OPNET UNIVERSITY
2000
Transceiver Pipeline and
Radio Modeling
Copyright © 2000 MIL 3, Inc.
Modeling Custom Wireless Effects– 1
�
OPNET UNIVERSITY
2000
Goals
• Introduce the OPNET Transceiver Pipeline
– Capabilities
– Defaults
• Modify pipeline
– Show openness and extensibility
– Model custom wireless effects
Copyright © 2000 MIL 3, Inc.
Modeling Custom Wireless Effects– 2
�
OPNET UNIVERSITY
2000
Overview
• Wireless modeling overview
• Transceiver pipeline
• Pipeline architecture and default stages
– Lab: Closure - Custom Pipeline Statistic
– Break
– Lab: Channel Match - Doppler Shifts
– Break
– Lab: Power, Inoise, ECC - Signal Lock vs. Power Lock
• Conclusion
Copyright © 2000 MIL 3, Inc.
Modeling Custom Wireless Effects– 3
�
OPNET UNIVERSITY
2000
Wireless Modeling Overview
• Wireless communications
– Broadcast medium
– Communication more likely to be problematic
– Less of a controlled environment than wireline
• Wireless channels need to be characterized appropriately
– Model real-world channel behavior
- Frequencies, power, line-of-sight, interference, etc.
– Channel characteristics affect higher layer protocol behavior
• Simulation tool must support wireless modeling
– Node mobility
- Car, ship, aircraft, satellite, etc.
– Link-budget-analysis computation
Copyright © 2000 MIL 3, Inc.
Modeling Custom Wireless Effects– 4
�
OPNET UNIVERSITY
2000
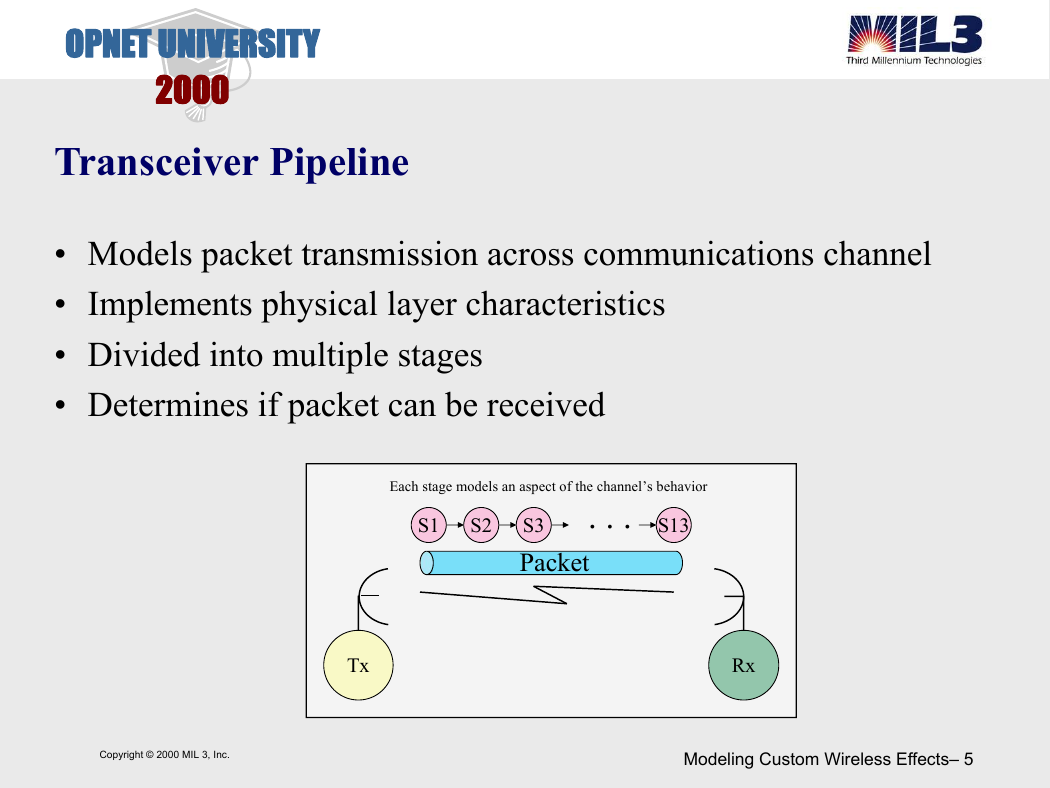
Transceiver Pipeline
• Models packet transmission across communications channel
• Implements physical layer characteristics
• Divided into multiple stages
• Determines if packet can be received
Each stage models an aspect of the channel’s behavior
. . .
S13
S1
S2
S3
Packet
Tx
Rx
Copyright © 2000 MIL 3, Inc.
Modeling Custom Wireless Effects– 5
�
OPNET UNIVERSITY
2000
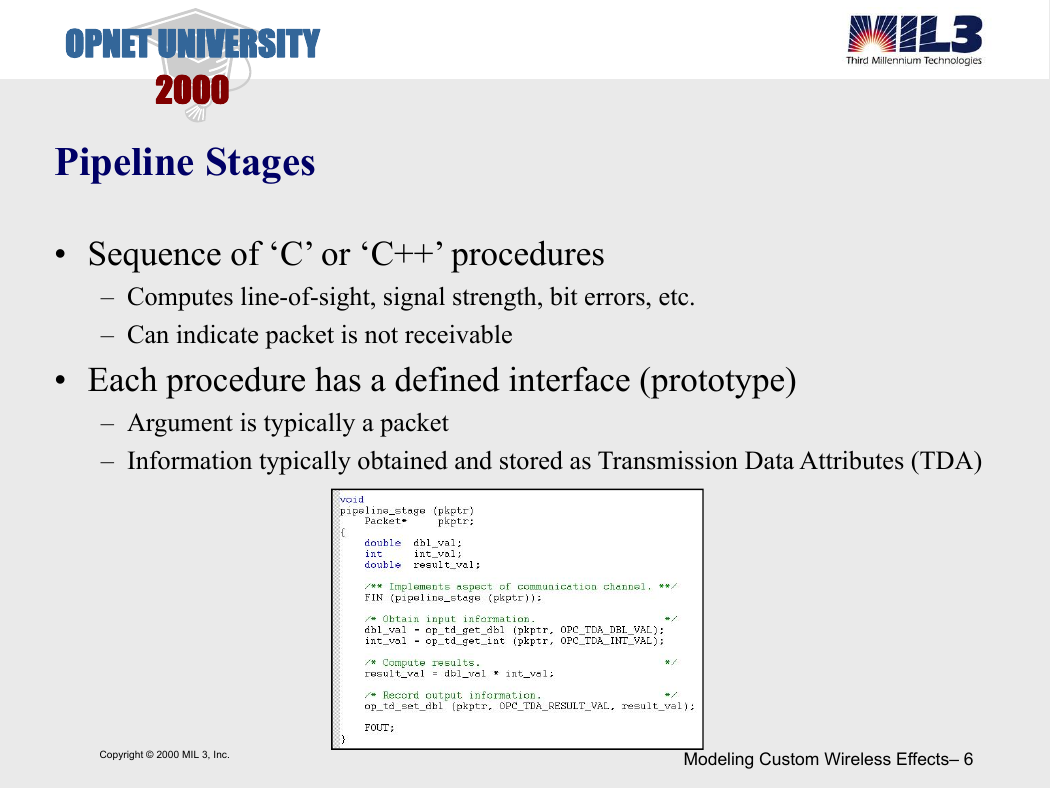
Pipeline Stages
• Sequence of ‘C’ or ‘C++’ procedures
– Computes line-of-sight, signal strength, bit errors, etc.
– Can indicate packet is not receivable
• Each procedure has a defined interface (prototype)
– Argument is typically a packet
– Information typically obtained and stored as Transmission Data Attributes (TDA)
Copyright © 2000 MIL 3, Inc.
Modeling Custom Wireless Effects– 6
�
OPNET UNIVERSITY
2000
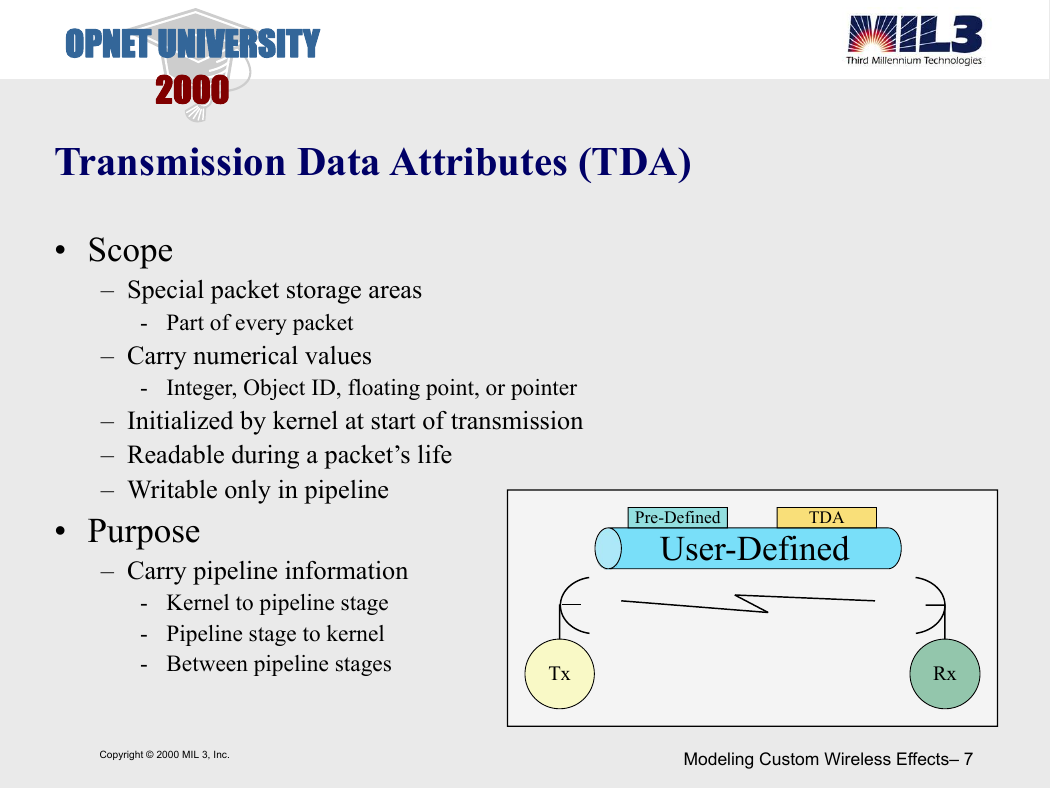
Transmission Data Attributes (TDA)
• Scope
– Special packet storage areas
- Part of every packet
– Carry numerical values
-
Integer, Object ID, floating point, or pointer
– Initialized by kernel at start of transmission
– Readable during a packet’s life
– Writable only in pipeline
• Purpose
– Carry pipeline information
- Kernel to pipeline stage
- Pipeline stage to kernel
- Between pipeline stages
Pre-Defined
TDA
User-Defined
Tx
Rx
Copyright © 2000 MIL 3, Inc.
Modeling Custom Wireless Effects– 7
�
OPNET UNIVERSITY
2000
Pipeline Models
• Scope
– Each stage uses a pipeline model
– Stages are referenced via a pipeline model object attributes
- Point-to-Point - link attributes
- Bus -Bus attributes
- Radio - transceiver attributes
– Stages must be compiled prior to reference
• Modeling method
– Create stage in context of the pipeline model
– Compile stage into object form
– Change pipeline model object attribute to reference stage
• NOTE: Stage and procedure (pipeline model context) can be used interchangeably
Copyright © 2000 MIL 3, Inc.
Modeling Custom Wireless Effects– 8
�











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc