Answers for industry.
Plant Simulation
Simulation and optimization of production systems and processes
Benefits
• Improve productivity of
existing facilities by as
much as 20 percent
• Reduce investment in
planning new facilities by as
much as 20 percent
• Cut inventory and
throughput time by as
much as 60 percent
• Optimize system
dimensions, including
buffer sizes
• Reduce investment risks
through early proof of
concept
• Maximize use of manu-
facturing resources
• Improve production line
design and schedule
Summary
Tecnomatix® Plant Simulation software
enables the simulation and optimization of
production systems and processes. Using
Plant Simulation, you can optimize material
flow, resource utilization and logistics for
all levels of plant planning from global pro-
duction facilities, through local plants, to
specific lines.
In times of increasing cost and time pres-
sures in production, along with ongoing
globalization, logistics has become a key
factor in the success of a company. The
need to deliver JIT (just-in-time)/ JIS (just-
in-sequence), introduce Kanban, plan and
build new, sustainable production facilities,
and manage global production networks
(to name a few) requires objective decision
criteria to help management evaluate and
compare alternative approaches.
Plant Simulation helps create digital models
of logistic systems (e.g., production) to
explore the systems’ characteristics and to
optimize their performance. The digital
model enables users to run experiments
and what-if scenarios without disturbing an
existing production system or – when used
in the planning process – long before the
real system is installed. Extensive analysis
tools, statistics and charts let users evalu-
ate different manufacturing scenarios and
make fast, reliable decisions in the early
stages of production planning.
Plant Simulation helps users:
• Detect and eliminate problems that oth-
erwise would require cost- and
time-consuming corrective measures
during production ramp-up
• Minimize the investment cost of produc-
tion lines without jeopardizing required
output
• Optimize the performance and energy
usage of existing production systems by
taking measures that have been verified
in a simulation environment prior to
implementation
Modeling manufacturing processes
Plant Simulation enables you to create
well-structured, hierarchical models of pro-
duction facilities, lines and processes. This
www.siemens.com/tecnomatix
�
Plant Simulation
Features
• Optimize systems for
reduced energy usage
• Simulation of complex
production systems and
control strategies
• Object-oriented, hierarchical
models encompassing
business, logistics and
production processes
• Dedicated application object
libraries for fast and
efficient system modeling
• Graphical outputs for
analysis of throughput,
resources and bottlenecks
• Automatic bottleneck
detection, Sankey diagrams
and Gantt charts
• 3D online visualization and
animation
• Integrated neural networks
and experiment handling
• Automated system
optimization via genetic
algorithms
• Value stream mapping and
simulation
• Open system architecture
supporting multiple
interfaces and integration
capacities (ActiveX, CAD,
Oracle SQL, ODBC, XML,
Socket, OPC, etc.)
is achieved through powerful object-ori-
ented architecture and modeling
capabilities that enable you to create and
maintain even highly complex systems,
including advanced control mechanisms.
Plant Simulation’s user interface follows
Microsoft Windows standards, making it
easy to get familiar and productive quickly.
Simulation models can be created quickly
by using components from application
object libraries dedicated to specific busi-
ness processes, such as assembly or
carbody manufacturing processes. Users
can choose from predefined resources,
order lists, operation plans and control
rules. By extending the library with your
own objects you can capture best-practice
engineering experiences for further simula-
tion studies.
Complex and detailed simulations can be
handled, understood and maintained much
better than in conventional simulation tools
by using Plant Simulation architectural
advantages like capsulation, inheritance
and hierarchy.
Simulating and analyzing system
performance
Plant Simulation models are used to opti-
mize throughput, relieve bottlenecks and
minimize work-in-process. The simulation
models take into consideration internal and
external supply chains, production
resources and business processes, allowing
you to analyze the impact of different
TECNOMATIX
production variations. Statistical analysis,
graphs and charts display the utilization of
buffers, machines and personnel. You can
generate extensive statistics and charts to
support dynamic analysis of performance
parameters including line workload, break-
downs, idle and repair time and proprietary
key performance factors.
Model visualization
In addition to the highly efficient 2D model
view of Plant Simulation, models may be
visualized in a 3D virtual environment using
Plant Simulation’s included libraries or your
own CAD data. The result is impressive 3D
virtual models that are synchronized at all
times with their 2D counterparts, allowing
you the flexibility to choose the appropriate
method of visualization without compro-
mising simulation and analysis needs.
Contact
Siemens Industry Software
Americas
Europe
Asia-Pacific +852 2230 3308
+1 314-264-8499
+44 (0) 1276 413200
www.siemens.com/tecnomatix
© 2013 Siemens Product Lifecycle Management
Software Inc. Siemens and the Siemens logo are
registered trademarks of Siemens AG. D-Cubed,
Femap, Geolus, GO PLM, I-deas, Insight, JT, NX,
Parasolid, Solid Edge, Teamcenter, Tecnomatix
and Velocity Series are trademarks or registered
trademarks of Siemens Product Lifecycle Man-
agement Software Inc. or its subsidiaries in the
United States and in other countries. All other
logos, trademarks, registered trademarks or ser-
vice marks used herein are the property of their
respective holders.
Y3 7541 4/13 B
�
Tecnomatix Plant Simulation
Value Stream Mapping
Implementation
The Plant Simulation Value Stream Mapping Library (TN75096) is an optional
extension to the Plant Simulation Standard or Professional license.
Summary
The Plant
Simulation Value
Stream Mapping
library supports the
user, taking into
account the
dynamic relation-
ships of complex
manufacturing
sequences to
increase the share
of value-added pro-
duction, variability,
quality, speed and
efficiency for
increased produc-
tion, while reducing
inventory and capi-
tal commitment, and securing on-time delivery.
Tecnomatix Plant
Simulation
Plant Simulation
helps you create
models of logistic
systems (e.g., pro-
duction) to explore
the systems’ charac-
teristics and to
optimize their per-
formance. The
digital model
enables users to run
experiments and
Benefits
• Increase productivity of
existing production facilities
by as much as 20 percent
• Reduce investment in
planning for new production
by as much as 20 percent
• Reduce inventories and cycle
time by as much as 60
percent
• Optimize the system
dimensions, including buffer
sizes
• Reduce investment risk
through early feasibility
analysis
• Increase resource utilization
• Better line planning and
allocation
Typical questions for the
simulation:
• How can we minimize the
investment costs?
• Is the required output
achieved?
• What happens when quantity
changes?
• How can stocks be reduced?
TECNOMATIX
www.siemens.com/tecnomatix
�
Tecnomatix Plant Simulation
TECNOMATIX
Tecnomatix Plant Simulation
Value Stream Mapping
Visualization, analysis and improvement of
dynamic value chains
what-if scenarios without disturbing an
existing production system or – when used
in the planning process – long before the
real system is installed. Plant Simulation
contains powerful object-oriented archi-
tecture and modeling capabilities that
enable you to create and maintain even
highly complex systems, including
advanced control mechanisms. Plant
Simulation’s user interface follows
Microsoft Windows standards, making it
easy for you to quickly become productive.
Simulation models can be created quickly
by using components from application
object libraries dedicated to specific busi -
ness processes. You can extend the library
with your own objects through a powerful
programming environment for the further-
ing of simulation capabilities. Tools for
automatic optimization, analysis of simula -
tion results and 3D visualization of
simulation models are also available.
Extensive analysis tools, statistics and
charts let users evaluate different manu -
facturing scenarios and make fast, reliable
decisions in the early stages of production
planning.
Plant Simulation helps users:
• Detect and eliminate problems that
otherwise would require cost- and time-
consuming correction measures during
production ramp-up
• Minimize the investment cost of
production lines without jeopardizing
required output
• Optimize the performance of existing
production systems by taking measures
that have been verified in a simulation
environment prior to implementation
�
• Easy to use through
Microsoft Windows
conformity
• Block libraries for the fast
and efficient modeling of
typical scenarios
• Graphs and diagrams
• Analysis of throughput,
resource utilization and
bottlenecks
Plant Simulation allows for the creation of
complex production systems and processes
in easy to understand computer models.
Using Plant Simulation, material flow,
resource utilization and supply chains at all
levels of corporate planning may be
optimized.
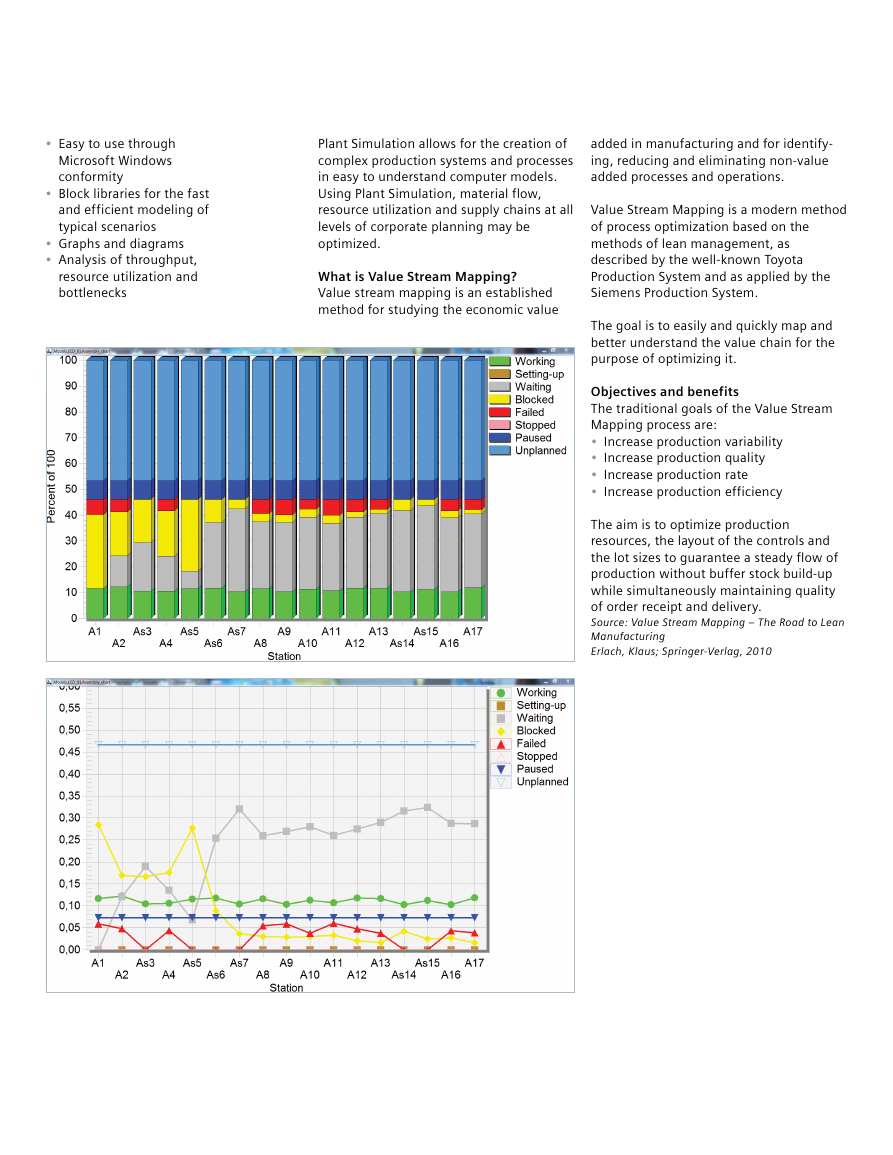
What is Value Stream Mapping?
Value stream mapping is an established
method for studying the economic value
added in manufacturing and for identify -
ing, reducing and eliminating non-value
added processes and operations.
Value Stream Mapping is a modern method
of process optimization based on the
methods of lean management, as
described by the well-known Toyota
Production System and as applied by the
Siemens Production System.
The goal is to easily and quickly map and
better understand the value chain for the
purpose of optimizing it.
Objectives and benefits
The traditional goals of the Value Stream
Mapping process are:
• Increase production variability
• Increase production quality
• Increase production rate
• Increase production efficiency
The aim is to optimize production
resources, the layout of the controls and
the lot sizes to guarantee a steady flow of
production without buffer stock build-up
while simultaneously maintaining quality
of order receipt and delivery.
Source: Value Stream Mapping – The Road to Lean
Manufacturing
Erlach, Klaus; Springer-Verlag, 2010
�
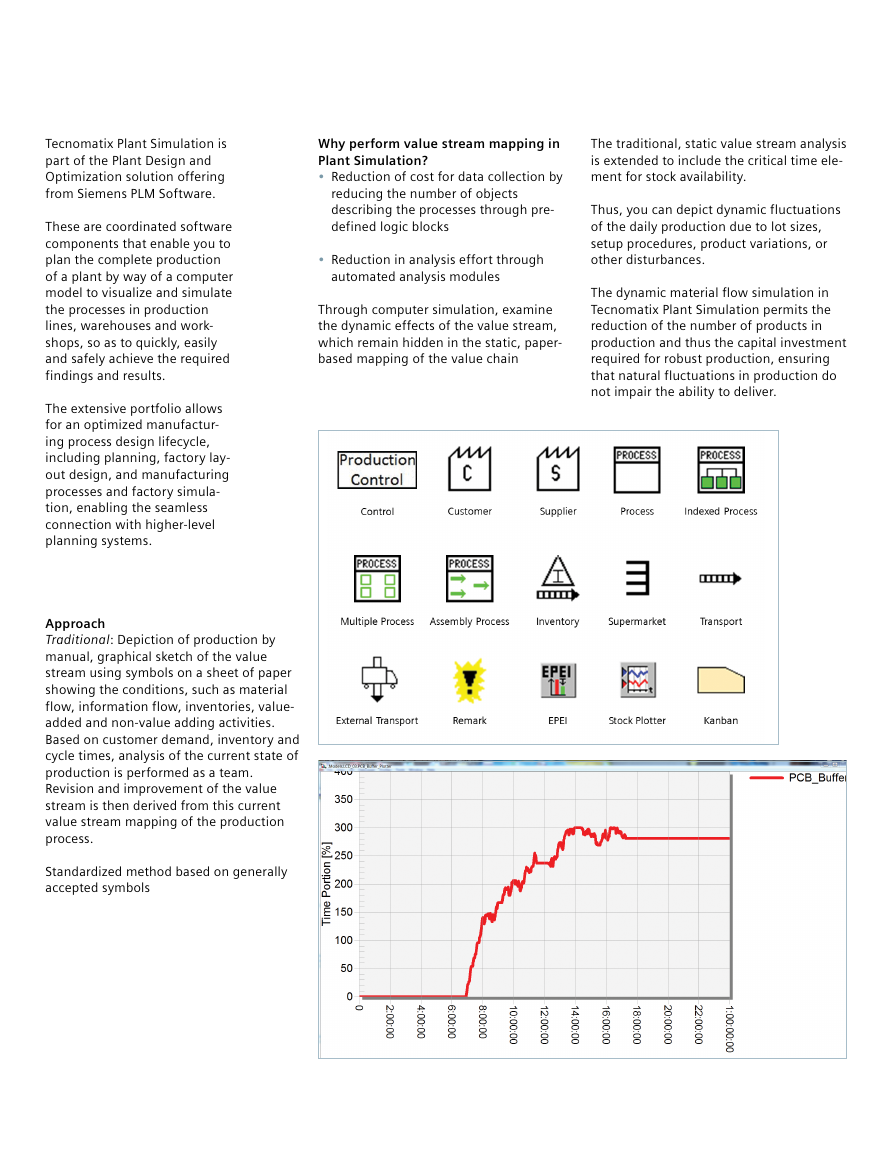
Why perform value stream mapping in
Plant Simulation?
• Reduction of cost for data collection by
The traditional, static value stream analysis
is extended to include the critical time ele -
ment for stock availability.
reducing the number of objects
describing the processes through pre-
defined logic blocks
• Reduction in analysis effort through
automated analysis modules
Through computer simulation, examine
the dynamic effects of the value stream,
which remain hidden in the static, paper-
based mapping of the value chain
Thus, you can depict dynamic fluctuations
of the daily production due to lot sizes,
setup procedures, product variations, or
other disturbances.
The dynamic material flow simulation in
Tecnomatix Plant Simulation permits the
reduction of the number of products in
production and thus the capital investment
required for robust production, ensuring
that natural fluctuations in production do
not impair the ability to deliver.
Tecnomatix Plant Simulation is
part of the Plant Design and
Optimization solution offering
from Siemens PLM Software.
These are coordinated software
components that enable you to
plan the complete production
of a plant by way of a computer
model to visualize and simulate
the processes in production
lines, warehouses and work-
shops, so as to quickly, easily
and safely achieve the required
findings and results.
The extensive portfolio allows
for an optimized manufactur-
ing process design lifecycle,
including planning, factory lay -
out design, and manufacturing
processes and factory simula-
tion, enabling the seamless
connection with higher-level
planning systems.
Approach
Traditional: Depiction of production by
manual, graphical sketch of the value
stream using symbols on a sheet of paper
showing the conditions, such as material
flow, information flow, inventories, value-
added and non-value adding activities.
Based on customer demand, inventory and
cycle times, analysis of the current state of
production is performed as a team.
Revision and improvement of the value
stream is then derived from this current
value stream mapping of the production
process.
Standardized method based on generally
accepted symbols
�
TECNOMATIX
Predefined core objects:
• Process
• Supplier
• Customer
• Stock
• Supermarket
• Internal and external
transport
• Predefined controls for
mapping of:
- Kanban processes
- Heijunka Box
- Compensation box
Predefined objects for analysis
and evaluation of:
• Throughput time
• Loading/unloading or waiting
time
• Value-added time
• Analysis of the process
utilization
• Availability of resources
(time sensitive)
Value Stream Mapping Library in Plant
Simulation
Predefined symbols based on the general
standard:
• Quick and easy to learn
• Predefined dialogs with configurable
user objects
• Control logics
• Analysis objects
Application
The Plant Simulation Value Stream
Mapping Library allows users to quickly
and easily map and improve their supply
chains with real dynamic behavior.
The Plant Simulation Value Stream
Mapping Library was developed in collabo -
ration with industry practitioners for use
by industry practitioners, providing the
necessary objects.
Contact
Siemens Industry Software
Americas
Europe
Asia-Pacific +852 2230 3333
+1 800 498 5351
+44 (0) 1276 702000
www.siemens.com/plm
© 2012 Siemens Product Lifecycle Management Software
Inc. All rights reserved. Siemens and the Siemens logo are
registered trademarks of Siemens AG. D-Cubed, Femap,
Geolus, GO PLM, I-deas, Insight, JT, NX, Parasolid, Solid
Edge, Teamcenter, Tecnomatix and Velocity Series are
trademarks or registered trademarks of Siemens Product
Lifecycle Management Software Inc. or its subsidiaries in
the United States and in other countries. All other logos,
trademarks, registered trademarks or service marks used
herein are the property of their respective holders.
X3 00000 7/12 B
�
Aerospace
Business challenges
Plan for airport upgrade and
passenger traffic increase
Keys to success
Use Tecnomatix Plant
Simulation for modeling air
cargo handling, passenger
flows in the international
terminal, as well as various
terminal performance
scenarios
Start with single application;
with success, implement
simulation across projects
Results
Bottlenecks identified at the
design stage and timely
corrections made
Investment risks reduced for
reconstruction of the
international terminal
Airport attained a
leadership position in the
Russian civil aviation market
Renovating Russia’s largest airport – virtually
Tecnomatix provides the tools to simulate optimum passenger and cargo handling workflows,
helping airport become a leader in the Russian civil aviation market
MOSCOW DOMODEDOVO AIRPORT
Moscow Domodedovo Airport is Russia’s largest airport. Handling 46 percent of air passengers in
Moscow, the airport is used by 74 airlines and serves 228 destinations across the globe, with 91
destinations exclusive to the Moscow region. The airport works with 46 foreign and 28 domestic
airlines. This includes 11 countries from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). In 2009
Moscow Domodedovo Airport handled 18.7 million passengers.
The cooperation between Domodedovo and Siemens PLM Software began in 1999, when Moscow
Domodedovo Airport implemented a major redevelopment program – among the largest European civil
aviation investment projects of the decade – with a proposed series of airport infrastructure upgrades
that required the development and evaluation of various designs.
Moscow Domodedovo Airport selected Siemens PLM Software as an instrumental technology provider
for its reconstruction program.
To effectively plan for the airport renovation, qualitative and quantitative efficiency indicators needed
to be set. In addition, the equipment, floor space and transport requirements needed to be determined.
Moscow Domodedovo Airport’s experts used advanced computer-aided design (CAD) tools and some of
the best practices of airports
globally to address these
requirements. Among Moscow
Domodedovo Airport’s strategic
tools for design and analysis is
the Plant Simulation solution,
part of Tecnomatix® software
from Siemens PLM Software.
The first assignment for
Tecnomatix was a cargo
handling simulation project. The
objective was to model the
handling of incoming air cargo
in order to identify bottlenecks
and to improve overall
efficiency. Within three weeks
the model had been developed.
Key information included the
aircraft landing schedule, the
TECNOMATIX
www.siemens.com/tecnomatix
�














 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc