Production Planning and Control
生产计划与控制
2022-6-13
�
v5.1 Introduction
v5.2 The newsboy model (报童模型)
v5.3 Lot Size-Reorder Point System (批量再订货点系统)
v5.4 Service Level in (Q, R) System
v5.5 Multi-product Systems
v5.6 Electronic Data Interchange(电子数据交换)
Ch5-2
�
5.1 Introduction
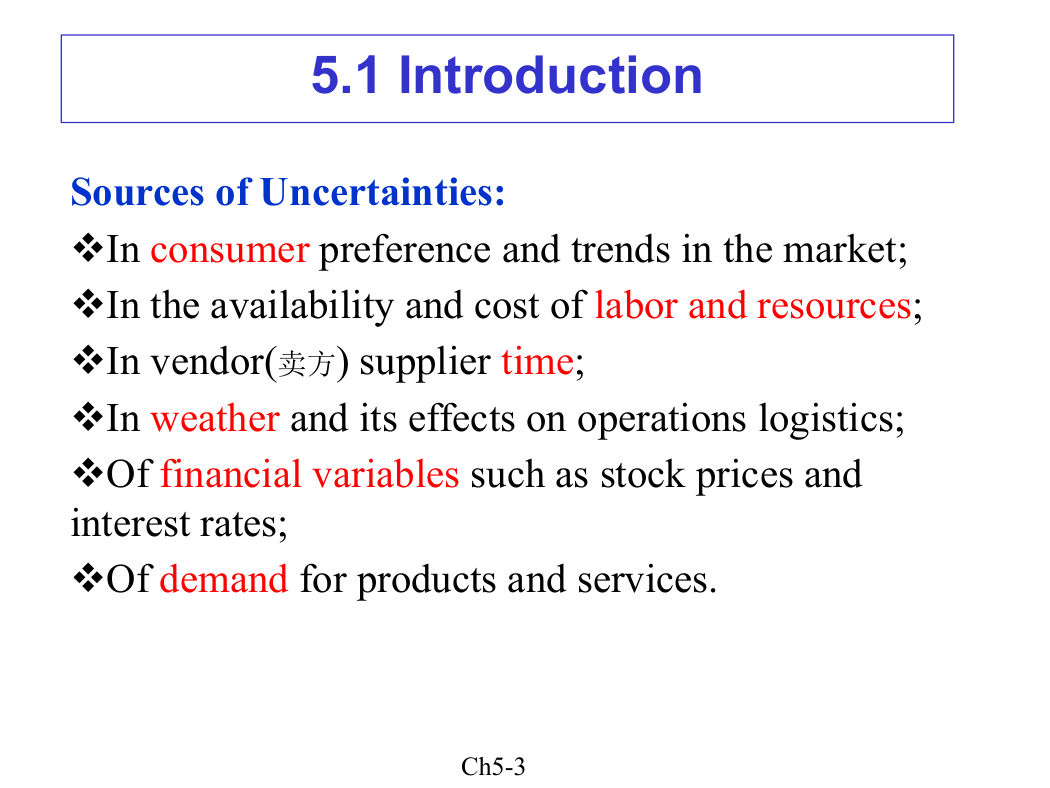
Sources of Uncertainties:
vIn consumer preference and trends in the market;
vIn the availability and cost of labor and resources;
vIn vendor(卖方) supplier time;
vIn weather and its effects on operations logistics;
vOf financial variables such as stock prices and
interest rates;
vOf demand for products and services.
Ch5-3
�
Introduction
Uncertainty means:
v A department store cannot exactly predicate the sales of a
particular item on any given day;
vAn airline cannot exactly predicate the number of people
that will choose to fly on any given flight.
How can these firms choose the number of items to keep
in inventory or the number of flights to schedule on any
given route?
vBased on the past experience for planning;
vMinimize expected cost or maximize the expected profit
when uncertainty is present!
Ch5-4
�
Why deterministic inventory control model?
As almost all inventory management has some level of
uncertainty, what is the value of the deterministic inventory
control model?
vProvide a basis for understanding the fundamental trade-offs
encountered in inventory management;
vMay be good approximations depending on the degree of
uncertainty in the demand.
Ch5-5
�
Why deterministic inventory control model?
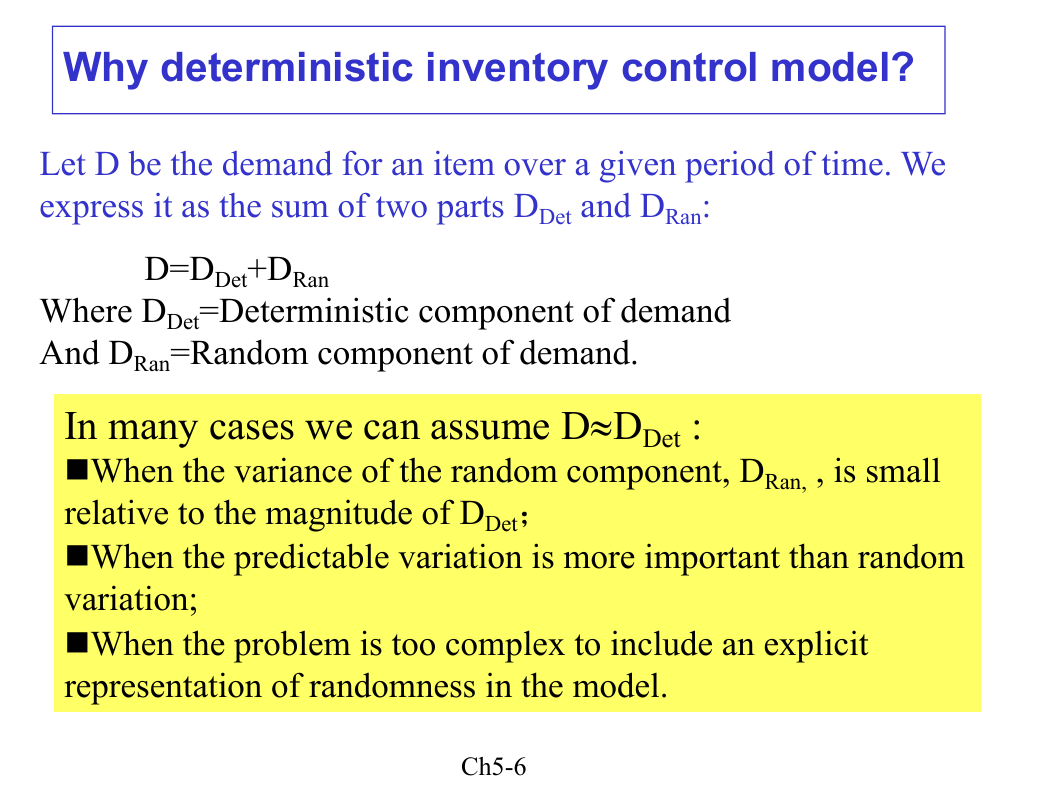
Let D be the demand for an item over a given period of time. We
express it as the sum of two parts DDet and DRan:
D=DDet+DRan
Where DDet=Deterministic component of demand
And DRan=Random component of demand.
In many cases we can assume DDDet :
nWhen the variance of the random component, DRan, , is small
relative to the magnitude of DDet;
nWhen the predictable variation is more important than random
variation;
nWhen the problem is too complex to include an explicit
representation of randomness in the model.
Ch5-6
�
Introduction
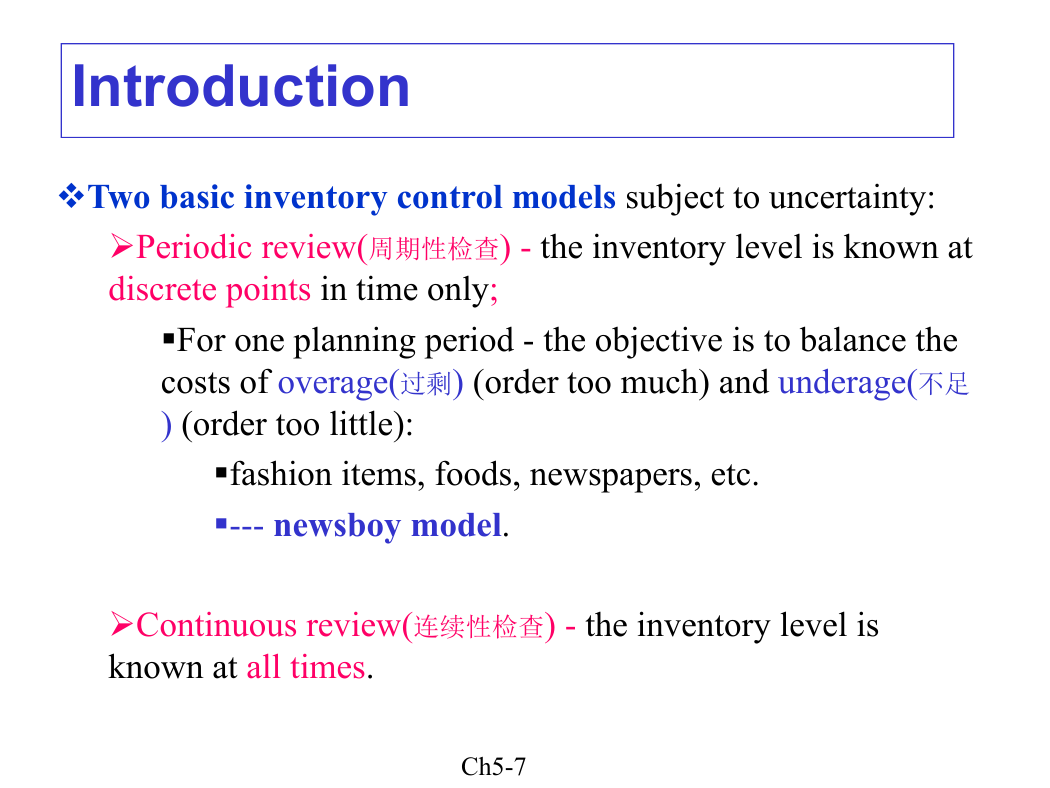
vTwo basic inventory control models subject to uncertainty:
ØPeriodic review(周期性检查) - the inventory level is known at
discrete points in time only;
§For one planning period - the objective is to balance the
costs of overage(过剩) (order too much) and underage(不足
) (order too little):
§fashion items, foods, newspapers, etc.
§--- newsboy model.
ØContinuous review(连续性检查) - the inventory level is
known at all times.
Ch5-7
�
5.2 The Newsboy Model
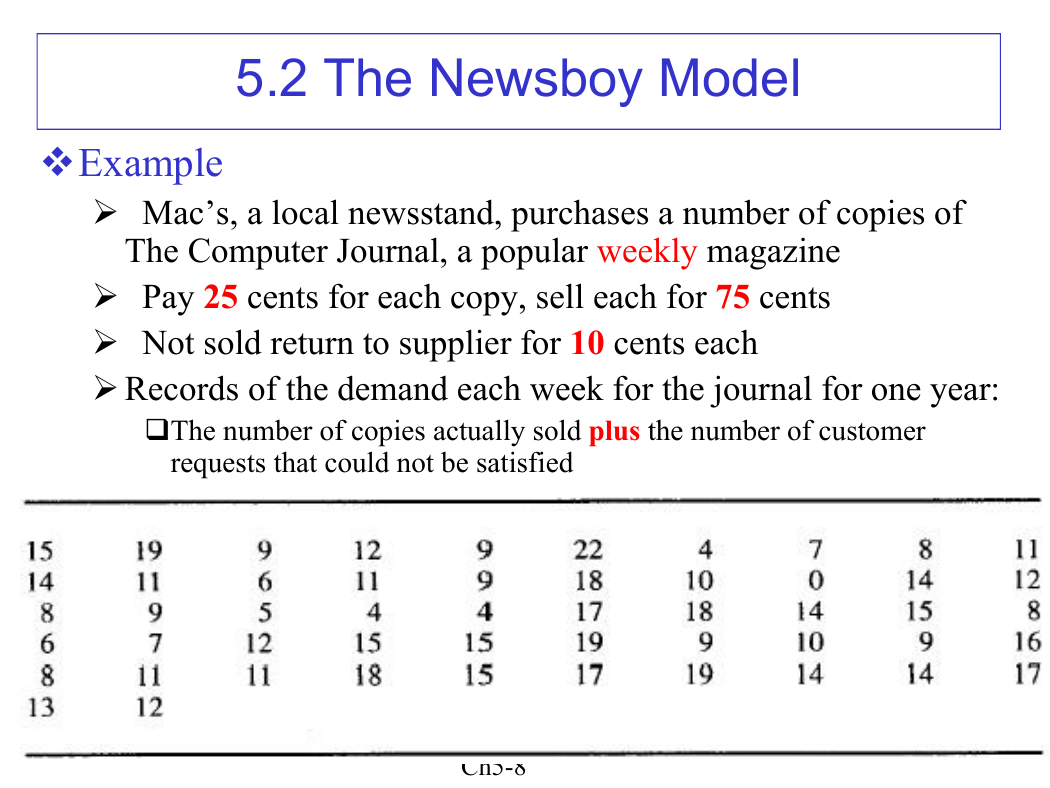
vExample
Ø Mac’s, a local newsstand, purchases a number of copies of
The Computer Journal, a popular weekly magazine
Ø Pay 25 cents for each copy, sell each for 75 cents
Ø Not sold return to supplier for 10 cents each
Ø Records of the demand each week for the journal for one year:
qThe number of copies actually sold plus the number of customer
requests that could not be satisfied
Ch5-8
�












 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc