�
5G White Paper:5G Mobile/Multi-Access Edge Computing
Executive Summary
Mobile / multi access edge computing (MEC) enables the applications, services and content deployed locally with
shorten distance through migrating the computing, storage and service capability to the edge of the network. Therefore,
MEC could greatly satisfy the technical requirements of eMBB, uRLLC and mMTC in the future 5G network.
Meanwhile, MEC allows operators open their Radio Access Network (RAN) edge to authorized third-parties, allowing
them to flexibly and rapidly deploy innovative applications and services towards mobile subscribers, enterprises and
vertical segments. This effectively enhances the intelligent level of operator’s mobile network. In this white paper, an
integrated future 5G MEC system architecture was proposed based on the analysis of various 5G MEC application
scenarios, requirements, and the MEC progress of ETSI and 3GPP. Moreover, the problems and challenges on the key
technologies of 5G MEC have also been stated in this whitepaper. Finally, the relationship between Fog Computing and
MEC has been clarified. We sincerely hope that the release of this white paper will help the industry and academy, and
look forward to promoting the healthy development of MEC in the future 5G with all sectors of the industry.
1
�
5G White Paper:5G Mobile/Multi-Access Edge Computing
Table of Contents
Executive Summary ............................................................................................................................................................ 1
1 Introduction ...................................................................................................................................................................... 5
2 Typical Scenarios and Technical Requirements ................................................................................................. 6
2.1 Typical Scenarios ................................................................................................................................... 6
2.2 Technical Requirements ....................................................................................................................... 11
3 System Architecture and Deployment Strategy ................................................................................................ 12
3.1 MEC System Architecture ................................................................................................................... 12
3.1.1 System Architecture of ETSI MEC ........................................................................................... 12
3.1.2 MEC Architecture in 3GPP ....................................................................................................... 15
3.2
Deployment Strategy ......................................................................................................................... 19
4 Key Technologies ......................................................................................................................................................... 21
4.1
Traffic Offloading .............................................................................................................................. 21
4.2
Cache and Acceleration ..................................................................................................................... 22
4.3
Bilateral Information Exchange for Network and Application .......................................................... 23
4.4 Mobility Management........................................................................................................................ 26
4.5
Charging ............................................................................................................................................ 27
4.6 MEC based FMC ............................................................................................................................... 28
4.7 MEC based Computing Offloading ................................................................................................... 29
4.7.1 System Architecture of MEC based Computing Offloading ..................................................... 29
4.7.2 MEC Computing Off-loading Scheme ...................................................................................... 31
3
�
5G White Paper:5G Mobile/Multi-Access Edge Computing
4.7.3 Synergic Edge-Cloud Scheduling .............................................................................................. 33
4.7.4 Micro Mobile Device Cluster Construction .............................................................................. 34
4.8
VIP Service Quality Assurance based on a Unified QoS .................................................................. 35
4.9 Management and orchestration of MEC platforms and applications ................................................. 36
4.9.1 NFVO/MEO .............................................................................................................................. 37
4.9.2 VNFM/MEPM........................................................................................................................... 38
4.9.3 VIM/VI ...................................................................................................................................... 39
4.10 MEC Security .................................................................................................................................... 40
4.11 MEC Managements ........................................................................................................................... 40
5 5G MEC and Fog Computing ..................................................................................................................................... 41
5.1
Introduction on Fog Computing ........................................................................................................ 41
5.2 MEC and Fog Computing .................................................................................................................. 44
6 Conclusion ...................................................................................................................................................................... 45
References .......................................................................................................................................................................... 46
Glossary ............................................................................................................................................................................... 47
Acknowledgement ........................................................................................................................................................... 49
4
�
5G White Paper:5G Mobile/Multi-Access Edge Computing
1 Introduction
With the rapid development of mobile internet, smart terminals (smart phone, tablet) have gradually replaced the
personal computers as the main tool for people’s daily use in working, study, social activities and entertainment [1]. At
the same time, massive IoT (Internet of Things) devices (smart meter, wireless monitoring terminal) have been widely
used in industry, agriculture, health, education, transportation, finance, energy, smart home and environment monitoring,
etc [2]. Through deploying business applications (online gaming, online education, online movie etc.) in the cloud
computing DC (Data Center), the smart terminals could access the cloud computing DC directly, which brings a lot
convenience to people’s life and changes the way they live. However, this greatly increases the network load and requires
a higher demand of network bandwidth as well [3][4].
In addition, in order to solve mobile terminal’s (especially cheap IoT devices) limited capability in computation,
storage and battery, the services that requires high complexity and high energy consumption should be moved to the
cloud computing DC. In this way, cheap terminal’s energy cost will be decreased and its battery life-time can be
extended [5]. However, the migration of computation load to cloud DC will bring a large number of data transmission
and the corresponding transmission delay. For some delay sensitive applications (industrial control applications), it will
cause serious negative effect. [6].
Therefore, in order to satisfy the future requirements from eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband), uRLLC
(Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication) and mMTC (Massive Machine Type Communication), MEC
(Mobile/Multi-Access Edge Computing) concept was proposed and got extensive attention from both academia and
industry. The ETSI (European Telecommunication Standard Institute) has set up the MEC Working Group in September
2014, which focused on the study of service scenarios, technical requirements, framework and architecture in MEC
[1][7]. Through migrating the computation, storage and servicing capability to the edge of network, MEC can make
application, service and content be deployed locally with short distance in a distributed way. To a certain extent, it will
satisfy the critical requirements of future eMBB, uRLLC, mMTC scenarios.
Based on the analysis of 5G MEC’s application scenarios, requirements, and the standard progress in both ETSI and
3GPP, this white paper proposed the integrated 5G MEC system architecture. Besides, this white paper put forward the
problems and challenges on the key technologies of 5G MEC. Finally, the relationship between Fog Computing and
MEC has been clarified.
5
�
5G White Paper:5G Mobile/Multi-Access Edge Computing
This white paper is version 1.0. Although this white paper is not comprehensive enough, and may need to continue to
be amended in some place; we still hope this white paper will be helpful to the academy and industry. With the freezing
of MEC technology standards and the deployment of 5G trial network, more new research results will be added to the
future version, and we welcome the entire industry colleague to make suggestions and comments.
2 Typical Scenarios and Technical Requirements
2.1 Typical Scenarios
According to the definition of ETSI ISG, MEC offers application developers and content providers cloud-computing
capabilities and an IT service environment at the edge of the network. This makes it possible to deploy the application,
service and content close to the UE in distributed manner. It thus enables the reduction of backhaul bandwidth demand,
which is a significant reduction in operating costs. ETSI also defined some open APIs to the 3rd party applications for
exposing radio network context information. It effectively enhances the intelligent level of mobile networks, and
promotes the integration of network and applications.
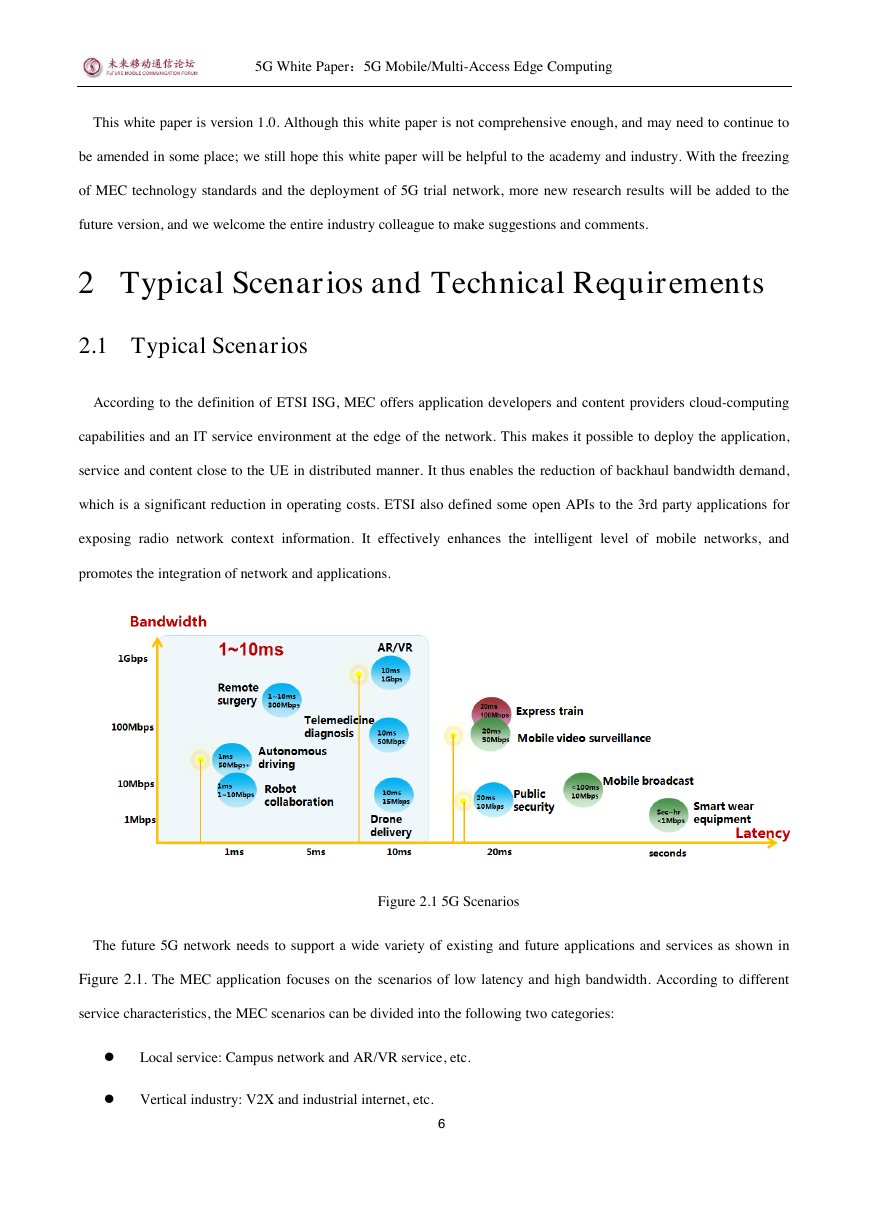
Figure 2.1 5G Scenarios
The future 5G network needs to support a wide variety of existing and future applications and services as shown in
Figure 2.1. The MEC application focuses on the scenarios of low latency and high bandwidth. According to different
service characteristics, the MEC scenarios can be divided into the following two categories:
Local service: Campus network and AR/VR service, etc.
Vertical industry: V2X and industrial internet, etc.
6
�
5G White Paper:5G Mobile/Multi-Access Edge Computing
➢ Local Service: Campus Network and AR/VR service, etc.
In order to better support the new services and explore the existing network capacity, more accurate indoor navigation,
and platform development and application integration need to be considered in MEC scenarios.
Typical Scenario 1: Campus Service
Massive traffic is generated locally. The traffic has to be terminated locally due to the privacy policy of local network.
MEC can provide a wireless communication network with high speed, which is safe, reliable, extensible and
cost-effective. The MEC traffic offloading functionality makes the traffic without having to go through the core network,
thereby reducing the latency, and the backhaul bandwidth consumption as shown in Figure 2.2.
Figure 2.2 Campus and Local Massive Traffic Service
Typical Scenario 2: Local Video Surveillance
In the scenario of local video surveillance, the traffic volume of video surveillance especially HD video is very huge.
The uplink bandwidth is about 16Mbps per 4k HD video. If all data are sent to central cloud, it will consume large
backhaul bandwidth. On the other hand, the video needs to be processed and analyzed timely to handle the emergency
situation. MEC can satisfy the requirement by offloading the traffic and processing the data locally to provide a better
user experience as shown in Figure 2.3.
7
�
5G White Paper:5G Mobile/Multi-Access Edge Computing
Figure 2.3 Local Video Surveillance
Besides video surveillance, a large number of scenarios like sports event live require low latency and high bandwidth
as shown in Figure 2.4. MEC can significantly enhance the user experience and reduce the operator network load.
Figure 2.4 Low Latency and High Bandwidth Scenarios
Typical Scenario 3: Augmented Reality
In this scenario, the doctor could make the surgery step by step with the help of clear pictures and words generated by
the AR medical application as shown in Figure 2.5. There are many scenarios for AR such as museum, city memorial,
sports event and concert. AR can enhance the people’s experience greatly.
8
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc