CIC
1.SpectreRF Overview
• SpectreRF is an optional feature added to Spectre ,and is
represented by 6 analyses:
1.PSS: Periodic Steady State Analysis
2.PAC: Periodic AC Analysis
3.PXF: Periodic Transfer Function Analysis
4.PNOISE: Periodic Noise Analysis
Tdnoise: Time Domain Noise
QPNOISE: Quasi-Periodic Noise (not discuss here)
5.PDISTO: Periodic Distortion Analysis
QPSS: Quasi-Periodic Steady State (not discuss here)
6.Envelope Analysis (not discuss here)
PAC, PXF, and PNOISE are similar in concept to AC, XF, and Noise.
However, they are applied to periodically-driven circuits such as mixers and
oscillators.
1-1
�
CIC
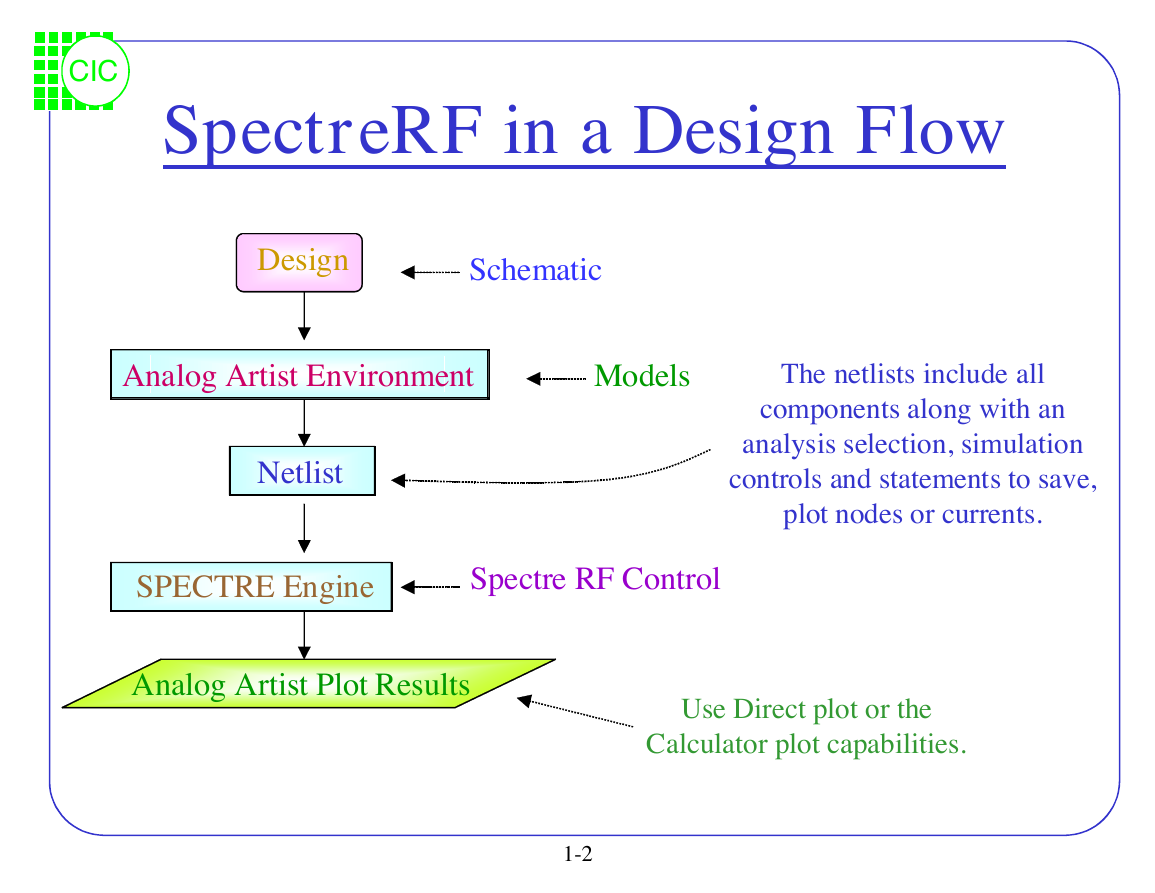
SpectreRF in a Design Flow
Design
Schematic
Analog Artist Environment
Models
Netlist
SPECTRE Engine
SpectreRF Control
The netlists include all
components along with an
analysis selection, simulation
controls and statements to save,
plot nodes or currents.
Analog Artist Plot Results
Use Direct plot or the
Calculator plot capabilities.
1-2
�
CIC
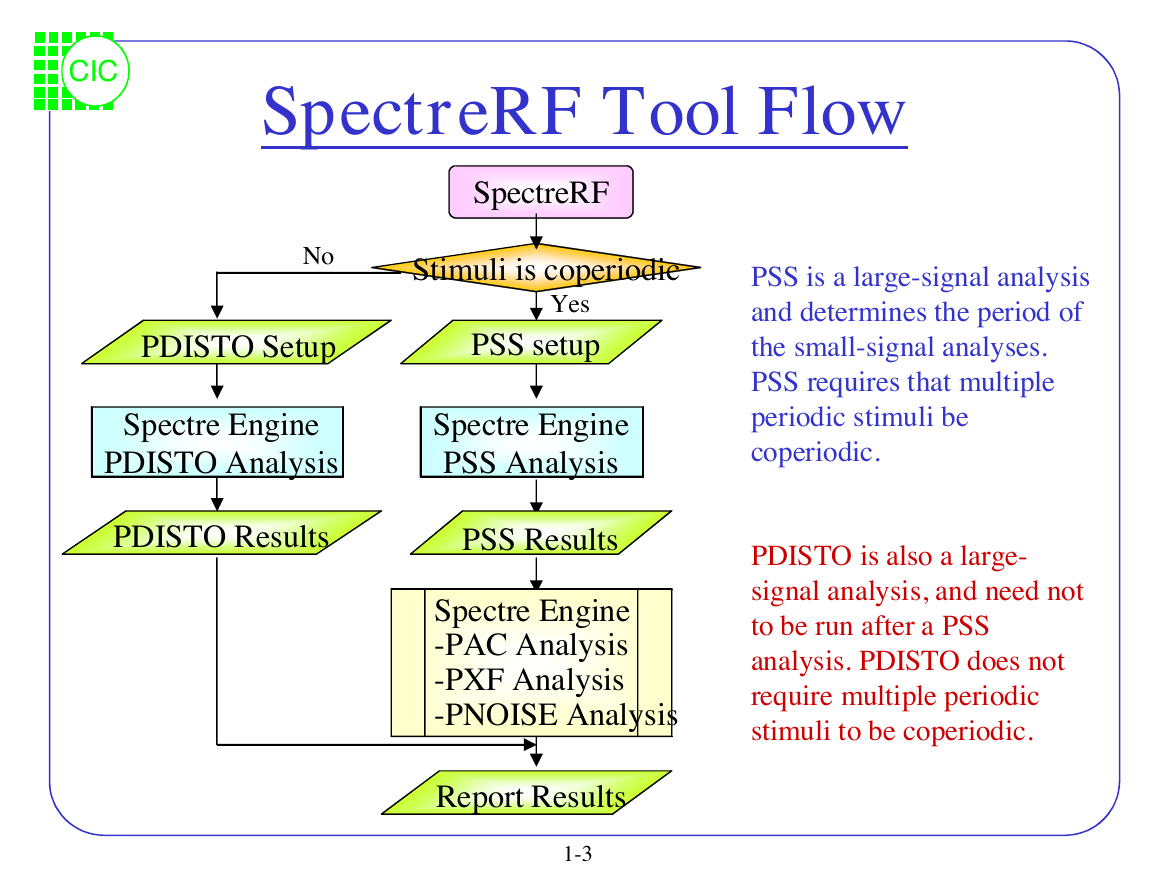
SpectreRF Tool Flow
No
PDISTO Setup
SpectreRF
Stimuli iscoperiodic
Yes
PSS setup
Spectre Engine
PDISTO Analysis
Spectre Engine
PSS Analysis
PDISTO Results
PSS Results
SpectreEngine
-PAC Analysis
-PXF Analysis
-PNOISE Analysis
Report Results
1-3
PSS is a large-signal analysis
and determines the period of
the small-signal analyses.
PSS requires that multiple
periodic stimuli be
coperiodic.
PDISTO is also a large-
signal analysis, and need not
to be run after a PSS
analysis. PDISTO does not
require multiple periodic
stimuli to be coperiodic.
�
CIC
SpectreRF Features
• Compute a steady-state solution efficiently and directly
• Handles very large circuits (~ 10,000 transistors)
• Displays results in both time and frequency domains
• Use Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) for better accuracy
• Displays standard RF measurements, such as s-parameter in Smith
chart, NF, IP3, and 1dB compression point in the Analog Artist design
environment.
• Performs oscillator analysis.
1-4
�
CIC
2.S-Parameter Analysis
• Linear Simulation:
– Entirely in the frequency domain
– A basic RF feature of the Spectre simulator
• Ports:
– Specify the port number on the psin ( or port); psin (or port)
can act as a source port or a load.
– Required properties for linear analysis: Resistance & Port
number
• Noise Analysis:
– UseNfminand NF for 2-port circuits ONLY.
2-1
�
CIC
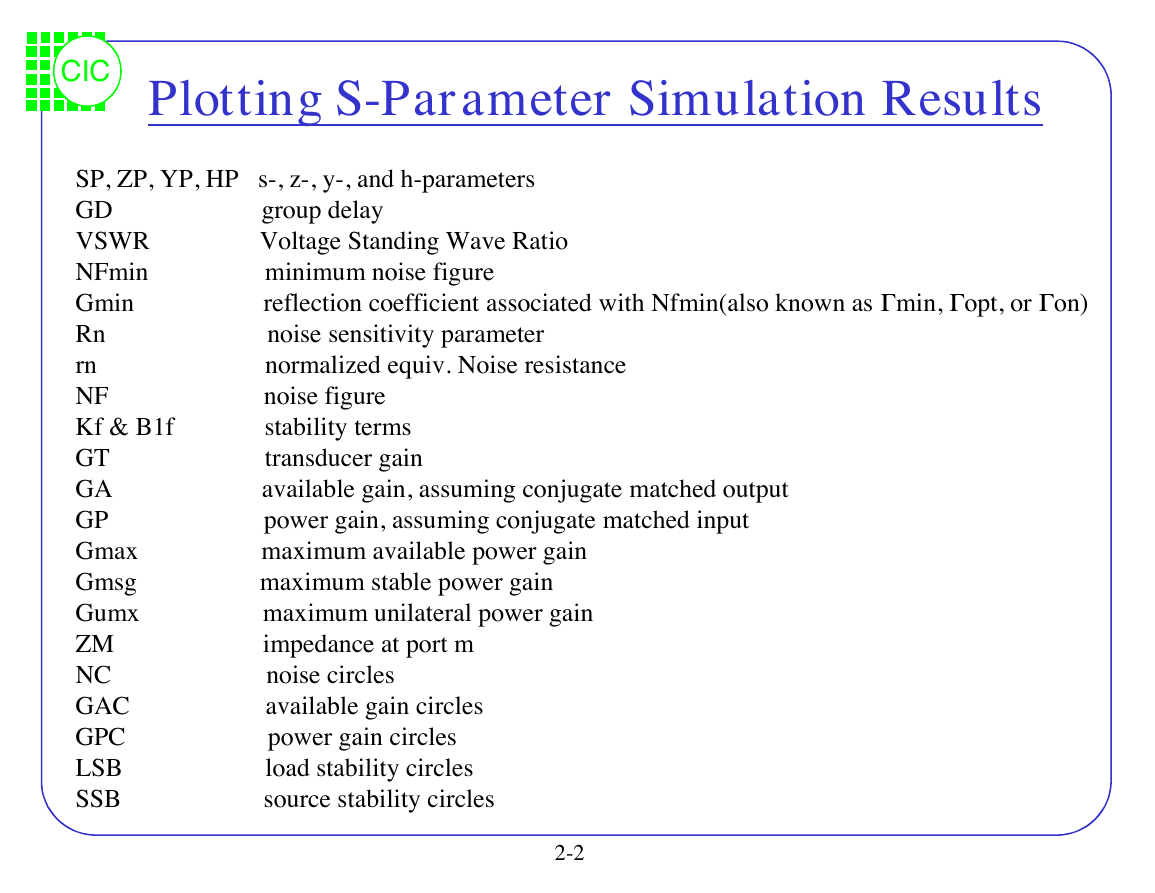
Plotting S-Parameter Simulation Results
G min, G opt, or G on)
SP, ZP, YP, HP s-, z-, y-, and h-parameters
GD group delay
VSWR Voltage Standing Wave Ratio
NFmin minimum noise figure
Gmin reflection coefficient associated withNfmin(also known as
Rn noise sensitivity parameter
rn normalized equiv. Noise resistance
NF noise figure
Kf& B1f stability terms
GT transducer gain
GA available gain, assuming conjugate matched output
GP power gain, assuming conjugate matchedinput
Gmax maximum available power gain
Gmsg maximum stable power gain
Gumx maximum unilateral power gain
ZM impedance at port m
NC noise circles
GAC available gain circles
GPC power gain circles
LSB load stability circles
SSB source stability circles
2-2
�
CIC
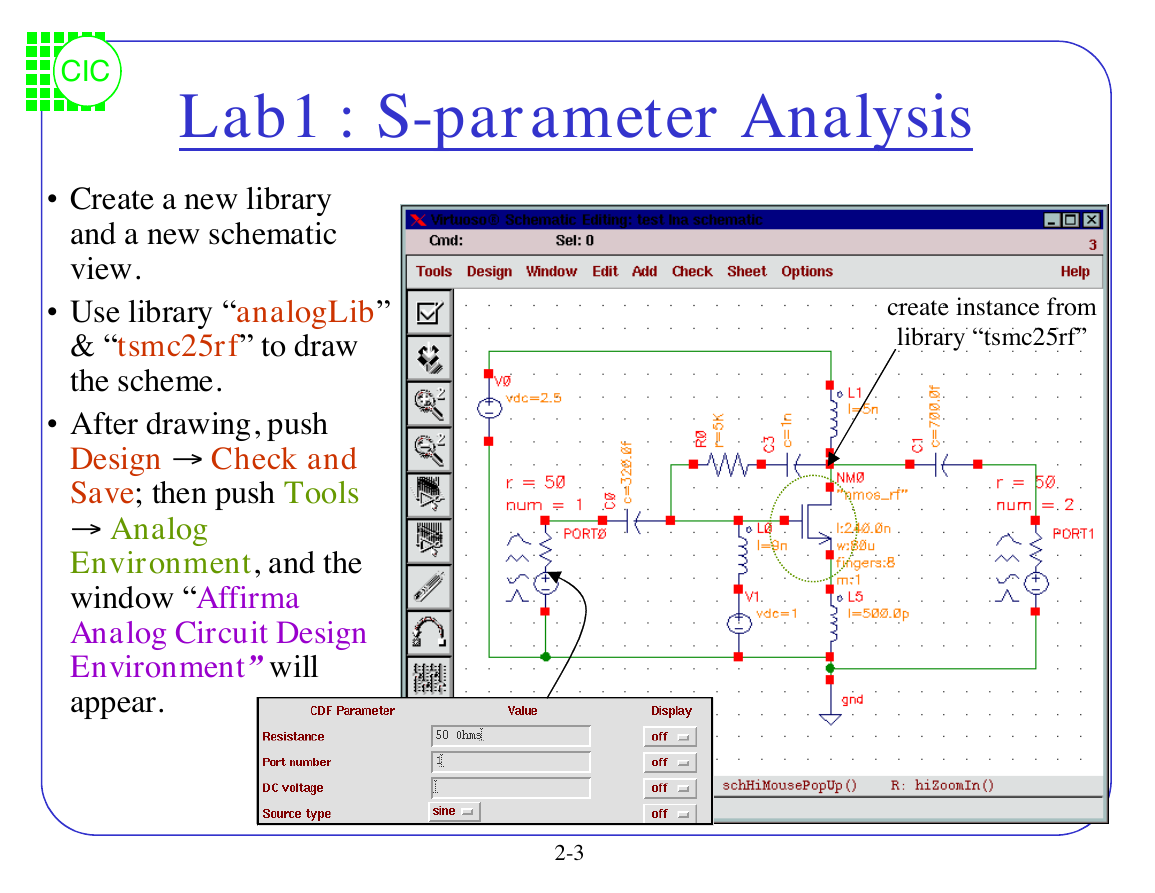
Lab1 : S-parameter Analysis
• Use library “analogLib”
& “tsmc25rf” to draw
the scheme.
• Create a new library
and a new schematic
view.
• After drawing, push
Design fi Checkand
Save; then push Tools
fi Analog
Environment, and the
window “Affirma
Analog Circuit Design
Environment” will
appear.
create instance from
library “tsmc25rf”
2-3
�
CIC
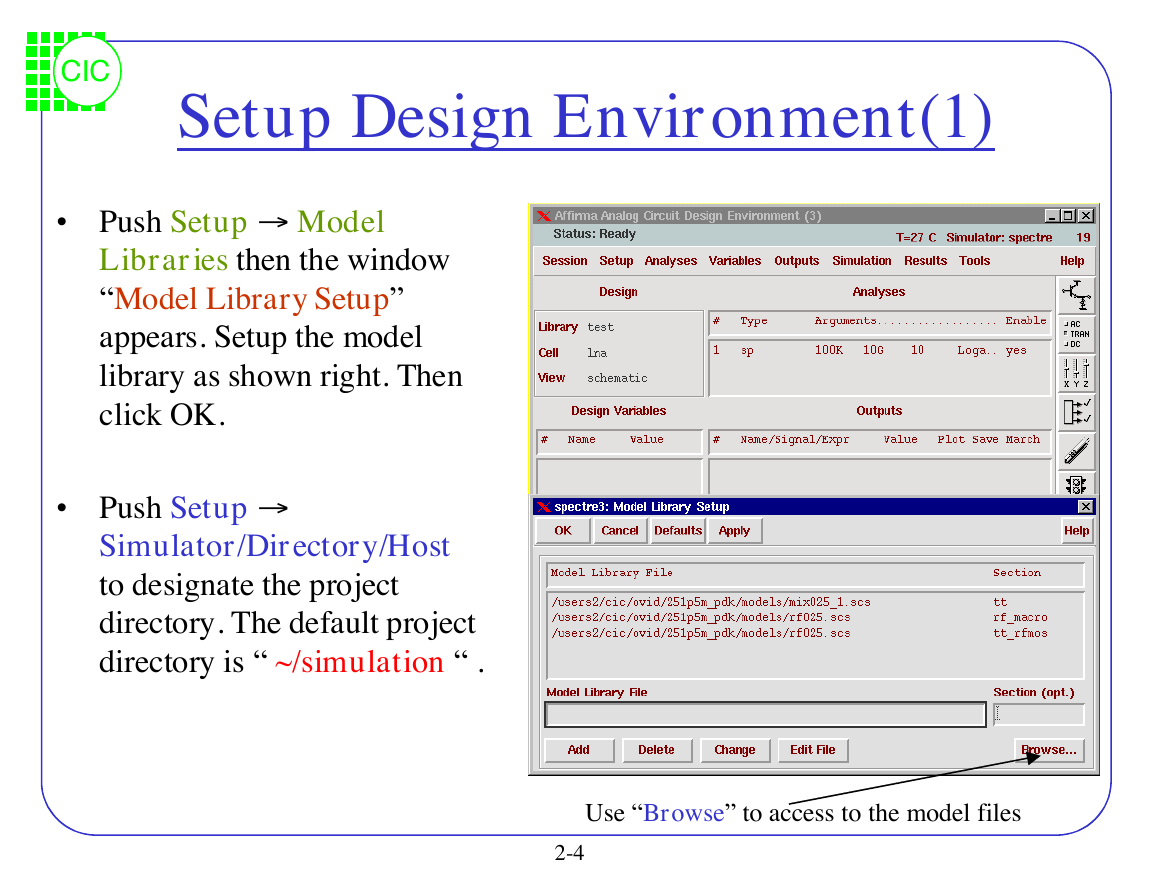
Setup Design Environment(1)
• Push Setup fi Model
Libraries then the window
“Model Library Setup”
appears. Setup the model
library as shown right. Then
click OK.
• Push Setup fi
Simulator/Directory/Host
to designate the project
directory. The default project
directory is “ ~/simulation “ .
Use “Browse” to access to the model files
2-4
�











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc