1 Scope
2 Normative references
3 Terms and definitions
4 Symbols (and abbreviated terms)
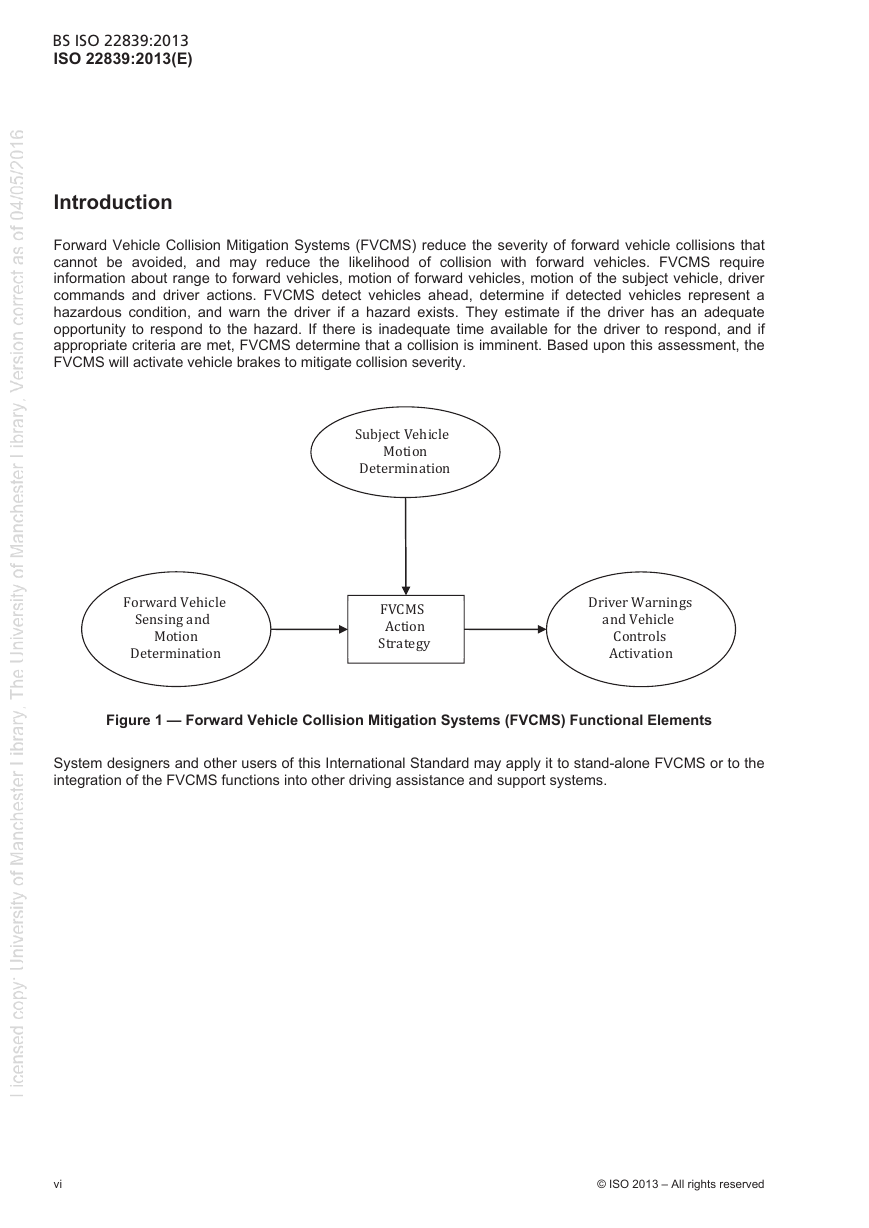
5 Classifications
5.1 System classification by curve radius capability
5.2 Classification by countermeasure types included
5.2.1 Collision Warning (CW) countermeasure
5.2.2 Speed Reduction Braking (SRB) countermeasure
5.2.3 Mitigation Braking (MB) Countermeasure
5.2.4 Combining countermeasures
6 Requirements
6.1 Minimum enabling capabilities
6.1.1 Light vehicle necessary functions
6.1.2 Heavy vehicle necessary functions
6.2 Operating model€— State Transition Diagram
6.2.1 State functional descriptions
6.2.1.1 FVCMS Off
6.2.1.2 FVCMS Inactive
6.2.1.3 FVCMS Active
6.3 Performance requirements
6.3.1 Target vehicle types
6.3.2 Collision types
6.3.3 Operating speed
6.3.3.1 Subject vehicle
6.3.3.1.1 Minimum subject vehicle speed (Vmin)
6.3.3.1.2 Maximum subject vehicle speed (Vmax)
6.3.3.2 Target vehicle
6.3.3.2.1 Minimum target vehicle speed
6.3.3.2.2 Maximum target vehicle speed
6.3.3.2.3 Maximum lateral offset (lateral discrimination)
6.3.3.2.4 Maximum lateral speed
6.3.3.3 Relative velocity
6.3.4 Target vehicle detection area
6.3.4.1 Minimum detection area
6.3.4.2 Detection range
6.3.4.3 Detection width and detection height
6.3.5 Target discrimination
6.3.5.1 Longitudinal discrimination
6.3.5.2 Lateral discrimination
6.3.5.3 Overhead discrimination
6.3.6 Countermeasure requirements
6.3.6.1 Provision of MB or SRB
6.3.6.2 Provision of CW
6.3.6.3 Brake light control
6.3.6.4 Mitigation braking requirements
6.3.6.4.1 Initiation of mitigation braking
6.3.6.4.1.1 Light vehicles
6.3.6.4.1.2 Heavy vehicles
6.3.6.4.2 Minimum deceleration in mitigation braking
6.3.6.4.2.1 Light vehicles
6.3.6.4.2.2 Heavy vehicles
6.3.6.4.3 Driver-commanded enhancement of mitigation braking
6.3.6.4.4 Termination of mitigation braking
6.3.6.4.5 Driver initiated override of mitigation braking
6.3.6.4.6 Braking with reduced traction
6.3.6.5 Speed reduction braking
6.3.6.5.1 Initiation of SRB
6.3.6.5.2 Maximum deceleration in SRB
6.3.6.5.3 Minimum effectiveness of SRB
6.3.6.5.4 SRB with reduced traction
6.3.6.5.5 Driver initiated override of speed reduction braking
6.3.6.6 Collision warning
6.3.7 Driver controls and human interface
6.3.7.1 Light vehicles
6.3.7.1.1 System limitation information
6.3.7.1.2 Driver disengagement of FVCMS
6.3.7.1.3 FVCMS fault indication
6.3.7.2 Heavy vehicles
6.3.7.2.1 Target vehicle detection information
6.3.7.2.2 FVCMS limitation information
6.3.7.2.3 Driver disengagement of FVCMS
6.3.7.2.4 System fault indication
7 Validation methods
7.1 Test target specification
7.1.1 Detectability specifications
7.1.1.1 Optical radar (i.e. lidar or ladar)
7.1.1.1.1 Vehicle target
7.1.1.1.2 Motorcycle target
7.1.1.1.3 Overhead target
7.1.1.2 Radio wave radar
7.1.1.2.1 Vehicle target
7.1.1.2.2 Motorcycle target
7.1.1.2.3 Overhead target
7.1.1.3 Passive optical sensor
7.1.1.3.1 Vehicle target
7.1.1.3.2 Motorcycle target
7.1.1.3.3 Overhead target
7.1.2 Test target physical constraints
7.1.2.1 Optical radar (i.e. lidar or ladar)
7.1.2.2 Radio wave radar
7.1.2.3 Passive optical sensor
7.2 Environmental conditions
7.2.1 Driving surface
7.2.2 Lighting conditions
7.2.3 Ambient air temperature
7.2.4 Horizontal visibility
7.3 Test method for detection zone
7.4 Test method for functional ability
7.5 Test method for target discrimination ability
7.5.1 Longitudinal discrimination test
7.5.2 Straight road lateral discrimination test
7.5.3 Straight road lateral offset discrimination test
7.5.4 Curved road lateral target discrimination test
7.5.5 Overhead discrimination test















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc