(计算前的)验证
一、检验赝势的好坏:
(一)方法:对单个原子进行计算;
(二)要求:1、对称性和自旋极化均采用默认值;
2、ENCUT 要足够大;
3、原胞的大小要足够大,一般设置为 15 Å足矣,对某些元素还可以取得
更小一些。
(三)以计算单个 Fe 原子为例:
1、INCAR 文件:
SYSTEM = Fe atom
ENCUT = 450.00 eV
NELMDL = 5
ISMEAR = 0
SIGMA=0.1
! make five delays till charge mixing,详细意义见注释一
2、POSCAR 文件:
0.00
1.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
1.00
atom
15.00
1.00
0.00
0.00
1
Direct
0 0 0
3、KPOINTS 文件:(详细解释见注释二。)
Automatic
0
Gamma
1 1 1
0 0 0
4、POTCAR 文件:(略)
注释一:关键词“NELMDL”:
A)此关键词的用途:指定计算开始时电子非自洽迭代的步数( 即
NELMDL gives the number of non-selfconsistent steps at the beginning),
�
目的是 make calculations faster。“非自洽”指的是保持 charge density
不变,由于 Charge density is used to set up the Hamiltonian, 所以“非自
洽”也指保持初始的哈密顿量不变。
B)默认值(default value):
NELMDL = -5
(当 ISTART=0, INIWAV=1, and IALGO=8 时)
NELMDL = -12
(当 ISTART=0, INIWAV=1, and IALGO=48 时)
NELMDL = 0
(其他情况下)
NELMDL might be positive or negative.
A positive number means that a delay is applied after each ionic
movement -- in general not a convenient option. (在每次核运动之后)
A negative value results in a delay only for the start-configuration. (只
在第一步核运动之前)
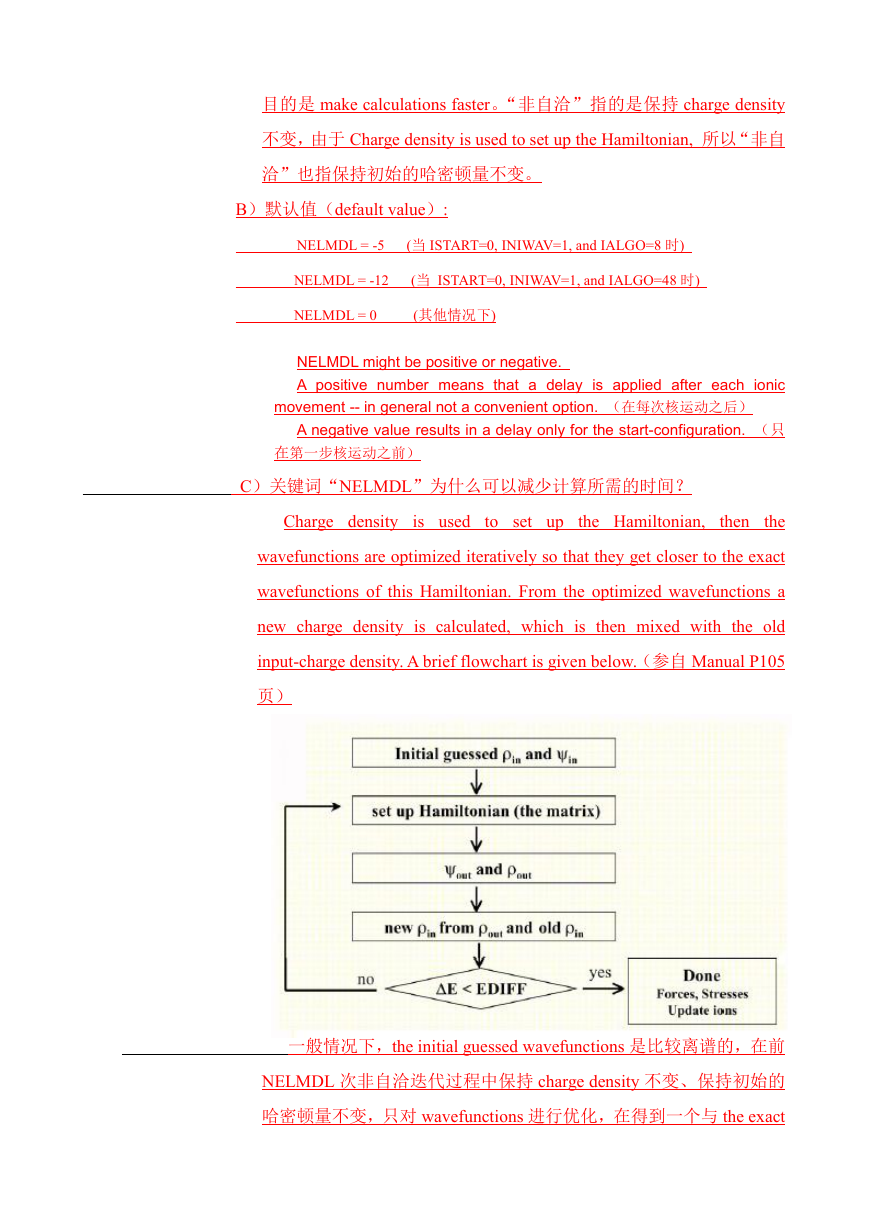
C)关键词“NELMDL”为什么可以减少计算所需的时间?
Charge density is used to set up the Hamiltonian,
then the
wavefunctions are optimized iteratively so that they get closer to the exact
wavefunctions of this Hamiltonian. From the optimized wavefunctions a
new charge density is calculated, which is then mixed with the old
input-charge density. A brief flowchart is given below.(参自 Manual P105
页)
一般情况下,the initial guessed wavefunctions 是比较离谱的,在前
NELMDL 次非自洽迭代过程中保持 charge density 不变、保持初始的
哈密顿量不变,只对 wavefunctions 进行优化,在得到一个与 the exact
�
wavefunctions of initial Hamiltonian 较为接近的 wavefunctions 后,再开
始同时优化 charge density。这样一来,计算时间要比一开始就同时优
化 charge density 和 wavefunctions 短得多。
注释二:为什么这里只需要一个 k 点?
For atoms and molecules, the Bloch theorem does not apply, hence there
is no need to use more than one single k-point. When more k-points are used,
only the interaction between the atoms (which should be zero) is described
more accurately.
(三)计算任务执行方法:
输入:vasp
(四)赝势好的判断标准:计算得到的 OUTCAR 文件中的“energy without entropy”能
量值在 0.001~0.01 eV 之间。
�
二、筛选合适的 ENCUT 大小:
(一)输入文件:
1、用脚本程序 optencut.sh 代替 INCAR 文件:
rm WAVECAR
for i in 100
150 200 250
300 350 400
450 500 550 600
do
cat > INCAR <> comment
done
2、POSCAR 文件:
bcc Fe
2.866
1.00
0.00
0.00
2
Direct
0
0.5 0.5 0.5
0
0
0.00
1.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
1.00
3、KPOINTS 文件:
Automatic generation
0
Monkhorst-Pack
9
0.0 0.0 0.0
9
9
4、POTCAR 文件:(略)
(二)计算任务执行方法:
输入:dos2unix optencut.sh
bash optencut.sh
(三)判别标准:计算完成后得到 comment 文件,它列出了在每个 ENCUT 时计算得到的
相应的总能,只要总能变化在 0.001 eV 左右就足够了。
�
三、选择合适的 k 点数目:
(一)输入文件:
1、INCAR 文件:
SYSTEM = bcc Fe
ENCUT = 450.00 eV
ISTART = 0 ; ICHARG = 2
ISMEAR = -5
PREC = Accurate
2、POSCAR 文件:
bcc Fe
2.866
1.00
0.00
0.00
2
Direct
0
0.5 0.5 0.5
0
0
0.00
1.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
1.00
3、用脚本程序 optkpoints.sh 代替 KPOINTS 文件:
rm WAVECAR
for i in 5
7
9
11
13
15
do
cat > KPOINTS <> comment
done
4、POTCAR 文件:(略)
(二)计算任务执行方法:
输入:dos2unix optkpoints.sh
bash optkpoints.sh
(三)判别标准:计算完成后得到 comment 文件,它列出了在 k 点数目与总能的对应值,
只要总能变化在 0.001 eV 左右就非常足够了。
�
四、优化选择合适的 SIGMA 值(展宽σ值):
(一)为什么要优化 SIGMA 值?
若展宽σ太小,则计算难以收敛;若展宽σ太大,则会产生多余的熵(entropy),
因此必须选择合适的σ值。(Too large smearing-parameters might result in a wrong total
energy, small smearing parameters require a large k-point mesh.)
(二)ISMEAR 和 SIGMA:
1、ISMEAR 和 SIGMA 这两个关键词要联合起来使用,前者用来指定 smearing 的方
法,后者用来指定 smearing 的展宽—— σ值。
2、ISMEAR 和 SIGMA 的默认值分别为 1 和 0.2。
3、ISMEAR 可能的取值为-5,-4,-3,-2,-1,0,N (N 表示正整数):
ISMEAR=-5,表示采用 Blochl 修正的四面体方法;
ISMEAR=-4,表示采用四面体方法,但是没有 Blochl 修正;
ISMEAR=-1,表示采用 Fermi-Dirac smearing 方法;
ISMEAR=0,表示采用 Gaussian smearing 方法;
ISMEAR=N,表示采用 Methfessel-Paxton smearing 方法,其中 N 是表示此方法中
and
的阶数,一般情况下 N 取 1 或 2, 但是 In most cases
leads to very similar results。
4、σ值一般在 0.1~0.3 eV 范围内。
5、ISMEAR 取值的一些经验:
(1)一般说来,无论是对何种体系,进行何种性质的计算,采用 ISMEAR=0 并
选择一个合适的 SIGMA 值,都能得到合理的结果。
(2)在进行静态计算(能量单点计算, no relaxation in metals)或态密度计算且 k 点
数目大于 4 时,取 ISMEAR=-5。
(3)当原胞较大而 k 点数目较小(小于 4 个)时,取 ISMEAR=0,并选择一个
合适的 SIGMA 值。(if the cell is too large (or if you use only a single or two k-points) use
ISMEAR=0 in combination with a small SIGMA=0.05)
(4)对半导体或绝缘体,不论是静态还是结构优化计算,都取 ISMEAR=-5。(Mind:
Avoid to use ISMEAR>0 for semiconductors and insulators, since it might cause problems. For
insulators use ISMEAR=0 or ISMEAR=-5.)
(5)对金属体系(for relaxations in metals),取 ISMEAR=1 或 2,并选择一个合适的
SIGMA 值。
(三)当采用 ISMEAR=0 或 N 时,如何优化选择合适的 SIGMA 值?
(以 bcc Fe 为例)
1、用脚本程序 optsigma.sh 代替 INCAR 文件:
�
rm WAVECAR
for i in 0.10 0.12 0.14 0.16 0.18 0.20 0.22 0.24 0.26 0.28 0.30
do
cat > INCAR <> comment
done
2、POSCAR 文件:
bcc Fe
2.866
1.00
0.00
0.00
2
Direct
0
0.5 0.5 0.5
0
0
0.00
1.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
1.00
3、KPOINTS 文件:
Automatic generation
0
Monkhorst-Pack
9
0.0 0.0 0.0
9
9
4、POTCAR 文件:(略)
(四)计算任务执行方法:
输入:dos2unix optsigma.sh
bash optsigma.sh
(五)判断标准:熵(entropy)越小越好,选择 entropy T*S EENTRO 值中最小的那个所对应的
SIGMA。( SIGMA should be as large as possible keeping the difference between the free energy and the total
energy (i.e. the term 'entropy T*S') in the OUTCAR file negligible (1 meV/atom).)
�
(五)注意:
1、当 k 点的数目发生变化后,要重新优化选择 SIGMA 值。
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc