操作系统实验报告
计算机 0703 班
200729
实验 3 进程同步和通信-生产者和消费者问题模拟
�
1. 目的:
调试、修改、运行模拟程序,通过形象化的状态显示,使学生理解进程的概
念,了解同步和通信的过程,掌握进程通信和同步的机制,特别是利用缓冲区进
行同步和通信的过程。通过补充新功能,使学生能灵活运用相关知识,培养创新
能力。
2. 内容及要求:
1) 调试、运行模拟程序。
2) 发现并修改程序中不完善的地方。
3) 修改程序,使用随机数控制创建生产者和消费者的过程。
4) 在原来程序的基础上,加入缓冲区的写互斥控制功能,模拟多个进程存取一
个公共缓冲区,当有进程正在写缓冲区时,其他要访问该缓冲区的进程必须等待,
当有进程正在读取缓冲区时,其他要求读取的进程可以访问,而要求写的进程应
该等待。
5) 完成 1)、2)、3)功能的,得基本分,完成 4)功能的加 2 分,有其它功能改进的
再加 2 分
3. 程序说明:
本程序是模拟两个进程,生产者(producer)和消费者(Consumer)工作。生
产者每次产生一个数据,送入缓冲区中。消费者每次从缓冲区中取走一个数据。
缓冲区可以容纳 8 个数据。因为缓冲区是有限的,因此当其满了时生产者进程应
该等待,而空时,消费者进程应该等待;当生产者向缓冲区放入了一个数据,应
唤醒正在等待的消费者进程,同样,当消费者取走一个数据后,应唤醒正在等待
的生产者进程。就是生产者和消费者之间的同步。
每次写入和读出数据时,都将读和写指针加一。当读写指针同样时,又一起
退回起点。当写指针指向最后时,生产者就等待。当读指针为零时,再次要读取
的消费者也应该等待。
为简单起见,每次产生的数据为 0-99 的整数,从 0 开始,顺序递增。两个
进程的调度是通过运行者使用键盘来实现的。
4. 程序使用的数据结构
进程控制块:包括进程名,进程状态和执行次数。
缓冲区:一个整数数组。
缓冲区说明块:包括类型,读指针,写指针,读等待指针和写等待指针。
5. 程序使用说明
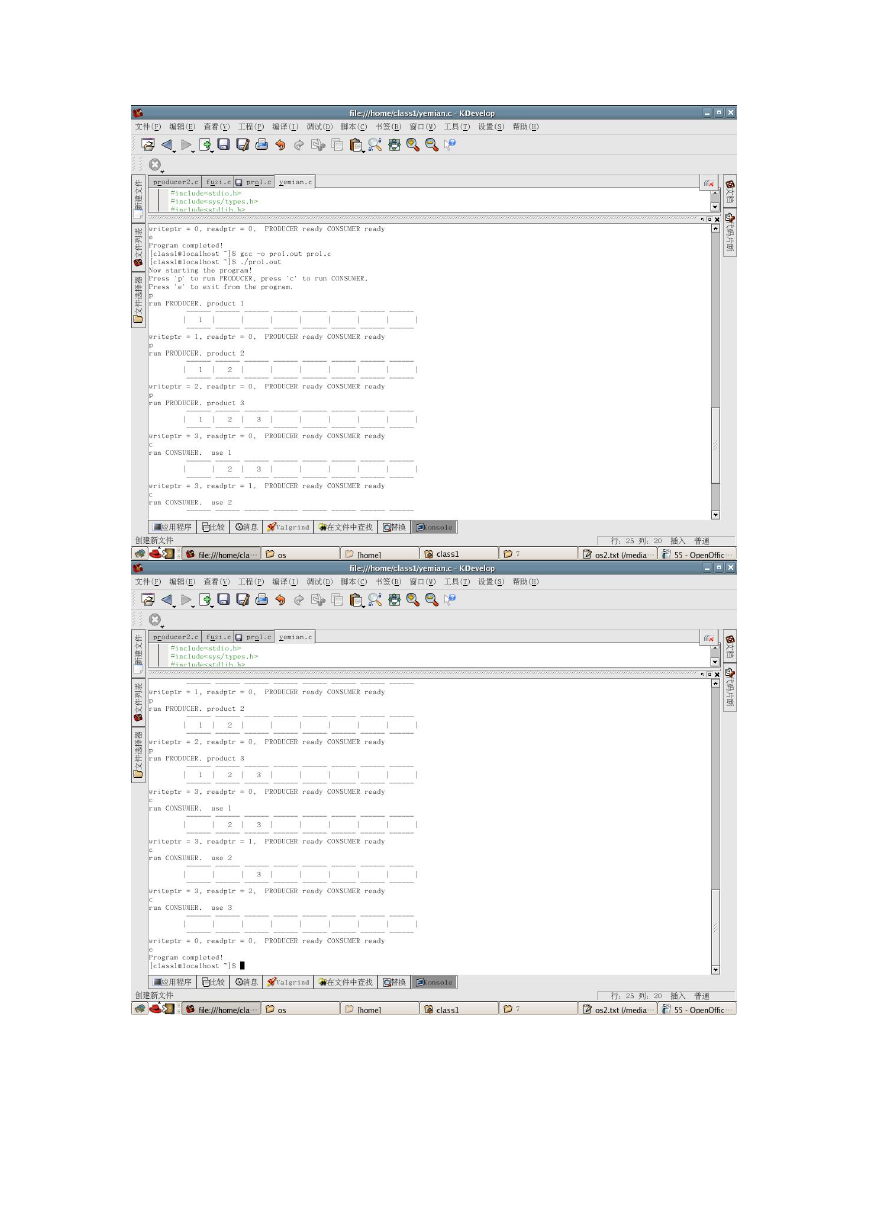
启动程序后,如果使用'p'键则运行一次生产者进程,使用'c'键则运行一次
消费者进程。通过屏幕可以观察到两个进程的状态和缓冲区变化的情况。
6.预习报告要求:
1) 题目,目的,要求
2) 初步理解的程序流程图
3) 拟修改、补充的源程序,指出原来程序错误所在,并说明程序中拟加入的功
�
能。
4) 新加功能预期运行结果的说明
6.实验报告要求:
1) 题目,目的,要求
2) 程序流程图
3) 最终运行的源程序及修改、补充的说明。
4) 运行结果及其说明
七.源程序
*/
*/
*/
*/
*/
PRODUCER_CONSUMER
*/
to produce message and
The program also demonstrates the synchronism between
PROGRAM NAME:
This program simulates two processes, producer which
put it into a buffer
/***************************************************************/
/*
/*
/* continues
/* [implemented by PIPE], and consumer which continues to get
/* message from the buffer and use it.
/*
*/
/* processes and uses of PIPE.
/***************************************************************/
#include
#define PIPESIZE 8
#define PRODUCER 0
#define CONSUMER 1
#define RUN
0
1
#define WAIT
2
#define READY
0
#define NORMAL
#define SLEEP
1
2
#define AWAKE
/* statu of process */
/* statu of process */
/* statu of process */
#include
struct pcb { char *name;
statu;
time;
};
struct pipetype { char type;
int
int
/* times of execution */
writeptr;
readptr;
int
int
struct pcb *pointp;
struct pcb *pointc;
/* write wait point */
*/
}; /* read wait point
int pipe[PIPESIZE];
struct pipetype pipetb;
struct pcb process[2];
main()
{ int output,ret,i;
�
char in[2];
int runp(),runc(),prn();
pipetb.type = 'c'; pipetb.writeptr = 0; pipetb.readptr = 0;
pipetb.pointp = pipetb.pointc = NULL;
process[PRODUCER].name = "Producer\0";
process[CONSUMER].name = "Consumer\0";
process[PRODUCER].statu = process[CONSUMER].statu = READY;
process[PRODUCER].time = process[CONSUMER].time = 0;
output = 0;
printf("Now starting the program!\n");
printf("Press 'p' to run PRODUCER, press 'c' to run CONSUMER.\n");
printf("Press 'e' to exit from the program.\n");
for(i=0;i<1000;i++)
{ in[0]='N';
while(in[0]=='N') { scanf("%s",in);
if(in[0]!='e'&&in[0]!='p'&&in[0]!='c') in[0]='N';}
if(in[0]=='e') { printf("Program completed!\n"); exit(0); }
if(in[0]=='p'&&process[PRODUCER].statu==READY) {
output = (output+1)%100;
if((ret=runp(output,process,pipe,&pipetb,PRODUCER))==SLEEP)
pipetb.pointp = &process[PRODUCER];
if(ret==AWAKE) {
(pipetb.pointc)->statu=READY; pipetb.pointc=NULL;
runc(process,pipe,&pipetb,CONSUMER); }
}
if(in[0]=='c'&&process[CONSUMER].statu==READY) {
if((ret=runc(process,pipe,&pipetb,CONSUMER))==SLEEP)
pipetb.pointc = &process[CONSUMER];
if(ret==AWAKE) {
(pipetb.pointp)->statu=READY; pipetb.pointp=NULL;
runp(output,process,pipe,&pipetb,PRODUCER); }
}
if(in[0]=='p'&&process[PRODUCER].statu==WAIT)
printf("PRODUCER is waiting, can't be scheduled.\n");
if(in[0]=='c'&&process[CONSUMER].statu==WAIT)
printf("CONSUMER is waiting, can't be scheduled.\n");
prn(process,pipe,pipetb); in[0]='N'; }
/* run producer */
}
runp(out,p,pipe,tb,t)
int out,pipe[],t;
struct pcb p[];
struct pipetype *tb;
{ p[t].statu = RUN; printf("run PRODUCER. product %d
",out);
if(tb->writeptr>=PIPESIZE) { p[t].statu=WAIT; return(SLEEP); }
�
pipe[tb->writeptr]=out; tb->writeptr++; p[t].time++;
p[t].statu=READY; if((tb->pointc)!=NULL) return(AWAKE);
return(NORMAL);
/* run consumer */
}
runc(p,pipe,tb,t)
int pipe[],t;
struct pcb p[];
struct pipetype *tb;
{ int c;
p[t].statu = RUN; printf("run CONSUMER. ");
if(tb->readptr>=tb->writeptr) { p[t].statu=WAIT; return(SLEEP); }
c = pipe[tb->readptr]; tb->readptr++;
printf(" use %d
if(tb->readptr>=tb->writeptr) tb->readptr=tb->writeptr=0;
p[t].time++; p[t].statu=READY;
",c);
//if(tb->pointp!=NULL)
if((tb->readptr)==0&&(tb->pointp)!=NULL) return(AWAKE);
return(NORMAL);
}
prn(p,pipe,tb)
int pipe[];
struct pipetype tb;
struct pcb p[];
{ int i;
printf("\n
"); for(i=0;i
=tb.readptr)&&(i�











 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc