Visual 3D Modeling from
Images
�
Introduction
u Goal
camera aroud
n Automatically extract a realistic 3D model by freely moving a
u Method
n Using a sequence of images
u Result
n 3D model: a scaled version of original object
�
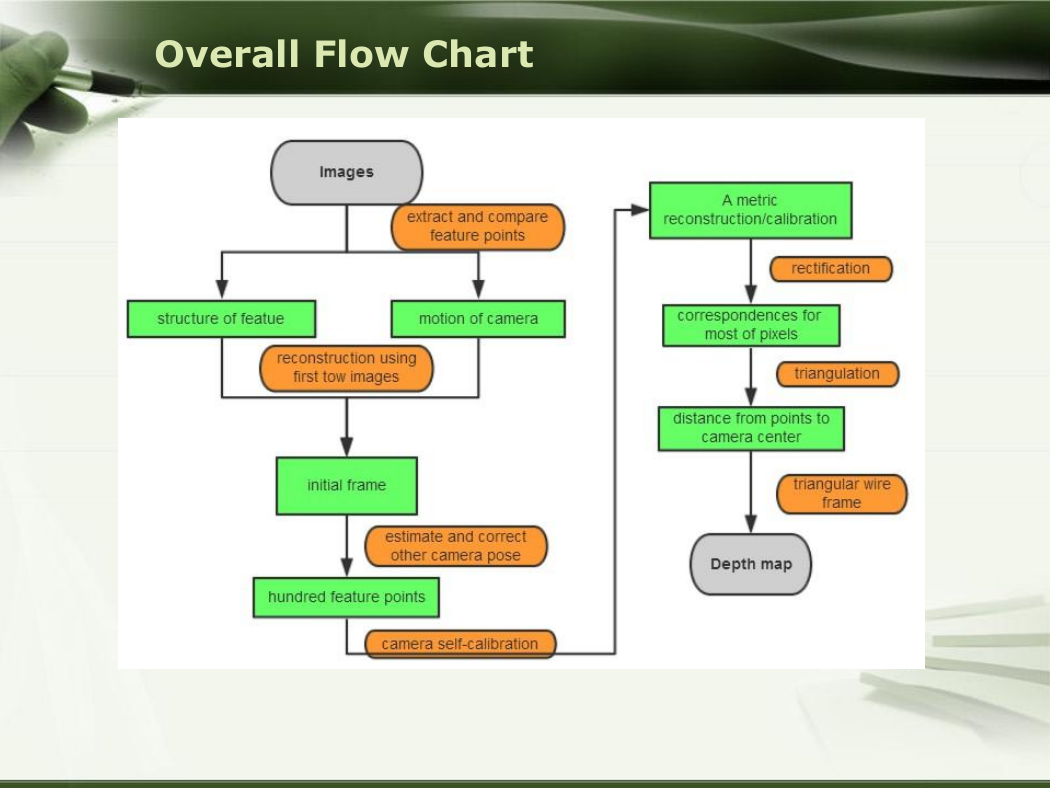
Overall Flow Chart
�
Feature Points
u Principle of feature points extraction
feature point should be sufficiently different from neighborhoods after a
small dispacement: corner(角点)
n
n
u Feature points matching
7x7 pixel widow
n matching methods:
a. sum-of-square differences(SSD:最小方差和)
b. normalized cross-correlation(NCC:归一化互相关)
Figure 1:corresponding corners
�
Feature Points
u Problems
n
scaling, rotation , lighting conditions...
->Matching using affinely in variant regions
n
outliers
->Robust algorithm:RANSAC (RANdom SAmpling Consensus:随机抽样一致性算
法)
u Other approaches
n
n
lines or curves
SIFT(Scale-invariant feature transform)
�
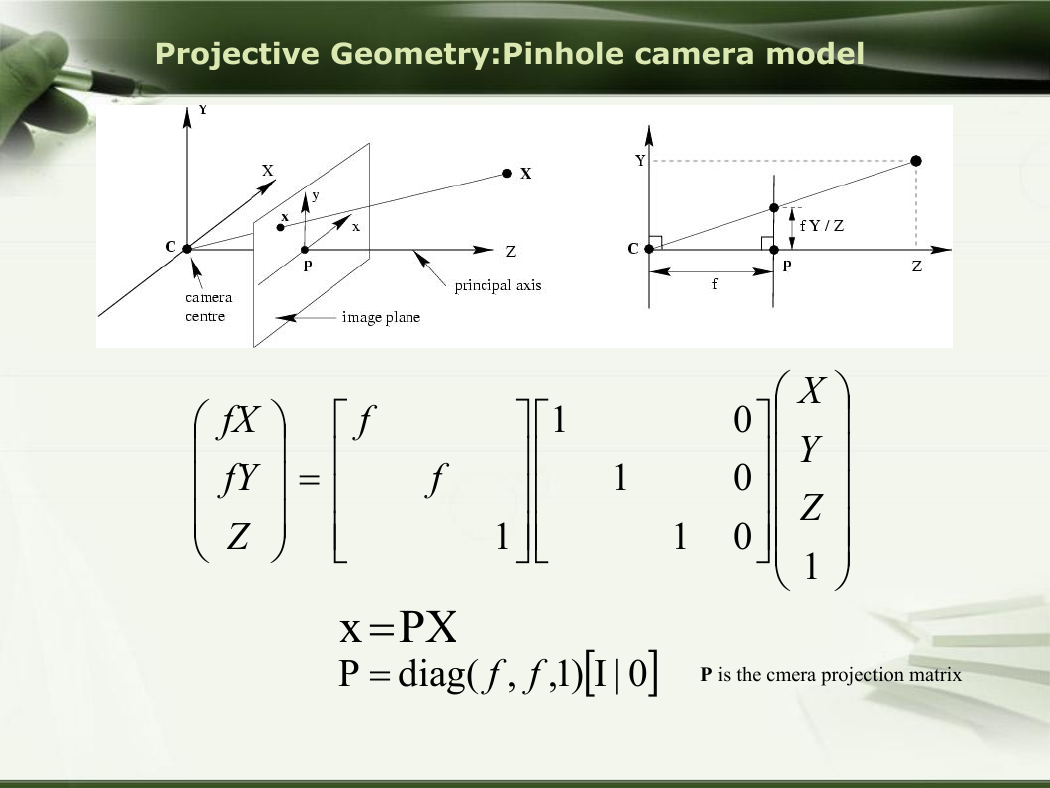
Projective Geometry:Pinhole camera model
fX
fY
Z
f
f
PXx
P
diag
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
X
Y
Z
1
(
f
,
f
0|I)1,
P is the cmera projection matrix
�
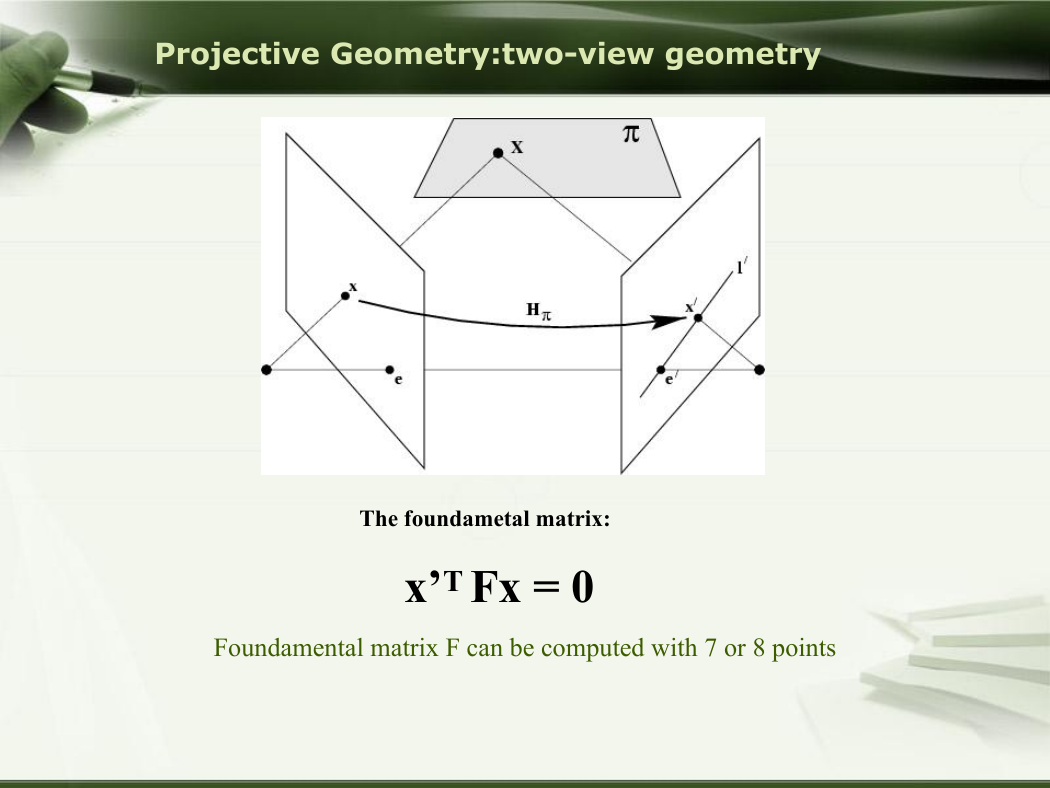
Projective Geometry:two-view geometry
The foundametal matrix:
x’T Fx = 0
Foundamental matrix F can be computed with 7 or 8 points
�
Structure and motion
u Select two views
n
n
sufficient features are matched
the views should not be too close to each other so that the initial structure
is well-conditioned
u Initial frame
P = [I|0] and P’ = [R|t]
�













 2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc
2023年江西萍乡中考道德与法治真题及答案.doc 2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc
2012年重庆南川中考生物真题及答案.doc 2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc
2013年江西师范大学地理学综合及文艺理论基础考研真题.doc 2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc
2020年四川甘孜小升初语文真题及答案I卷.doc 2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc
2020年注册岩土工程师专业基础考试真题及答案.doc 2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc
2023-2024学年福建省厦门市九年级上学期数学月考试题及答案.doc 2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc
2021-2022学年辽宁省沈阳市大东区九年级上学期语文期末试题及答案.doc 2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc
2022-2023学年北京东城区初三第一学期物理期末试卷及答案.doc 2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc
2018上半年江西教师资格初中地理学科知识与教学能力真题及答案.doc 2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc
2012年河北国家公务员申论考试真题及答案-省级.doc 2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc
2020-2021学年江苏省扬州市江都区邵樊片九年级上学期数学第一次质量检测试题及答案.doc 2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc
2022下半年黑龙江教师资格证中学综合素质真题及答案.doc