·第 1 页:Vega 和 Vega Prime 比较
·第 2 页:The Vega Prime™ Desktop Tutor
·第 3 页:VP 工作流程
·第 4 页:ACF 文件总体结构
·第 5 页:创建场景
·第 6 页:函数介绍
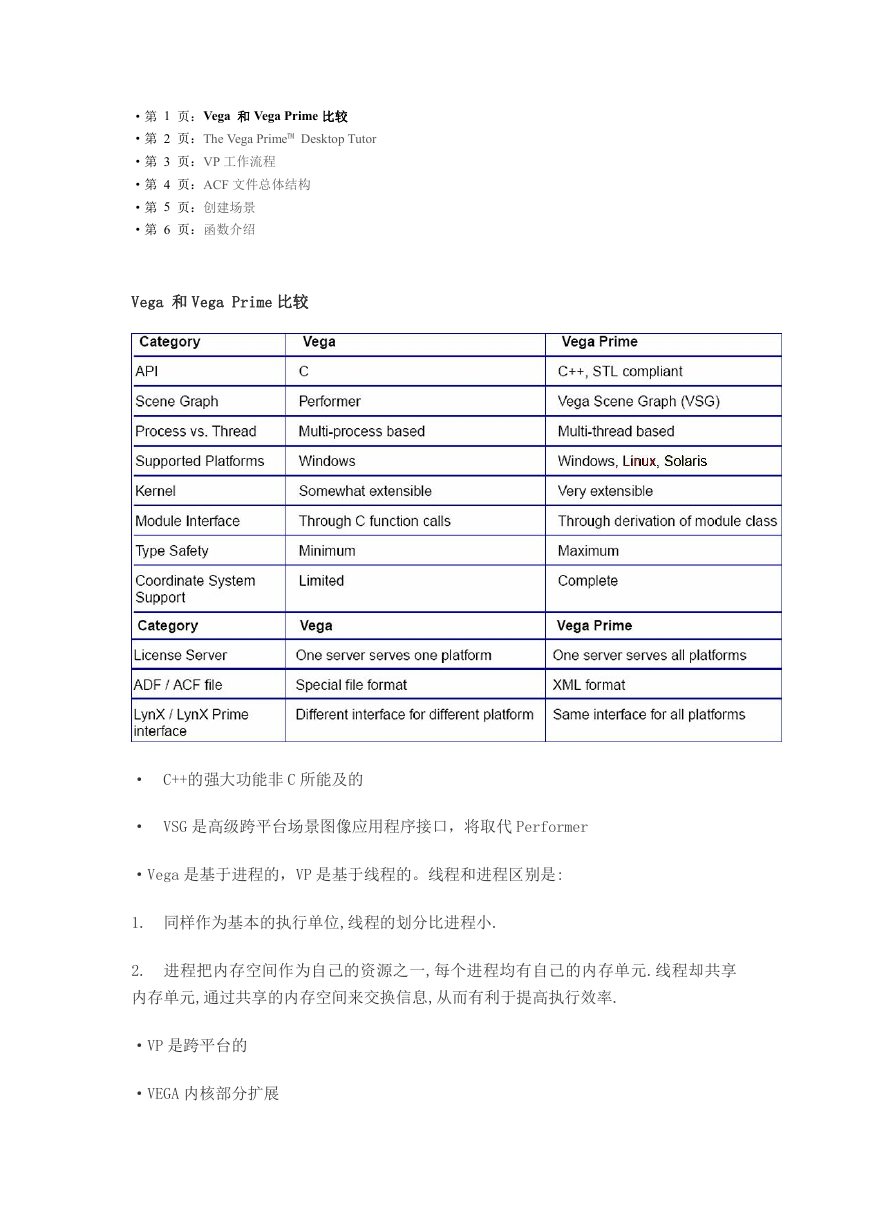
Vega 和 Vega Prime 比较
· C++的强大功能非 C 所能及的
· VSG 是高级跨平台场景图像应用程序接口,将取代 Performer
·Vega 是基于进程的,VP 是基于线程的。线程和进程区别是:
1. 同样作为基本的执行单位,线程的划分比进程小.
2. 进程把内存空间作为自己的资源之一,每个进程均有自己的内存单元.线程却共享
内存单元,通过共享的内存空间来交换信息,从而有利于提高执行效率.
·VP 是跨平台的
·VEGA 内核部分扩展
�
· 模块接口:VEGA 通过 C 功能调用,而 VP 是通过模块类
·VP 中 ADF/ACF 文件类型采用 XML
XML 是 eXtensible Markup Language 的缩写,意为可扩展的标记语言。XML 是一套
定义语义标记的规则,这些标记将文档分成许多部件并对这些部件加以标识。它不像超
文本标记语言 HTML(Hypertext Markup Language)或是格式化的程序。这些语言定义
了一套固定的标记,用来描述一定数目的元素。XML 是一种元标记语言,用户可以定义
自己需要的标记。这些标记必须根据某些通用的原理来创建,XML 标记描述的是文档的
结构和意义,而不描述页面元素的格式化。可用样式单为文档增加格式化信息。文档本
身只说明文档包括什么标记,而不是说明文档看起来是什么样的。
XML 优点:
⑴ XML 遵循严格的语法要求。如果语法有丝毫差错,分析器都会停止对它的进一步处理,
相应地,除了错误提示外,你看不到任何的显示信息。
⑵ XML 允许各种不同的专业(如音乐、化学、数学等)开发与自己的特定领域有关的标
记语言。
⑶ XML 的最大能量来源于它不仅允许你定义自己的一套标记,而且这些标记不必仅限于
对于显示格式的描述。XML 允许你根据各种不同的规则来制定标记,比如根据商业规则,
根据数据描述甚至根据数据关系来制定标记。
⑷ 由于 XML 是非专有的并易于阅读和编写,就使得它成为在不同的应用间交换数据的
理想格式。
⑸ 由于标记是有含义的,所以即使过了很长时间用户仍然可以很容易的理解 XML 文档。
⑹ XML 是基于 W3C 定制的开放标准,从而使得基于 XML 的应用具有广泛性。
⑺ 在因特网上如果 Web 页是 XML 格式的,则搜索会更高效,而且不仅可以搜索数据,
还可以在搜索中加入与数据相关的上下文信息,这样就形成了更精确的搜索机制。
TOM 如是说
相对于 VEGA 来说,VP 是 MULITGEN 公司未来发展的主流,它的功能也将是 VEGA 不可以
比肩的。
�
VP 工作流程
·初始化
· 定义
· 配置
·帧循环
·关闭
初始化和关闭是在 vp::namespace 中定义的,定义,配置,帧循环等是在 vpKernel
类中定义的。VpApp 是基于初始化,定义,配置,帧循环, 关闭工作流程构造的,所有
的 VpApp 类成员函数都是内嵌虚函数,因而易扩展。vpApp 同时提供一些实用的键盘输
入来触发图象模式通道。
典型的 VP 程序如下:
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//初始化
vp::initialize(argc, argv);
//创建 vpApp 实例
vpApp *app = new vpApp;
//载入 acf 文件
if (argc <= 1)
app->define("simple.acf");
else
app->define(argv[1]);
// 配置
app->configure();
�
// 帧循环
app->run();
app->unref();
// 关闭
vp::shutdown();
return 0;
}
vp::initialize 实现以下功能:
• Check out the licenses from the license server.
• Initialize static variables and singleton classes.
• Initialize memory allocator.
• Initialize rendering library.
• Initialize scene graph.
• Initialize ACF parser.
• Initialize module interface.
• Initialize kernel classes.
vp::shutdown 实现以下功能:
1. Free the memories allocated by the kernel classes.
2. Call the shutdown method on modules so that they can clean up the
memories allocated through out the application.
3. Terminate asynchronous threads.
4. Return the licenses back to the license server.
�
定义:
类实例在定义中创建和初始化。
类实例可通过代码创建或通过传递 ACF 文件给 vpKernel::define 方法 (或
vpApp::define, 若 vpApp 已经使用). ACF 文件中的类实例将在 VP 解析文件时自动创
建。
vpKernel::define()
vpKernel::define( const char *filename )
配置:
在定义系统后,VP 配置定义阶段设置的值, 如多线程模式,线程优先和处理器分配等,
同时也建立基于附加消息的类实例之间的关系。
帧循环:
while ( s_vpKernel->beginFrame() != 0 )
s_vpKernel->endFrame();
vpKernel
上面提到:“初始化和关闭是在 vp::namespace 中定义的,定义,配置,帧循
环等是在 vpKernel 类中定义的。”学习了解 vpKernel 是很有必要的。
VpKernel 类是 vsServiceMgr 类的衍生类. 核心功能包括帧循环的控制和 vsServices
的管理。其它功能包括:
·创建 vsTraversalUpdate 实例并控制运行
·遍历访问所有的在 kernel 登记并由 vpKernel::update 触发的 vpScenes
·发送相关配置和帧循环控制信息给所有的 vpModules
事件处理列举:
• vpKernel::EVENT_CONFIGURE—Subscribers are notified at configuration stage.
�
• vpKernel::EVENT_ON_FIRST_FRAME—Subscribers are notified at execution of
the first frame cycle.
• vpKernel::EVENT_PRE_UPDATE_TRAVERSAL—Subscribers are notified in
vpKernel::update, before the update traversal starts.
The function signature for this event is virtual void notify(Event, const
vpKernel*). When the event happens, the function is called. So, you have to
know the signature of the function of each event.
• vpKernel::EVENT_POST_UPDATE_TRAVERSAL—Subscribers are notified in
vpKernel::update, after the update traversal finishes.
The function signature for this event is virtual void notify(Event, const
vpKernel*).
• vpKernel::EVENT_ON_LAST_FRAME—Subscribers are notified at execution of the
last frame cycle.
• vpKernel::EVENT_SYNC_SCENE_GRAPH—Subscribers are notified at sending
syncSceneGraph messages to services.
• vpKernel::EVENT_PROCESS_NON_LATENCY_CRITICAL—Subscribers are notified at
performing non-latency-critical processing.
• vpKernel::EVENT_PROCESS_LATENCY_CRITICAL—Subscribers are notified at
performing latency-critical processing.
• vpKernel::EVENT_SHUTDOWN—Subscribers are notified at shutting down the
frame loop.
�
配置:
配置成功返回 vsgu::SUCCESS:
vpKernel::configure()
vpKernel::configure()
判断是否配置:
vpKernel::isConfigured()
vpKernel::isConfigured()
实例:
返回实例:
vpKernel::instance()
vpKernel::instance()
帧循环:
可以分为以下 5 个主要步骤:
• beginFrame
• syncWithSceneGraph
• processNonLatencyCritical
• endFrame
• processLatencyCritical
更新:
vpKernel::update()
vpKernel::update()
vpPipeline
�
vpPipeline 管理窗口和硬件图象管道之间的映射。
构造函数:
vpPipeline::vpPipeline()
vpPipeline::vpPipeline()
在窗口中加入新窗口:
vpPipeline::addWindow()
vpPipeline::addWindow( vpWindow *window, int location = -1 )
删除窗口:
vpPipeline::removeWindow()
vpPipeline::removeWindow( vpWindow *window )
在指定迭代程序删除窗口
vpPipeline::erase_window()
vpPipeline::erase_window( const_iterator_window it )
迭代程序有 vpPipeline::begin_window, vpPipeline::end_window,
vpPipeline::get_iterator_window
其他的还有:
vpPipeline::begin_window()
vpPipeline::begin_window() const
vpPipeline::end_window()
vpPipeline::end_window() const
vpPipeline::empty_window()
vpPipeline::empty_window() const
�















 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc