5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
基于 BGP 的 IPv6 路由网络测量
宋西瑞1,徐明伟2**
(1. 北京邮电大学网络与交换国家重点实验室,北京 100876;
2. 清华大学计算机系,北京 100083)
摘要:IPv4 地址基本消耗殆尽,IPv6 地址部署加快。因此,对 IPv6 网络的测量成为一个热
点。目前对于 IPv4 网络测量的研究比较多,对于 IPv6 网络的测量还比较少。BGP 作为主要
的域间路由协议,采取增量更新的方式进行路由更新。BGP update 数据变化情况能够很好
的反映出整个网络的变化情况。因此本文分析 IPv6 路由网络的 BGP 数据,从而分析网络的
发展情况。从 routeviews 自动下载指定的 update 数据,对数据处理,分类。然后根据分类情
况,测量 IPv6 路由网络的发展情况。先从总体测量了 IPv6 网络的发展情况,然后根据分类
情况,分析 IPv6 网络的稳定情况和健康发展情况。
关键词:计算机网络;IPv6;BGP;网络测量
中图分类号:TP393.2
IPv6 routing network measurement based on BGP
(1. State Key Laboratory Of Networking And Switching Technology,Beijing University of Posts
and Telecommunications,Beijing 100876;
SONG Xirui1, XU Mingwei2
2. Computer Science Department,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100083)
Abstract: With IPv4 addresses use up, IPv6 addresses deploy faster. Therefore, the survey of IPv6
network become a hot. Current research for IPv4 network measurement is more, for IPv6 network
measurement is relatively less. BGP as a main inter-domain routing protocol, adopts the method of
incremental updating routing updates.BGP update can well reflect the changes of the change of the
whole network. So this article analyzed the BGP of IPv6 routing network to analyze the
development of the network. This article from routeviews automatically download the specified
the update data rom routeviews, then ata processing and classification. Then, according to the
classification to measure the development of IPv6 routing network. Generally measured the IPv6
network development situation first, then according to the classification, analysis of the stable and
healthy development of the IPv6 network.
Key words: Computer network; IPv6; BGP;etwork measurement
0 引言
随着 IPv4 地址的消耗殆尽,加快了向 IPv6 网络过渡的速度。特别是经过 2010 年“IPv6
World day” 和 2011 年“IPv6 world day launch”之后。随着 IPv6 网络部署的加快,网络的稳
定性也成为我们关注的焦点。由于 IPv6 还未完全商业化,IPv6 网站正在快速发展以及 IPv6
网络协议与 IPv4 网络协议规范的不同,这些都可能导致 IPv6 路由与 IPv4 路由特性不同。
因此测量 IPv6 网络的稳定是非常必要的。
IPv4 网络的发展已经很成熟,目前有很多工作研究 IPv4 网络的稳定性。由于 IPv6 网络
才刚刚起步,对于 IPv6 网络的测量还比较少。主要是通过测量一些宏观数据,比如前缀数
量,as-path 长度等来反映 IPv6 网络部署的情况,对于 IPv6 网络的稳定性测量比较少。
边界网关协议(BGP)是一种自治系统(AS)的路由交换协议[1]。其主要功能是与其他 BGP
作者简介:宋西瑞(1990-),男,硕士,网络测量
通信联系人:徐明伟(1971-),男,教授,计算机网络,路由算法. E-mail: xmw@cernet.edu.cn
- 1 -
�
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
系统交换网络可达信息。BGP 属于外部网关路由协议,可以实现自治系统间无环路的域间
路由,是连接整个互联网的主要协议。由于 BGP 协议是增量更新,其 update 信息的变化情况
可以很好地反应整个网络的稳定性情况。因此我们选择通过 BGP update 信息的波动情况来
分析路由网络的稳定性情况。但是目前通过 BGP update 数据对 IPv6 路由网络的稳定的研究
比较少,主要的研究仍然是针对 IPv4 网络。
综上,本文从 routeviews 下载 IPv6 BGP update 数据。首先对数据进行解析和删除冗余
数据,的到可处理的 update 数据,然后对利用[1][2]的方法对 IPv6 网络 BGP update 数据进
行分类,分类获得各种 update 类别的比例情况,进一步分析路由网络的稳定性情况。分析
IPv6 路由网络的发展情况等。
1 相关工作
1.1 BGP 路由稳定性测量
《Internet routing instability》 [2]将 BGP update 数据进行分类。分为按照各个类别的比例,
分为正常 update,病态 update 等,从而在此基础上推断 IPv4 网络的稳定性情况,健康情况。
《Internet routing instability revisited》[3]在 2006 年在其基础上对 IPv4 网络 update 数据进行更
加细致的分类,重新测量了 2006 年时各个类别的比例情况,从而分析出正常 update,病态
update 的比例情况,并且与 1998 年文章比较,分析 IPv4 网络发展情况。
还有一些其他的对 BGP update 数据进行分类的方法来分析网络的行为:《Observation
and Analysis of BGP Behavior under Stress》[4]对 BGP update 进行分类,分析了各种故障中各
个类别的比例变化情况,分析不同故障下 BGP 的行为表现。《Differentiated BGP Update
Processing for Improved Routing Convergence》[5]对 update 按照其是否 forward_path tree 进行
分类,设定优先级,区别不同优先级的 update 数据。
还有其他工作研究全球路由的稳定性。《Global Routing Instabilities Triggered by Code
Red II and Nimda Worm Attacks》[6]分析了 Code Red II 和 Nimda Worm 攻击时对于全球路
由动态性的影响。《Studying Interdomain Routing over Long Timescales》[7]分析了 2005 年到
2011 年的 RIPE 与 routeviews 数据分析了全球路由状态的变化情况。《Longitual Study of BGP
Monitor Session Failures》[8]通过研究 8 年的数据分析 local BGP monitor 对于 Session failure
的影响。
1.2
IPv6 网络测量
针对 IPv4 网络的测量研究已经进行的非常多,前一章节的研究都是针对 IPv4 网络的研
究,现阶段已经开始有一些研究针对 IPv6 网络,目前开展的还比较少。
《Measuring the deployment of IPv6: topology, routing and performance》 [9]研究显示 IPv6
网络在逐渐成熟,虽然过程非常缓慢。目前核心网络服务商已经部署 IPv6,但是边缘网络
还比较滞后。IPv6 的路由动态拓扑结构在很大程度上类似于 IPv4。我们的测量结果表明,如
果 AS_path 是相同的,IPv6 与 IPv4 表现相当。否则,IPv6 的表现会比 IPv4 差。
《IPv6 evolution, stability and deployment》 [10]得出 2006 年以后,IPv6 网络以 O(d2)速度
发展,此外,网络本身和它的路由系统变得越来越稳定。作者分析 IPv6 网络发现其 AS 层分布
的遵循“Power-Law Distribution”,但是 AS 层拓扑不能描述为“Small-World Model”。
- 2 -
�
中国科技论文在线
2 数据处理
80
2.1 数据来源
http://www.paper.edu.cn
从 routeviews 官网下载 BGP update 数据。routeviews 是美国俄勒冈大学的项目[11],从
2001 年开始收集全球的 BGP 更新数据(每隔 15 分钟存储一次)和 RIB 表数据(每隔 2 小
时存储一次)。自动从监测点 routeviews6 下载从 2006 年-2014 年每年 6 月的 update 数据和
对应的 rib 数据。routeviews6 节点从其对应的 peer 节点手机 update 数据和 rib 数据,routeviews6
节点是纯 IPv6 网络的节点,收集到得 update 与 rib 数据都是 IPv6 地址的。
2.2 解析,删除冗余数据
原始数据是按照二进制压缩格式存储。用 bgpdump 工具进行解析原始数据,得到可读
的文本文件。接下来需要删除 update 文件中的冗余数据。删除冗余数据指的是是删除 BGP
reset 消息。BGP 的工作机制如下:BGP 系统启动时,与连接的路由交换整个路由表信息。
之后更新路由表,只交换更新信息,即只有增量信息在系统运行过程中,通过接收和发送
KEEPALIVE 消息来检测互相之间连接是否正常 BGP 发送优选的 BGP 路由给对等体。在主
干网上路由表中路由信息已经达到数万条。每次交换整个路由表中的信息,会导致 update
的数量急剧上升,影响我们分析不正常 update 造成的影响。所以需要删除 update 的 reset 消
息。
利用 MCT 算法[12]删除 collector 与其 peer 之间的 reset 消息。这样就删除了 reset 消息对
于 update 数据的影响。删除过程如下:首先读取 rib 文件,获得每对 peer 之间大概有多少前
缀。之后统计每对 peer 以某个前缀为起始,查询到所有前缀 update 所需要的时间,整个的
时间趋势应该是 V 型走势,间隔用时最短的查询过程就推断为 reset 的过程。找到对应的 peer,
以及 reset 的起始时间和结束时间,然后删除该时间区间内所有的 update 消息。
3 数据分析
85
90
95
100
3.1 整体分析
图 1 表示前缀数量增长趋势,反映出 prefix 在 2010 年之前总体增长发展比较缓慢,在
2010 年之后,经过 IPv6 World day 和 IPv6 world launch day。IPv6 网络中 prefix 数量增长大
大加快。
105
图 1 prefix 数量增长趋势
Fig.1 The prefix number growth
- 3 -
�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
110
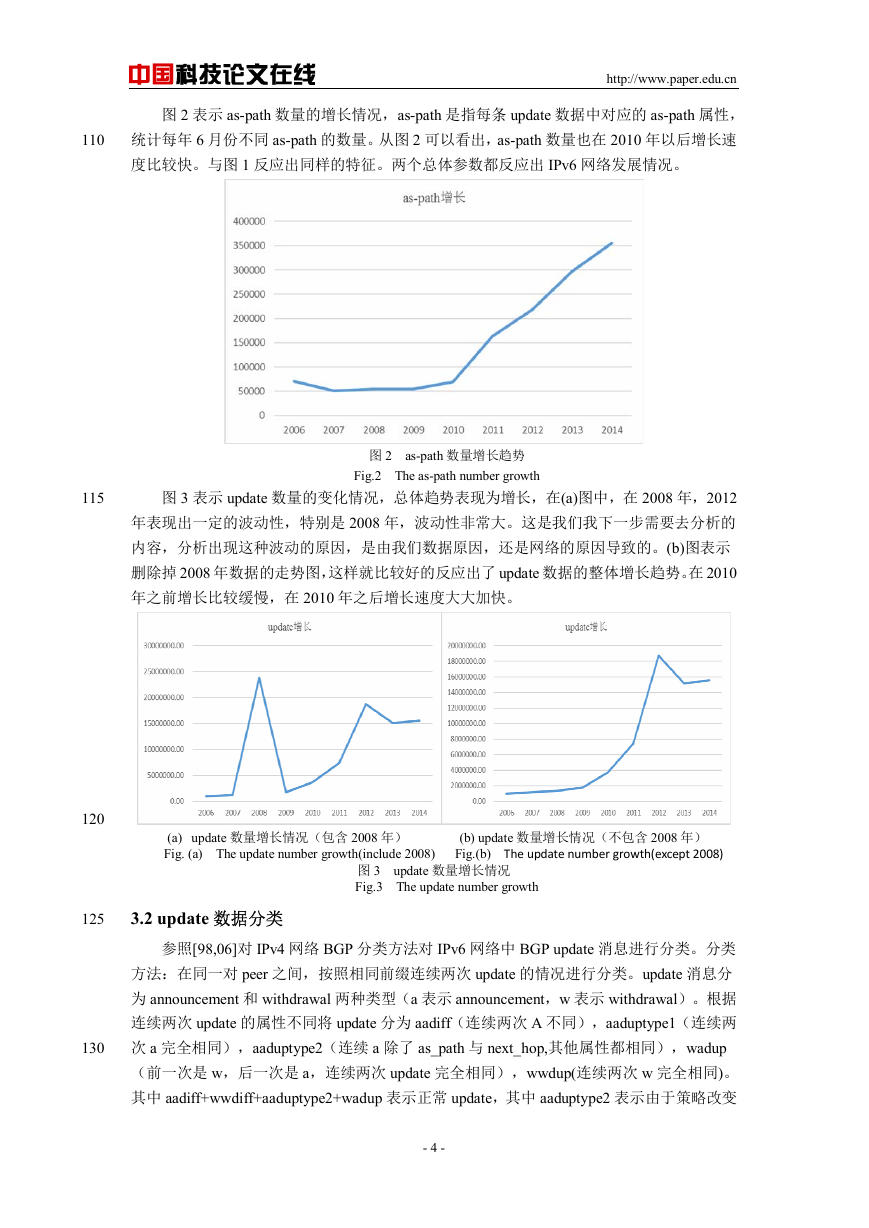
图 2 表示 as-path 数量的增长情况,as-path 是指每条 update 数据中对应的 as-path 属性,
统计每年 6 月份不同 as-path 的数量。从图 2 可以看出,as-path 数量也在 2010 年以后增长速
度比较快。与图 1 反应出同样的特征。两个总体参数都反应出 IPv6 网络发展情况。
图 2 as-path 数量增长趋势
Fig.2 The as-path number growth
115
图 3 表示 update 数量的变化情况,总体趋势表现为增长,在(a)图中,在 2008 年,2012
年表现出一定的波动性,特别是 2008 年,波动性非常大。这是我们我下一步需要去分析的
内容,分析出现这种波动的原因,是由我们数据原因,还是网络的原因导致的。(b)图表示
删除掉 2008 年数据的走势图,这样就比较好的反应出了 update 数据的整体增长趋势。在 2010
年之前增长比较缓慢,在 2010 年之后增长速度大大加快。
120
(a) update 数量增长情况(包含 2008 年) (b) update 数量增长情况(不包含 2008 年)
Fig. (a) The update number growth(include 2008) Fig.(b) The update number growth(except 2008)
图 3 update 数量增长情况
Fig.3 The update number growth
125
3.2 update 数据分类
参照[98,06]对 IPv4 网络 BGP 分类方法对 IPv6 网络中 BGP update 消息进行分类。分类
方法:在同一对 peer 之间,按照相同前缀连续两次 update 的情况进行分类。update 消息分
为 announcement 和 withdrawal 两种类型(a 表示 announcement,w 表示 withdrawal)。根据
连续两次 update 的属性不同将 update 分为 aadiff(连续两次 A 不同),aaduptype1(连续两
次 a 完全相同),aaduptype2(连续 a 除了 as_path 与 next_hop,其他属性都相同),wadup
(前一次是 w,后一次是 a,连续两次 update 完全相同),wwdup(连续两次 w 完全相同)。
其中 aadiff+wwdiff+aaduptype2+wadup 表示正常 update,其中 aaduptype2 表示由于策略改变
130
- 4 -
�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
引起的 update。wwdup+aaduptype1 表示不正常的 update。
135
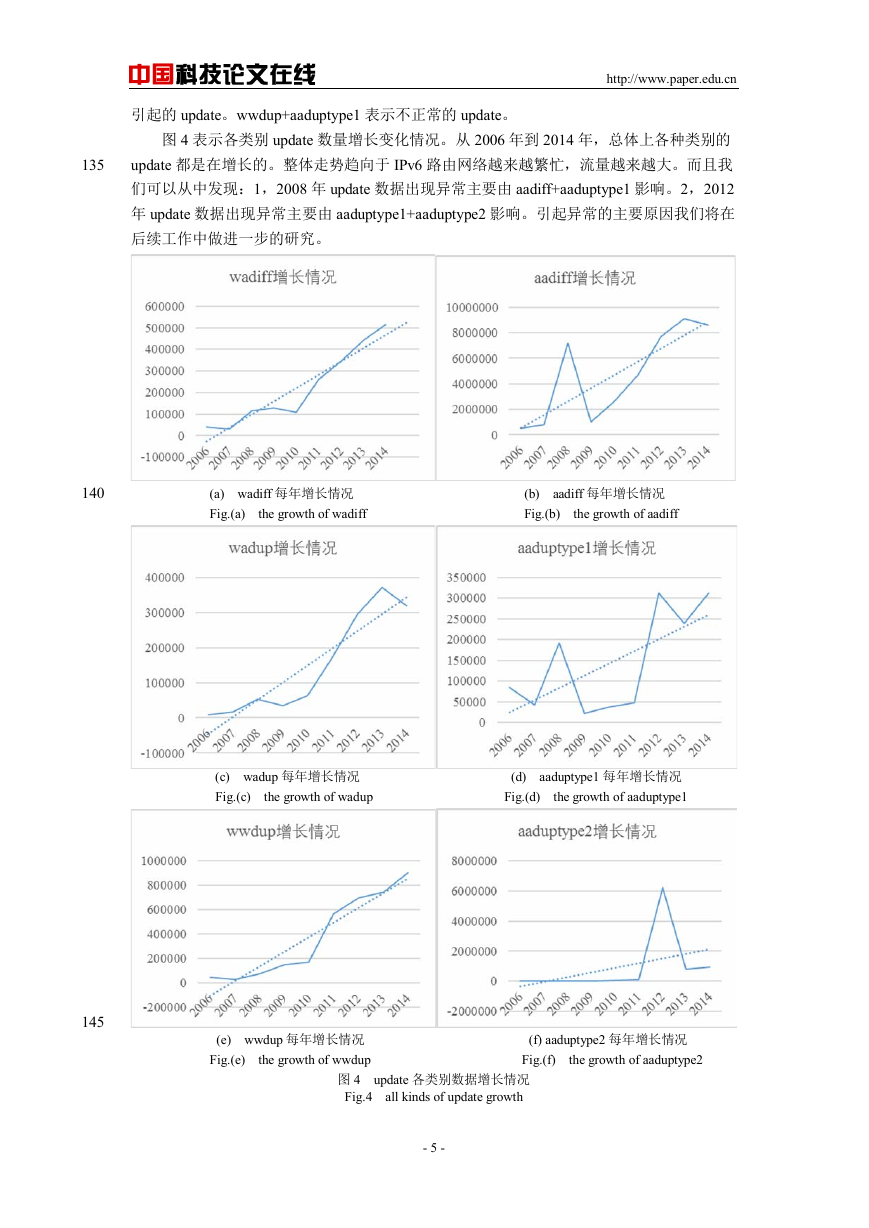
图 4 表示各类别 update 数量增长变化情况。从 2006 年到 2014 年,总体上各种类别的
update 都是在增长的。整体走势趋向于 IPv6 路由网络越来越繁忙,流量越来越大。而且我
们可以从中发现:1,2008 年 update 数据出现异常主要由 aadiff+aaduptype1 影响。2,2012
年 update 数据出现异常主要由 aaduptype1+aaduptype2 影响。引起异常的主要原因我们将在
后续工作中做进一步的研究。
140
(a) wadiff 每年增长情况 (b) aadiff 每年增长情况
Fig.(a) the growth of wadiff Fig.(b) the growth of aadiff
(c) wadup 每年增长情况 (d) aaduptype1 每年增长情况
Fig.(c) the growth of wadup Fig.(d) the growth of aaduptype1
145
(e) wwdup 每年增长情况 (f) aaduptype2 每年增长情况
Fig.(e) the growth of wwdup Fig.(f) the growth of aaduptype2
图 4 update 各类别数据增长情况
Fig.4 all kinds of update growth
- 5 -
�
中国科技论文在线
3.3 分析 IPv6 路由网络发展的情况
150
http://www.paper.edu.cn
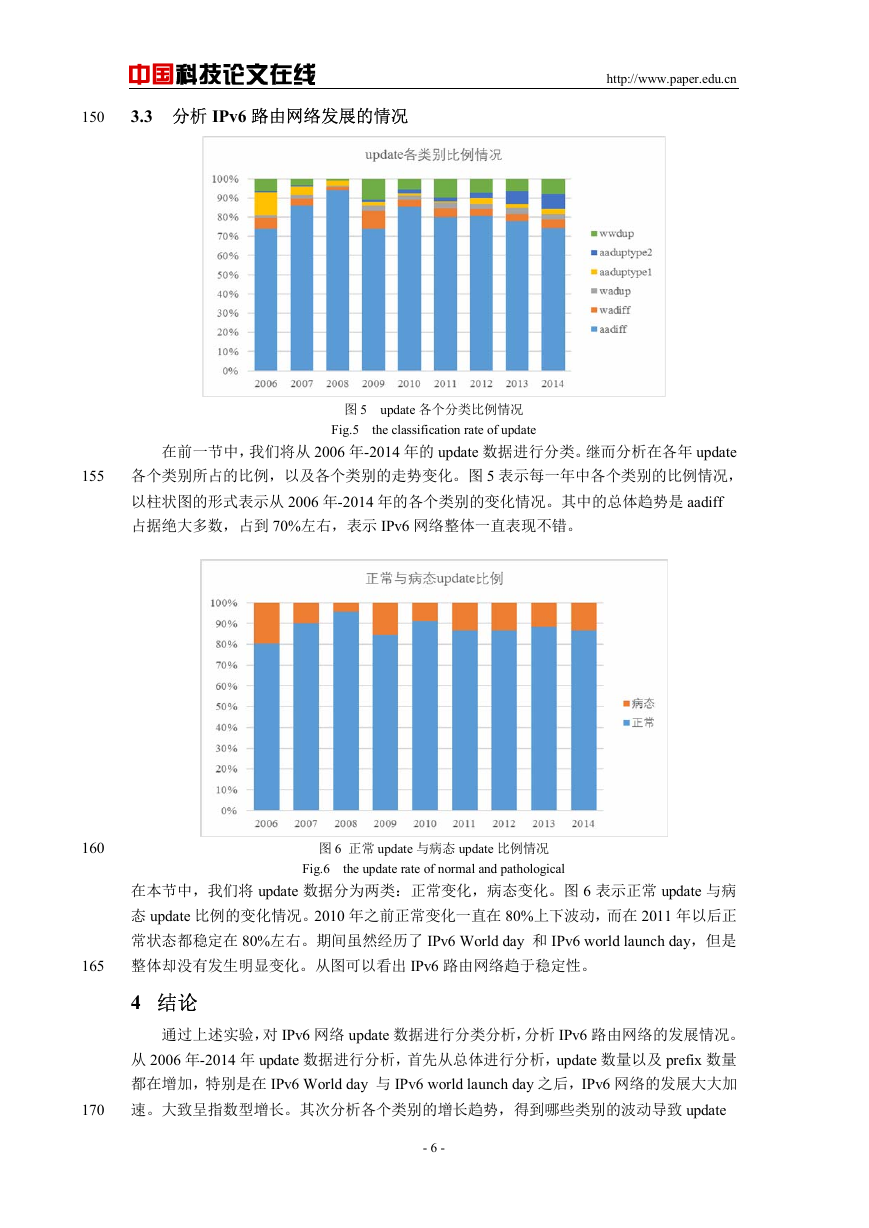
图 5 update 各个分类比例情况
Fig.5 the classification rate of update
155
在前一节中,我们将从 2006 年-2014 年的 update 数据进行分类。继而分析在各年 update
各个类别所占的比例,以及各个类别的走势变化。图 5 表示每一年中各个类别的比例情况,
以柱状图的形式表示从 2006 年-2014 年的各个类别的变化情况。其中的总体趋势是 aadiff
占据绝大多数,占到 70%左右,表示 IPv6 网络整体一直表现不错。
图 6 正常 update 与病态 update 比例情况
Fig.6 the update rate of normal and pathological
在本节中,我们将 update 数据分为两类:正常变化,病态变化。图 6 表示正常 update 与病
态 update 比例的变化情况。2010 年之前正常变化一直在 80%上下波动,而在 2011 年以后正
常状态都稳定在 80%左右。期间虽然经历了 IPv6 World day 和 IPv6 world launch day,但是
整体却没有发生明显变化。从图可以看出 IPv6 路由网络趋于稳定性。
4 结论
通过上述实验,对 IPv6 网络 update 数据进行分类分析,分析 IPv6 路由网络的发展情况。
从 2006 年-2014 年 update 数据进行分析,首先从总体进行分析,update 数量以及 prefix 数量
都在增加,特别是在 IPv6 World day 与 IPv6 world launch day 之后,IPv6 网络的发展大大加
速。大致呈指数型增长。其次分析各个类别的增长趋势,得到哪些类别的波动导致 update
160
165
170
- 6 -
�
中国科技论文在线
http://www.paper.edu.cn
发生波动变化。最后分析了 IPv6 网络发展情况,分析随着时间各个类别的变化趋势,并且
分类为正常的 update 与病态的 update,在 2006 年-2010 年之间,各个类别的波动性比较大,
在 2010 年之后,比较稳定,正常的 update 趋近在 80%左右。
[参考文献] (References)
175
180
185
190
195
[1] Y. Rekhter, T. Li, and S. Hares, A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4), RFC 4271, 2006.
[2] Labovitz C, Malan G, Jahanian F. Internet routing instability[J]. IEEE\/ACM Transactions on Networking,
1998, 6(5): 515-528.
[3] Li J,Guidero M,Wu Z,Purpus E,Ehrenkranz T. BGP routing dynamics revisited[J]. Computer Communication
Review, 2007.
[4] Wang L,Zhao X L, Pei D,Bush R,Massey D,Mankin A,Wu S,Zhang L X. Observation and analysis of BGP
behavior under stress[J]., 2002.
[5] Sun W,Mao Z,Shin K G. Differentiated BGP Update Processing for Improved Routing Convergence[J].
International Conference on Network Protocols, 2006.
[6] J. Cowie and A. T. Ogielski, Global Routing Instabilities Triggered by Code Red II and Nimda Worm
Attacks, Renesys Corp., Technical Report, Dec. 2001
[7] Comarela G, Gursun G, Crovella M. Studying interdomain routing over long timescales[J]. Proceedings of the
2013 Conference on Internet Measurement Conference, 2013.
[8] Cheng P, Zhao X, Zhang B. Longitudinal study of BGP monitor session failures[J]. Acm Sigcomm Computer
Communication Review, 2010.
[9] Dhamdhere A,Luckie M,Huffaker B Claffy K,Elmokashfi A,Aben E. Measuring the deployment of IPv6
(topology, routing and performance)[J]., 2012.
[10] Jiang X K,Bi J,Wang Y Y,He Z J,Zhang W,Tian H C.IPv6 evolution, stability and deployment[J].
International Conference on Network Protocols, 2011.
[11] routeviews project.http://routeviews.org/
[12] Zhang B,Kambhampati V,Lad M,Massey D, Zhang L.Identifying BGP routing table transfers[J]. ACM
Special Interest Group on Data Communication, 2005.
- 7 -
�











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc