Computer Vision - June o3, 2oo9
Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG)
& Support Vector Machines (SVM)
HOG: fixed spatial
relationships
Bernt Schiele
TU Darmstadt, Germany
http://www.mis.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de/cv/
schiele@cs.tu-darmstadt.de
g
n
i
t
u
p
m
o
C
d
e
t
n
e
m
g
u
A
y
r
o
s
n
e
S
d
n
a
l
a
u
t
p
e
c
r
e
P
�
Lecture Overview
Recognition (part 1/2)
• Object Recognition (Schiele)
‣
Intro - Some basics of digital image processing (2 weeks)
‣ Object Recognition for Identification (1-2 weeks)
• Global and local feature approaches
‣ Object Recognition for Categorization (4 weeks)
• Object Detection (specific object classes)
• Local Features & Interest Points (scale and affine invariant)
• Bag-of-Words for Object Categorization
• Histograms of Oriented Gradients & Support Vector Machines
• Part Representations, Combination with Segmentation
Computer Vision - June o3, 2oo9
Bernt Schiele - TU Darmstadt
2
�
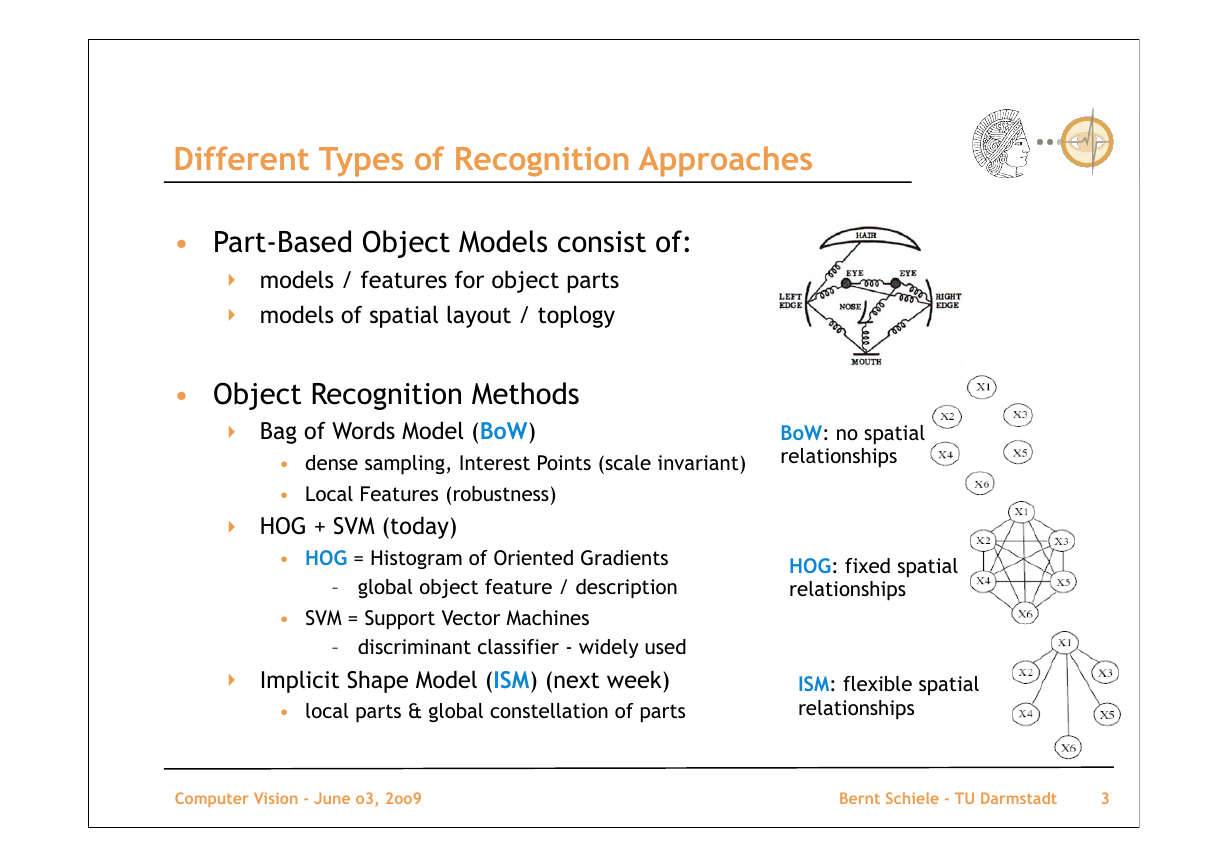
Different Types of Recognition Approaches
• Part-Based Object Models consist of:
‣ models / features for object parts
‣ models of spatial layout / toplogy
• Object Recognition Methods
‣ Bag of Words Model (BoW)
• dense sampling, Interest Points (scale invariant)
• Local Features (robustness)
‣ HOG + SVM (today)
• HOG = Histogram of Oriented Gradients
– global object feature / description
• SVM = Support Vector Machines
‣
– discriminant classifier - widely used
Implicit Shape Model (ISM) (next week)
• local parts & global constellation of parts
BoW: no spatial
relationships
HOG: fixed spatial
relationships
ISM: flexible spatial
relationships
Computer Vision - June o3, 2oo9
Bernt Schiele - TU Darmstadt
3
�
Overview of Today
• Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG)
‣ global descriptor for object detection
‣
‣
sliding window approach
(slides mostly taken from Dalal’s PhD-defense)
• Support Vector Machines (SVM)
‣ general intro
‣
linear SVM
Computer Vision - June o3, 2oo9
Bernt Schiele - TU Darmstadt
4
�
Goals & Applications of HOG
• Original Goal: Detect and Localize people in Images and Videos
• Applications:
Images, films & multi-media analysis
‣
‣ Pedestrian detection for autonomous cars
‣ Visual surveillance, behavior analysis
Computer Vision - June o3, 2oo9
Bernt Schiele - TU Darmstadt
5
�
Difficulties of People / Object Detection
• Some of the Difficulties
‣ Wide variety of articulated poses
‣ Variable appearance and clothing
‣ Complex backgrounds
‣ Unconstrained illumination
‣ Occlusions, different scales
‣ Videos sequences involves motion of the subject,
the camera and the objects in the background
• Main assumption for HOG:
upright fully visible people
Computer Vision - June o3, 2oo9
Bernt Schiele - TU Darmstadt
6
�
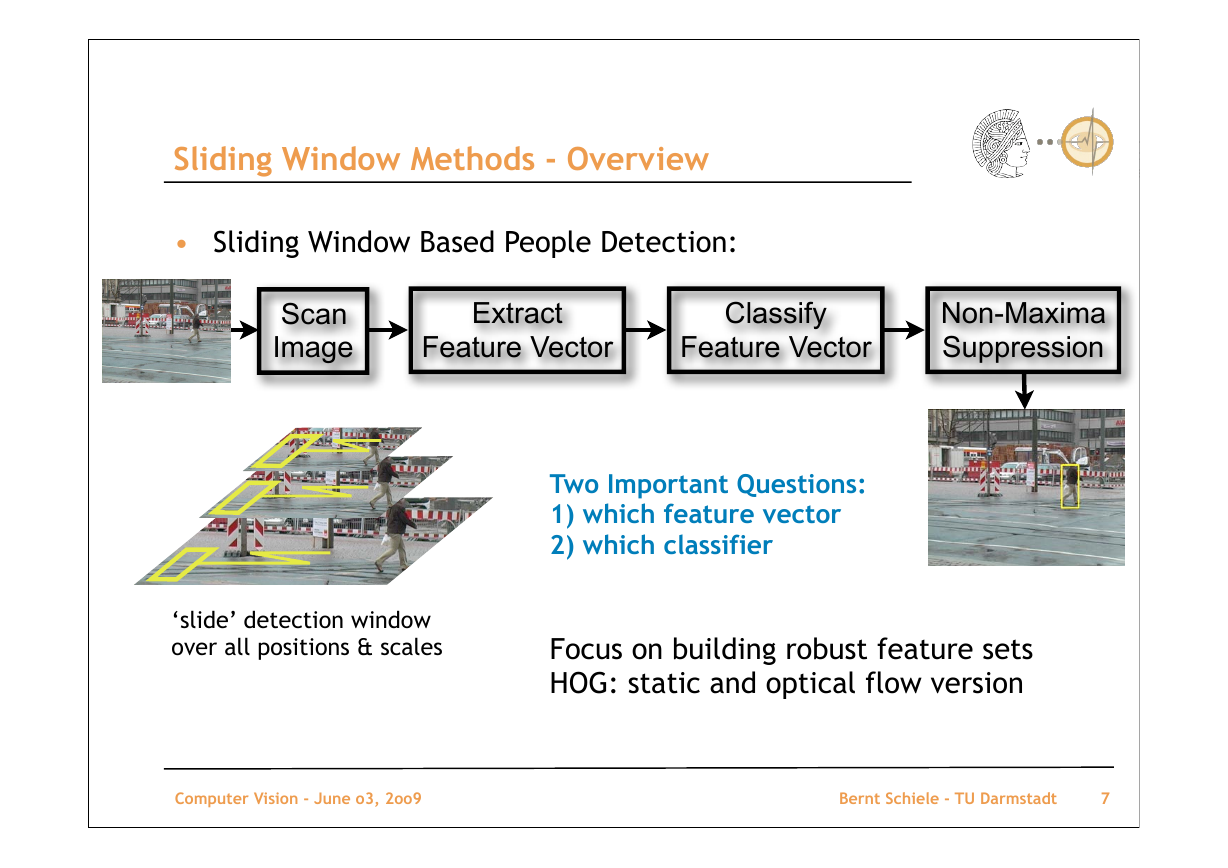
Sliding Window Methods - Overview
• Sliding Window Based People Detection:
Two Important Questions:
1) which feature vector
2) which classifier
‘slide’ detection window
over all positions & scales
Focus on building robust feature sets
HOG: static and optical flow version
Computer Vision - June o3, 2oo9
Bernt Schiele - TU Darmstadt
7
ScanImageExtract Feature VectorClassify Feature VectorNon-MaximaSuppression�
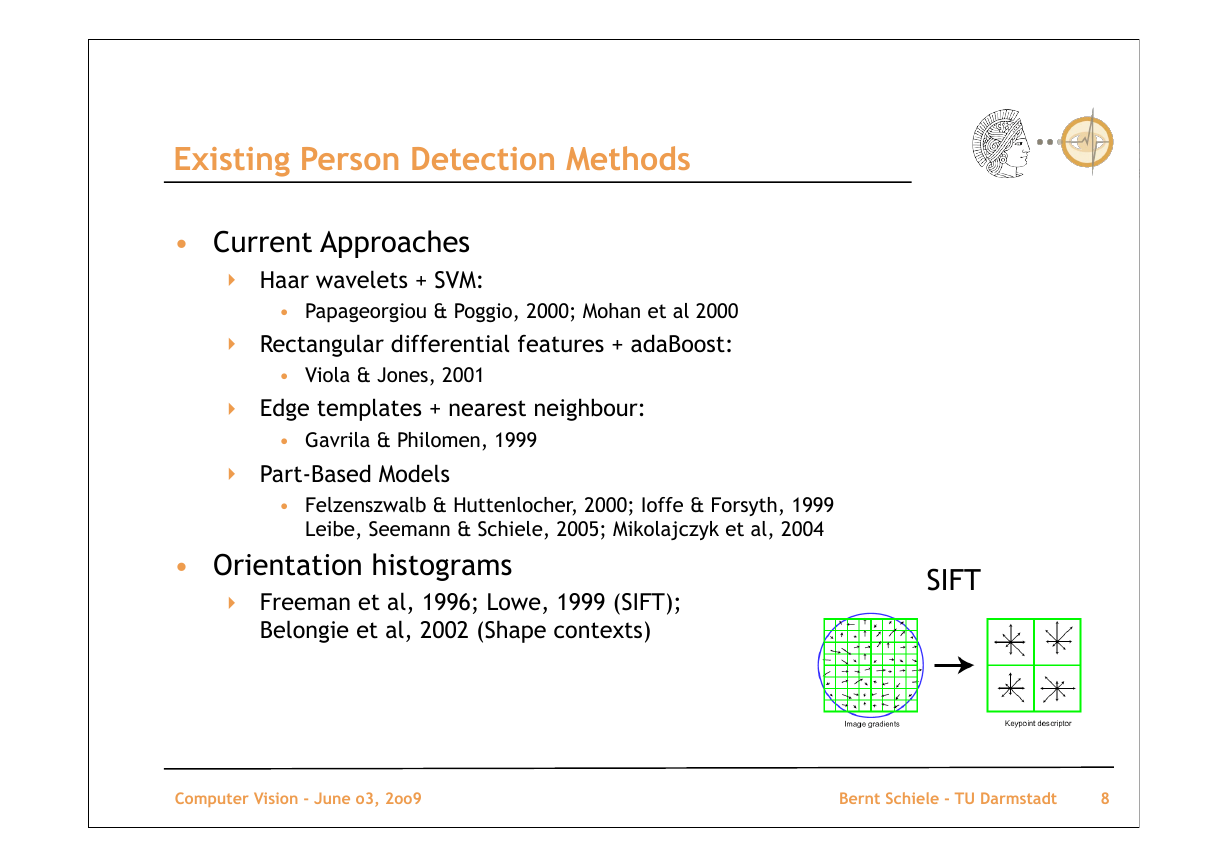
Existing Person Detection Methods
• Current Approaches
‣ Haar wavelets + SVM:
• Papageorgiou & Poggio, 2000; Mohan et al 2000
‣ Rectangular differential features + adaBoost:
‣ Edge templates + nearest neighbour:
‣ Part-Based Models
• Gavrila & Philomen, 1999
• Viola & Jones, 2001
• Felzenszwalb & Huttenlocher, 2000; Ioffe & Forsyth, 1999
Leibe, Seemann & Schiele, 2005; Mikolajczyk et al, 2004
• Orientation histograms
‣ Freeman et al, 1996; Lowe, 1999 (SIFT);
Belongie et al, 2002 (Shape contexts)
SIFT
Computer Vision - June o3, 2oo9
Bernt Schiele - TU Darmstadt
8
�










 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc