使用 C# vs2010 读写 Excel 的实例
说明:本例是参考 Microsoft MSND 实例,并通过作者本人修改调试通过的。作者会将每一
步的操作写得经量详细,主要是方便初学学习,为像我一样的初学者节约大量的学习时间,
少走一些不必要的弯路。
为了是代码简单,本例选择了建立一个控制台程序:工程名为MSDNEXCEL
第一步:添加using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel; 引用,该应用在
D:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 10.0\Visual Studio Tools for Office\PIA\Office12目录下。引用文
件为:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.dll
其中注意:(1)D:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 10.0 为作者安装 vs2010 的目录,每个人情
况不一样;
(2)Visual Studio Tools for Office\PIA 目录下会有不同的 office 版本文件夹功选择,我装的是 offic2003
所以选着的是 office12 文件夹。
第二步:添加一个简单的收入账户类Account 注明:该类摘抄的是MSDN中实例里面的类。
public class Account
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public double Balance { get; set; }
}
第三步:添加一个静态方法static void DisplayInExcel(IEnumerable
accounts) 摘抄自
MSND
static void DisplayInExcel(IEnumerable accounts)
{
var excelApp = new Excel.Application();
// Make the object visible.
excelApp.Visible = true;
// Create a new, empty workbook and add it to the collection returned
// by property Workbooks. The new workbook becomes the active workbook.
// Add has an optional parameter for specifying a praticular template.
// Because no argument is sent in this example, Add creates a new workbook.
excelApp.Workbooks.Add();
// This example uses a single workSheet. The explicit type casting is
// removed in a later procedure.
Excel._Worksheet workSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)excelApp.ActiveSheet;
workSheet.Cells[1, "A"] = "ID Number";
workSheet.Cells[1, "B"] = "Current Balance";
var row = 1;
foreach (var acct in accounts)
{
row++;
workSheet.Cells[row, "A"] = acct.ID;
workSheet.Cells[row, "B"] = acct.Balance;
� }
workSheet.Columns[1].AutoFit();
workSheet.Columns[2].AutoFit();
}
第四步:
在Main()函数中添加如下代码:
var bankAccounts = new List
{
new Account
{
ID = 345678,
Balance = 541.27
},
new Account
{
ID = 1230221,
Balance = -127.44
}
};
DisplayInExcel(bankAccounts);
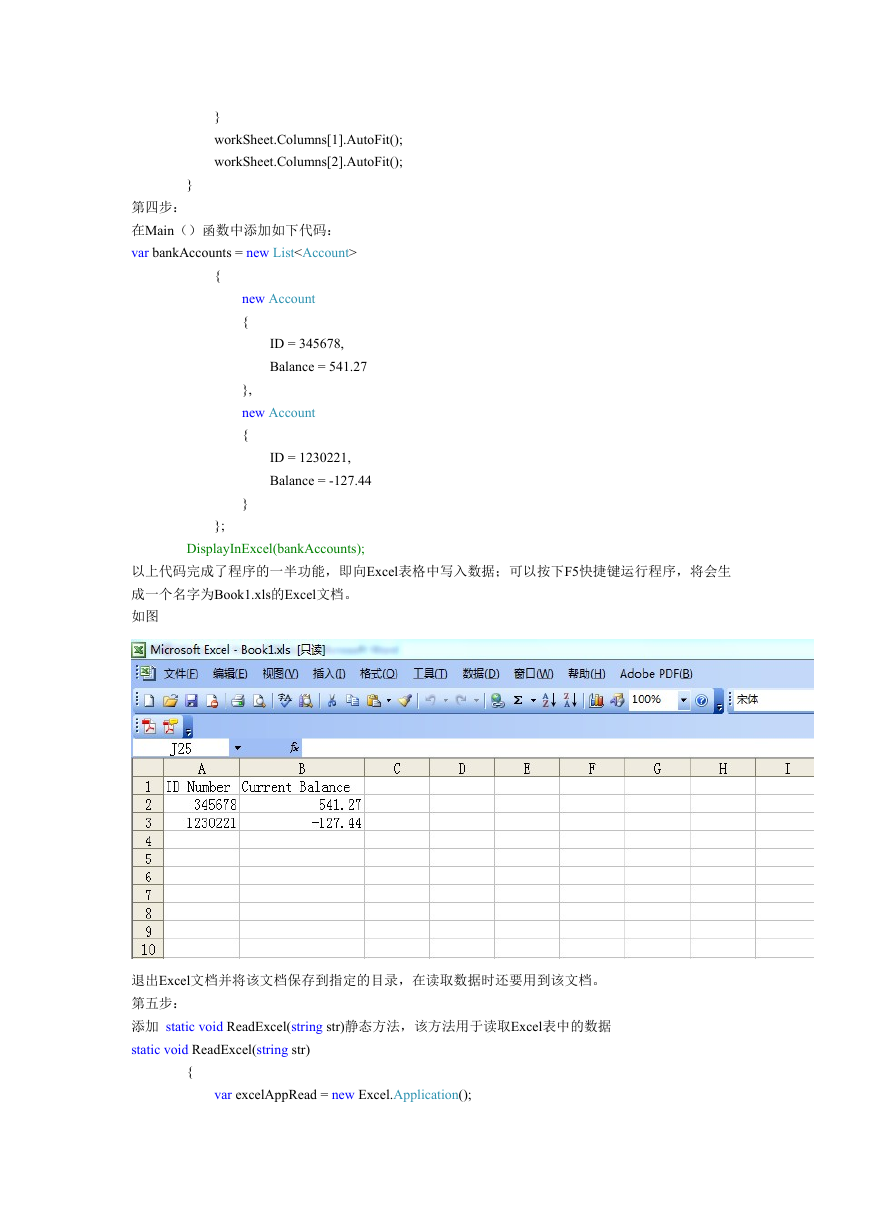
以上代码完成了程序的一半功能,即向Excel表格中写入数据;可以按下F5快捷键运行程序,将会生
成一个名字为Book1.xls的Excel文档。
如图
退出Excel文档并将该文档保存到指定的目录,在读取数据时还要用到该文档。
第五步:
添加 static void ReadExcel(string str)静态方法,该方法用于读取Excel表中的数据
static void ReadExcel(string str)
{
var excelAppRead = new Excel.Application();
� excelAppRead.Application.Workbooks.Open(str);
Account temp ;
Excel._Worksheet workSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)excelAppRead.ActiveSheet;
var count = workSheet.Cells.Count;
for (int i = 2; i <4; i++)
{
temp = new Account();
temp.ID = int.Parse(workSheet.Cells[i, "A"].Text);
temp.Balance = double.Parse(workSheet.Cells[i, "B"].Text);
Console.WriteLine("ID: {0}\t;Balance: {1}", temp.ID,temp.Balance);
}
}
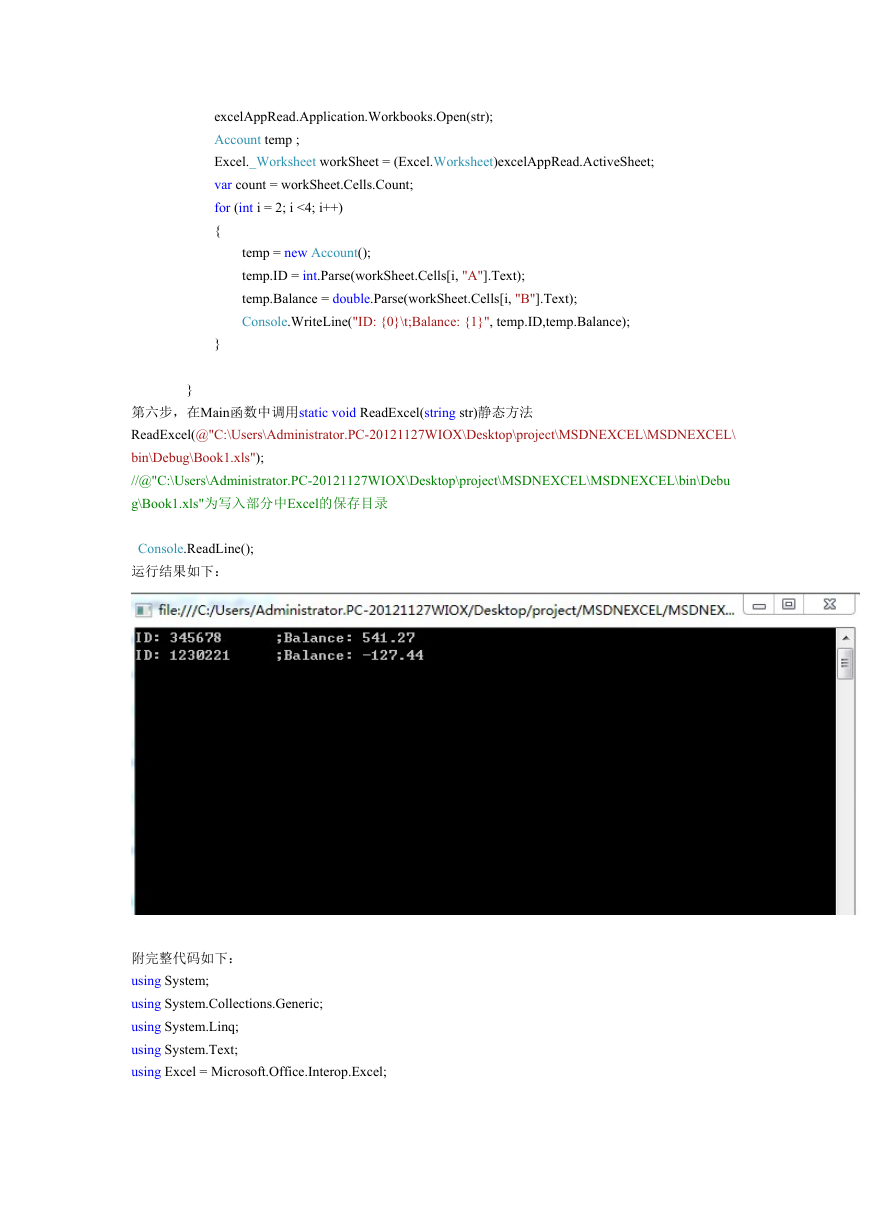
第六步,在Main函数中调用static void ReadExcel(string str)静态方法
ReadExcel(@"C:\Users\Administrator.PC-20121127WIOX\Desktop\project\MSDNEXCEL\MSDNEXCEL\
bin\Debug\Book1.xls");
//@"C:\Users\Administrator.PC-20121127WIOX\Desktop\project\MSDNEXCEL\MSDNEXCEL\bin\Debu
g\Book1.xls"为写入部分中Excel的保存目录
Console.ReadLine();
运行结果如下:
附完整代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
�
namespace MSDNEXCEL
{
public class Account
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public double Balance { get; set; }
}
class Program
{
static void DisplayInExcel(IEnumerable
accounts)
{
var excelApp = new Excel.Application();
// Make the object visible.
excelApp.Visible = true;
// Create a new, empty workbook and add it to the collection returned
// by property Workbooks. The new workbook becomes the active workbook.
// Add has an optional parameter for specifying a praticular template.
// Because no argument is sent in this example, Add creates a new workbook.
excelApp.Workbooks.Add();
// This example uses a single workSheet. The explicit type casting is
// removed in a later procedure.
Excel._Worksheet workSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)excelApp.ActiveSheet;
workSheet.Cells[1, "A"] = "ID Number";
workSheet.Cells[1, "B"] = "Current Balance";
var row = 1;
foreach (var acct in accounts)
{
row++;
workSheet.Cells[row, "A"] = acct.ID;
workSheet.Cells[row, "B"] = acct.Balance;
}
workSheet.Columns[1].AutoFit();
workSheet.Columns[2].AutoFit();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var bankAccounts = new List
{
new Account
{
ID = 345678,
Balance = 541.27
},
� new Account
{
ID = 1230221,
Balance = -127.44
}
};
// DisplayInExcel(bankAccounts);
ReadExcel(@"C:\Users\Administrator.PC-20121127WIOX\Desktop\project\MSDNEXCEL\MSDNEXCEL\
bin\Debug\Book1.xls");
//@"C:\Users\Administrator.PC-20121127WIOX\Desktop\project\MSDNEXCEL\MSDNEXCEL\bin\Debu
g\Book1.xls"为写入部分中Excel的保存目录
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void ReadExcel(string str)
{
var excelAppRead = new Excel.Application();
excelAppRead.Application.Workbooks.Open(str);
Account temp ;
Excel._Worksheet workSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)excelAppRead.ActiveSheet;
var count = workSheet.Cells.Count;
for (int i = 2; i <4; i++)
{
temp = new Account();
temp.ID = int.Parse(workSheet.Cells[i, "A"].Text);
temp.Balance = double.Parse(workSheet.Cells[i, "B"].Text);
Console.WriteLine("ID: {0}\t;Balance: {1}", temp.ID,temp.Balance);
}
}
}
}
�








 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc