example解析
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
namespace ob = ompl::base;
namespace og = ompl::geometric;
namespace po = boost::program_options;
bool isStateValidEasy(const ob::SpaceInformation *si, const ob::State *state) {
const auto *s = state->as();
double x = s->getX(), y = s->getY();
/
/
空
间
状
态
的
定
义
h
t
t
p
:
/
/
o
m
p
l
.
k
a
v
r
a
k
i
l
a
b
.
o
r
g
/
c
l
a
s
s
o
m
p
l
_
1
_
1
b
a
s
e
_
1
_
1
S
c
o
p
e
d
S
t
a
t
e
.
h
t
m
l
/
/
几
何
问
题
通
常
所
需
要
的
类
集
h
t
t
p
:
/
/
o
m
p
l
.
k
a
v
r
a
k
i
l
a
b
.
o
r
g
/
c
l
a
s
s
o
m
p
l
_
1
_
1
g
e
o
m
e
t
r
i
c
_
1
_
1
S
i
m
p
l
e
S
e
t
u
p
.
h
t
m
l
/
/
定
义
了
O
M
P
L
版
本
号
信
息
,
及
相
关
功
能
是
否
编
译
过
~
/
/
程
序
命
令
行
参
数
的
输
入
及
解
析
h
t
t
p
s
:
/
/
b
l
o
g
.
c
s
d
n
.
n
e
t
/
m
o
r
n
i
n
g
_
c
o
l
o
r
/
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
/
d
e
t
a
i
l
s
/
5
0
2
4
1
9
8
7
/
/
行
驶
路
径
的
约
束
条
件
�
return si->satisfiesBounds(s) && (x < 5 || x>13 || (y > 8.5 && y < 9.5));
}
bool isStateValidHard(const ob::SpaceInformation *si, const ob::State *state) {
return si->satisfiesBounds(state);
}
void printTrajectory(const ob::StateSpacePtr& space, const std::vector& pt) {
if (pt.size() != 3) throw ompl::Exception("3 arguments required for trajectory option");
const unsigned int num_pts = 50;
ob::ScopedState<> from(space), to(space), s(space);
std::vector reals;
from[0] = from[1] = from[2] = 0.;
to[0] = pt[0];
to[1] = pt[1];
to[2] = pt[2];
std::cout << "distance: " << space->distance(from(), to()) << "\npath:\n";
for (unsigned int i = 0; i <= num_pts; ++i)
{
space->interpolate(from(), to(), (double)i / num_pts, s());
reals = s.reals();
std::cout << "path " << reals[0] << ' ' << reals[1] << ' ' << reals[2] << ' ' <<
std::endl;
}
}
void printDistanceGrid(const ob::StateSpacePtr& space) {
const unsigned int num_pts = 200;
ob::ScopedState<> from(space), to(space);
from[0] = from[1] = from[2] = 0.;
/
/
p
r
i
n
t
t
h
e
d
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
f
o
r
(
x
,
y
,
t
h
e
t
a
)
f
o
r
a
l
l
p
o
i
n
t
s
i
n
a
3
D
g
r
i
d
i
n
S
E
(
2
)
/
/
o
v
e
r
[
-
5
,
5
)
x
[
-
5
,
5
)
x
[
-
p
i
,
p
i
)
.
/
/
/
/
T
h
e
o
u
t
p
u
t
s
h
o
u
l
d
b
e
r
e
d
i
r
e
c
t
e
d
t
o
a
f
i
l
e
,
s
a
y
,
d
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
.
t
x
t
.
T
h
i
s
/
/
c
a
n
t
h
e
n
b
e
r
e
a
d
a
n
d
p
l
o
t
t
e
d
i
n
M
a
t
l
a
b
l
i
k
e
s
o
:
/
/
x
=
r
e
s
h
a
p
e
(
l
o
a
d
(
'
d
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
.
t
x
t
'
)
,
2
0
0
,
2
0
0
,
2
0
0
)
;
/
/
f
o
r
i
=
1
:
2
0
0
,
/
/
c
o
n
t
o
u
r
f
(
s
q
u
e
e
z
e
(
x
(
i
,
:
,
:
)
)
,
3
0
)
;
/
/
a
x
i
s
e
q
u
a
l
;
a
x
i
s
t
i
g
h
t
;
c
o
l
o
r
b
a
r
;
p
a
u
s
e
;
/
/
e
n
d
;
/
*
o
f
s
t
r
e
a
m
o
u
t
f
;
o
u
t
f
.
o
p
e
n
(
"
d
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
.
t
x
t
"
)
;
*
/
�
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < num_pts; ++i)
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < num_pts; ++j)
for (unsigned int k = 0; k < num_pts; ++k)
{
}
num_pts - 1.);
}
to[0] = 5. * (2. * (double)i / num_pts - 1.);
to[1] = 5. * (2. * (double)j / num_pts - 1.);
to[2] = boost::math::constants::pi() * (2. * (double)k /
void plan(const ob::StateSpacePtr &space, bool easy) {
ob::ScopedState<> start(space), goal(space);
ob::RealVectorBounds bounds(2);
bounds.setLow(0);
int k=bounds.high.size();
if (easy)
bounds.setHigh(18);
else
{
}
bounds.high[0] = 6;
bounds.high[1] = .6;
space->as()->setBounds(bounds);
og::SimpleSetup ss(space);
const ob::SpaceInformation *si = ss.getSpaceInformation().get();
auto isStateValid = easy ? isStateValidEasy : isStateValidHard;
ss.setStateValidityChecker([isStateValid, si](const ob::State *state) {return isStateValid(si,
state); });
if (easy) {
start[0] = start[1] = 1.0; start[2] = 0;
goal[0] = goal[1] = 16; goal[2] = -.99*boost::math::constants::pi();
}
else
/
/
o
u
t
f
<
<
s
p
a
c
e
-
>
d
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
(
f
r
o
m
(
)
,
t
o
(
)
)
<
<
"
"
;
/
/
s
t
d
:
:
c
o
u
t
<
<
s
p
a
c
e
-
>
d
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
(
f
r
o
m
(
)
,
t
o
(
)
)
<
<
'
\
n
'
;
/
/
o
u
t
f
.
c
l
o
s
e
(
)
;
/
/
根
据
所
使
用
的
空
间
分
配
状
态
/
/
边
界
空
间
的
维
度
此
处
2
维
每
个
维
度
都
有
个
l
o
w
和
h
i
g
h
值
故
b
o
u
n
d
s
.
l
o
w
有
两
个
值
/
/
a
s
转
换
为
某
个
实
例
所
需
要
的
类
型
/
/
构
造
所
需
的
规
划
空
间
/
/
对
此
空
间
的
有
效
性
进
行
检
查
h
t
t
p
:
/
/
o
m
p
l
.
k
a
v
r
a
k
i
l
a
b
.
o
r
g
/
s
t
a
t
e
V
a
l
i
d
a
t
i
o
n
.
h
t
m
l
/
/
函
数
作
为
右
值
赋
值
给
函
数
指
针
,
成
员
函
数
需
取
地
址
后
赋
值
给
函
数
指
针
(
语
法
)
�
{
}
start[0] = start[1] = .5; start[2] = .5*boost::math::constants::pi();;
goal[0] = 5.5; goal[1] = .5; goal[2] = .5*boost::math::constants::pi();
ss.setStartAndGoalStates(start, goal);
ss.getSpaceInformation()->setStateValidityCheckingResolution(0.005);
ss.setup();
ss.print();
ob::PlannerStatus sloved = ss.solve(
);
if (sloved) {
vector reals;
cout << "solution" << endl;
ss.simplifySolution();
og::PathGeometric path = ss.getSolutionPath();
path.interpolate();
path.printAsMatrix(cout);
}
else
cout << "no solution" << endl;
}
int main(int argc,char** argv) {
cout << OMPL_VERSION << endl;
argc = 7;
argv[0] = "";
argv[1] = "--easyplan";
argv[2] = "--trajectory";
argv[3] = "7.1";
argv[4] = "6.2";
argv[5] = "1.34";
argv[6] = "--distance";
try
{
po::options_description desc("Options");
/
/
可
选
的
参
数
,
从
而
获
得
更
多
的
输
出
信
息
/
/
设
置
需
要
验
证
状
态
有
效
性
的
分
辨
率
,
以
便
将
两
个
状
态
之
间
的
运
动
视
为
有
效
。
该
值
指
定
为
空
间
范
围
的
一
部
分
/
/
自
动
创
建
规
划
所
需
的
类
,
s
l
o
v
e
(
)
函
数
的
/
*
c
o
n
s
t
b
a
s
e
:
:
P
l
a
n
n
e
r
T
e
r
m
i
n
a
t
i
o
n
C
o
n
d
i
t
i
o
n
&
p
t
c
*
/
/
/
按
时
间
,
也
有
按
自
定
义
函
数
/
/
尝
试
简
化
当
前
路
径
,
简
化
方
式
,
默
认
0
s
内
简
化
,
或
按
自
定
义
函
数
简
化
/
/
获
取
路
径
,
/
/
默
认
插
值
,
指
定
插
值
数
量
插
值
法
/
/
打
印
矩
阵
形
式
/
/
深
入
浅
出
b
o
o
s
t
:
:
p
r
o
g
r
a
m
_
o
p
t
i
o
n
s
,
命
令
行
或
配
置
文
件
读
取
参
数
选
项
h
t
t
p
s
:
/
/
b
l
o
g
.
c
s
d
n
.
n
e
t
/
W
i
n
d
g
s
_
Y
F
/
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
/
d
e
t
a
i
l
s
/
8
1
2
0
1
4
5
6
/
/
输
入
参
数
的
描
述
�
desc.add_options()
("help", "show help message")
("dubins", "use Dubins state space")
("dubinssym", "use symmetrized Dubins state space")
("reedsshepp", "use reeds-shepp state space(default)")
("easyplan", "easy planning problem & print path")
("hardplan", "hard planning problem & print path")
("trajectory", po::value>()->multitoken(), "print x y theta
from start goal")
());
("distance", "print distance grid")
;
po::variables_map vm;
po::store(po::parse_command_line(argc, argv, desc), vm);
po::notify(vm);
if (vm.count("help")) { cout << desc << "/n"; return 1; };
ob::StateSpacePtr space(make_shared() );
if (vm.count("dubins")!=0u)
space = make_shared();
if (vm.count("dubinssym")!=0u)
space = make_shared(1., true);
if (vm.count("easyplan") != 0u)
plan(space, true);
if (vm.count("hardplan") != 0u)
plan(space, false);
if (vm.count("trajectory") != 0u)
printTrajectory(space, vm["trajectroy"].as>
if (vm.count("distance") != 0u)
printDistanceGrid(space);
}
catch (const std::exception&e)
{
}
cerr << "error:" << e.what() << "\n";
return 1;
catch (...) {
/
/
m
u
l
t
i
t
o
k
e
n
(
)
的
作
用
就
是
告
诉
编
译
器
,
该
选
项
可
接
受
多
个
值
/
/
容
器
,
用
于
存
储
解
析
后
的
选
项
,
是
s
t
d
:
:
m
a
p
的
派
生
类
,
可
以
像
关
联
容
器
一
样
使
用
/
/
命
令
行
的
参
数
用
s
t
o
r
e
解
析
出
来
并
存
储
至
v
m
/
/
更
新
所
有
外
部
变
量
/
/
c
o
u
n
t
(
)
-
>
检
测
某
个
选
项
是
否
被
输
入
/
/
指
向
r
e
e
d
s
s
h
e
p
p
状
态
空
间
的
智
能
指
针
/
/
对
称
d
u
b
i
n
s
状
态
空
间
/
/
v
a
r
i
a
b
l
e
s
_
m
a
p
(
选
项
存
储
器
)
是
s
t
d
:
:
m
a
p
的
派
生
类
,
可
以
像
关
联
容
器
一
样
使
用
,
通
过
o
p
e
r
a
t
o
r
[
]
来
取
出
其
中
的
元
素
.
但
其
内
部
的
元
素
类
型
v
a
l
u
e
_
t
y
p
e
是
b
o
o
s
t
:
:
a
n
y
,
用
来
存
储
不
确
定
类
型
的
参
数
值
,
必
须
通
过
模
板
成
员
函
数
a
s
<
t
y
p
e
>
(
)
做
类
型
转
换
后
,
才
能
获
取
其
具
体
值
.
�
cerr << "exception of unkonw type!\n";
}
return 0;
}
参考学习1
原博链接:https://blog.csdn.net/ljq31446/article/category/7534293
code
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //绑定函数
using namespace std;
namespace ob = ompl::base;
namespace og = ompl::geometric;
bool isStateValid(const ob::State *state) {
const ob::SE3StateSpace::StateType *se3state = state->as();
const ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType *pos = se3state-
>as(0);
const ob::SO3StateSpace::StateType *rot = se3state->as(1);
return (const void *)rot != (const void *)pos;
}
/
/
抽
象
类
型
转
换
为
我
们
期
望
类
型
/
/
提
取
第
1
、
2
状
态
的
组
成
,
并
转
换
为
我
们
期
望
的
/
/
确
定
状
态
是
否
可
行
,
这
里
一
直
为
t
r
u
e
,
避
免
编
译
器
警
告
�
void planWithSimpleSetup() {
ob::StateSpacePtr space(new ob::SE3StateSpace());
ob::RealVectorBounds bounds(3);
bounds.setHigh(1);
bounds.setLow(-1);
space->as()->setBounds(bounds);
og::SimpleSetup ss(space);
ss.setStateValidityChecker(boost::bind(&isStateValid,_1));
ob::ScopedState<> start(space),goal(space);
start.random();
goal.random();
start.print();
ss.setStartAndGoalStates(start, goal);
ob::PlannerPtr planner(new og::RRT(ss.getSpaceInformation()));
ss.setPlanner(planner);
ob::PlannerStatus solved = ss.solve(1.0);
if (solved) {
}
else
cout << "Found solution\n" << endl;
ofstream osf0("path0.txt");
ss.getSolutionPath().printAsMatrix(osf0);
ofstream osf1("path1.txt");
ss.simplifySolution();
ss.getSolutionPath().printAsMatrix(osf1);
cout << "No found" << endl;
}
int main(int, char**) {
cout << "OMPL_VERSION:" << OMPL_VERSION << endl;
planWithSimpleSetup();
/
/
声
明
我
们
规
划
所
在
的
空
间
维
度
/
/
设
置
三
维
空
间
的
边
界
/
/
定
义
一
个
简
易
类
/
/
路
径
约
束
检
查
,
使
用
b
i
n
d
绑
定
函
数
,
参
考
h
t
t
p
s
:
/
/
b
l
o
g
.
c
s
d
n
.
n
e
t
/
g
i
e
p
y
/
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
/
d
e
t
a
i
l
s
/
4
5
0
4
6
7
3
7
/
/
随
机
创
建
一
个
起
始
点
和
目
标
点
/
/
加
入
起
终
点
/
/
设
定
规
划
方
法
/
/
在
规
划
的
时
间
内
解
决
/
/
解
决
则
导
出
生
成
的
路
径
�
return 0;
}
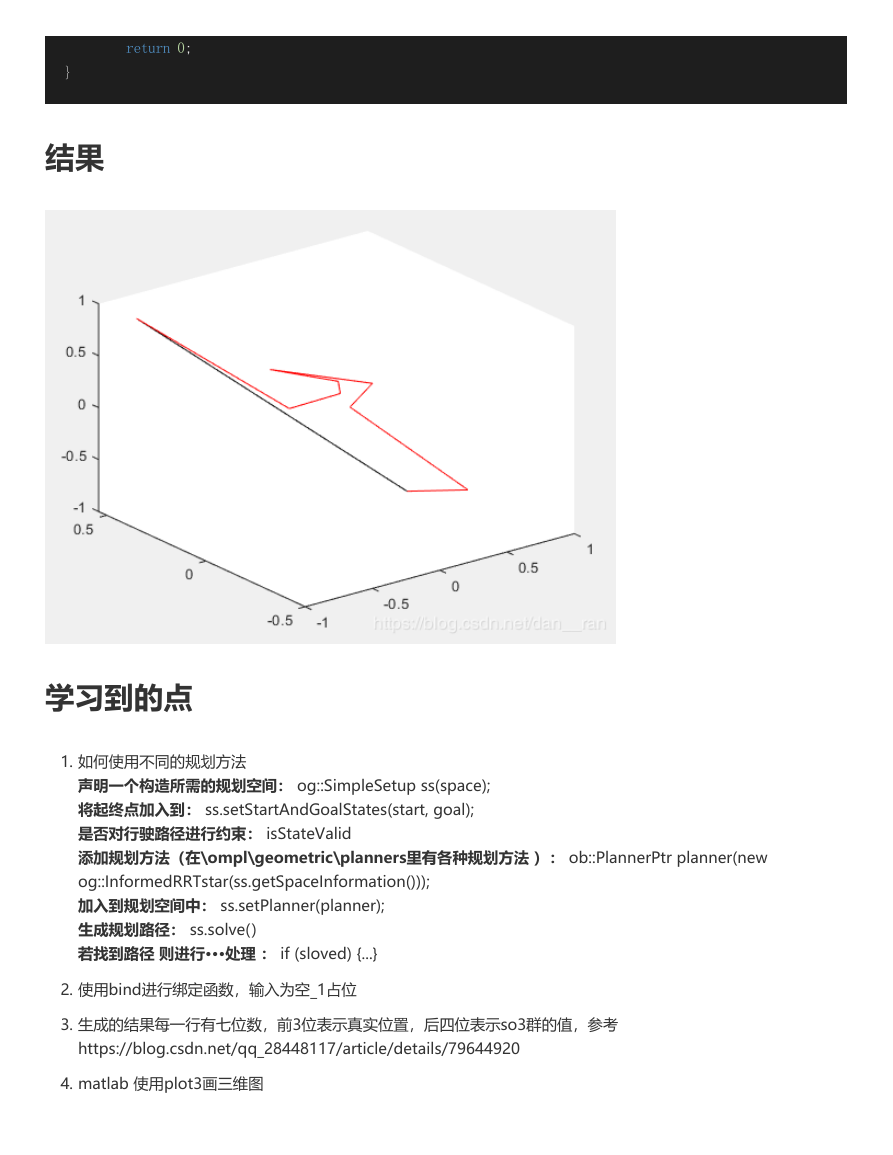
结果
学习到的点
1. 如何使用不同的规划方法
声明一个构造所需的规划空间: og::SimpleSetup ss(space);
将起终点加入到: ss.setStartAndGoalStates(start, goal);
是否对行驶路径进行约束: isStateValid
添加规划方法(在\ompl\geometric\planners里有各种规划方法 ): ob::PlannerPtr planner(new
og::InformedRRTstar(ss.getSpaceInformation()));
加入到规划空间中: ss.setPlanner(planner);
生成规划路径: ss.solve()
若找到路径 则进行···处理 : if (sloved) {...}
2. 使用bind进行绑定函数,输入为空_1占位
3. 生成的结果每一行有七位数,前3位表示真实位置,后四位表示so3群的值,参考
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_28448117/article/details/79644920
4. matlab 使用plot3画三维图
�














 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc