Edited by LZF
Chapter 1 软件过程
1. According to Brooks, which of the following is not an essential difficulty of software
development?
A. conformity
B. changeability
C. correctness
D. invisibility
答案:C
软件的本质困难定义出了软件开发的不变事实 software development invariants ,
其主要包括:复杂性(complexity)、一致性(conformity)、可变性(changeablity)、不可见性
(invisibility)
2. The “repeatable” level of CMM (Level 2 ) means that:
A. continuous process improvement is in place
B. both management and engineering processes are codified and followed
C. none of the above
D. metrics are used to control the process
答案:C
能力成熟度模型 capacity maturity model,CMM :
Initial:
Unpredictable and undisciplined process that depends on the current staff
Repeatable:
repeatable project management;
consistent time and effort predictions for similar projects
Defined: both management and engineering processes are codified and followed
Managed: metrics are used to control the process
Optimizing: continuous process improvement is in place
�
3. UML models include:
A. state change models
B. state models
C. behavior models
D. all of the above
答案:D
UML 模型可以分为三组:
状态模型 state models :描述静态数据结构;
行为模型 behavior models :描述对象协作 collaboration ;
状态变更模型 state change models :描述随着时间推移,系统所允许的状态;
4. Process-oriented integration is an integration:
A. that links application interfaces (that is, services defined through an interface
abstraction)
B. in which information is externalized from multiple software systems into a common
user interface
C. on the level of databases or application programming interfaces (APIs) that
externalize
information for consumption by other applications
D. none of the above
答案:D
面向接口的集成(Interface-oriented integration):
that links application interfaces (that is, services defined through an
interface
abstraction)
面向信息的集成(Information-oriented integration):
on the level of databases or application programming interfaces (APIs) that
externalize
information for consumption by other applications
面向用户的集成(Portal-oriented)——特殊的面向信息集成
in which information is externalized from multiple software systems into a
common
user interface(用户界面)
面向过程的集成(process-oriented):
that link application
5. Which of the following is not an approach to carry out system planning:
A. all of the above
B. SWOT
C. ERP
D. ISA
答案:C
系统规划(system planning)的方式:
SWOT:自顶向下
价值链模型(value chain model,VCM)
业务过程重组(business process re-engineering,BPR)
信息系统体系架构(information system architecture,ISA):自底向上
�
6. Which of the following is a primary activity of the VCM approach:
A. services
B. administration and infrastructure
C. human resource management
D. none of the above
答案:A
Primary activity of the VCM approach: 为最终产品创造或增加价值
内部物流;
操作;
外部物流;
销售和市场;
服务;
Support activities of the VCM approach: 不直接增加产品价值,但不可或缺
行政管理和基础架构(administration and infrastructure);
人力资源管理(human resource management);
研发;
IS 研发;
7. Which of the following is not considered a participant (perspective) in the ISA approach:
A. all of the above
B. subcontractor
C. manager
D. owner
答案:C
ISA框架被描述为一个 5(1-5)*6(A-F) 的表格:
行表示用于复杂工程产品构建的不同视角(perspectives)
规划者(Planners):确定系统范围;
所有者(Owner):定义企业概念模型;
设计者(Designer):详细说明系统物理模型;
建造者(Builders):提供详细的技术解决方案;
承包者(Subcontractors):提供系统构件
列表示每个参与者所从事的六种不同的描述(descriptions)或体系结构模型
(architectural model)
8. Which of the following is not a modeling technique of the structured approach to systems
development:
A. DFD
B. ERD
C. all of the above
D. UML
答案:D
结构化方法:功能性、过程性和强制性的方法,从系统建模的角度看,其主要基于两种技术
数据流图(Data Flow Diagram,DFD):过程建模
实体关系图(Entity Relationship Diagram,ERD):数据建模
9. Which of the following is not considered to be an iterative and incremental development
model/method:
�
A. the spiral model
B. model-driven architecture
C. none of the above
D. functional decomposition
答案:D
Iterative and incremental development model/method:
敏捷开发模型(agile software development)
螺旋模型(the spiral model)
IBM Rational 统一过程(IBM Rational Unified Process,RUP)
模型驱动的体系结构(Model Driven Architecture,DMA)
AOP
知识点:
三个重要的IS概念:
数据:代表涉及业务活动的价值、质量、概念和时间的原始事实;
信息:增值事实,即已经被处理并概括为产品增值事实的数据,揭示了新的特征和趋
势;
知识:对信息的理解,由经验或研究获得;
软件开发的本质
软件开发的不变事实
软件的本质困难
复杂性(complexity):软件规模的函数,以及组成软件产品的构件之间相互依
存关系的函数;
一致性(conformity):应用软件必须与其依赖的软硬件平台一致,也必须与现
有的信息系统相一致,以便于集成;
可变性(changeability):由于业务过程和需求是不断变化的,所以在开发应用
软件时也必须能够容纳这些变化;
不可见性(invisibility):尽管应用软件提供了可见的输出,但是负责输出的代
码通常隐藏在“不可见”的程序语句、二进制代码库和周边系统软件中;
软件开发的意外事件
软件开发意外事件与三个因素相关:
利益相关者(stakeholders):客户和开发者
过程(process)
建模(modeling)
开发 or 集成
面向接口的集成(Interface-oriented integration):
that links application interfaces (that is, services defined through an
interface
abstraction)
面向信息的集成(Information-oriented integration):
on the level of databases or application programming interfaces
(APIs) that externalize
information for consumption by other applications
面向用户的集成(Portal-oriented)——特殊的面向信息集成
in which information is externalized from multiple software
systems into a common
�
user interface(用户界面)
面向过程的集成(process-oriented):
that link application
系统规划
SWOT
VCM
BRP
ISA
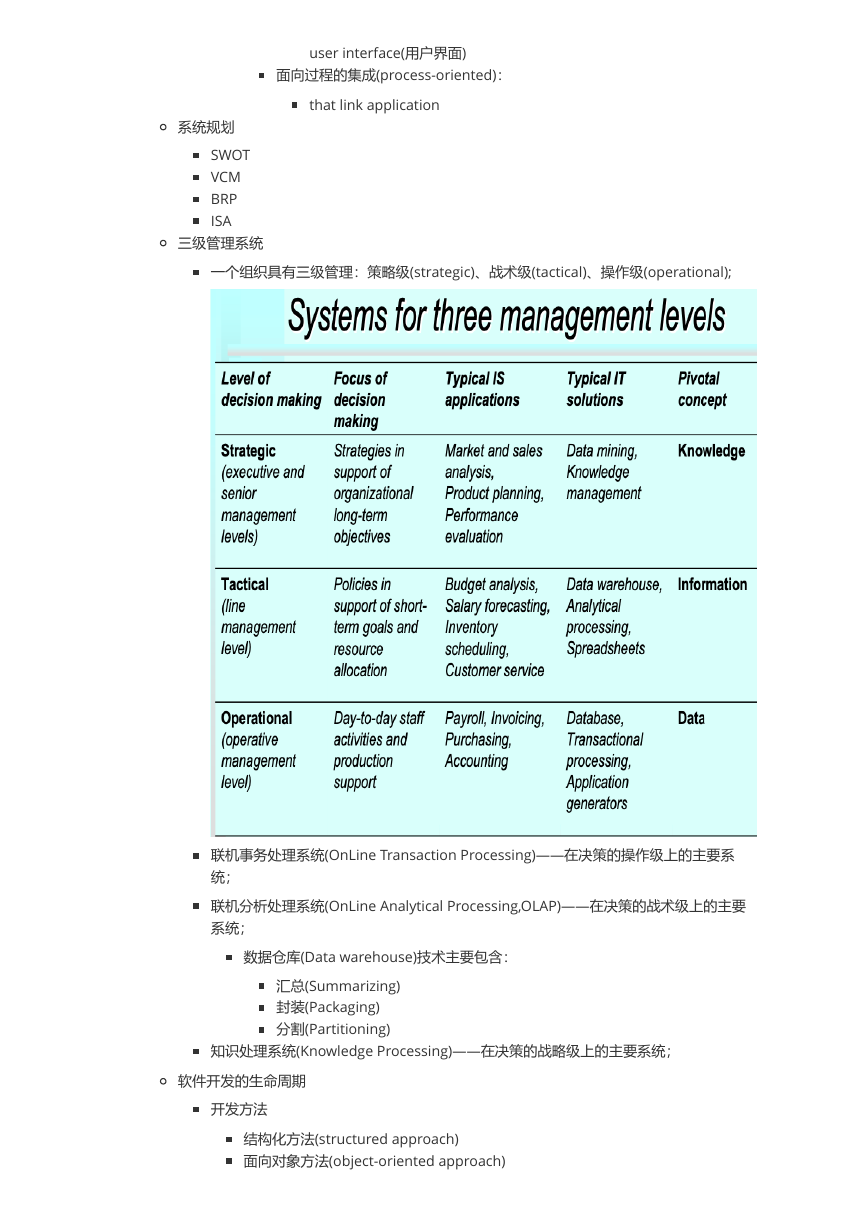
三级管理系统
一个组织具有三级管理:策略级(strategic)、战术级(tactical)、操作级(operational);
联机事务处理系统(OnLine Transaction Processing)——在决策的操作级上的主要系
统;
联机分析处理系统(OnLine Analytical Processing,OLAP)——在决策的战术级上的主要
系统;
数据仓库(Data warehouse)技术主要包含:
汇总(Summarizing)
封装(Packaging)
分割(Partitioning)
知识处理系统(Knowledge Processing)——在决策的战略级上的主要系统;
软件开发的生命周期
开发方法
结构化方法(structured approach)
面向对象方法(object-oriented approach)
�
生命周期的阶段
业务分析(business analysis):又叫做需求分析(requirements analysis)
目的:其主要目的是确定(determine)(业务分析)和详细说明(specify)(系统分
析)客户的需求;
业务分析主要分为以下部分:
需求确定(requirements determination)
功能性需求
非功能性需求
需求说明(requirements specification)
系统设计(system design)
体系结构设计(architectural design)
详细设计(detail design)
实现(implement)
集成与部署(integration and deployment)
运行与维护(operation and maitenance)
跨越生生命周期的活动
系统规划:
估计(estimate)项目的可交付性、成本、时间、风险、里程碑和资源需求的活
动,它也包括对开发方法、过程、工具、标准和团队组织的选择。
度量:
度量开发时间和工作量(developing time and effort);
度量应用于软件产品的质量和复杂性(quality and complexity)方面;
度量的一个重要的应用是在生命周期的不同阶段度量开发模型,评估过程的
效果并改进工作质量;
测试(testing):
基于可执行的(execution-based)测试包括:
规格说明测试 testing to specs :黑盒测试;
代码测试 testing to code :白盒测试。
开发模型
螺旋模型(the spiral model)
IBM Rational Unified Process,RUP
模型驱动的体系结构(Model Driven Architecture,DMA)
敏捷开发模型(agile software development),最知名的敏捷开发包括:
极限编程(Extreme Programming,XP);
特征驱动(feature-driven)开发;
学习开发(learn development);
面向切面编程(Aspect-Oriented Programming,AOP)
Chapter 2 需求确定
1. In BPMN, an atomic process is also called an:
A. event
B. task
C. activity
D. job
�
答案:B
业务过程建模表示法(Business Process Modeling Notation,BPMN)
关于过程:
业务过程可能是手工(manually)操作的活动或自动化的automated服务;
至少一个输入与输出流;
过程可能是原子的(atomic)和复合的(composite):
原子过程:也被称为任务;
复合过程
2. In BPMN, a message flow is the following modeling element:
A. artifact
B. connector
C. swimlane
D. flow object
答案:B
BPMN提供了四种基本的建模元素:
流对象(flow object)
事件(event);
活动(activity);
路由(gateway);
连接对象(connecting objects)
序列流(Sequence flow)
消息流(Message flow)
关联(Association)
泳池/泳道(pools/swimlanes)
人工制品(artifacts)
数据对象(Data object)
组(Group)
注释(Annatation)
3. In solution envisioning(解决方案构想) , the modeling element that determines the business
value of a piece of the functionality is a:
A. solution case
B. capability case
C. business use case
D. business case
答案:B
能力用例
4. Which requirements elicitation(需求引导) method works with the notion of a probortunity
statement:
A. brainstorming
B. none of the above
C. questionnaire
D. JAD
答案:A
�
需求引导的传统方法:
面谈(Interview)
调查表(Questionnaire)
观察(observation)
文档和软件系统的研究(study of documents and software systems)
需求引导的现代方法:
原型法(prototyping)
头脑风暴(brainstorming):问题机会陈述(probortunity statement)
联合应用开发(Joint application deveplopment, JAD)
快速应用开发(rapid application development, RAD)
5. Which requirements elicitation method works with the notion of trigger question:
A. none of the above
B. JAD
C. RAD
D. questionnaire
答案:A
6. An interface requirement is a:
A. system service
B. functional requirement
C. none of the above
D. system constraint
答案:D
系统服务(system service):功能性需求(functional requirement)
系统的范围(scope of system);
必要的业务功能(necessary business functions);
所需的数据结构(required data structures);
系统约束(system constraint):非功能性需求(nonfunctional requirement)
可用性(usability):定义使用系统的难易程度;
可复用性(reusability):定义在新系统的开发中,重复使用之前已实现的软件构件的容
易程度;
可靠性(reliability):与系统失效的频率和严重性以及系统从失效中恢复的程度相关;
性能(performance):通过系统响应时间、事务处理时间、资源开销等决定;
效率(efficiency):与取得软件成果或达到软件目标的成本和时间相关;
适应性(supportability):定义了系统被理解、修改、完善和拓展的容易程度;包括可理
解性(understandability)、可维护性(maintainability)和可拓展性(scalability)
知识点:
解决方案构想:
实现支撑:
效果
效率
优势
三阶段
业务能力探索(business capacity exploration)
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc