i.MX 6Dual/6Quad Applications Processors for Consumer Products Data Sheet
1 Introduction
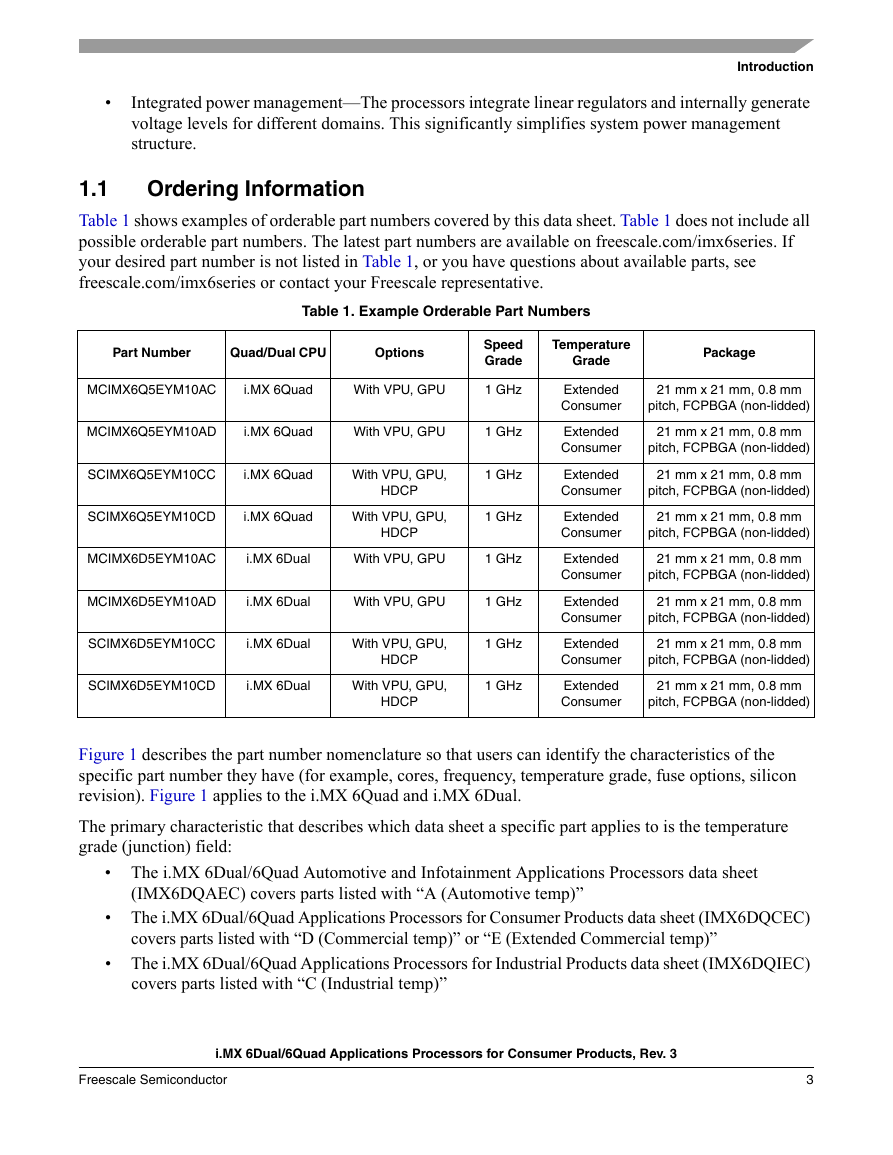
1.1 Ordering Information
1.2 Features
1.3 Updated Signal Naming Convention
2 Architectural Overview
2.1 Block Diagram
3 Modules List
3.1 Special Signal Considerations
3.2 Recommended Connections for Unused Analog Interfaces
4 Electrical Characteristics
4.1 Chip-Level Conditions
4.1.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
4.1.2 Thermal Resistance
4.1.2.1 FCPBGA Package Thermal Resistance
4.1.3 Operating Ranges
4.1.4 External Clock Sources
4.1.5 Maximum Supply Currents
4.1.6 Low Power Mode Supply Currents
4.1.7 USB PHY Current Consumption
4.1.7.1 Power Down Mode
4.1.8 SATA Typical Power Consumption
4.1.9 PCIe 2.0 Maximum Power Consumption
4.1.10 HDMI Maximum Power Consumption
4.2 Power Supplies Requirements and Restrictions
4.2.1 Power-Up Sequence
4.2.2 Power-Down Sequence
4.2.3 Power Supplies Usage
4.3 Integrated LDO Voltage Regulator Parameters
4.3.1 Digital Regulators (LDO_ARM, LDO_PU, LDO_SOC)
4.3.2 Regulators for Analog Modules
4.3.2.1 LDO_1P1
4.3.2.2 LDO_2P5
4.3.2.3 LDO_USB
4.4 PLL Electrical Characteristics
4.4.1 Audio/Video PLL Electrical Parameters
4.4.2 528 MHz PLL
4.4.3 Ethernet PLL
4.4.4 480 MHz PLL
4.4.5 MLB PLL
4.4.6 ARM PLL
4.5 On-Chip Oscillators
4.5.1 OSC24M
4.5.2 OSC32K
4.6 I/O DC Parameters
4.6.1 XTALI and RTC_XTALI (Clock Inputs) DC Parameters
4.6.2 General Purpose I/O (GPIO) DC Parameters
4.6.3 DDR I/O DC Parameters
4.6.3.1 LPDDR2 Mode I/O DC Parameters
4.6.3.2 DDR3/DDR3L Mode I/O DC Parameters
4.6.4 LVDS I/O DC Parameters
4.6.5 MLB 6-Pin I/O DC Parameters
4.7 I/O AC Parameters
4.7.1 General Purpose I/O AC Parameters
4.7.2 DDR I/O AC Parameters
4.7.3 LVDS I/O AC Parameters
4.7.4 MLB 6-Pin I/O AC Parameters
4.8 Output Buffer Impedance Parameters
4.8.1 GPIO Output Buffer Impedance
4.8.2 DDR I/O Output Buffer Impedance
4.8.3 LVDS I/O Output Buffer Impedance
4.8.4 MLB 6-Pin I/O Differential Output Impedance
4.9 System Modules Timing
4.9.1 Reset Timing Parameters
4.9.2 WDOG Reset Timing Parameters
4.9.3 External Interface Module (EIM)
4.9.3.1 EIM Interface Pads Allocation
4.9.3.2 General EIM Timing-Synchronous Mode
4.9.3.3 Examples of EIM Synchronous Accesses
4.9.3.4 General EIM Timing-Asynchronous Mode
4.9.4 DDR SDRAM Specific Parameters (DDR3/DDR3L and LPDDR2)
4.9.4.1 DDR3/DDR3L Parameters
4.9.4.2 LPDDR2 Parameters
4.10 General-Purpose Media Interface (GPMI) Timing
4.10.1 Asynchronous Mode AC Timing (ONFI 1.0 Compatible)
4.10.2 Source Synchronous Mode AC Timing (ONFI 2.x Compatible)
4.10.3 Samsung Toggle Mode AC Timing
4.10.3.1 Command and Address Timing
4.10.3.2 Read and Write Timing
4.11 External Peripheral Interface Parameters
4.11.1 AUDMUX Timing Parameters
4.11.2 ECSPI Timing Parameters
4.11.2.1 ECSPI Master Mode Timing
4.11.2.2 ECSPI Slave Mode Timing
4.11.3 Enhanced Serial Audio Interface (ESAI) Timing Parameters
4.11.4 Ultra High Speed SD/SDIO/MMC Host Interface (uSDHC) AC Timing
4.11.4.1 SD/eMMC4.3 (Single Data Rate) AC Timing
4.11.4.2 eMMC4.4/4.41 (Dual Data Rate) eSDHCv3 AC Timing
4.11.4.3 SDR50/SDR104 AC Timing
4.11.4.4 Bus Operation Condition for 3.3 V and 1.8 V Signaling
4.11.5 Ethernet Controller (ENET) AC Electrical Specifications
4.11.5.1 ENET MII Mode Timing
4.11.5.2 RMII Mode Timing
4.11.5.3 RGMII Signal Switching Specifications
4.11.6 Flexible Controller Area Network (FlexCAN) AC Electrical Specifications
4.11.7 HDMI Module Timing Parameters
4.11.7.1 Latencies and Timing Information
4.11.7.2 Electrical Characteristics
4.11.8 Switching Characteristics
4.11.9 I2C Module Timing Parameters
4.11.10 Image Processing Unit (IPU) Module Parameters
4.11.10.1 IPU Sensor Interface Signal Mapping
4.11.10.2 Sensor Interface Timings
4.11.10.3 Electrical Characteristics
4.11.10.4 IPU Display Interface Signal Mapping
4.11.10.5 IPU Display Interface Timing
4.11.10.6 Synchronous Interfaces to Standard Active Matrix TFT LCD Panels
4.11.11 LVDS Display Bridge (LDB) Module Parameters
4.11.12 MIPI D-PHY Timing Parameters
4.11.12.1 Electrical and Timing Information
4.11.12.2 D-PHY Signaling Levels
4.11.12.3 HS Line Driver Characteristics
4.11.12.4 Possible DVCMTX and DVOD Distortions of the Single-ended HS Signals
4.11.12.5 D-PHY Switching Characteristics
4.11.12.6 High-Speed Clock Timing
4.11.12.7 Forward High-Speed Data Transmission Timing
4.11.12.8 Reverse High-Speed Data Transmission Timing
4.11.12.9 Low-Power Receiver Timing
4.11.13 HSI Host Controller Timing Parameters
4.11.13.1 Synchronous Data Flow
4.11.13.2 Pipelined Data Flow
4.11.13.3 Receiver Real-Time Data Flow
4.11.13.4 Synchronized Data Flow Transmission with Wake
4.11.13.5 Stream Transmission Mode Frame Transfer
4.11.13.6 Frame Transmission Mode (Synchronized Data Flow)
4.11.13.7 Frame Transmission Mode (Pipelined Data Flow)
4.11.13.8 DATA and FLAG Signal Timing Requirement for a 15 pF Load
4.11.13.9 DATA and FLAG Signal Timing
4.11.14 MediaLB (MLB) Characteristics
4.11.14.1 MediaLB (MLB) DC Characteristics
4.11.14.2 MediaLB (MLB) Controller AC Timing Electrical Specifications
4.11.15 PCIe PHY Parameters
4.11.15.1 PCIE_REXT Reference Resistor Connection
4.11.16 Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) Timing Parameters
4.11.17 SATA PHY Parameters
4.11.17.1 Transmitter and Receiver Characteristics
4.11.17.2 SATA_REXT Reference Resistor Connection
4.11.18 SCAN JTAG Controller (SJC) Timing Parameters
4.11.19 SPDIF Timing Parameters
4.11.20 SSI Timing Parameters
4.11.20.1 SSI Transmitter Timing with Internal Clock
4.11.20.2 SSI Receiver Timing with Internal Clock
4.11.20.3 SSI Transmitter Timing with External Clock
4.11.20.4 SSI Receiver Timing with External Clock
4.11.21 UART I/O Configuration and Timing Parameters
4.11.21.1 UART RS-232 I/O Configuration in Different Modes
4.11.21.2 UART RS-232 Serial Mode Timing
4.11.22 USB HSIC Timings
4.11.22.1 Transmit Timing
4.11.22.2 Receive Timing
4.11.23 USB PHY Parameters
5 Boot Mode Configuration
5.1 Boot Mode Configuration Pins
5.2 Boot Devices Interfaces Allocation
6 Package Information and Contact Assignments
6.1 Updated Signal Naming Convention
6.2 21 x 21 mm Package Information
6.2.1 Case FCPBGA, 21 x 21 mm, 0.8 mm Pitch, 25 x 25 Ball Matrix
6.2.1.1 21 x 21 mm Bare Die Package
6.2.2 21 x 21 mm Ground, Power, Sense, and Reference Contact Assignments
6.2.3 21 x 21 mm, 0.8 mm Pitch Ball Map
7 Revision History
Contact Information















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc