JESD209-4B
1 Scope
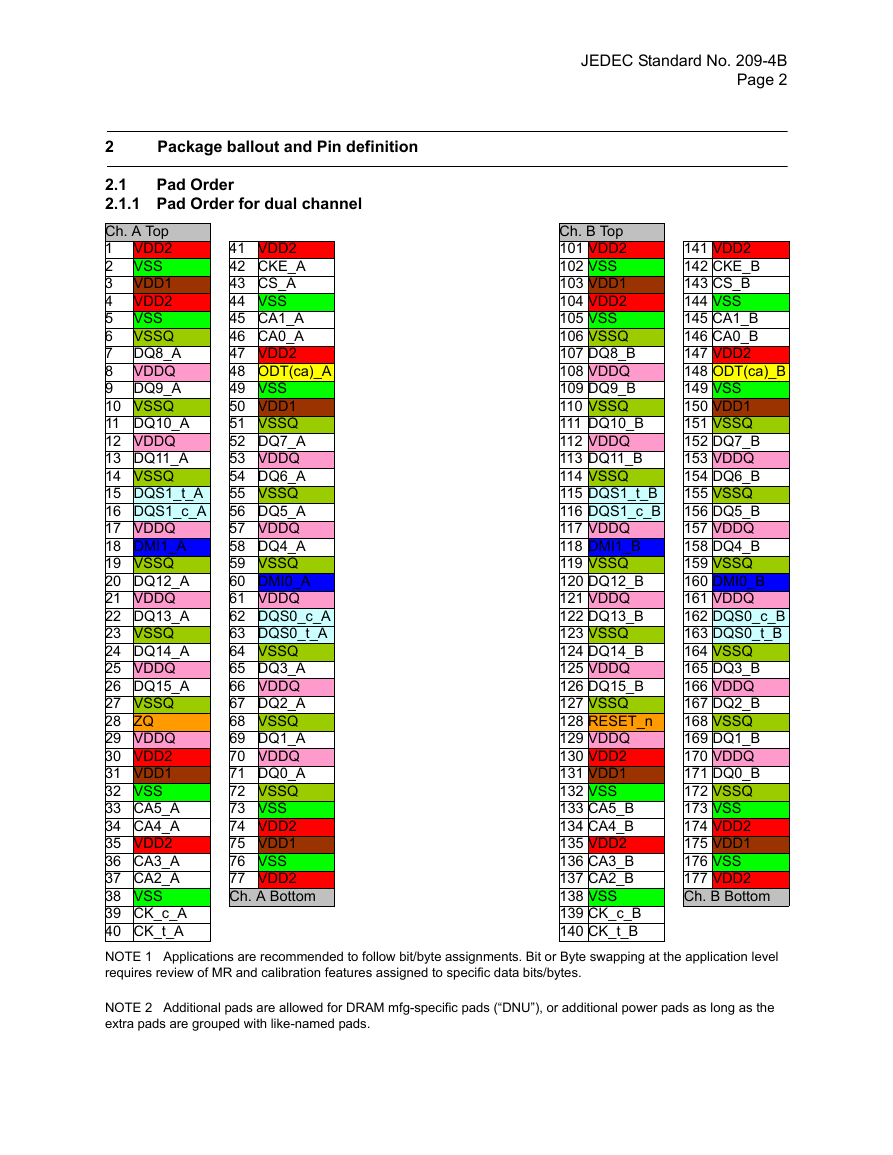
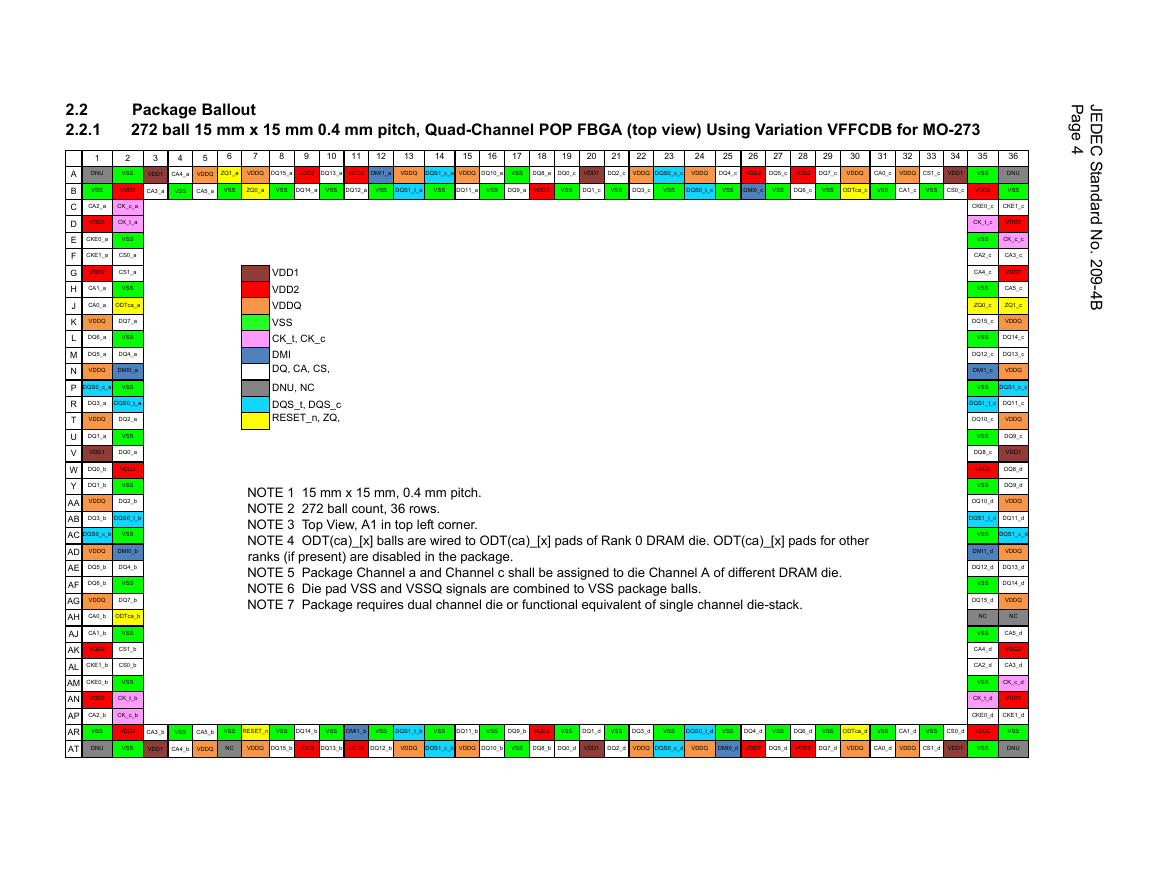
2 Package ballout and Pin definition
2.5 Pad Definition and Description
3 Functional Description
3.1 LPDDR4 SDRAM Addressing
3.2 Simplified LPDDR4 State Diagram
3.3 Power-up, Initialization and Power-off Procedure
3.4 Mode Register Definition
MR0 Register Information
MR1 Register Information
MR2 Register Information
MR3 Register Information
MR4 Register Information
MR5 Register Information
MR6 Register Information
MR7 Register Information
MR8 Register Information
MR11 Register Information (MA[5:0] = 0BH)
MR12 Register Information
MR13 Register Information
MR22 Register Information (MA[5:0] = 16H)
4 Command Definitions and Timing Diagrams
4.1 Activate Command
4.2 8-Bank Device Operation
4.3 Core Timing
4.4 Read and Write Access Operations
4.5 Read Preamble and Postamble
4.6 Burst Read Operation
4.7 Read Timing
4.8 tDQSCK Timing Table
4.9 Write Preamble and Postamble
4.10 Burst Write Operation
4.11 Write Timing
4.12 Read and Write Latencies
4.13 Write and Masked Write operation DQS controls (WDQS Control)
4.14 Postamble and Preamble merging behavior
4.15 MASKED WRITE OPERATION
4.16 LPDDR4 Data Mask (DM) and Data Bus Inversion (DBIdc) Function
4.17 Precharge Operation
4.18 Auto-Precharge Operation
4.19 Refresh command
4.20 Refresh Requirement
4.21 Self Refresh Operation
4.21.1 Self Refresh Entry and Exit
4.21.2 Power Down Entry and Exit during Self Refresh
4.21.3 Command input Timing after Power Down Exit
4.22 Self Refresh Abort
4.23 MRR, MRW, MPC Command during tXSR, tRFC
4.24 MODE REGISTER READ(MRR)
4.25 Mode Register Write (MRW) Operation
4.26 VREF Current Generator (VRCG)
4.27 CA VREF Training
4.28 DQ VREF Training
4.29 Command Bus Training
4.29.1 Training Sequence for single-rank systems
4.29.2 Training Sequence for multi-rank systems
4.30 Frequency Set Point
4.31 Mode Register Write-WR Leveling Mode
4.43 On Die Termination for Command/Address Bus
4.44 On-Die Termination
4.45 On Die Termination for DQ, DQS and DMI
4.48 Power-Down Mode
4.49 Input Clock Stop and Frequency Change
4.50.1 Command Truth Table
5 Absolute Maximum DC Ratings
6 AC and DC Operating Conditions
7 AC and DC Input/Output Measurement levels
8 Input/Output Capacitance
9 IDD Specification Parameters and Test Conditions
10 Electrical Characteristics and AC Timing
Annex A Differences Between Revisions
Standards Improvement Form













 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc