Software Design Specification
Z-Wave Protocol Overview
Document No.:
SDS10243
Version:
8
Description:
This document is a high-level description of the Z Wave Protocol.
Written By:
JFR;PSH;ABR;JBU
Date:
2008-12-04
Reviewed By:
CHL;JKA
Partners Only
Restrictions:
Approved by:
Date
2008-12-04
CET
13:49:23
Initials Name
JFR
Jørgen Franck
Justification
on behalf of NTJ
This document is the property of Zensys A/S. The data contained herein, in whole or in
part, may not be duplicated, used or disclosed outside the recipient for any purpose. This
restriction does not limit the recipient's right to use information contained in the data if it is
obtained from another source without restriction.
CONFIDENTIAL
�
SDS10243-8
Z-Wave Protocol Overview
2008-12-04
Doc. Rev Date
By
20050128
JFR
Pages
affected
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
JFR
20060105 MVO All
3.4
20070228
All
JFR All
ABR 3.5
JFR
JFR All
ABR 5.1.4.1 & 6.4
20070509
20080626
20081124
20081126
20081202
3.4.2 & 3.4.4
REVISION RECORD
Brief description of changes
Removed paragraph about assignment of home and node ID
Removed paragraph about controller replication
New 1st page/header/footer contents. New Doc No
Frequently listening routing slaves and Zensor Net routing slaves added
Table of figures added
Confidential in footer removed
Random home ID after reset in controllers and slaves added
ZDK 5.0x supports FLiRS and Zensor Net only.
Minor typos corrected
Explorer frame type and explorer route resolution added
Zensys A/S
Revision Record and Tables of Contents
Page ii of iv
CONFIDENTIAL
�
SDS10243-8
Z-Wave Protocol Overview
2008-12-04
Table of Contents
3.3.1
3.3.2
3.3.2.1
3.3.2.2
3.3.3
3.3.4
3.4.1
3.4.2
3.4.3
3.4.4
1 ABBREVIATIONS.................................................................................................................................1
2
INTRODUCTION...................................................................................................................................2
2.1 Purpose ..............................................................................................................................................2
2.2 Scope .................................................................................................................................................2
2.3 Audience and Prerequisites ...............................................................................................................2
3 Z-WAVE PROTOCOL...........................................................................................................................3
3.1 Overview.............................................................................................................................................3
3.2 Controller and Slave nodes................................................................................................................3
3.3 Controllers ..........................................................................................................................................4
Portable Controller......................................................................................................................4
Static Controller ..........................................................................................................................4
Static Update Controller ......................................................................................................5
SUC ID Server.....................................................................................................................5
Installer Controller ......................................................................................................................5
Bridge Controller.........................................................................................................................5
3.4 Slaves.................................................................................................................................................5
Slave...........................................................................................................................................5
Routing Slave .............................................................................................................................6
Enhanced Slave .........................................................................................................................6
Zensor Net Routing Slave ..........................................................................................................6
3.5 Home ID and Node ID ........................................................................................................................6
4 MAC LAYER .........................................................................................................................................8
4.1 Collision avoidance ............................................................................................................................8
5 TRANSFER LAYER............................................................................................................................10
5.1 Frame Layout ...................................................................................................................................10
Singlecast Frame Type.............................................................................................................11
5.1.1
Transfer Acknowledge Frame Type .........................................................................................11
5.1.2
5.1.3 Multicast Frame Type ...............................................................................................................11
5.1.4
Broadcast Frame Type.............................................................................................................12
Explorer Frame Type.........................................................................................................12
6 ROUTING LAYER...............................................................................................................................14
6.1 Frame Layout ...................................................................................................................................14
Routed Singlecast Frame Type................................................................................................14
Routed Acknowledge Frame Type ...........................................................................................14
6.2 Routing Table ...................................................................................................................................15
6.3 Route to Node ..................................................................................................................................15
6.4 Explorer Route Resolution ...............................................................................................................15
Last Working Route ..................................................................................................................16
The Explorer Search process...................................................................................................16
7 APPLICATION LAYER.......................................................................................................................17
7.1 Frame Layout ...................................................................................................................................17
Application Layer Frame Format ..............................................................................................17
7.2 Node information ..............................................................................................................................18
Node Information Frame Flow..................................................................................................18
8 REFERENCES....................................................................................................................................19
7.1.1
7.2.1
5.1.4.1
6.1.1
6.1.2
6.4.1
6.4.2
Zensys A/S
Revision Record and Tables of Contents
Page iii of iv
CONFIDENTIAL
�
SDS10243-8
Z-Wave Protocol Overview
List of Figures
2008-12-04
Figure 1 Z-Wave Protocol Layers............................................................................................................... 3
Figure 2 Z-Wave network comprising of controllers and slaves................................................................. 4
Figure 3 Z-Wave data stream..................................................................................................................... 8
Figure 4 Manchester coding ....................................................................................................................... 8
Figure 5 Collision avoidance ...................................................................................................................... 8
Figure 6 Z-Wave basic frame format........................................................................................................ 10
Figure 7 Singlecast transmission.............................................................................................................. 11
Figure 8 Multicast transmission................................................................................................................ 11
Figure 9 Broadcast transmission.............................................................................................................. 12
Figure 10 Routed singlecast transmission ............................................................................................... 14
Figure 11 Routed singlecast transmission ............................................................................................... 14
Figure 12 Network topology and routing table.......................................................................................... 15
Figure 13 Z-Wave application frame format ............................................................................................. 17
Figure 14 Z-Wave command class range ................................................................................................ 17
Figure 15 Get node info frame flow .......................................................................................................... 18
Zensys A/S
Revision Record and Tables of Contents
Page iv of iv
CONFIDENTIAL
�
SDS10243-8
Z-Wave Protocol Overview
2008-12-04
1 ABBREVIATIONS
Abbreviation
EOF
FLiRS
MAC
PIR
RF
SIS
SOF
SUC
TTL
ZDK
Explanation
End Of Frame
Frequently Listening Routing Slave
Media Access Control
Passive Infra Red movement sensor
Radio Frequency
SUC ID Server
Start Of Frame
Static Update Controller
Time-To-Live
Z-Wave Developer’s Kit
Zensys A/S
Abbreviations
CONFIDENTIAL
Page 1 of 19
�
SDS10243-8
Z-Wave Protocol Overview
2008-12-04
2
INTRODUCTION
2.1 Purpose
The purpose of this document is to describe the Z-WaveTM Radio Frequency Protocol that provides
reliable and robust wireless communication between the nodes in a Z-Wave mesh network.
2.2 Scope
The scope of this document is to give an overview of the following protocol layers:
• The MAC layer
• The Transfer Layer
• The Routing Layer
• The Frame Layer
2.3 Audience and Prerequisites
The audience of this document is Z-Wave partners and Zensys A/S.
Zensys A/S
Introduction
CONFIDENTIAL
Page 2 of 19
�
SDS10243-8
Z-Wave Protocol Overview
2008-12-04
3 Z-WAVE PROTOCOL
3.1 Overview
The Z-Wave protocol is a low bandwidth half-duplex protocol designed for reliable and robust wireless
communication in a low cost control mesh network. The protocols main purpose is to communicate short
control messages in a reliable manner from a control unit to one or more nodes in the network.
The protocol is not designed to transfer large amounts of data or to transfer any kind of streaming or
timing critical data.
The protocol consist of 4 layers, the MAC Layer that controls the RF media, the Transfer Layer that
handles frame integrity checks, acknowledgements, and retransmissions, the Routing Layer that controls
the routing of frames in the network and application interface; and finally the Application Layer controls
the payload in the transmitted and received frames.
Application Layer
Routing Layer
Transfer Layer
MAC Layer
RF Media
For a description of the four layers, refer to chapters 4 to 7.
Figure 1 Z-Wave Protocol Layers
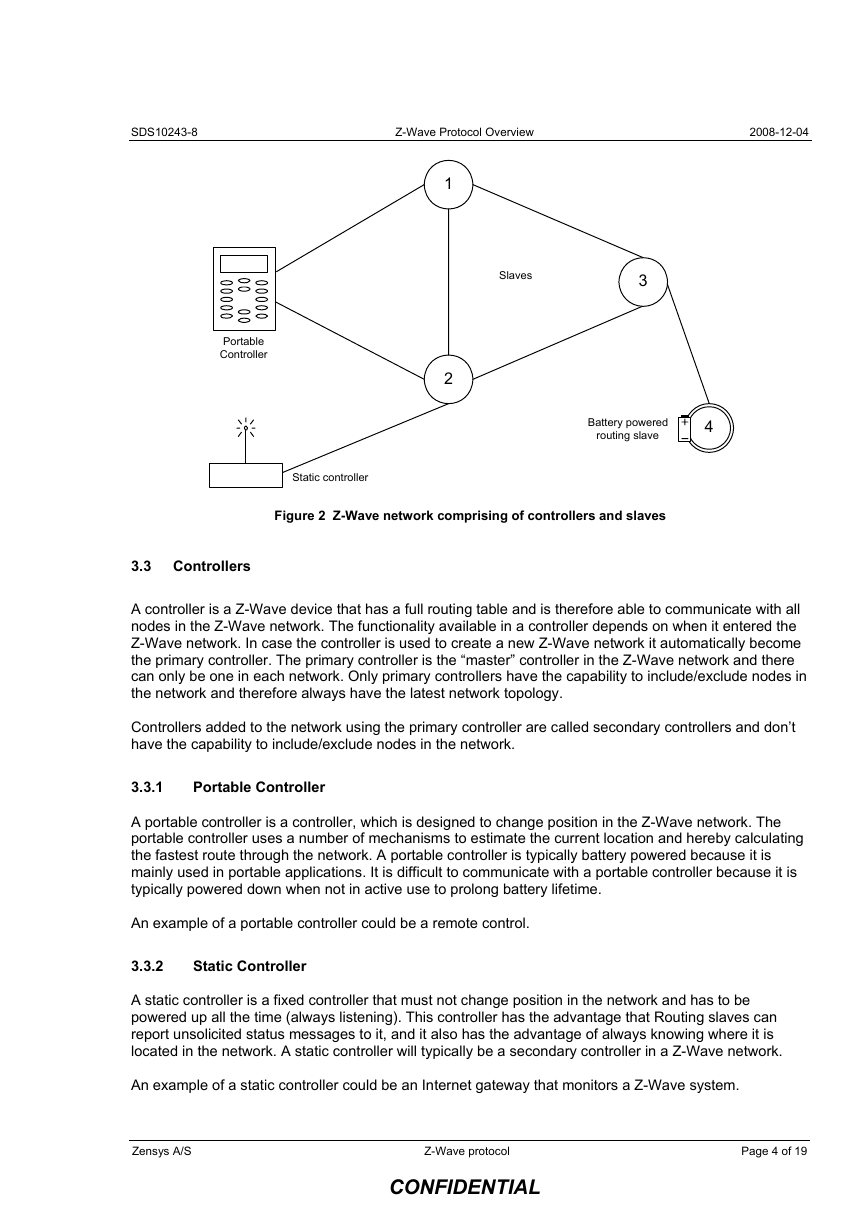
3.2 Controller and Slave nodes
The Z-Wave protocol has two basic kinds of devices; controlling devices and slave nodes. Controlling
devices are the nodes in a network that initiate control commands and sends out the commands to other
nodes, and slave nodes are the nodes that reply on and execute the commands. Slave nodes can also
forward commands to other nodes, which make it possible for the controller to communicate with nodes
out of the direct radio wave reach.
Zensys A/S
Z-Wave protocol
CONFIDENTIAL
Page 3 of 19
�
SDS10243-8
Z-Wave Protocol Overview
2008-12-04
1
2
Slaves
3
Battery powered
routing slave
4
Portable
Controller
Static controller
Figure 2 Z-Wave network comprising of controllers and slaves
3.3 Controllers
A controller is a Z-Wave device that has a full routing table and is therefore able to communicate with all
nodes in the Z-Wave network. The functionality available in a controller depends on when it entered the
Z-Wave network. In case the controller is used to create a new Z-Wave network it automatically become
the primary controller. The primary controller is the “master” controller in the Z-Wave network and there
can only be one in each network. Only primary controllers have the capability to include/exclude nodes in
the network and therefore always have the latest network topology.
Controllers added to the network using the primary controller are called secondary controllers and don’t
have the capability to include/exclude nodes in the network.
3.3.1
Portable Controller
A portable controller is a controller, which is designed to change position in the Z-Wave network. The
portable controller uses a number of mechanisms to estimate the current location and hereby calculating
the fastest route through the network. A portable controller is typically battery powered because it is
mainly used in portable applications. It is difficult to communicate with a portable controller because it is
typically powered down when not in active use to prolong battery lifetime.
An example of a portable controller could be a remote control.
3.3.2
Static Controller
A static controller is a fixed controller that must not change position in the network and has to be
powered up all the time (always listening). This controller has the advantage that Routing slaves can
report unsolicited status messages to it, and it also has the advantage of always knowing where it is
located in the network. A static controller will typically be a secondary controller in a Z-Wave network.
An example of a static controller could be an Internet gateway that monitors a Z-Wave system.
Zensys A/S
Z-Wave protocol
CONFIDENTIAL
Page 4 of 19
�













 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc