协议分析与设计实验报告
一. 实验题目:
1. 将停止等待协议条件改为:报文和应答均会出错,切都会丢
失,接收方没有无线接收能力,这就是我们通常所说的实用
停止协议。请用 PROMELA 进行描述,并用 SPIN 模拟运行、
一般性验证、无进展循环验证和人为加入错误进行验证。
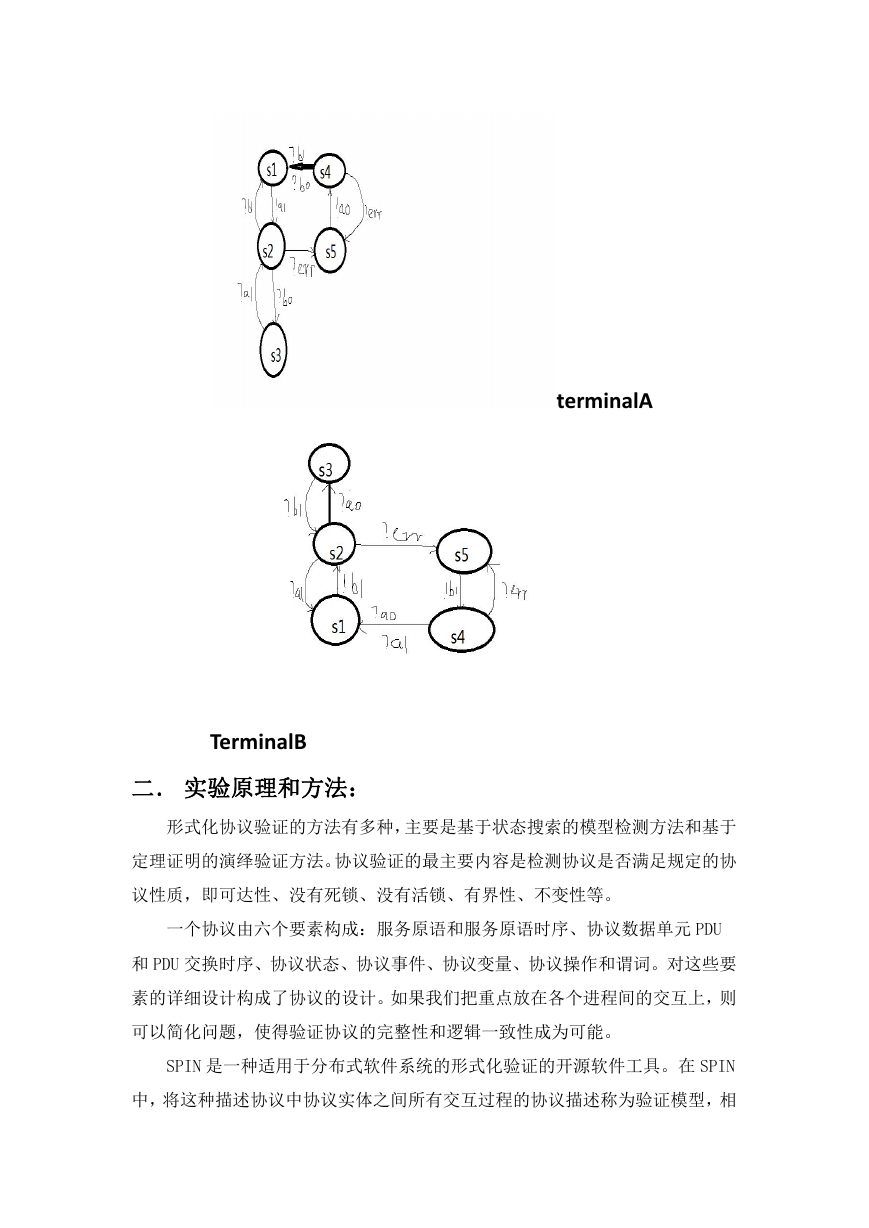
2. 请根据图写出著名的 AB 协议的 PROMELA 描述,并验证“A
获取的每一个报文至少有一次是正确的,而 B 接收的每一个
报文至多有一个是正确的”。
�
terminalA
TerminalB
二. 实验原理和方法:
形式化协议验证的方法有多种,主要是基于状态搜索的模型检测方法和基于
定理证明的演绎验证方法。协议验证的最主要内容是检测协议是否满足规定的协
议性质,即可达性、没有死锁、没有活锁、有界性、不变性等。
一个协议由六个要素构成:服务原语和服务原语时序、协议数据单元 PDU
和 PDU 交换时序、协议状态、协议事件、协议变量、协议操作和谓词。对这些要
素的详细设计构成了协议的设计。如果我们把重点放在各个进程间的交互上,则
可以简化问题,使得验证协议的完整性和逻辑一致性成为可能。
SPIN 是一种适用于分布式软件系统的形式化验证的开源软件工具。在 SPIN
中,将这种描述协议中协议实体之间所有交互过程的协议描述称为验证模型,相
�
当于一个有限状态机(FSM),而描述验证模型的语言称为 PROMELA,它可以很方
便地描述形式化验证模型中的系统各种行为。
三. 源代码:
1. #define MAXSEQ 5
mtype={Msg,Ack,Nak,Err,Dis};
chan SenderToReceiver=[1] of {mtype,byte,byte};
chan ReceiverToSender=[1] of {mtype,byte,byte};
proctype SENDER(chan InCh,OutCh)
{
byte SendData;
byte SendSeq;
byte ReceivedSeq;
SendData=MAXSEQ-1;
do
::SendData=(SendData+1)%MAXSEQ;
again: if
::OutCh!Msg(SendData,SendSeq)
::OutCh!Msg(SendData,SendSeq)
::OutCh!Msg(SendData,SendSeq)
::OutCh!Msg(SendData,SendSeq)
::OutCh!Msg(SendData,SendSeq)
::OutCh!Msg(SendData,SendSeq)
::OutCh!Msg(SendData,SendSeq)
::OutCh!Msg(SendData,SendSeq)
::OutCh!Msg(SendData,SendSeq)
::OutCh!Err(0,0)
::OutCh!Dis(0,0)
fi;
if
::timeout->goto again
::InCh?Dis(0,0)->goto again
::InCh?Err(0,0)->goto again
::InCh?Nak(ReceivedSeq,0)->
end1:
goto again
::InCh?Ack(ReceivedSeq,0)->
if
::(ReceivedSeq==SendSeq)->goto
progress
�
::(ReceivedSeq!=SendSeq)->
end2:
goto again
fi
fi;
progress:
SendSeq=1-SendSeq;
od;
}
proctype RECEIVER(chan InCh,OutCh)
{
byte ReceivedData;
byte ReceivedSeq;
byte ExpectedData;
byte ExpectedSeq;
do
::InCh?Msg(ReceivedData,ReceivedSeq)->
if
::(ReceivedSeq==ExpectedSeq)->
assert(ReceivedData==ExpectedData);
progress:
ExpectedSeq=1-ExpectedSeq;
ExpectedData=(ExpectedData+1)%MAXSEQ;
if
OutCh!Ack(ReceivedSeq,0);
OutCh!Ack(ReceivedSeq,0);
OutCh!Ack(ReceivedSeq,0);
::OutCh!Ack(ReceivedSeq,0);
::OutCh!Ack(ReceivedSeq,0);
::OutCh!Ack(ReceivedSeq,0);
::OutCh!Ack(ReceivedSeq,0);
::OutCh!Ack(ReceivedSeq,0);
::OutCh!Ack(ReceivedSeq,0);
::OutCh!Ack(ReceivedSeq,0);
OutCh!Err(0,0);
OutCh!Dis(0,0);
::
::
::
::
::
�
ExpectedSeq=1-ExpectedSeq;
ExpectedData=(ExpectedData+4)%MAXSEQ;
fi
::(ReceivedSeq!=ExpectedSeq)->
if
::OutCh!Nak(ReceivedSeq,0);
::OutCh!Err(0,0);
fi
fi
::InCh?Err(0,0)->OutCh!Nak(ReceivedSeq,0);
::InCh?Dis(0,0)->skip;
od;
}
init
{
atomic
{
run SENDER(ReceiverToSender,SenderToReceiver);
run RECEIVER(SenderToReceiver,ReceiverToSender);
}
}
2. mtype = {Err,a,b};
chan SenderToReceiver = [1] of {mtype,byte};
chan ReceiverToSender = [1] of {mtype,byte};
proctype A_SENDER(chan InCh, OutCh)
{
S5:
if
::OutCh!a(0)
::OutCh!Err(0)
fi;
if
::InCh?Err(0)-> goto S5
::InCh?b(0)-> goto S1
::InCh?b(1)-> goto S1
fi;
S1:
if
::OutCh!a(1)
�
::OutCh!Err(0)
fi;
if
::InCh?Err(0)-> goto S5
::InCh? b(1)-> goto S1
::InCh?b(0)-> goto S1
fi;
}
proctype B_RECEIVER(chan InCh, OutCh)
{
if
::InCh?Err(0)-> goto S5
::InCh?a(0) -> goto S1
::InCh?a(1)-> goto S1
S5:
if
S1:
if
fi;
fi;
if
fi;
::OutCh!b(0)
::OutCh!Err(0)
::InCh?Err(0)-> goto S5
::InCh?a(0) -> goto S1
::InCh?a(1)-> goto S1
::OutCh!b(1)
::OutCh!Err(0)
fi;
if
::InCh?Err(0)-> goto S5
::InCh?a(1)-> goto S1
::InCh?a(0)-> goto S1
fi;
}
proctype B_SENDER(chan InCh, OutCh)
{
S5:
if
::OutCh!b(0)
::OutCh!Err(0)
fi;
if
::InCh?Err(0)-> goto S5
�
::InCh?a(0) -> goto S1
::InCh?a(1)-> goto S1
fi;
S1:
if
::OutCh!b(1)
::OutCh!Err(0)
fi;
if
::InCh?Err(0)-> goto S5
::InCh?a(1)-> goto S1
::InCh?a(0)-> goto S1
fi;
}
proctype A_RECEIVER(chan InCh, OutCh)
{
if
::InCh?Err(0)-> goto S5
::InCh?b(0)-> goto S1
::InCh?b(1)-> goto S1
fi;
if
S5:
::OutCh!a(0)
::OutCh!Err(0)
fi;
if
::InCh?Err(0)-> goto S5
::InCh?b(0)-> goto S1
::InCh?b(1)-> goto S1
fi;
S1:
if
::OutCh!a(1)
::OutCh!Err(0)
fi;
if
::InCh?Err(0)-> goto S5
::InCh? b(1)-> goto S1
::InCh?b(0)-> goto S1
fi;
}
init
{
atomic
�
{
run A_SENDER(ReceiverToSender,SenderToReceiver);
run B_RECEIVER(SenderToReceiver, ReceiverToSender);
}
{
/*
atomic
run B_SENDER(ReceiverToSender,SenderToReceiver);
run A_RECEIVER(SenderToReceiver, ReceiverToSender);
}*/
}
四. 结果与截图:
1.
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc