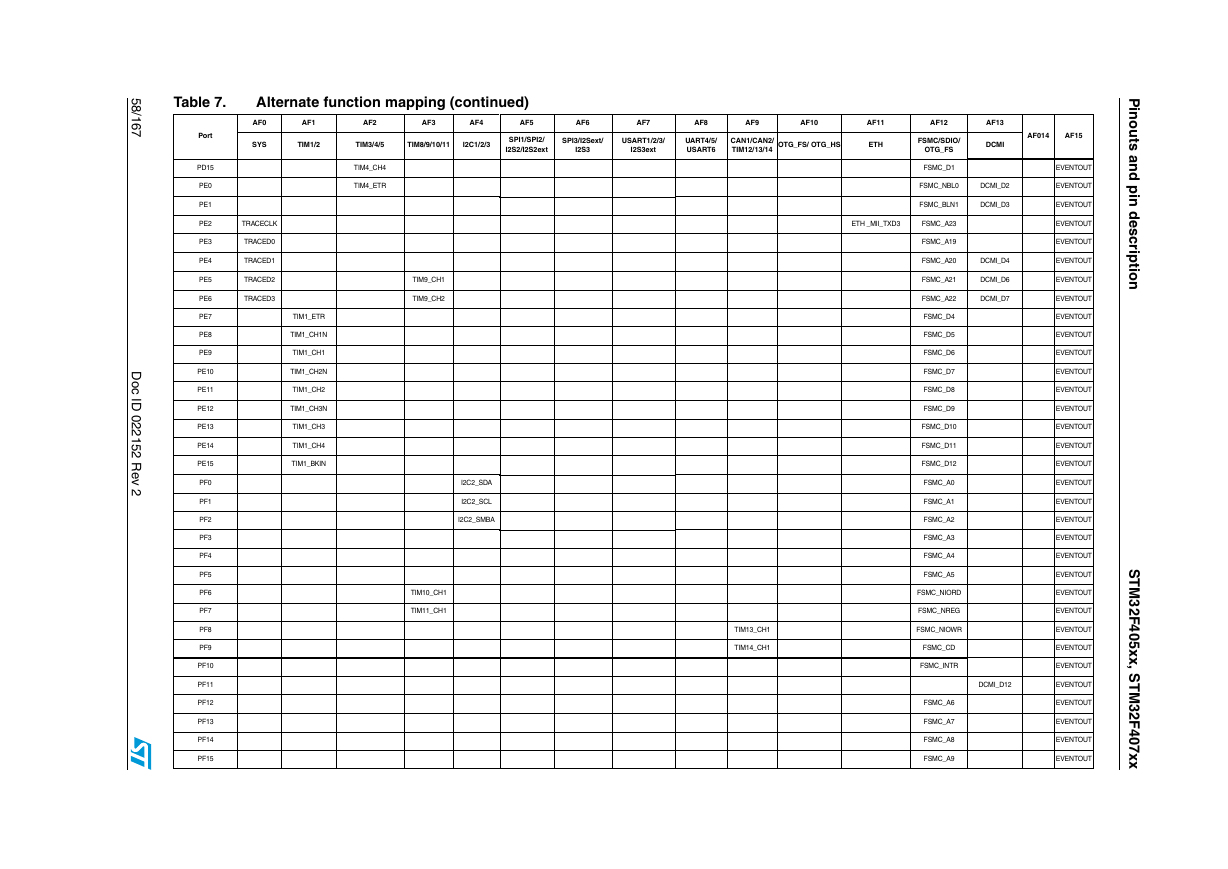
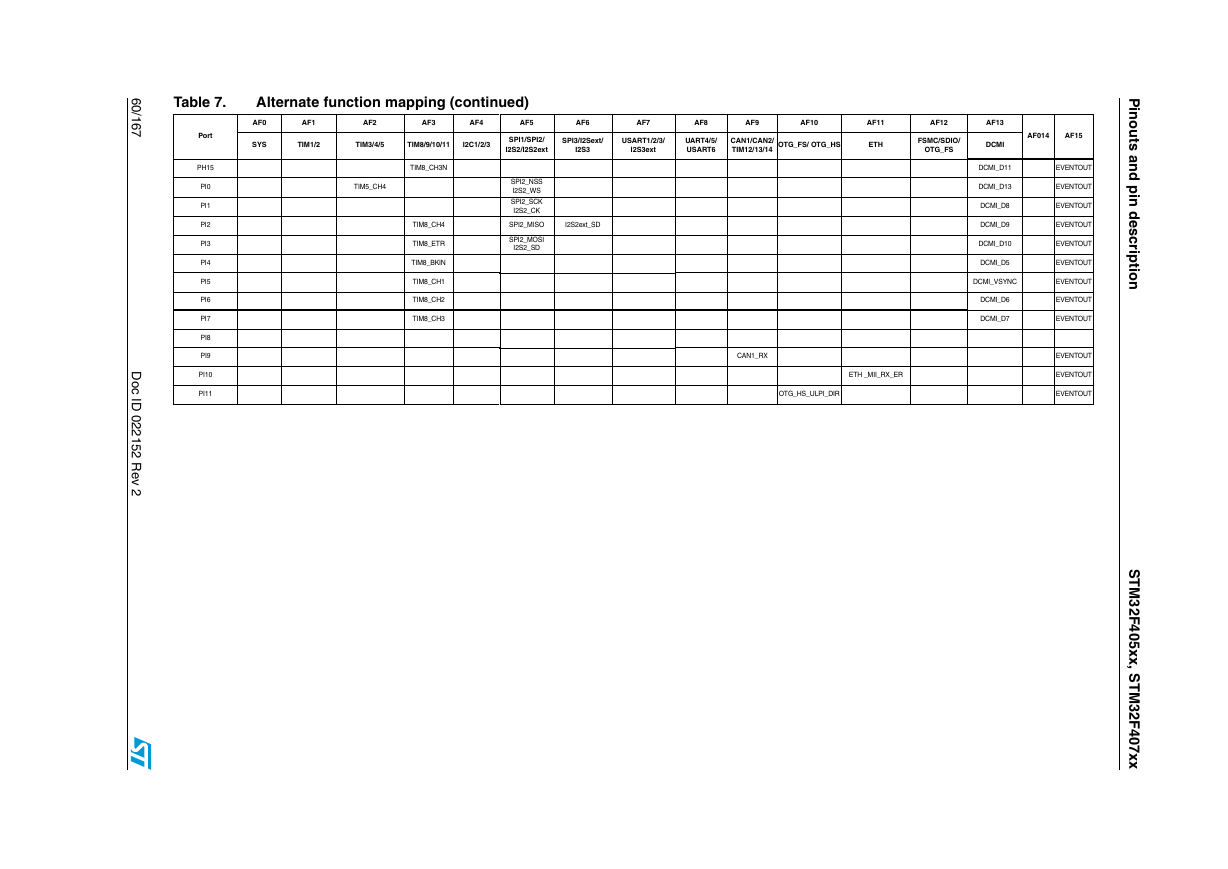
Table 7. Alternate function mapping (continued)
4 Memory map
Figure 15. Memory map
5 Electrical characteristics
5.1 Parameter conditions
5.1.1 Minimum and maximum values
5.1.2 Typical values
5.1.3 Typical curves
5.1.4 Loading capacitor
5.1.5 Pin input voltage
Figure 16. Pin loading conditions
Figure 17. Pin input voltage
5.1.6 Power supply scheme
Figure 18. Power supply scheme
5.1.7 Current consumption measurement
Figure 19. Current consumption measurement scheme
5.2 Absolute maximum ratings
Table 8. Voltage characteristics
Table 9. Current characteristics
Table 10. Thermal characteristics
5.3 Operating conditions
5.3.1 General operating conditions
Table 11. General operating conditions (continued)
Table 12. Limitations depending on the operating power supply range
5.3.2 VCAP1/VCAP2 external capacitor
Figure 20. External capacitor CEXT
Table 13. VCAP1/VCAP2 operating conditions
5.3.3 Operating conditions at power-up / power-down (regulator ON)
Table 14. Operating conditions at power-up / power-down (regulator ON)
5.3.4 Operating conditions at power-up / power-down (regulator OFF)
Table 15. Operating conditions at power-up / power-down (regulator OFF)
5.3.5 Embedded reset and power control block characteristics
Table 16. Embedded reset and power control block characteristics (continued)
5.3.6 Supply current characteristics
Table 17. Typical and maximum current consumption in Run mode, code with data processing running from Flash memory (ART accelerator disabled)
Table 18. Typical and maximum current consumption in Run mode, code with data processing running from Flash memory (ART accelerator enabled) or RAM
Figure 21. Typical current consumption vs temperature, Run mode, code with data processing running from Flash (ART accelerator ON) or RAM, and peripherals OFF
Figure 22. Typical current consumption vs temperature, Run mode, code with data processing running from Flash (ART accelerator ON) or RAM, and peripherals ON
Figure 23. Typical current consumption vs temperature, Run mode, code with data processing running from Flash (ART accelerator OFF) or RAM, and peripherals OFF
Figure 24. Typical current consumption vs temperature, Run mode, code with data processing running from Flash (ART accelerator OFF) or RAM, and peripherals ON
Table 19. Typical and maximum current consumption in Sleep mode
Table 20. Typical and maximum current consumptions in Stop mode
Table 21. Typical and maximum current consumptions in Standby mode
Table 22. Typical and maximum current consumptions in VBAT mode
Figure 25. Typical VBAT current consumption (LSE and RTC ON/backup RAM OFF)
Figure 26. Typical VBAT current consumption (LSE and RTC ON/backup RAM ON)
Table 23. Switching output I/O current consumption
Table 24. Peripheral current consumption (continued)
5.3.7 Wakeup time from low-power mode
Table 25. Low-power mode wakeup timings
5.3.8 External clock source characteristics
Table 26. High-speed external user clock characteristics
Table 27. Low-speed external user clock characteristics
Figure 27. High-speed external clock source AC timing diagram
Figure 28. Low-speed external clock source AC timing diagram
Table 28. HSE 4-26 MHz oscillator characteristics
Figure 29. Typical application with an 8 MHz crystal
Table 29. LSE oscillator characteristics (fLSE = 32.768 kHz)
Figure 30. Typical application with a 32.768 kHz crystal
5.3.9 Internal clock source characteristics
Table 30. HSI oscillator characteristics
Table 31. LSI oscillator characteristics
Figure 31. ACCLSI versus temperature
5.3.10 PLL characteristics
Table 32. Main PLL characteristics (continued)
Table 33. PLLI2S (audio PLL) characteristics (continued)
5.3.11 PLL spread spectrum clock generation (SSCG) characteristics
Table 34. SSCG parameters constraint
Figure 32. PLL output clock waveforms in center spread mode
Figure 33. PLL output clock waveforms in down spread mode
5.3.12 Memory characteristics
Table 35. Flash memory characteristics
Table 36. Flash memory programming
Table 37. Flash memory programming with VPP
Table 38. Flash memory endurance and data retention
5.3.13 EMC characteristics
Table 39. EMS characteristics
Table 40. EMI characteristics
5.3.14 Absolute maximum ratings (electrical sensitivity)
Table 41. ESD absolute maximum ratings
Table 42. Electrical sensitivities
5.3.15 I/O current injection characteristics
Table 43. I/O current injection susceptibility
5.3.16 I/O port characteristics
Table 44. I/O static characteristics
Table 45. Output voltage characteristics
Table 46. I/O AC characteristics (continued)
Figure 34. I/O AC characteristics definition
5.3.17 NRST pin characteristics
Table 47. NRST pin characteristics
Figure 35. Recommended NRST pin protection
5.3.18 TIM timer characteristics
Table 48. Characteristics of TIMx connected to the APB1 domain
Table 49. Characteristics of TIMx connected to the APB2 domain
5.3.19 Communications interfaces
Table 50. I2C characteristics
Figure 36. I2C bus AC waveforms and measurement circuit
Table 51. SCL frequency (fPCLK1= 42 MHz.,VDD = 3.3 V)
Table 52. SPI characteristics
Figure 37. SPI timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA = 0
Figure 38. SPI timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA = 1(1)
Figure 39. SPI timing diagram - master mode(1)
Table 53. I2S characteristics
Figure 40. I2S slave timing diagram (Philips protocol)(1)
Figure 41. I2S master timing diagram (Philips protocol)(1)
Table 54. USB OTG FS startup time
Table 55. USB OTG FS DC electrical characteristics
Figure 42. USB OTG FS timings: definition of data signal rise and fall time
Table 56. USB OTG FS electrical characteristics
Table 57. USB FS clock timing parameters
Table 58. USB HS DC electrical characteristics
Table 59. USB HS clock timing parameters
Figure 43. ULPI timing diagram
Table 60. ULPI timing
Table 61. Ethernet DC electrical characteristics
Figure 44. Ethernet SMI timing diagram
Table 62. Dynamics characteristics: Ethernet MAC signals for SMI
Figure 45. Ethernet RMII timing diagram
Table 63. Dynamics characteristics: Ethernet MAC signals for RMII
Figure 46. Ethernet MII timing diagram
Table 64. Dynamics characteristics: Ethernet MAC signals for MII
5.3.20 12-bit ADC characteristics
Table 65. ADC characteristics (continued)
Table 66. ADC accuracy at fADC = 30 MHz
Figure 47. ADC accuracy characteristics
Figure 48. Typical connection diagram using the ADC
Figure 49. Power supply and reference decoupling (VREF+ not connected to VDDA)
Figure 50. Power supply and reference decoupling (VREF+ connected to VDDA)
5.3.21 Temperature sensor characteristics
Table 67. TS characteristics
5.3.22 VBAT monitoring characteristics
Table 68. VBAT monitoring characteristics
5.3.23 Embedded reference voltage
Table 69. Embedded internal reference voltage
5.3.24 DAC electrical characteristics
Table 70. DAC characteristics (continued)
Figure 51. 12-bit buffered /non-buffered DAC
5.3.25 FSMC characteristics
Figure 52. Asynchronous non-multiplexed SRAM/PSRAM/NOR read waveforms
Table 71. Asynchronous non-multiplexed SRAM/PSRAM/NOR read timings
Figure 53. Asynchronous non-multiplexed SRAM/PSRAM/NOR write waveforms
Table 72. Asynchronous non-multiplexed SRAM/PSRAM/NOR write timings
Figure 54. Asynchronous multiplexed PSRAM/NOR read waveforms
Table 73. Asynchronous multiplexed PSRAM/NOR read timings
Figure 55. Asynchronous multiplexed PSRAM/NOR write waveforms
Table 74. Asynchronous multiplexed PSRAM/NOR write timings
Figure 56. Synchronous multiplexed NOR/PSRAM read timings
Table 75. Synchronous multiplexed NOR/PSRAM read timings
Figure 57. Synchronous multiplexed PSRAM write timings
Table 76. Synchronous multiplexed PSRAM write timings
Figure 58. Synchronous non-multiplexed NOR/PSRAM read timings
Table 77. Synchronous non-multiplexed NOR/PSRAM read timings
Figure 59. Synchronous non-multiplexed PSRAM write timings
Table 78. Synchronous non-multiplexed PSRAM write timings
Figure 60. PC Card/CompactFlash controller waveforms for common memory read access
Figure 61. PC Card/CompactFlash controller waveforms for common memory write access
Figure 62. PC Card/CompactFlash controller waveforms for attribute memory read access
Figure 63. PC Card/CompactFlash controller waveforms for attribute memory write access
Figure 64. PC Card/CompactFlash controller waveforms for I/O space read access
Figure 65. PC Card/CompactFlash controller waveforms for I/O space write access
Table 79. Switching characteristics for PC Card/CF read and write cycles in attribute/common space
Table 80. Switching characteristics for PC Card/CF read and write cycles in I/O space
Figure 66. NAND controller waveforms for read access
Figure 67. NAND controller waveforms for write access
Figure 68. NAND controller waveforms for common memory read access
Figure 69. NAND controller waveforms for common memory write access
Table 81. Switching characteristics for NAND Flash read cycles
Table 82. Switching characteristics for NAND Flash write cycles
5.3.26 Camera interface (DCMI) timing specifications
Table 83. DCMI characteristics
5.3.27 SD/SDIO MMC card host interface (SDIO) characteristics
Figure 70. SDIO high-speed mode
Figure 71. SD default mode
Table 84. SD / MMC characteristics
5.3.28 RTC characteristics
Table 85. RTC characteristics
6 Package characteristics
6.1 Package mechanical data
Figure 72. LQFP64 – 10 x 10 mm 64 pin low-profile quad flat package outline
Figure 73. Recommended footprint(1)
Table 86. LQFP64 – 10 x 10 mm 64 pin low-profile quad flat package mechanical data
Figure 74. LQFP100, 14 x 14 mm 100-pin low-profile quad flat package outline
Figure 75. Recommended footprint(1)
Table 87. LQPF100 – 14 x 14 mm 100-pin low-profile quad flat package mechanical data
Figure 76. LQFP144, 20 x 20 mm, 144-pin low-profile quad flat package outline
Figure 77. Recommended footprint(1)
Table 88. LQFP144, 20 x 20 mm, 144-pin low-profile quad flat package mechanical data
Figure 78. UFBGA176+25 - ultra thin fine pitch ball grid array 10 × 10 × 0.6 mm, package outline
Table 89. UFBGA176+25 - ultra thin fine pitch ball grid array 10 × 10 × 0.6 mm mechanical data
Figure 79. LQFP176 24 x 24 mm, 144-pin low-profile quad flat package outline
Table 90. LQFP176, 24 x 24 mm, 144-pin low-profile quad flat package mechanical data
6.2 Thermal characteristics
Table 91. Package thermal characteristics
7 Part numbering
Table 92. Ordering information scheme
Appendix A Application block diagrams
A.1 Main applications versus package
Table 93. Main applications versus package for STM32F407xx microcontrollers
A.2 Application example with regulator OFF
Figure 80. Regulator OFF/internal reset ON
Figure 81. Regulator OFF/internal reset OFF
A.3 USB OTG full speed (FS) interface solutions
Figure 82. USB controller configured as peripheral-only and used in Full speed mode
Figure 83. USB controller configured as host-only and used in full speed mode
Figure 84. USB controller configured in dual mode and used in full speed mode
A.4 USB OTG high speed (HS) interface solutions
Figure 85. USB controller configured as peripheral, host, or dual-mode and used in high speed mode
A.5 Complete audio player solutions
Figure 86. Complete audio player solution 1
Figure 87. Complete audio player solution 2
Figure 88. Audio player solution using PLL, PLLI2S, USB and 1 crystal
Figure 89. Audio PLL (PLLI2S) providing accurate I2S clock
Figure 90. Master clock (MCK) used to drive the external audio DAC
Figure 91. Master clock (MCK) not used to drive the external audio DAC
A.6 Ethernet interface solutions
Figure 92. MII mode using a 25 MHz crystal
Figure 93. RMII with a 50 MHz oscillator
Figure 94. RMII with a 25 MHz crystal and PHY with PLL
8 Revision history
Table 94. Document revision history (continued)






 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc