一、题目
编写遗传算法程序,求解 10 城市的旅行商问题。
二、问题描述
TSP 问题即旅行商问题可以简单的描述为:已知 N 个城市之间的相互距
离.现有一个旅行商必须遍历这 N 个城市,并且每个城市只能访一次,最后必须返回出发
城市。如何安排他对这些城市的访问次序,可使旅行路线的总长度最短?
利用遗传算法,在一定时间内求得近似最优解的可能性比较大。目标是:
1)设计用遗传算法解决 TSP 问题的程序;
2)求出该 TSP 问题的(近似)最短路程;
3)求得相应的城市遍历序列;
三、算法设计
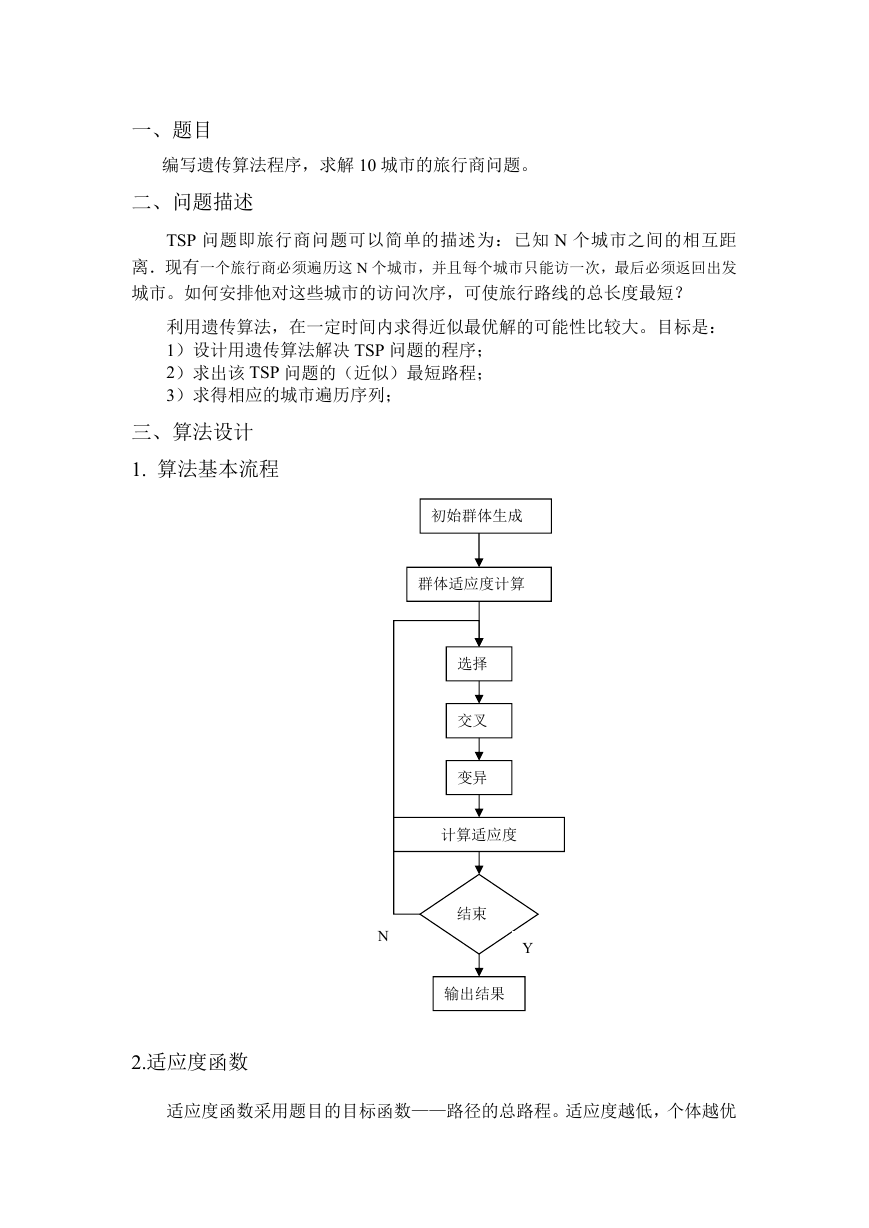
1. 算法基本流程
初始群体生成
群体适应度计算
选择
交叉
变异
计算适应度
N
结束
Y
输出结果
2.适应度函数
适应度函数采用题目的目标函数——路径的总路程。适应度越低,个体越优
�
秀。
3.选择算子
在遗传个体的选择上,先人工保留最优种子,再采用轮盘赌法选择保留一部
分个体,用轮盘赌法的理由是在“择优录取”的原则上增加选择的随机性。在轮
盘赌过程中,如果按适应度来划分,将导致适应度高的劣质个体被选择的概率更
大,于是设计了一个变换,用最坏适应度减去该个体的适应度,再进行轮盘赌选
择。另外,为了保持群体的“生命力”,我们在选择的同时又引入随机的新个体,
与保留的个体进行“杂交”,产生下一代。
4.交叉算子
采 用 顺 序 交 叉 、 双 亲 双 子 遗 传 的 算 法 。 随 机 选 择 两 个 交 叉 点 A 、 B
(0
#include
#include
#include
#include
//能产生的路径总数
void init(FILE *fp);
void lunpan(int count);
int fab(int n);
void ga();
double countTSP(int index); //求解各路径的总路程
void minTSP(int gen);
void variant(); //变异
//遗传算法求解
//获取当前种群中最短的一条路径
�void crossGA(); // 交叉变换
void choice(); //选择
void replace();//替换
void showinfor();
struct CityNode
{
int num;
double x;
double y;
int reserved;
};
struct CityLine
{
int general;
CityNode *city[30];//30 为城市的最大规模
double sum;
};
CityNode *city[30];
int n=0;
CityLine *father[30],*fatherbest,*sontmp,*allbest,*choices[10];//30 为种群规模
double sum[30],min,variance=0.3,minall=0; //各个体的总路程 变异概率为 0.3
FILE *result;
void main()
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("city.txt","r");
result=fopen("result.txt","a");
if(fp==NULL)
{
printf("can not open file!");
return;
}
printf("......START......\n");
init(fp);
fclose(fp);
fclose(result);
printf("......END......\n");
}
�
void init(FILE *fp)
{
int count;
fseek(fp,0,1);
sontmp=(CityLine *)malloc(sizeof(CityLine));
allbest=(CityLine *)malloc(sizeof(CityLine));
fatherbest=(CityLine *)malloc(sizeof(CityLine));
for(int ch=0;ch<10;ch++)
choices[ch]=(CityLine *)malloc(sizeof(CityLine));
//读取文件数据 初始化节点信息
while (!feof(fp)&&n<10)
{
city[n]=(CityNode *)malloc(sizeof(CityNode));
city[n]->num=n;
fscanf(fp,"%lf %lf",&city[n]->x,&city[n]->y);
printf("city[%d]->x=%lf city[%d]->y=%lf\n",n,city[n]->x,n,city[n]->y);
fprintf(result,"city[%d]->x=%lf city[%d]->y=%lf\n",n,city[n]->x,n,city[n]->y);
city[n]->reserved=0;
n++;
}
count=fab(n);
printf("%d\n",count);
if(50>=count)
{
lunpan(count);
}
else
{
}
ga();
}
int fab(int n)
{
if(n==0 || n==1)
return 1;
else
return n*fab(n-1);
}
�
void lunpan(int count)
{
int r=0;
srand(time(NULL)); //随机数种子
for(int i=0;igeneral=0;
for(int k=0;kreserved=0;
}
for(int j=0;jreserved==0)
{
father[i]->city[j]=city[r];
city[r]->reserved=1;
printf("%d
\n",r);
}
else
{
//若节点已存在于个体 重新选择其他新的节点
while(1)
{
r=(int)((double)rand() / ((double)RAND_MAX + 1) * n);
if(city[r]->reserved==0)
{
father[i]->city[j]=city[r];
city[r]->reserved=1;
printf("%d
\n",r);
break;
}
}
}
}
sum[i]= countTSP(i);
father[i]->sum=sum[i];
printf("%lf \n",sum[i]);
}
�
}
void ga()
{
//生成第一代种群
int r=0;
srand(time(NULL));
for(int i=0;i<30;i++)
{
father[i]=(CityLine *)malloc(sizeof(CityLine));
father[i]->general=1;
for(int k=0;kreserved=0;
}
for(int j=0;jreserved==0)
{
father[i]->city[j]=city[r];
city[r]->reserved=1;
city[r]->num=r;
",r);
printf("%d
//若节点已存在于个体 重新选择其他新的节点
while(1)
{
r=(int)((double)rand() / ((double)RAND_MAX + 1) * n);
if(city[r]->reserved==0)
{
father[i]->city[j]=city[r];
city[r]->reserved=1;
city[r]->num=r;
printf("%d
",r);
break;
}
else
{
//
//
}
}
}
�
//
}
//
}
sum[i]= countTSP(i);
father[i]->sum=sum[i];
printf("%lf \n",sum[i]);
showinfor();
minTSP(father[0]->general);
minall=min;
allbest=fatherbest;
allbest->general=fatherbest->general;
allbest->sum=minall;
for(int j=0;jcity[j]=fatherbest->city[j];
//生成一个随机数,看是否能产生变异
if(variance>=(double)rand() / ((double)RAND_MAX + 1) * 10)
{
printf("Can variance \n");
fprintf(result,"Can variance \n");
variant();
}
//交叉
//选择群体中部分优秀的个体
choice();
printf("Cross begining...\n");
fprintf(result,"Cross begining...\n");
crossGA();
}
double countTSP(int index)
{
double a=0,x1,y1,tmp;
for(int i=0;icity[i]->x-father[index]->city[i+1]->x;
y1=father[index]->city[i]->y-father[index]->city[i+1]->y;
tmp=sqrt(x1*x1+y1*y1);
a=a+tmp;
x1=father[index]->city[0]->x-father[index]->city[n-1]->x;
y1=father[index]->city[0]->y-father[index]->city[n-1]->y;
}
�
tmp=sqrt(x1*x1+y1*y1);
a=a+tmp;
return a;
}
void minTSP(int gen)
{
int a;
min=sum[0];
for(int i=0;i<30;i++)
{
if(min>=sum[i] && sum[i]!=0)
{
min=sum[i];
a=i;
}
}
//
fatherbest=father[a];
fatherbest->general=gen;
fatherbest->sum=min;
//保存种群中最优的一条路径
for(int jj=0;jjcity[jj]=father[a]->city[jj];
printf("当代最优个体编号为: %d \n",a+1);
fprintf(result,"当代最优个体编号为: %d \n",a+1);
printf("最短路程是: %lf \n",sum[a]);
fprintf(result,"最短路程是: %lf \n",sum[a]);
printf("这是第 %d 代的最短路程: \n",gen);
fprintf(result,"这是第 %d 代的最短路程: \n",gen);
for(int j=0;jcity[j]->num);
",fatherbest->city[j]->num);
}
printf("\n");
fprintf(result,"\n");
}
void variant()
{
//变异过程为随机变异 n 条 每条交换任意两个节点的位置
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc