一. 实验目的及实验环境
掌握贪心算法的基本思想和熟悉常用使用案例。加深对贪心算法的理解。
实验环境:Dev c++
二. 实验内容
4-11 删数问题
问题描述:给定 n 位正整数 a,去掉其中任意 k≤n 个数字后,剩下的数字按
原次序排列组成一个新的正整数。对于给定的 n 位正整数 a 和正整数 k,设计一
个算法找出剩下数字组成的新数最小的删数方案。
5-8 整数变换问题
问题描述:关于整数 i 的变换 f 和 g 定义如下:f(i)=3i;g(i)=[i/2].
试设计一个算法,对于给定的 2 个整数 n 和 m,用最少的 f 和 g 变换次数将
n 变换为 m
例如,可以将整数 15 用 4 次变换将它变换为整数 4:4=gfgg(15)。当整数 n
不可能变换为整数 m 时,算法应如何处理?
三.方案设计
4-11
public class removenewbits {
// ignore exceptions
public static int RNB(int a, int k) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(a + "");
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < sb.length() - 1
&& sb.charAt(j) <= sb.charAt(j + 1); j++) {
}
sb.delete(j, j + 1);
}
return sb.length() == 0 ? 0 : Integer.parseInt(sb.toString());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int min = RNB(178543,4 );
System.out.println(min);
}
}
5-8
#include
int m;
int tempcount,bestcount;
int temp1[100]={0};
int temp2[100]={0};
void dfs(int t)
�
{
if(t==m){
}
return;
}
if(tempcount0){
temp1[tempcount]=1;
dfs(temp);
}
tempcount--;
temp=3*t;
tempcount++;
if(tempcount=1;i--){
if(temp2[i]==2)
printf("f");
if(temp2[i]==1)
printf("g");
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
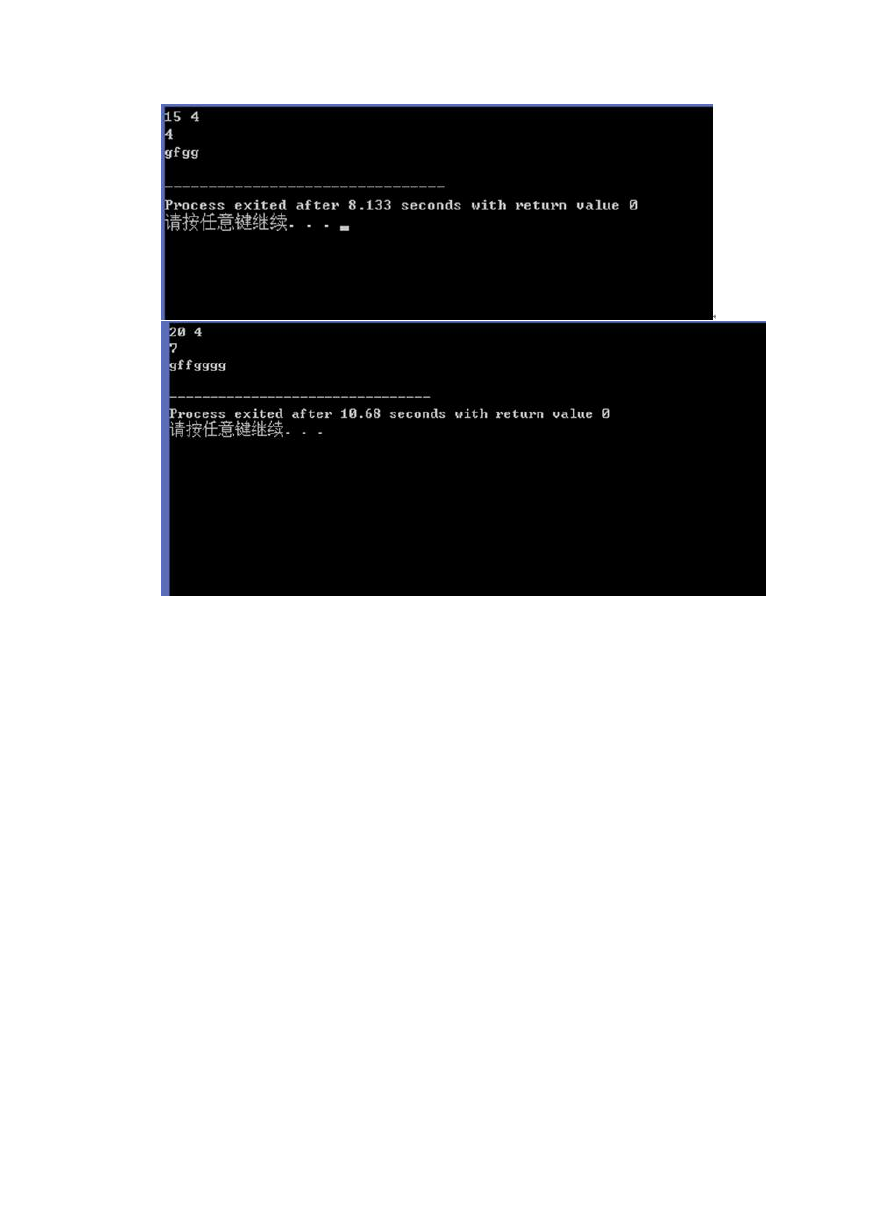
四.测试数据及运行结果
4-11
�
5-8
�
�







 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc