Doctoral Training Programme Ghent University
1
Doctoral School of the Faculty of Automatic Control and Computer Engineering
Department of Electrical energy, Systems and Automation
University of Ghent
Technical University ‘Gh. Asachi’ of Iasi
Department of Automatic Control and Applied Informatics
DISTRIBUTED MPC FOR DYNAMICALLY
COUPLED SYSTEMS
PhD Student: Eng. Anca MAXIM
Coordinators: Prof. dr. eng. Robin DE KEYSER & Prof. dr. eng. Corneliu LAZAR
Co-supervisors: Dr. Eng. Clara M. IONESCU
Assist. Prof. dr. eng. Constantin F. CARUNTU
�
Outline
2
Introduction
State of art
Method Implementation
Theoretical description
Matlab implementation
Process information
Simulation Results
Possible improvements
Non-cooperative DMPC
Conclusions
�
Introduction
3
Large Scale System= Complex Process consisting in Independent but
Interacting subsystems.
Control demands: • performance
• efficiency
• interactions eradication
Control approaches:
• centralized
•decentralized
•distributed
�
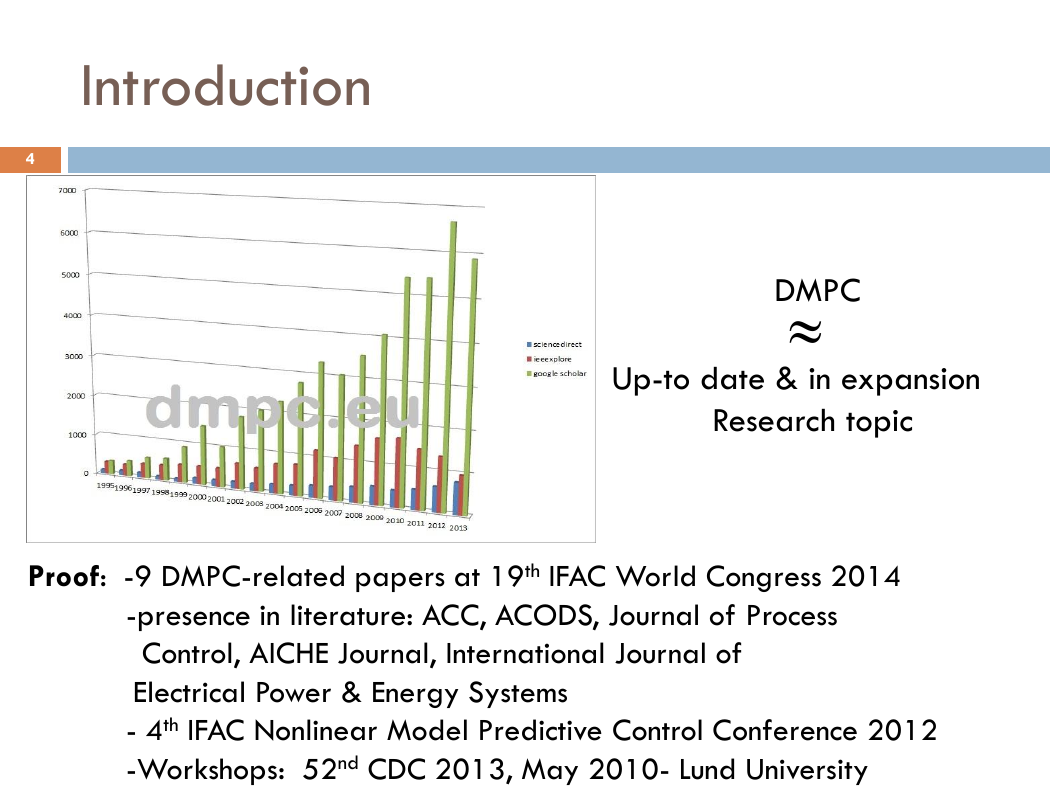
Introduction
4
DMPC
Up-to date & in expansion
Research topic
Proof: -9 DMPC-related papers at 19th IFAC World Congress 2014
-presence in literature: ACC, ACODS, Journal of Process
Control, AICHE Journal, International Journal of
Electrical Power & Energy Systems
- 4th IFAC Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Conference 2012
-Workshops: 52nd CDC 2013, May 2010- Lund University
�
State of Art
5
DMPC
Lyapunov – based DMPC
Game-Theory based DMPC
Cooperative/Non Cooperative DMPC
•J.M. Maestre, D. Munoz de la Pena, E.F. Camacho, Distributed model
predictive control based on a cooperative game, Optim. Control Appl.
Meth 32, 2011, Pages 153-176
• Each agent plays a cooperative game
• three options for control input: - Shifted trajectory
- The altruist trajectory
- The selfish trajectory
• closed-loop stability via terminal constraint
�
Outline
6
Introduction
State of art
Method Implementation
Theoretical description
Matlab implementation
Process information
Simulation Results
Possible improvements
Non-cooperative DMPC
Conclusions
�
Method Implementation
Theoretical Description
7
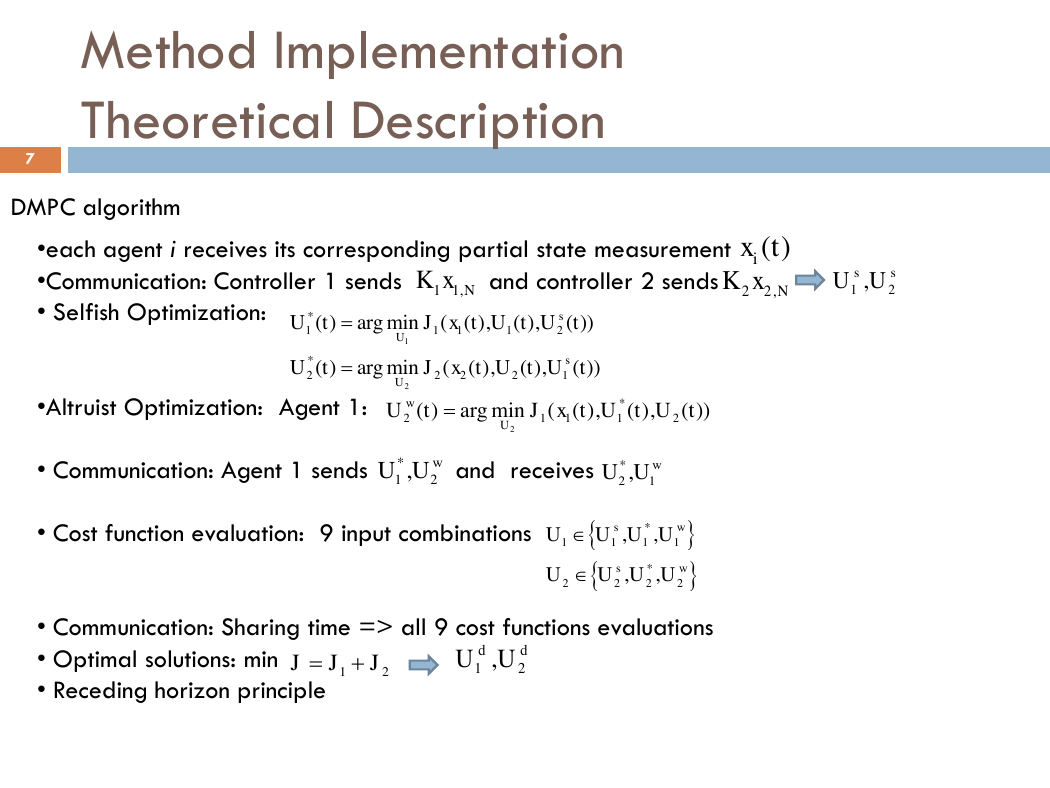
DMPC algorithm
•each agent i receives its corresponding partial state measurement
•Communication: Controller 1 sends and controller 2 sends
• Selfish Optimization:
•Altruist Optimization: Agent 1:
• Communication: Agent 1 sends and receives
• Cost function evaluation: 9 input combinations
• Communication: Sharing time => all 9 cost functions evaluations
• Optimal solutions: min
• Receding horizon principle
()ixt11,NKx22,NKx12,ssUU12*11112*22221()argmin((),(),())()argmin((),(),())sUsUUtJxtUtUtUtJxtUtUt2*21112()argmin((),(),())wUUtJxtUtUt*12,wUU*21,wUU*1111*2222,,,,swswUUUUUUUU12,ddUU12JJJ�
Method Implementation
Matlab approach
8
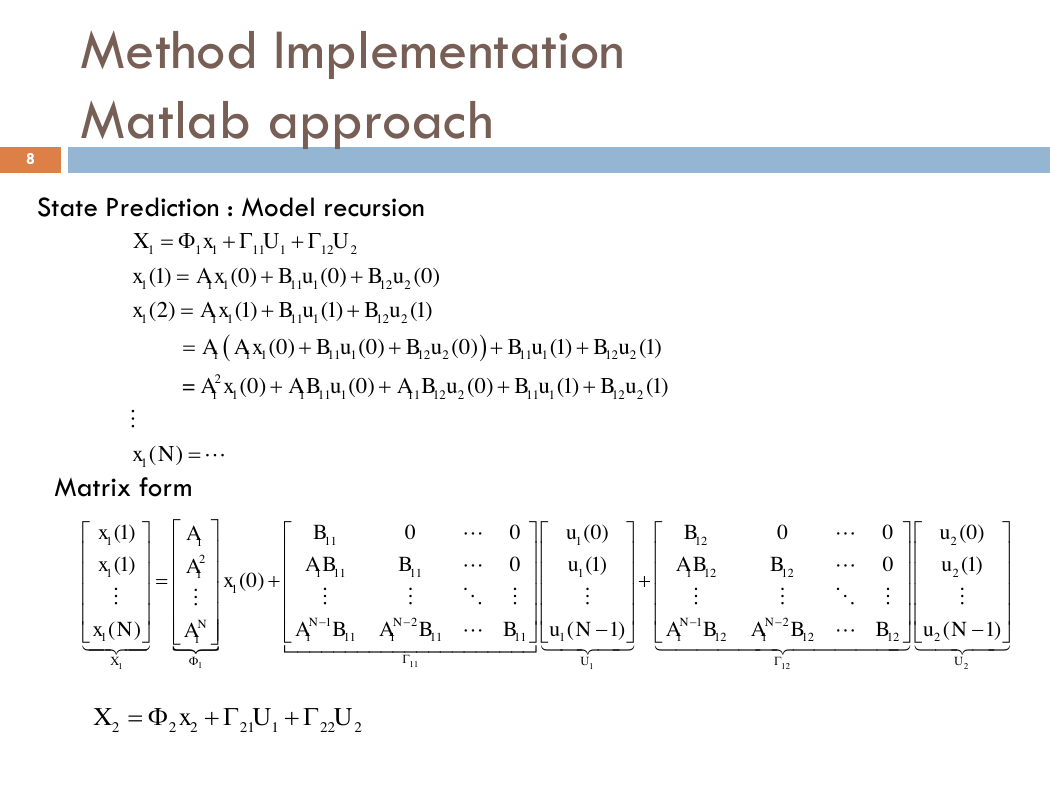
State Prediction : Model recursion
Matrix form
1111111221111111221111111221111111221111222111111111221111221(1)(0)(0)(0)(2)(1)(1)(1) (0)(0)(0)(1)(1) = (0)(0)(0)(1)(1)(XxUUxAxBuBuxAxBuBuAAxBuBuBuBuAxABuABuBuBuxN)1111111111212111111111212111211111111111(1)00(0)00(1)0(1)0(0)()(1)NNNXUxBuBAxABBuABBAxxNABABBuNA1222212112112122(0)(1)(1)NNUuuABABBuN222211222XxUU�









 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc