LTE系统全网信令流程
Introduction
As a new wireless mobile communication technology, LTE (Long Term Evolution)
provide all kinds of services through network access procedures. So when you
are trying to understand the LTE technology, the network access procedure is just
in the close front of your eyes.
This document is trying to describe the general procedure handlings among the
network elements under LTE network architecture, by way of showing you the
procedure handlings in figures. From these figures, you will get an overview of the
LTE general procedures, such as: “The System Information Handling”, “The
Random Access Procedure”, “The Attach Procedure”, “The TAU Procedure”, “The
Handover Procedure”, etc.
The first several figures show the introduction of protocol layer stacks among
network elements, such as: protocol layer stacks“between UE-MME”, “between
UE-PDN GW”, etc. From these protocol layer stacks introduction, you will learn
the peer-to-peer protocol layers among several related network elements, it will
help you to understand LTE procedures’ working mechanism stuff. And after,
begins the description of the LTE general procedure, in an order from “System
information handling”to “ANR Measurement procedure”, with the “access
procedure”, “handover procedure”, “inter-RAT operation procedure”,……, in the
middle. From these procedure figures description, you can get the deep details of
the LTE network access procedure, and it will finally direct you to found a whole-
system-view of LTE architecture.
This document is suitable for the guys who want to know the LTE general
procedure, or use it as a reference book.
2009-11-06
LTE PDU L3 R&D Team
0
�
Abbreviations
MME
UE
MS
eNodeB
GW
PCRF
H-PCRF
V-PCRF
HSS
EIR
UTRAN
E-UTRAN
GERAN
PLMN
HPLMN
VPLMN
HLR
VLR
CBC
OMC
BSC
BTS
BSS
CN
MSC/SGSN
Inter-RAT
MBMS
MCE
RNC
Mobility Management Entity
User Equipment
Mobile Station
evolved NodeB
GateWay
Policy and Charging Rules Fuction
Home-PCRF
Visited-PCRF
Home Subscriber Server
Equipment Identity Register
Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network
evolved UTRAN
GSM/EDGE Radio Access Network
Public Land Mobile Network
Home PLMN
Visited PLMN
Home Location Register
Visitor Location Register
Cell Broadcast Centre
Operation and Maintenance Center
Base Station Controler
Base Transceiver Station
Base Station Subsystem
Core Network
Mobile-services Switching Centre/Serving GPRS Support Node
Radio Access Technology
Media Broadcast and Multicast System
Multi-cell/multicast Coordination Entity
Radio Network Controler
1
�
Network elements functions
eNodeB functions:
-
-
Header compression and user plane ciphering;
MME selection when no routeing to an MME can be determined from the information provided by the
UE;
UL bearer level rate enforcement based on UE-AMBR and MBR via means of uplink scheduling
(e.g. by limiting the amount of UL resources granted per UE over time);
DL bearer level rate enforcement based on UE-AMBR;
UL and DL bearer level admission control;
Transport level packet marking in the uplink, e.g. setting the DiffServ Code Point, based on the QCI of
the associated EPS bearer.
-
-
-
-
NAS signalling;
NAS signalling security;
Inter CN node signalling for mobility between 3GPP access networks (terminating S3);
UE Reachability in ECM-IDLE state (including control and execution of paging retransmission);
Tracking Area list management;
PDN GW and Serving GW selection;
MME selection for handovers with MME change;
SGSN selection for handovers to 2G or 3G 3GPP access networks;
Roaming (S6a towards home HSS);
Authentication;
Authorization;
Bearer management functions including dedicated bearer establishment;
Lawful Interception of signalling traffic;
Warning message transfer function (including selection of appropriate eNB);
UE Reachability procedures.
MME functions:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SGSN functions:
-
-
-
Inter EPC node signalling for mobility between 2G/3G and E-UTRAN 3GPP access networks;
PDN and Serving GW selection: the selection of S-GW/P-GW by the SGSN is as specified for the MME;
MME selection for handovers to E-UTRAN 3GPP access network.
2
�
Network elements functions
Serving GW functions:
-
-
the local Mobility Anchor point for inter-eNodeB handover;
sending of one or more "end marker" to the source eNodeB, source SGSN or source RNC immediately after
switching the path during inter-eNodeB and inter-RAT handover, especially to assist the reordering function
in eNodeB.
Mobility anchoring for inter-3GPP mobility (terminating S4 and relaying the traffic between 2G/3G system
and PDN GW);
ECM-IDLE mode downlink packet buffering and initiation of network triggered service request procedure;
Lawful Interception;
Packet routeing and forwarding;
Transport level packet marking in the uplink and the downlink, e.g. setting the DiffServ Code Point, based
on the QCI of the associated EPS bearer;
Accounting for inter-operator charging. For GTP-based S5/S8, the Serving GW generates accounting data
per UE and bearer;
Interfacing OFCS according to charging principles and through reference points specified in TS 32.240 [51].
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
PDN GW functions:
-
-
-
-
Per-user based packet filtering (by e.g. deep packet inspection);
Lawful Interception;
UE IP address allocation;
Transport level packet marking in the uplink and downlink, e.g. setting the DiffServ Code Point, based on
the QCI of the associated EPS bearer;
Accounting for inter-operator charging;
UL and DL service level charging as defined in TS 23.203 [6]
(e.g. based on SDFs defined by the PCRF, or based on deep packet inspection defined by local policy);
Interfacing OFCS through according to charging principles and through reference points specified in
TS 32.240 [51].
UL and DL service level gating control as defined in TS 23.203 [6];
UL and DL service level rate enforcement as defined in TS 23.203 [6]
(e.g. by rate policing/shaping per SDF);
UL and DL rate enforcement based on APN-AMBR
(e.g. by rate policing/shaping per aggregate of traffic of all SDFs of the same APN that are associated with
Non-GBR QCIs);
3
�
Network elements functions
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
DL rate enforcement based on the accumulated MBRs of the aggregate of SDFs with the same GBR
QCI
(e.g. by rate policing/shaping);
DHCPv4 (server and client) and DHCPv6 (client and server) functions;
The network does not support PPP bearer type in this version of the specification. Pre-Release 8 PPP
functionality of a GGSN may be implemented in the PDN GW;
packet screening.
UL and DL bearer binding as defined in TS 23.203 [6];
UL bearer binding verification as defined in TS 23.203 [6];
Functionality as defined in RFC 4861 [32];
Accounting per UE and bearer.
H-PCRF functions:
-
-
-
terminates the Rx reference point for home network services;
terminates the S9 reference point for roaming with local breakout;
associates the sessions established over the multiple reference points (S9, Rx), for the same UE's IP-
CAN session (PCC session binding).
V-PCRF functions:
-
-
terminates the Gx and S9 reference points for roaming with local breakout;
terminates Rx for roaming with local breakout and visited operator's Application Function.
4
�
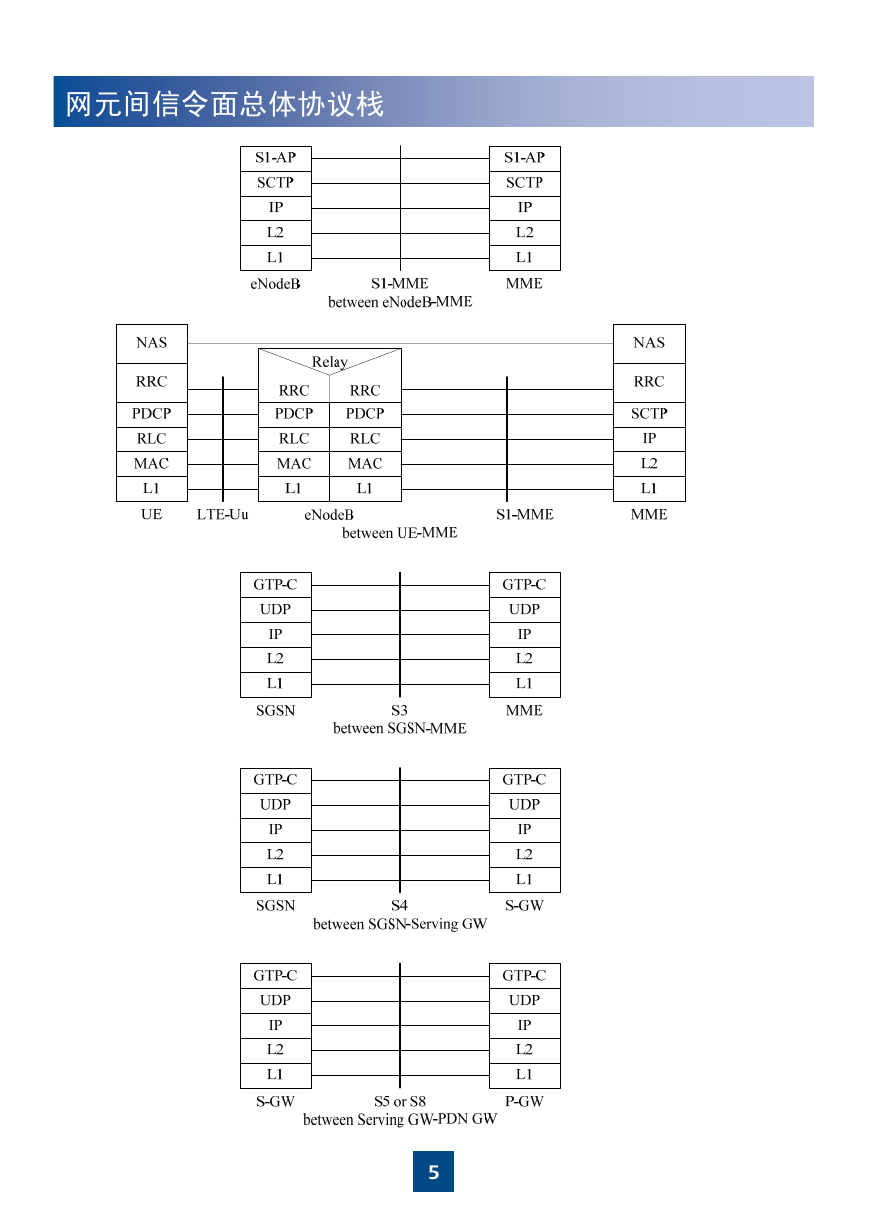
网元间信令面总体协议栈
5
�
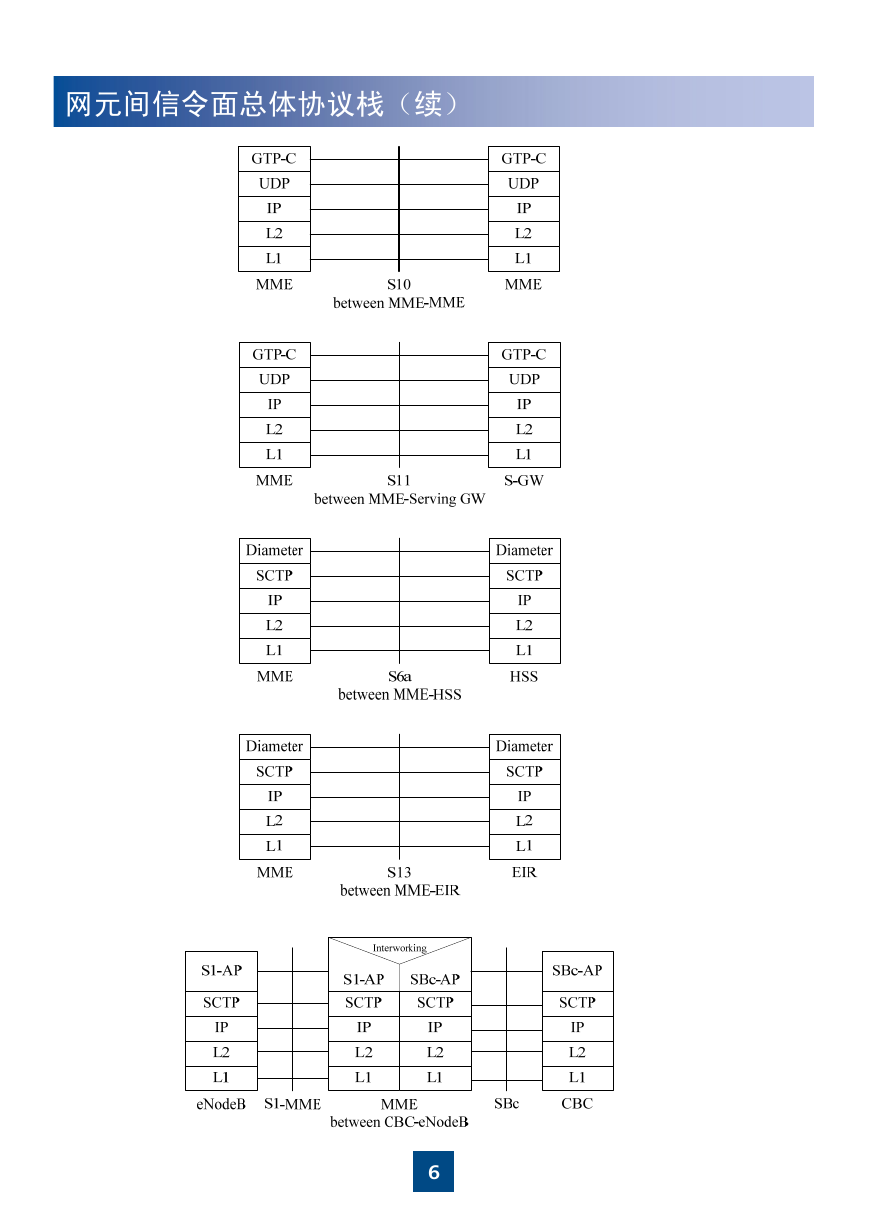
网元间信令面总体协议栈(续)
6
�
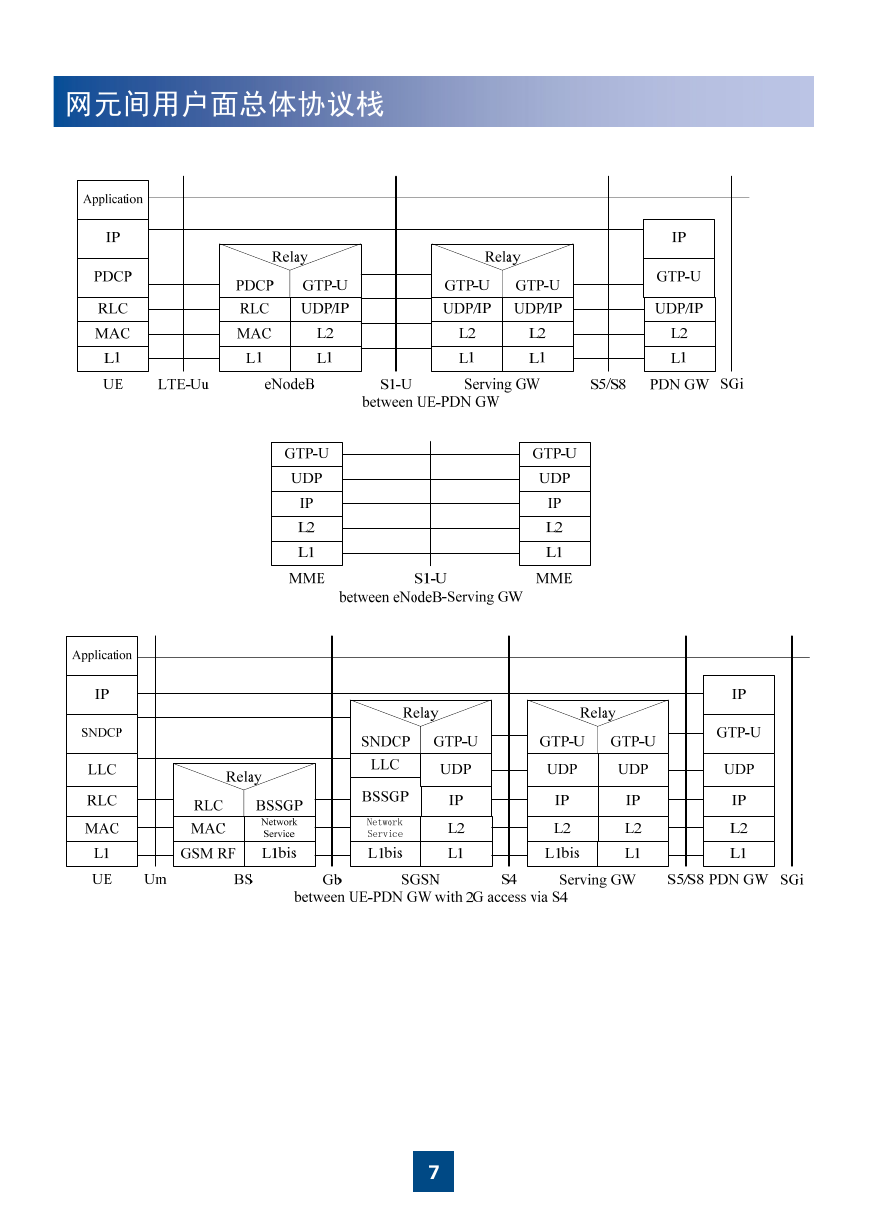
网元间用户面总体协议栈
7
�













 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc