Vehicle Networks��V2X communication protocols ��Univ.-Prof. Dr. Thomas Strang, Dipl.-Inform. Matthias Röckl
Outline
Wireless Access for Vehicular Environments�Rationale
Wireless Access for Vehicular Environments (WAVE) ���IEEE 802.11p + 1609.x + SAE 2735
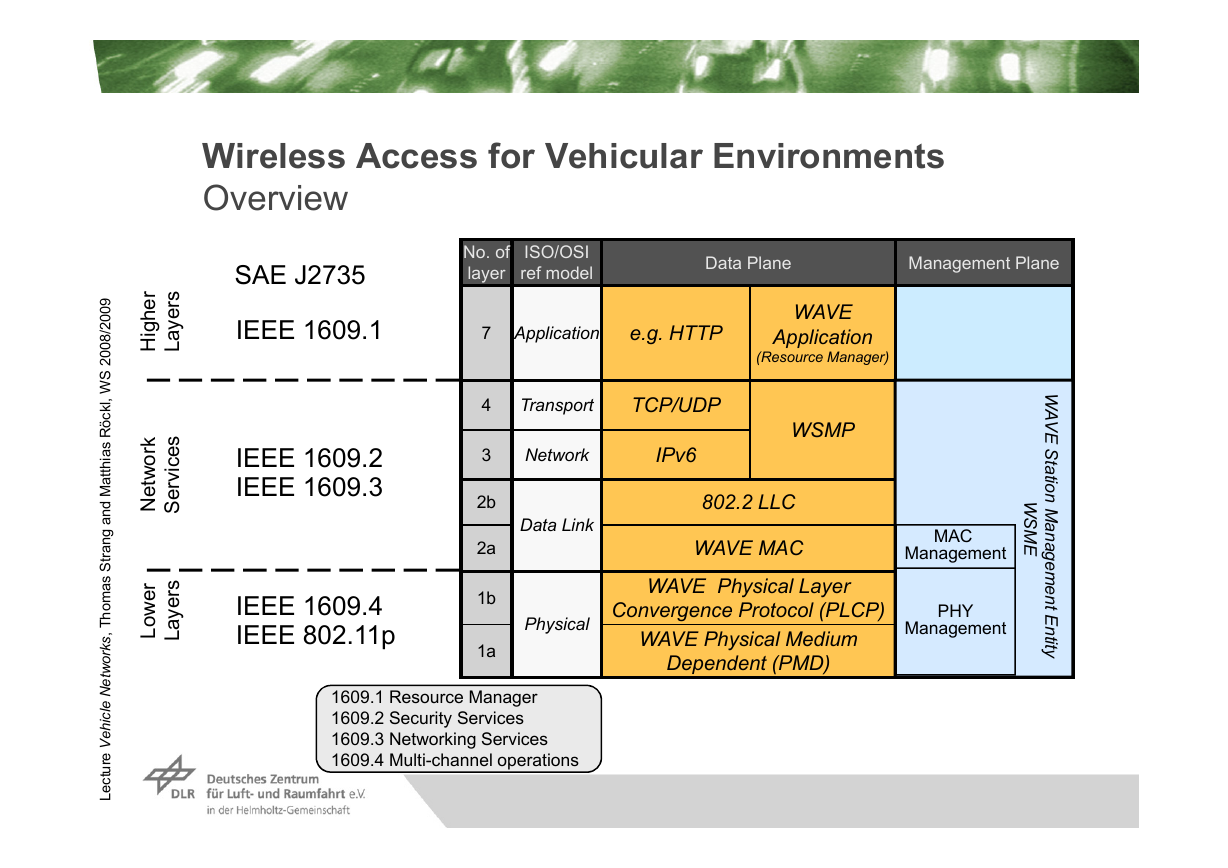
Wireless Access for Vehicular Environments�Overview
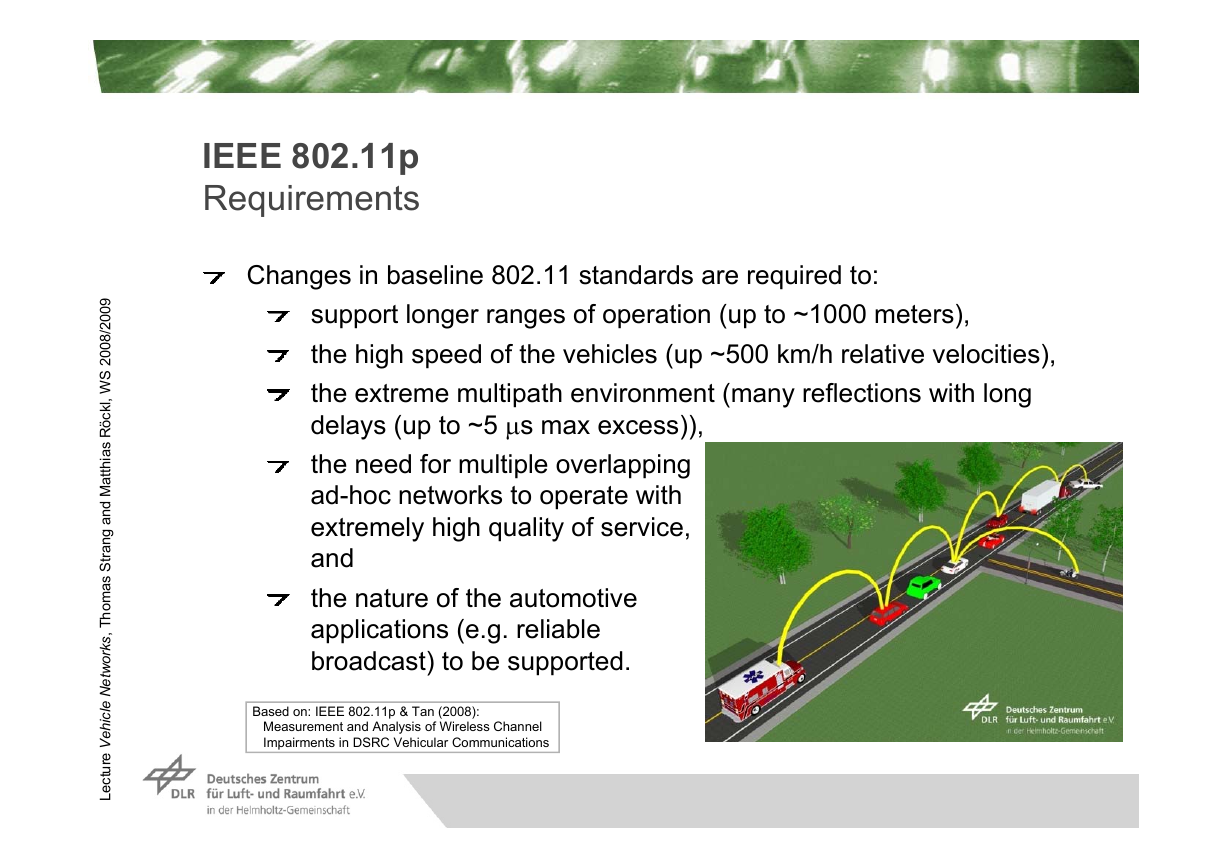
IEEE 802.11p�Requirements
IEEE 802.11p�Overview
IEEE 802.11p �Communication entities
IEEE 802.11p�Vehicle-2-Pedestrian
IEEE 802.11p�Pedestrian?
V2X frequency bands
IEEE 802.11p�Frequency band
IEEE 802.11p �Multi-channel
IEEE 802.11p�Operation modes
IEEE 802.11p�PHY
IEEE 802.11p�PHY: Comparison to IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11p�MAC
IEEE 1609.4�Extension for multi-channel coordination
IEEE 1609.4 �Channel Coordination
IEEE 1609.3�Networking Services
IEEE 1609.3�WAVE Short Message Protocol (WSMP)
SAE J2735�Message Dispatcher
SAE J2735�Basic message set definition
Car-2-Car Communication Consortium (C2C-CC)��&��ETSI TC ITS
Car-to-Car Communication Consortium�Partners
Car-2-Car Communication Consortium�Protocol stack
Car-to-Car Communication Consortium�Objectives of the First Demonstration (October 2008)
Demonstration self-restricted�to just two message types: CAM and DEN
Use Cases – Warning of Road Works
Use Cases – Emergency Vehicle (EV)
Use Cases – Broken Down Vehicle / � Post Crash Warning
Use Cases – Motorcycle Warning / � Intersection Assistance
Car-2-Car Communication Consortium�Focus and on-going discussions
Car-2-Car Communication Consortium / ETSI TC ITS�Relationship











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc